| 1 |
ROGER C, ABID N, DUBOURG L, et al. Composition of urinary calculi: lessons from a French epidemiologic retrospective study[J]. Prog Urol, 2020, 30(6): 339-345.
|
| 2 |
WU J, YANG Z D, WEI J, et al. Association between serum magnesium and the prevalence of kidney stones: a cross-sectional study[J]. Biol Trace Elem Res, 2020, 195(1): 20-26.
|
| 3 |
ZENG G H, ZHAO Z J, WU W Q, et al. Interconversion of stone composition profiles from two recurrent stone episodes in stone formers[J]. Clin Chem Lab Med, 2014, 52(7): 1019-1024.
|
| 4 |
ZHU W, ZHAO Z J, CHOU F J, et al. The protective roles of estrogen receptor β in renal calcium oxalate crystal formation via reducing the liver oxalate biosynthesis and renal oxidative stress-mediated cell injury[J]. Oxid Med Cell Longev, 2019, 2019: 5305014.
|
| 5 |
LI Y H, MA G X, LV Y N, et al. Efficacy of obcordata A from Aspidopterys obcordata on kidney stones by inhibiting NOX4 expression[J].Molecules,2019,24(10): E1957.
|
| 6 |
QIN B L, WANG Q, LU Y C, et al. Losartan ameliorates calcium oxalate-induced elevation of stone-related proteins in renal tubular cells by inhibiting NADPH oxidase and oxidative stress[J]. Oxid Med Cell Longev, 2018, 2018: 1271864.
|
| 7 |
CHEN Y L, YE L H, LI W J, et al. Hyperoside protects human kidney‑2 cells against oxidative damage induced by oxalic acid[J]. Mol Med Rep, 2018, 18(1): 486-494.
|
| 8 |
DENG Z Y, WANG M J, FAN Y H, et al. Salviae miltiorrhizae and ligustrazine hydrochloride injection combined with mecobalamin for treating diabetic peripheral neuropathy: a protocol for systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. Medicine (Baltimore), 2021, 100(3): e24103.
|
| 9 |
ZHUANG Z, WANG Z H, HUANG Y Y, et al. Protective effect and possible mechanisms of ligustrazine isolated from Ligusticum wallichii on nephropathy in rats with diabetes: a preclinical systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. J Ethnopharmacol, 2020, 252: 112568.
|
| 10 |
LEI W, NI J N, XIA X T, et al. Searching for synergistic calcium antagonists and novel therapeutic regimens for coronary heart disease therapy from a Traditional Chinese Medicine, Suxiao Jiuxin Pill[J]. J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci, 2018, 1092: 220-227.
|
| 11 |
YE T T, LI Y F, XIONG D, et al. Combination of Danshen and ligustrazine has dual anti-inflammatory effect on macrophages and endothelial cells[J]. J Ethnopharmacol, 2021, 266: 113425.
|
| 12 |
ALI B H, AL-SALAM S, AL-HUSSEINI I, et al. Comparative protective effect of N-acetyl cysteine and tetramethylpyrazine in rats with gentamicin nephrotoxicity[J].J Appl Toxicol,2009,29(4): 302-307.
|
| 13 |
焦 浩, 曹 静. 紫草素在治疗小鼠草酸钙肾结石中的作用[J]. 中国临床药理学杂志, 2020, 36(20): 3253-3256.
|
| 14 |
刘 敏. 去乙酰化酶SIRT3在草酸钙肾结石形成中的作用和机制研究[D]. 上海: 第二军医大学, 2016.
|
| 15 |
孙溪峰. 吡格列酮通过PPARγ-miR-23-Irf1/Pknox1轴调节M1/M2型巨噬细胞极化从而减少肾炎症损伤和草酸钙晶体形成的实验研究[D]. 武汉: 华中科技大学, 2019.
|
| 16 |
邓聿胤, 吕纪华, 王 丽, 等. 广金钱草总黄酮片对大鼠肾结石的作用[J]. 世界中西医结合杂志, 2019, 14(9): 1252-1255, 1259.
|
| 17 |
WANG Z H, BAI Y J, WANG J H, et al. The preventive and therapeutic effects of α-lipoic acid on ethylene glycol-induced calcium oxalate deposition in rats[J]. Int Urol Nephrol, 2020, 52(7): 1227-1234.
|
| 18 |
LIU H R, YE T, YANG X Q, et al. H19 promote calcium oxalate nephrocalcinosis-induced renal tubular epithelial cell injury via a ceRNA pathway[J]. EBioMedicine, 2019, 50: 366-378.
|
| 19 |
SUN X Y, ZHANG H, LIU J, et al. Repair activity and crystal adhesion inhibition of polysaccharides with different molecular weights from red algae Porphyra yezoensis against oxalate-induced oxidative damage in renal epithelial cells[J]. Food Funct, 2019, 10(7): 3851-3867.
|
| 20 |
PENG Y H, YANG C, SHI X L, et al. Sirt3 suppresses calcium oxalate-induced renal tubular epithelial cell injury via modification of FoxO3a-mediated autophagy[J]. Cell Death Dis, 2019, 10(2): 34.
|
| 21 |
PEERAPEN P, CHAIYARIT S, THONGBOONKERD V. Protein network analysis and functional studies of calcium oxalate crystal-induced cytotoxicity in renal tubular epithelial cells[J]. Proteomics, 2018, 18(8): e1800008.
|
| 22 |
DOU C X, SHANG Z Y, QIAO J Y, et al. Clostridium butyricum protects IPEC-J2 cells from ETEC K88-induced oxidative damage by activating the Nrf2/ARE signaling pathway[J]. Oxid Med Cell Longev, 2021, 2021: 4464002.
|
| 23 |
SHAW P, CHATTOPADHYAY A. Nrf2-ARE signaling in cellular protection: mechanism of action and the regulatory mechanisms[J]. J Cell Physiol, 2020, 235(4): 3119-3130.
|
| 24 |
ESLAMI M, ESFANDYARI S, AGHAHOSSEINI M,et al. Astaxanthin protects human granulosa cells against oxidative stress through activation of NRF2/ARE pathway and its downstream phase Ⅱ enzymes[J]. Cell J, 2021, 23(3): 319-328.
|
| 25 |
SASIKUMAR R, JYOTI DAS A, CHANDRA DEKA S. In vitro cytoprotective activity of cyanidin 3-glucoside extracts from Haematocarpus validus pomace on streptozotocin induced oxidative damage in pancreatic β-cells[J]. Saudi J Biol Sci, 2021, 28(9): 5338-5348.
|
| 26 |
LIU J W, LIN H J, YUAN L W, et al. Protective effects of anwulignan against HCl/ethanol-induced acute gastric ulcer in mice[J]. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med, 2021, 2021: 9998982.
|
| 27 |
FENG L, KE N W, CHENG F, et al. The protective mechanism of ligustrazine against renal ischemia/reperfusion injury[J]. J Surg Res, 2011, 166(2): 298-305.
|
| 28 |
ZHAI L, ZHANG P, SUN R Y, et al. Cytoprotective effects of CSTMP, a novel stilbene derivative, against H2O2-induced oxidative stress in human endothelial cells[J]. Pharmacol Rep, 2011, 63(6): 1469-1480.
|
| 29 |
YAN S, YUE Y Z, ZONG Y, et al. Tetramethylpyrazine improves postoperative tissue adhesion: a drug repurposing[J]. Chin J Integr Med, 2019, 25(7): 554-560.
|
| 30 |
YAN S, YUE Y Z, ZENG L, et al. Ligustrazine nanoparticles nano spray’s activation on Nrf2/ARE pathway in oxidative stress injury in rats with postoperative abdominal adhesion[J]. Ann Transl Med, 2019, 7(16): 379.
|
| 31 |
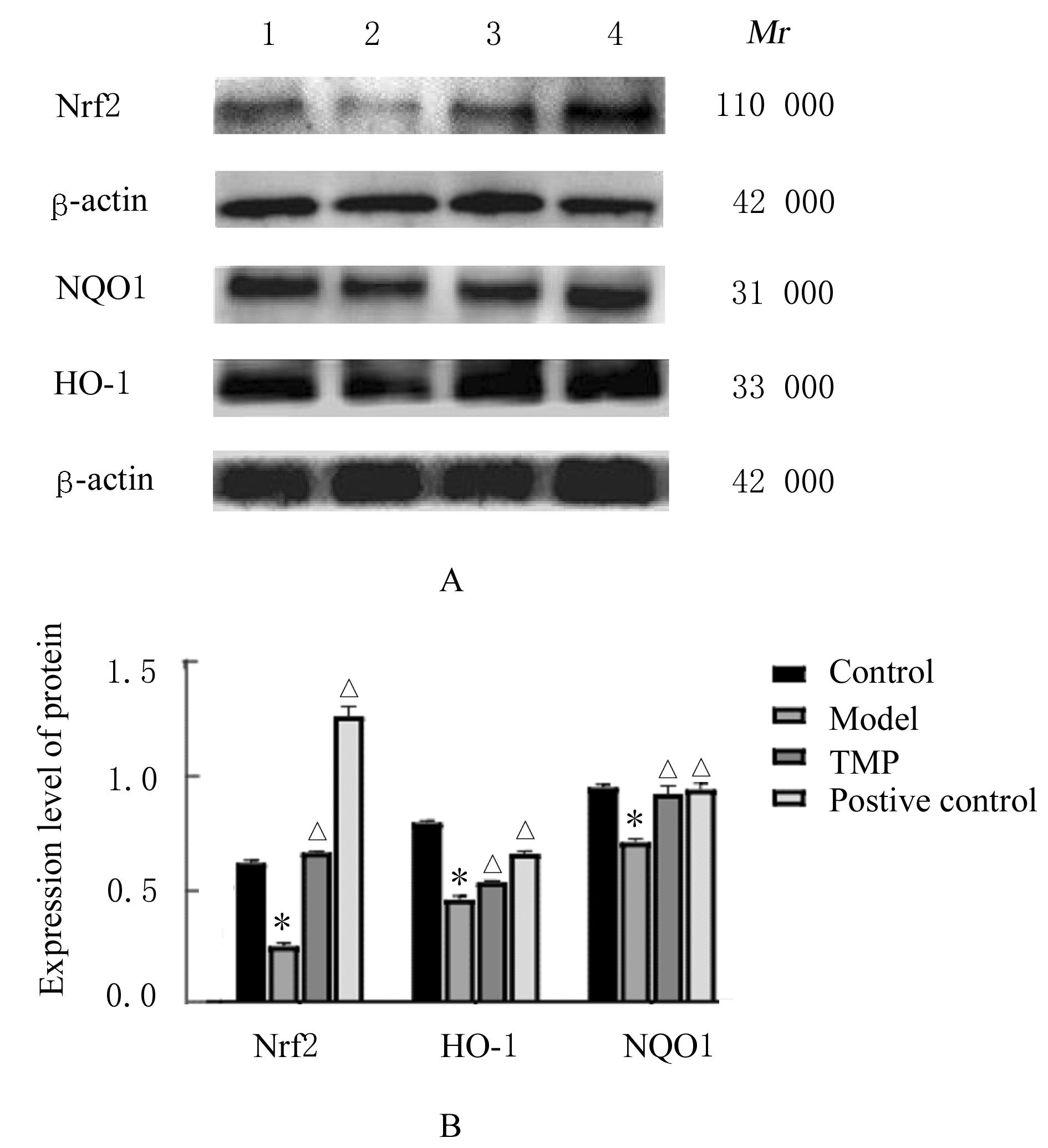
XI J H, JING J F, ZHANG Y B, et al. SIRT3 inhibited the formation of calcium oxalate-induced kidney stones through regulating NRF2/HO-1 signaling pathway[J]. J Cell Biochem, 2018. DOI: 10.1002/jcb.28109 .
doi: 10.1002/jcb.28109
|
 )
)