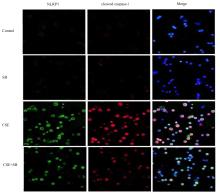
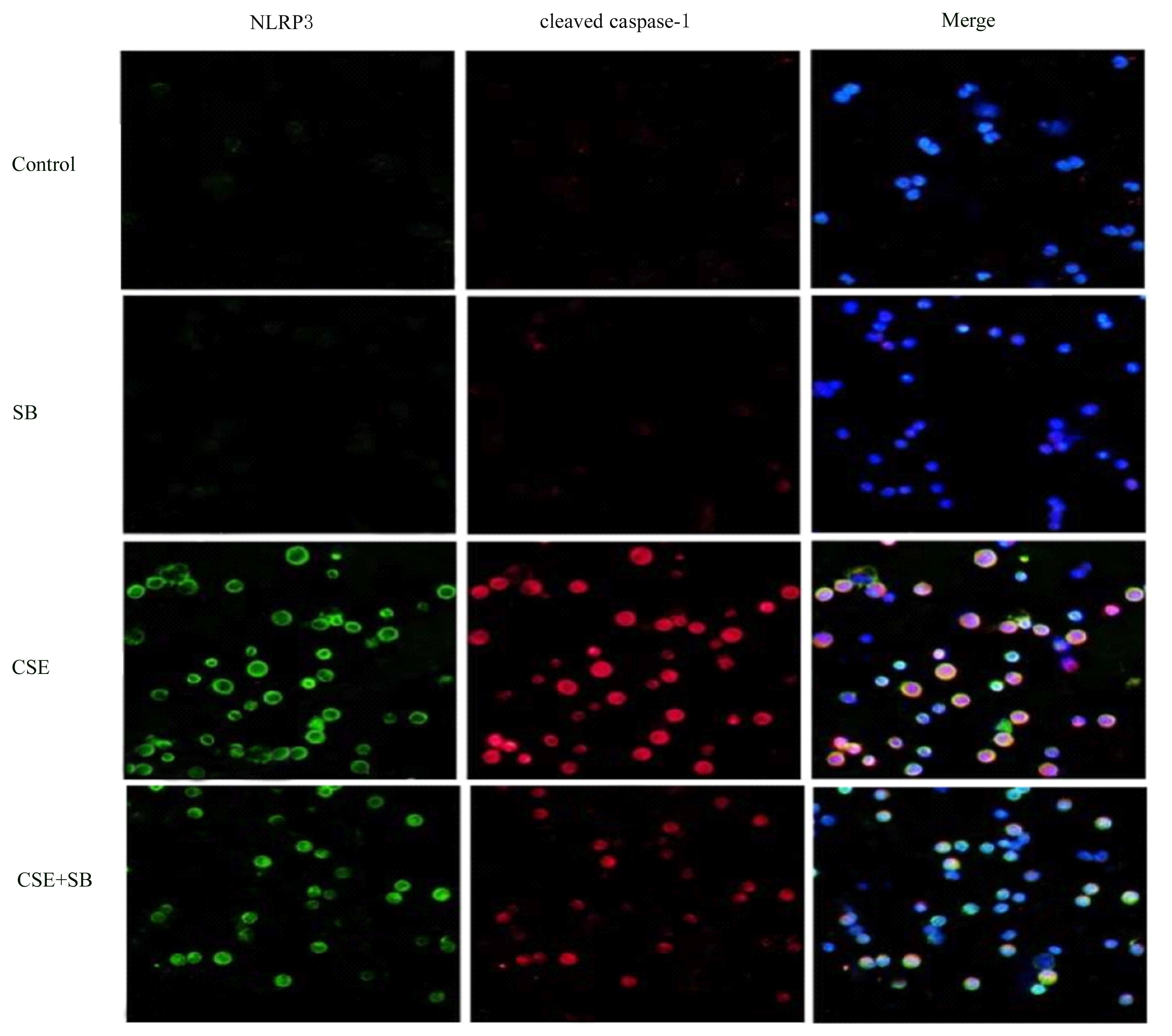
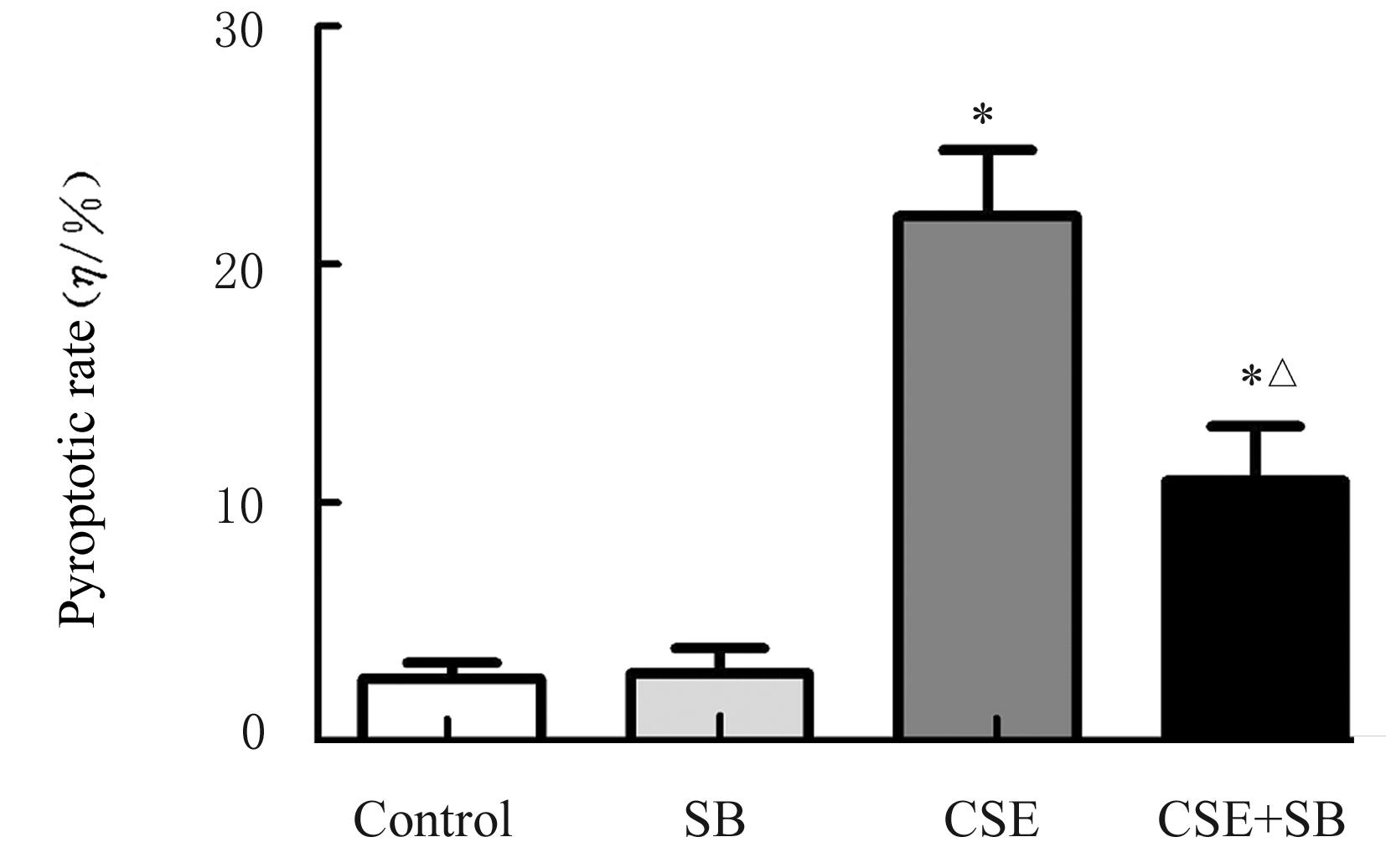
Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition) ›› 2022, Vol. 48 ›› Issue (3): 744-754.doi: 10.13481/j.1671-587X.20220324
• Research in basic medicine • Previous Articles
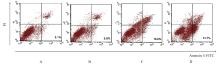
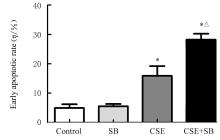
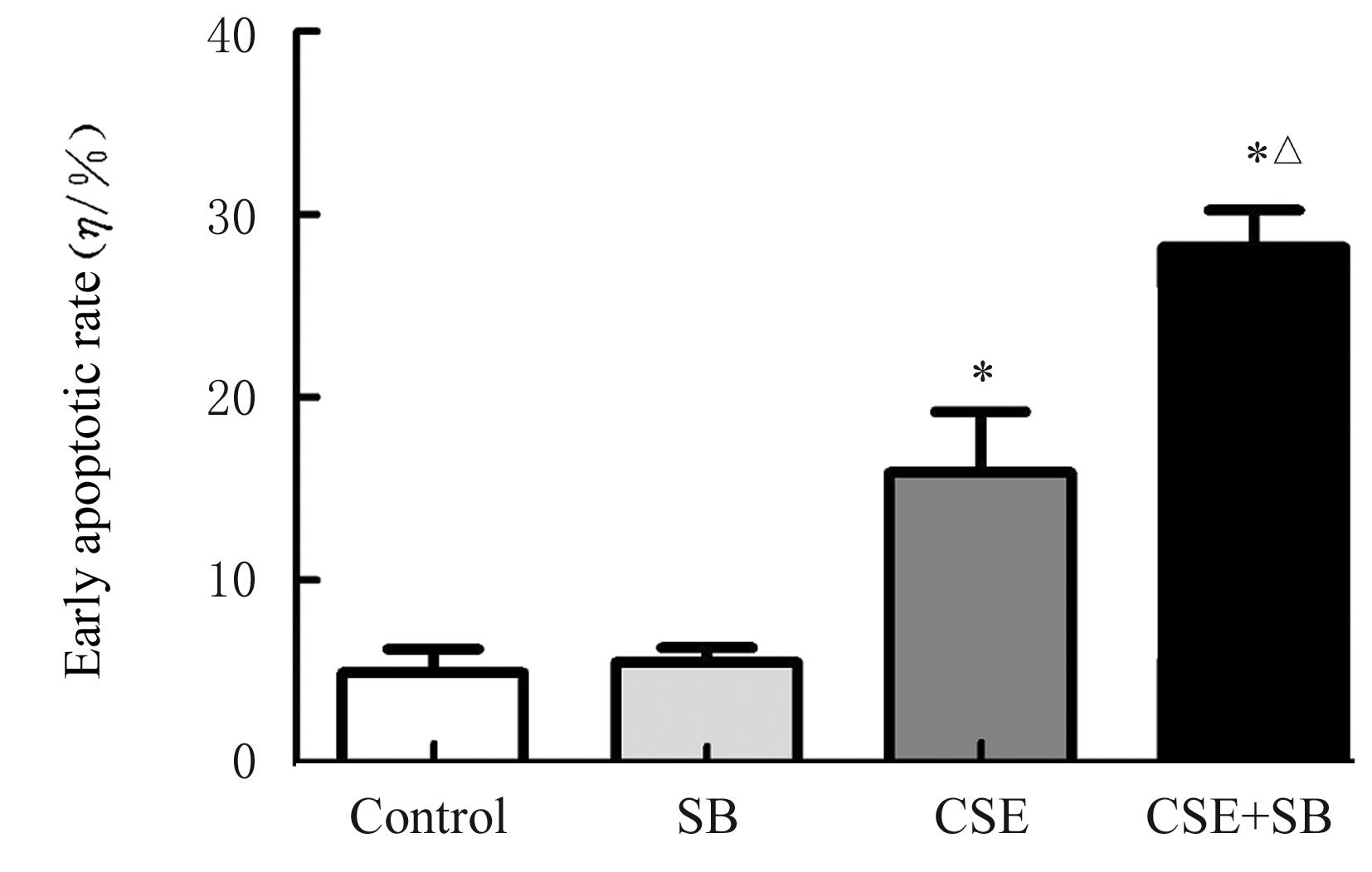
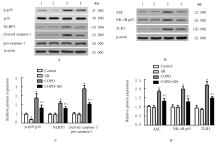
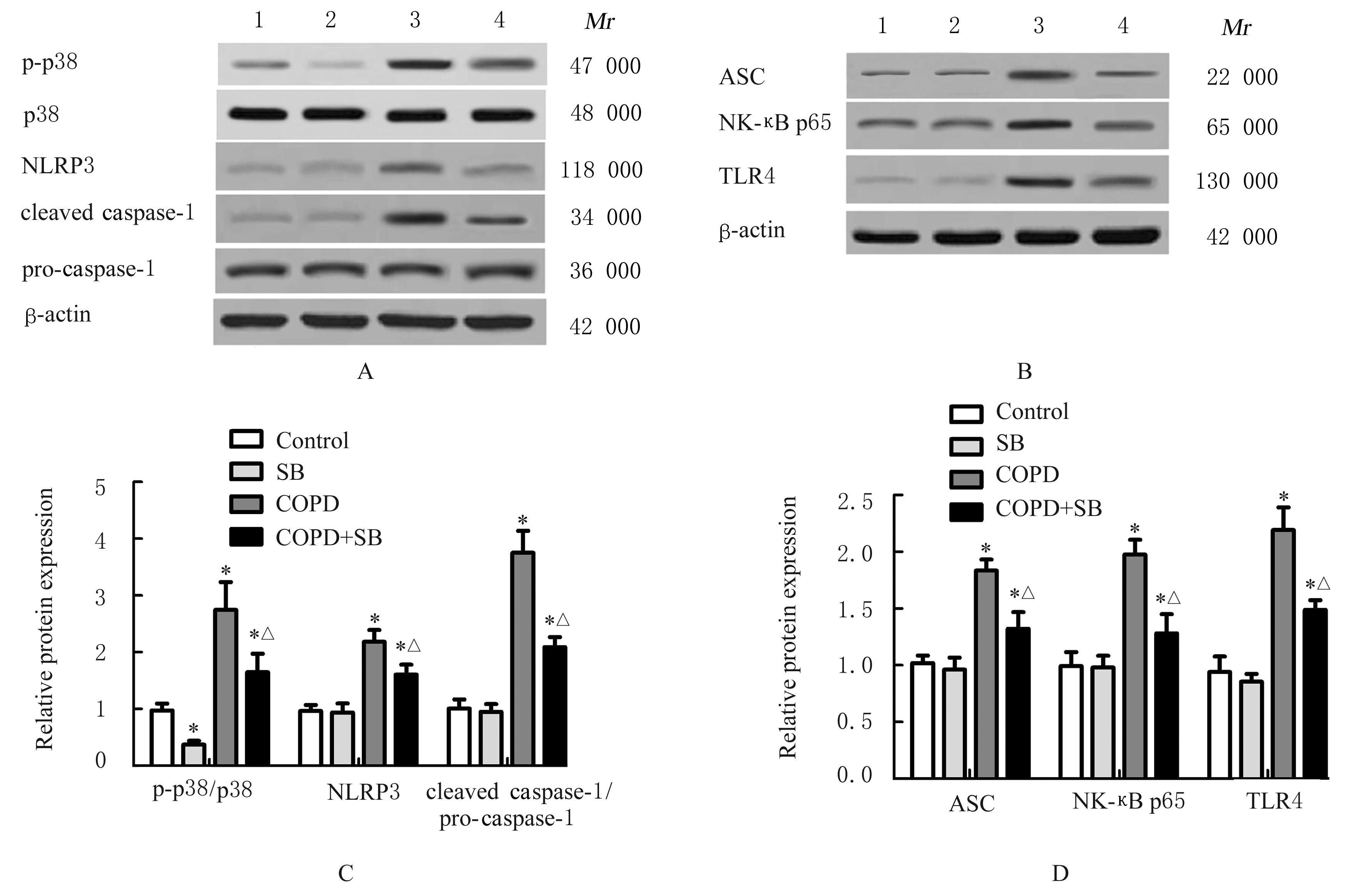
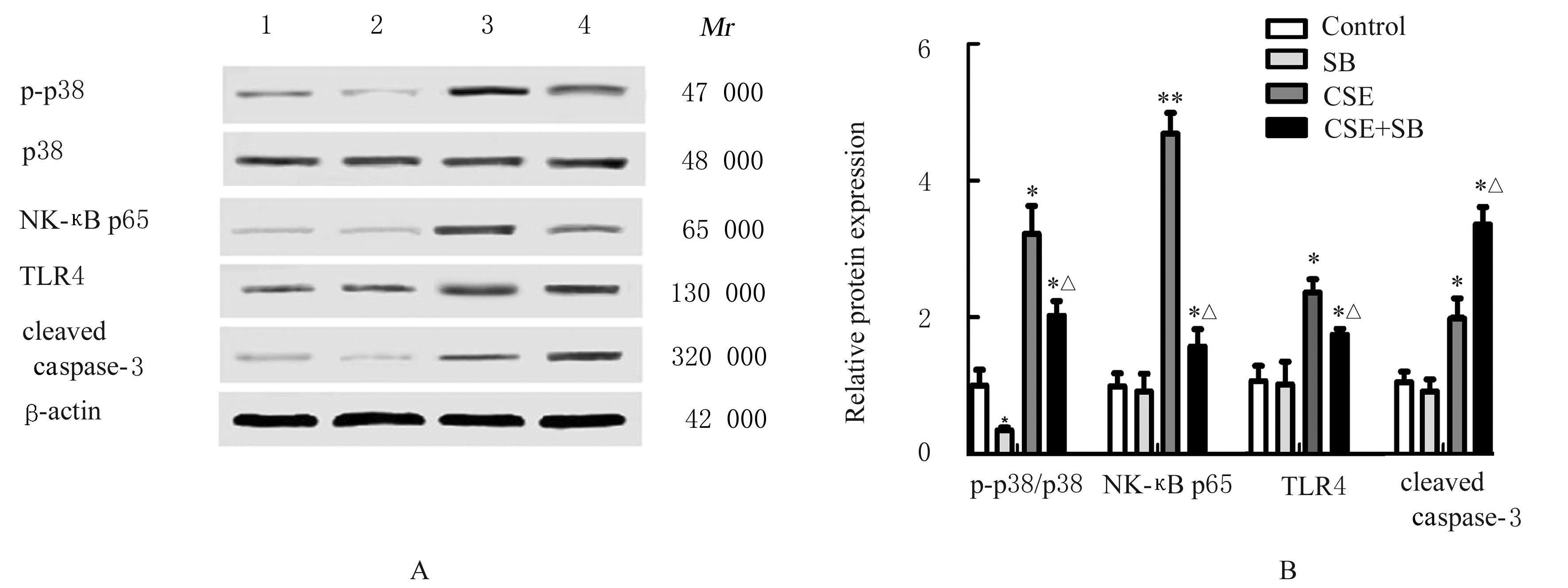
Improvement effect of p38 MAPK inhibitor on chronic obstructive pulmonary disease injury in mice through inhibiting cell pyrotosis mediated by NLRP3 pathway
Ming LI,Qiuting WANG,Shan CHEN,Huifang SHI( )
)
- Department of Respiratory Medicine,Second Affiliated Hospital,Hainan Medical College,Haikou 570311,China
-
Received:2021-08-20Online:2022-05-28Published:2022-06-21 -
Contact:Huifang SHI E-mail:touming_915717@163.com
CLC Number:
- R563.13
Cite this article
Ming LI,Qiuting WANG,Shan CHEN,Huifang SHI. Improvement effect of p38 MAPK inhibitor on chronic obstructive pulmonary disease injury in mice through inhibiting cell pyrotosis mediated by NLRP3 pathway[J].Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2022, 48(3): 744-754.
share this article
Tab. 1
Number of inflammatory cells in BALF of mice in various groups"
| Group | No. of total leukocytes | No. of neutrophils | No. of macrophages | No. of lymphocytes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Control | 7.41±1.35 | 2.79±0.33 | 3.51±0.48 | 5.66±1.49 |
| SB | 6.82±1.26 | 2.84±0.64 | 4.02±0.41 | 6.17±1.01 |
| COPD | 42.19±5.49* | 12.61±2.38* | 17.91±2.18* | 19.84±3.18* |
| COPD+SB | 17.11±3.02*△ | 8.73±1.25*△ | 12.58±1.26*△ | 14.55±2.90*△ |
| F | 36.106 | 19.187 | 31.439 | 28.215 |
| P | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 |
Tab. 2
Levels of inflammatory factors in BALF of mice in various groups [n=6,x±s,ρB /(ng·L-1)]"
| Group | TNF-α | IL-6 | IL-1β | IL-18 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Control | 82.16±15.09 | 77.41±13.33 | 14.51±4.28 | 20.03±3.05 |
| SB | 79.31±20.11 | 70.79±14.26 | 15.09±3.17 | 19.85±2.71 |
| COPD | 331.28±49.30** | 376.21±51.48** | 235.66±34.20** | 84.62±16.15* |
| COPD+SB | 259.17±32.85*△ | 265.11±14.72*△ | 91.83±27.57**△△ | 62.05±11.42*△ |
| F | 20.055 | 44.682 | 24.273 | 39.095 |
| P | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 |
| 1 | LAREAU S C, FAHY B, Meek P, et al. Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD)[J]. Am J Respir Crit Care Med, 2019,199(1):P1-P2. |
| 2 | BISWAS S K. Acute and chronic effects of cigarette smoking on sRAGE[J]. Am J Respir Crit Care Med, 2019, 199(6): 805. |
| 3 | 查震球, 何玉琢, 徐 伟, 等. 吸烟对慢性阻塞性肺疾病及呼吸道症状的影响[J]. 中华疾病控制杂志, 2020, 24(1): 46-51, 56. |
| 4 | 梅 旦, 张玲玲, 魏 伟. 细胞焦亡机制及与疾病的关系[J]. 生理科学进展, 2020, 51(2): 151-156. |
| 5 | 陈 昕, 林媛珍, 钟小宁. 细胞焦亡在慢性阻塞性肺疾病中的研究进展[J]. 重庆医科大学学报, 2020,45(6): 703-707. |
| 6 | PINKERTON J W, KIM R Y, ROBERTSON A A B, et al. Inflammasomes in the lung[J]. Mol Immunol, 2017, 86: 44-55. |
| 7 | ZHOU R X, YANG X Y, LI X H, et al. Recombinant CC16 inhibits NLRP3/caspase-1-induced pyroptosis through p38 MAPK and ERK signaling pathways in the brain of a neonatal rat model with sepsis[J]. J Neuroinflammation, 2019, 16(1): 239. |
| 8 | LI D D, REN W Y, JIANG Z L, et al. Regulation of the NLRP3 inflammasome and macrophage pyroptosis by the p38 MAPK signaling pathway in a mouse model of acute lung injury[J]. Mol Med Rep, 2018, 18(5): 4399-4409. |
| 9 | MARUMO S, HOSHINO Y, KIYOKAWA H, et al. p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase determines the susceptibility to cigarette smoke-induced emphysema in mice[J]. BMC Pulm Med, 2014, 14: 79. |
| 10 | PARK S H, KO J W, SHIN N R, et al. 4-Hydroxycinnamic acid protects mice from cigarette smoke-induced pulmonary inflammation via MAPK pathways[J]. Food Chem Toxicol, 2017, 110: 151-155. |
| 11 | JIANG J J, CHEN S M, LI H Y, et al. TLR3 inhibitor and tyrosine kinase inhibitor attenuate cigarette smoke/poly I: C-induced airway inflammation and remodeling by the EGFR/TLR3/MAPK signaling pathway[J]. Eur J Pharmacol, 2021, 890: 173654. |
| 12 | GENG Y, MA Q, LIU Y N, et al. Heatstroke induces liver injury via IL-1β and HMGB1-induced pyroptosis[J]. J Hepatol, 2015, 63(3): 622-633. |
| 13 | WANG C, XU J Y, YANG L, et al. Prevalence and risk factors of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease in China (the China Pulmonary Health[CPH]study): a national cross-sectional study[J]. Lancet,2018,391(10131): 1706-1717. |
| 14 | YANG W L, NI H Y, WANG H F, et al. NLRP3 inflammasome is essential for the development of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease[J]. Int J Clin Exp Pathol, 2015, 8(10): 13209-13216. |
| 15 | DIMA E, KOLTSIDA O, KATSAOUNOU P, et al. Implication of Interleukin (IL)-18 in the pathogenesis of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD)[J]. Cytokine, 2015, 74(2): 313-317. |
| 16 | FU J J, MCDONALD V M, BAINES K J, et al. Airway IL-1β and systemic inflammation as predictors of future exacerbation risk in asthma and COPD[J]. Chest, 2015, 148(3): 618-629. |
| 17 | HOU L, YANG Z W, WANG Z K, et al. NLRP3/ASC-mediated alveolar macrophage pyroptosis enhances HMGB1 secretion in acute lung injury induced by cardiopulmonary bypass[J]. Lab Invest, 2018, 98(8): 1052-1064. |
| 18 | FINK S L, COOKSON B T. Caspase-1-dependent pore formation during pyroptosis leads to osmotic lysis of infected host macrophages[J]. Cell Microbiol, 2006,8(11): 1812-1825. |
| 19 | MATIKAINEN S, NYMAN T A, CYPRYK W. Function and regulation of noncanonical caspase-4/5/11 inflammasome[J]. J Immunol, 2020, 204(12): 3063-3069. |
| 20 | WREE A, EGUCHI A, MCGEOUGH M D, et al. NLRP3 inflammasome activation results in hepatocyte pyroptosis, liver inflammation, and fibrosis in mice[J]. Hepatology, 2014, 59(3): 898-910. |
| 21 | ZHANG L, XING R L, HUANG Z Q, et al. Inhibition of synovial macrophage pyroptosis alleviates synovitis and fibrosis in knee osteoarthritis[J]. Mediators Inflamm, 2019, 2019: 2165918. |
| 22 | JONES H D, CROTHER T R, GONZALEZ-VILLALOBOS R A, et al. The NLRP3 inflammasome is required for the development of hypoxemia in LPS/mechanical ventilation acute lung injury[J]. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol, 2014, 50(2): 270-280. |
| 23 | WU D D, PAN P H, LIU B, et al. Inhibition of alveolar macrophage pyroptosis reduces lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury in mice[J]. Chin Med J (Engl), 2015, 128(19): 2638-2645. |
| 24 | NIE Y J, WANG Z X, CHAI G S, et al. Dehydrocostus lactone suppresses LPS-induced acute lung injury and macrophage activation through NF-κB signaling pathway mediated by p38 MAPK and Akt[J]. Molecules, 2019, 24(8): E1510. |
| 25 | YAO H W, EDIRISINGHE I, RAJENDRASOZHAN S,et al. Cigarette smoke-mediated inflammatory and oxidative responses are strain-dependent in mice[J]. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol, 2008, 294(6): L1174-L1186. |
| 26 | MENG A H, ZHANG X P, WU S Y, et al. In vitro modeling of COPD inflammation and limitation of p38 inhibitor - SB203580[J]. Int J Chron Obstruct Pulmon Dis, 2016, 11: 909-917. |
| 27 | 邢 栋,王焕焕,吕 勃.细胞程序性坏死与细胞焦亡[J].生理科学进展,2020,51(2):113-116. |
| 28 | 杨 柳,刘强胜,张 彬,等.抑制组织蛋白酶B对脓毒症急性肺损伤小鼠肺组织细胞焦亡的影响[J].解放军医学杂志,2022,47(3):213-218. |
| 29 | SINGHAL P C, BHASKARAN M, PATEL J, et al. Role of p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase phosphorylation and Fas-Fas ligand interaction in morphine-induced macrophage apoptosis[J]. J Immunol, 2002, 168(8): 4025-4033. |
| [1] | Guanhu LI,Qingxu LANG,Chunyan LIU,Qin LIU,Mengrou GENG,Xiaoqian LI,Zhenqi WANG. Inhibitory effect of valproic acid combined with X-ray irradiation on proliferation of breast cancer MDA-MB-231 cells and its mechanism [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2022, 48(3): 622-629. |
| [2] | Qiuting CAO,Jingchun HAN,Xiaofei ZHANG. Effect of silencing helicase BLM gene on chemotherapy sensitivity of irinotecan in colorectal cancer cells and its mechanism [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2022, 48(3): 657-667. |
| [3] | Cuilan LIU,Fengai HU,Jing LIU,Dan WANG,Changyun QIU,Dunjiang LIU,Di ZHAO. Effect of adiponectin receptor agonist AdiopRon on biological behaviors of glioma cells and its mechanism [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2022, 48(3): 702-710. |
| [4] | Ming xing YANG,Wen DONG,Ji LI. Inductive effect of peiminine on apoptosis of lung cancer A549 cells and its mechanism [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2022, 48(3): 711-717. |
| [5] | Suxian CHEN,Zehui GU,Yangfei MA,Qi TAN,Qi LI,Yadi WANG. Promotion effect of rutin on apoptosis of human colon cancer SW480 cells and its mechanism [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2022, 48(2): 356-363. |
| [6] | Zhihui ZHAO,Xianghua BAI,Jinling HE,Weiqin DUAN,Min LIU,Shengmao ZHANG. Inhibitory effect of sufentanil on apoptosis of myocardial cells in myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury rats and its mechanism [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2022, 48(2): 364-373. |
| [7] | Ye TIAN, ABUDU MIJITI·Abudu Kelimu,Peng WANG,Mo SHA,Qi CUI. Effects of polarization state of tumor-associated macrophages on self-renewal ability and vasculogenic mimicry of prostate cancer stem cells [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2022, 48(2): 374-382. |
| [8] | Feilong REN,Huanyu LUO,Shize ZHENG,Xinyi FAN,Chunxia REN,Yuan MENG,Hong ZHAO,Ce SHI,Hongchen SUN. Effects of C3a-C3aR axis on inflammatory response and tissue damage in chronic periodontitis model mice by promoting M1-type polarization of macrophages [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2022, 48(1): 1-8. |
| [9] | Guangsong XU,Haibing JIANG,Jing PAN,Guoqing LI. Inhibitory effects of betulinic acid on migration and invasion of gastric cancer MGC-803 cells and their mechanisms [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2022, 48(1): 122-128. |
| [10] | Wenxiong SUN,Pu LI. Expression of SOCS3 in peripheral blood mononuclear cells of patients with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma and its effect on autophagy and apoptosis of OCI-LY7 cells [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2022, 48(1): 172-179. |
| [11] | Leihua CUI,Yubo HOU,Chang SU,Minghe LI,Xin NIE. Effect of N-acetylcysteine on apoptosis of MC3T3-E1 cells induced by nicotine and its mechanism [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2022, 48(1): 26-32. |
| [12] | Yu ZHU,Jingjing WANG,Fang WU. Expression of miR-150-5p in kidney tissue of diabetic nephropathy model mice and its effect on MPC5 mouse podocyte injury and mechanism [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2022, 48(1): 44-51. |
| [13] | Zhaohui WAN,Liang ZENG,Hui ZHOU. Effect of overexpression of Bax inhibitor 1 on cardiomyocyte apoptosis in rats with acute myocardial infarction and its mechanism [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2022, 48(1): 74-81. |
| [14] | Daiqiang HUANG,Pengfei LIU,Jianbin HE,Jingxue SUN,Lin YUAN,Jing YUAN,Lei ZHAO. Effect of sevoflurane exposure during pregnancy period on maternal behavior of offspring of mice and protection mechanism of H2 [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2021, 47(6): 1347-1352. |
| [15] | Runhong MU,Yijiu AI,Yupeng LI,Rui LIN,Siping YE,Fang MA,Xiao GUO. Expression of recombinant human IL-17A in gastric cancer tissue and its effects on proliferation, invasion, migration and apoptosis of gastric cancer BGC-823 cells [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2021, 47(6): 1510-1517. |
|
||