Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition) ›› 2023, Vol. 49 ›› Issue (3): 625-633.doi: 10.13481/j.1671-587X.20230310
• Research in basic medicine • Previous Articles Next Articles
Relationship between syndrome manifestations and differentially expressed genes in rat model of type 2 diabetes mellitus with Qi and Yin deficiency explored through transcriptomics
Xiaowei HUANG1,Siqi ZHANG1,2,Yixin ZHANG3,Bo LIU2,Xin WANG2,Fenglan JI2,Runze YANG1,2,Huibo XU2,Tao DING2( )
)
- 1.Department of Chinese Pharmacology,School of Pharmacy,Changchun University of Traditional Chinese Medicine,Changchun 130117,China
2.Pharmacodynamic and Toxicological Evaluation Center,Jilin Academy Traditional Chinese Medicine Sciences,Changchun 130021,China
3.Drug Clinical Trial Institution,China-Japan Union Hospital,Jilin University,Changchun 130033,China
-
Received:2022-06-21Online:2023-05-28Published:2023-06-20 -
Contact:Tao DING E-mail:dtdingtao@163.com
CLC Number:
- R96
Cite this article
Xiaowei HUANG,Siqi ZHANG,Yixin ZHANG,Bo LIU,Xin WANG,Fenglan JI,Runze YANG,Huibo XU,Tao DING. Relationship between syndrome manifestations and differentially expressed genes in rat model of type 2 diabetes mellitus with Qi and Yin deficiency explored through transcriptomics[J].Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2023, 49(3): 625-633.
share this article
Tab. 1
Body masses of rats in various groups"
| Group | n | Body mass | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (week) 1 | 5 | 9 | 13 | 17 | 21 | ||
| Blank | 18 | 254.09±9.32 | 463.67±40.55 | 519.73±48.51 | 555.86±65.17 | 599.91±62.44 | 612.71±62.93 |
| Model | 14 | 255.14±14.65 | 424.60±39.23* | 436.36±53.88** | 447.32±63.67** | 460.39±72.43** | 462.57±73.30** |
| Drug evidence | 17 | 246.83±9.56 | 435.32±28.63 | 440.85±46.28 | 467.01±56.26 | 471.45±61.51 | 486.79±67.55 |
Tab. 2
Daily food intakes and water intakes of rats in various groups"
| Group | n | Food intakes (g·d-1) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (week) 6 | 9 | 12 | 15 | 18 | 21 | ||
| Blank | 18 | 29.11±0.62 | 27.55±2.18 | 24.43±2.96 | 26.48±4.55 | 29.07±1.11 | 23.18±1.96 |
| Model | 14 | 33.89±0.98* | 37.54±4.45* | 35.63±5.56* | 36.69±5.78* | 35.05±4.83* | 34.10±3.69* |
| Drug evidence | 17 | 33.55±1.54 | 38.49±0.89 | 35.01±1.16 | 37.19±3.06 | 37.55±2.73 | 33.30±2.96 |
Tab. 3
Mental state scores, sport scores, foot temperatures, griping force, respiratory rates,and pulse amplitudes of rats in various groups"
| Group | n | Mental state score | Sport score | Foot temperature(θ/℃) | Griping force(m·g-1) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (week) 21 | 21 | 0 | 21 | 0 | 21 | |||
| Blank | 18 | 0.11±0.32 | 0.11±0.32 | 32.47±3.27 | 29.92±1.36 | 1 136.96±118.12 | 1 994.56±1.39 | |
| Model | 14 | 1.86±0.36* | 1.93±0.27* | 30.76±1.36 | 31.88±1.94* | 1 123.04±106.44 | 1 590.20±78.57* | |
| Drug evidence | 17 | 1.41±0.51△ | 1.35±0.49△△ | 31.10±1.51 | 29.53±1.51△△ | 1 117.39±122.89 | 1 722.35±101.37△△ | |
| Group | n | Respiratory rate (times·min-1) | Pulse amplitude(U·V-1) | |||||
| (week) 0 | 21 | 0 | 21 | |||||
| Blank | 18 | 96.04±12.90 | 97.23±19.29 | 0.013±0.005 | 0.018±0.006 | |||
| Model | 14 | 94.49±17.82 | 95.54±20.96 | 0.014±0.005 | 0.008±0.003* | |||
| Drug evidence | 17 | 102.19±18.84 | 108.65±20.34 | 0.021±0.017 | 0.017±0.011△△ | |||
Tab. 7
Levels of CD4,CD8,cAMP,cGMP, and CD4/CD8 and cAMP/cGMP in serum of rats in various groups"
| Group | CD4 [ρB/(μg·L-1)] | CD8 [ρB/(μg·L-1)] | CD4/CD8 | cAMP [сB/nmol·L-1)] | cGMP [сB/nmol·L-1)] | cAMP/cGMP | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Blank | 85.88±11.78 | 47.05±6.82 | 1.83±0.17 | 12.18±1.85 | 92.35±17.15 | 0.13±0.01 | |
| Model | 66.25±10.15* | 42.03±3.51 | 1.57±0.18* | 14.67±0.83* | 68.98±9.14* | 0.22±0.03* | |
| Drug evidence | 84.34±10.25△ | 41.40±4.78 | 2.04±0.20△ | 13.96±1.33 | 91.18±8.78△ | 0.15±0.01△ |
Tab.8
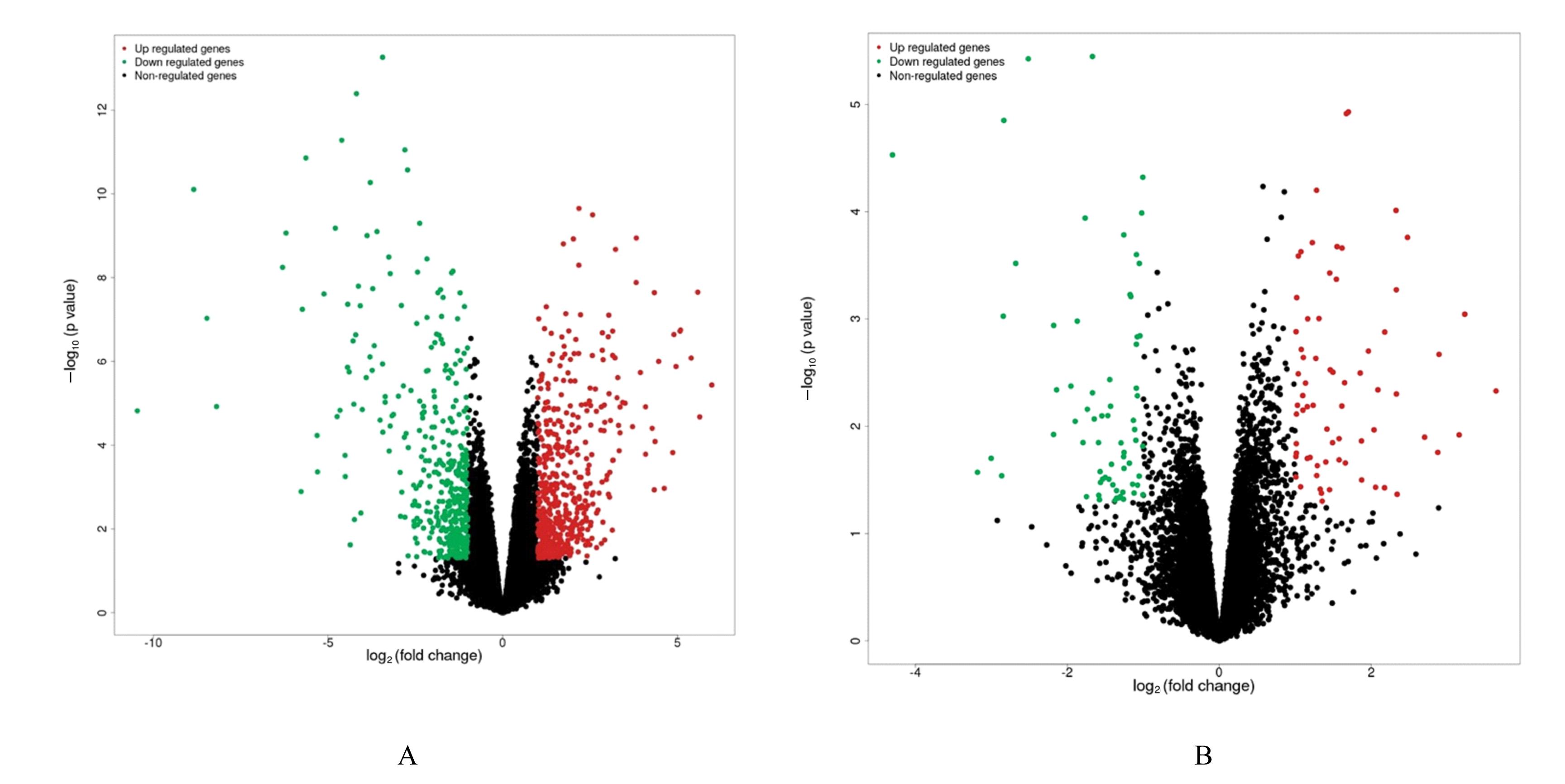
Differential expressed genes in model group"
| Number | ID | Gene | P value |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | ENSRNOG00000018851 | Ppp2r2b | 5.88E-06 |
| 2 | ENSRNOG00000055620 | AABR07065768.3 | 9.53E-06 |
| 3 | ENSRNOG00000047534 | AABR07027447.1 | 3.37E-05 |
| 4 | ENSRNOG00000057376 | AABR07051548.2 | 1.73E-04 |
| 5 | ENSRNOG00000058780 | Igfbp1↑ | 2.31E-04 |
| 6 | ENSRNOG00000061431 | AABR07061134.1 | 4.70E-04 |
| 7 | ENSRNOG00000003538 | Adamts4↑ | 5.48E-04 |
| 8 | ENSRNOG00000061722 | RF00100 | 8.18E-04 |
| 9 | ENSRNOG00000033376 | AABR07065782.1 | 8.65E-04 |
| 10 | ENSRNOG00000027024 | Rgs16 | 9.17E-04 |
| 11 | ENSRNOG00000050855 | LOC100911994 | 1.39E-03 |
| 12 | ENSRNOG00000022932 | Serhl2 | 3.37E-03 |
| 13 | ENSRNOG00000019822 | Gadd45b | 4.30E-03 |
| 14 | ENSRNOG00000002345 | Rasgef1b | 5.96E-03 |
| 15 | ENSRNOG00000059981 | AABR07065750.3 | 7.30E-03 |
| 16 | ENSRNOG00000008971 | Hnf4g | 7.60E-03 |
| 17 | ENSRNOG00000061190 | RF00560 | 8.41E-03 |
| 18 | ENSRNOG00000060987 | AABR07051716.2 | 8.57E-03 |
| 19 | ENSRNOG00000059083 | RF00405 | 9.11E-03 |
| 20 | ENSRNOG00000052382 | RF00026 | 1.24E-02 |
| 21 | ENSRNOG00000000640 | Egr2↑ | 1.60E-02 |
| 22 | ENSRNOG00000046667 | Fosb | 1.83E-02 |
| 23 | ENSRNOG00000042526 | Wfdc6a | 2.79E-02 |
| 24 | ENSRNOG00000049944 | Slc25a22 | 3.05E-02 |
| 25 | ENSRNOG00000001843 | Bcl6 | 3.36E-02 |
| 26 | ENSRNOG00000057661 | AABR07029863.2 | 3.84E-02 |
| 27 | ENSRNOG00000053770 | RF00398 | 4.86E-02 |
Tab.9
Differential expressed genes in drug evidence group"
| Number | ID | Gene | P value |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | ENSRNOG00000012980 | Hyls1 | 1.95E-04 |
| 2 | ENSRNOG00000006019 | G0s2↓ | 4.26E-04 |
| 3 | ENSRNOG00000003228 | Mid1ip1↓ | 6.32E-04 |
| 4 | ENSRNOG00000016167 | Spata2L | 9.98E-04 |
| 5 | ENSRNOG00000011490 | Angptl8 | 1.33E-03 |
| 6 | ENSRNOG00000007152 | Bhlhe40↓ | 2.00E-03 |
| 7 | ENSRNOG00000038025 | Rpp38 | 2.33E-03 |
| 8 | ENSRNOG00000020990 | Fgf21 | 1.06E-02 |
| 9 | ENSRNOG00000011180 | Irx5 | 1.31E-02 |
| 10 | ENSRNOG00000051425 | RF00420 | 1.37E-02 |
| 11 | ENSRNOG00000035606 | Mir3554 | 1.43E-02 |
| 12 | ENSRNOG00000059406 | Ier5 | 1.46E-02 |
| 13 | ENSRNOG00000017560 | Mdk | 2.06E-02 |
| 14 | ENSRNOG00000061688 | RF00425 | 2.15E-02 |
| 15 | ENSRNOG00000057339 | RF00601 | 3.87E-02 |
| 16 | ENSRNOG00000056608 | RF00019 | 3.91E-02 |
| 17 | ENSRNOG00000056868 | RF00026 | 4.21E-02 |
| 1 | GAN L, JIANG T T, YI W J, et al. Study on potential biomarkers of energy metabolism-related to early-stage Yin-deficiency-heat syndrome based on metabolomics and transcriptomics[J]. Anat Rec (Hoboken),2020,303(8):2109-2120. |
| 2 | 张 宁,李自辉,赵洪伟,等.基于转录组测序技术研究玄参提取物干预阴虚火旺甲状腺功能亢进大鼠的分子机制[J].中华中医药杂志,2022,37(2):709-713. |
| 3 | 陈 惠,辛丽丽,龚婕宁.基于全转录组测序技术的转录组学在中医药领域的应用前景分析[J].环球中医药,2013,6(10):759-763. |
| 4 | 张晓萌,李健春,王 琼,等.转录组测序技术在中医药领域的应用[J].中国现代中医药,2016,18(8):1084-1087. |
| 5 | 张译心,王 鑫,刘 博,等.2型糖尿病气阴两虚病证结合动物模型的制备及评价指标的建立[J].中国实验动物学报,2021,29(2):219-229. |
| 6 | 郑筱萸.中药新药临床研究指导原则:试行[M].北京:中国医药科技出版社,2002:233-234. |
| 7 | 丁润蓉, 孙华磊, 刘亚萍, 等. 紫檀芪对2型糖尿病大鼠肾损伤的改善作用[J]. 郑州大学学报(医学版), 2022, 57(1): 18-22. |
| 8 | 李 倩, 马建华. 固定复方降糖药在2型糖尿病治疗中更具优势[J].中国实用内科杂志,2022,42(11): 894-898. |
| 9 | 吴昭利,李仁廷,司海龙.培元抗癌汤联合TP方案治疗气虚血瘀型中晚期肺癌的效果及对免疫功能、MMP-9、CYFRA21-1水平、CAFs阳性率的影响[J].临床医学研究与实践,2021,6(31):128-130. |
| 10 | 邓艳华,陈璐佳,刘宏飞,等.玉屏风散加味对气虚易感人群免疫功能的影响[J].中国现代医生,2021,59(29):138-141. |
| 11 | 俞若熙,张 妍,刘铜华,等.“体-衰相关论”及阴虚质与衰老的相关性探析[J].中华中医药杂志,2015,30(12):4211-4214. |
| 12 | 孙 娟,杨文龙,刘方铭.阴虚型颈椎病大鼠模型的建立与评价[J].时珍国医国药,2021,32(11):2811-2815. |
| 13 | 马 露,王俊峰.基于cAMP、cGMP分布和比值探析六经辨证阴阳量化指标[J].中医临床研究,2017,9(27):4-6. |
| 14 | 王蕾蕾,高学敏,贾 岚,等.青钱柳对阴虚型2型糖尿病大鼠内分泌-免疫-环核苷酸系统的影响[J].中华中医药杂志,2021,36(2):736-740. |
| 15 | 李爱云,钟丛丛,张 宁.小檗碱抑制NF-κB p65改善肝脏糖异生的作用研究[J].中华中医药杂志,2019,34(5):1956-1960. |
| 16 | 陈玮钰, 舒发明, 王 涵, 等. 细胞色素P450家族在肝脏代谢相关疾病中的作用[J]. 临床肝胆病杂志, 2022, 38(9): 2182-2187. |
| 17 | SMITH T J. Insulin-like growth factor-I regulation of immune function: a potential therapeutic target in autoimmune diseases?[J].Pharmacol Rev,2010,62(2):199-236. |
| 18 | DOWERY R, BENHAMOU D, BENCHETRIT E, et al. Peripheral B cells repress B-cell regeneration in aging through a TNF-α/IGFBP-1/IGF-1 immune-endocrine axis[J].Blood,2021,138(19):1817-1829. |
| 19 | SHANG X Q, LIU K L, LI Q, et al. ADAMTS4 is upregulated in colorectal cancer and could be a useful prognostic indicator of colorectal cancer[J].Rev Assoc Med Bras(1992),2020,66(1):42-47. |
| 20 | COOK M E, JARJOUR N N, LIN C C, et al. Transcription factor Bhlhe40 in immunity and autoimmunity[J].Trends Immunol,2020,41(11):1023-1036. |
| 21 | FORSBERG E A, BOTUSAN I R, WANG J, et al. Carnosine decreases IGFBP1 production in db/db mice through suppression of HIF-1[J].J Endocrinol, 2015,225(3):159-167. |
| 22 | SAE-LEE C, MOOLSUWAN K, CHAN L, et al. ChREBP regulates itself and metabolic genes implicated in lipid accumulation in β-cell line[J].PLoS One,2016,11(1):e0147411. |
| 23 | KIM M J, SIM D Y, LEE H M, et al. Hypolipogenic effect of shikimic acid via inhibition of MID1IP1 and phosphorylation of AMPK/ACC[J].Int J Mol Sci,2019,20(3):582. |
| 24 | ZHANG X D, HECKMANN B L, CAMPBELL L E, et al. G0S2: a small giant controller of lipolysis and adipose-liver fatty acid flux[J].Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Cell Boil Lipids,2017,1862(10 Pt B):1146-1154. |
| 25 | LIANG Y C, YANG M T, LIN C J, et al. Bidens Pilosa and its active compound inhibit adipogenesis and lipid accumulation via down-modulation of the C/EBP and PPARγ pathways[J]. Sci Rep, 2016,11(6):24285. |
| 26 | 董又滋, 赵泉霖, 王毓国. 基于GEO数据库的黄芪-当归药对治疗糖尿病合并心血管并发症的分子机制研究[J]. 解放军医学杂志, 2022, 47(12): 1190-1200. |
| [1] | Jing GUAN,Shen HA,Hao YUAN,Ying CHEN,Pengju LIU,Zhi LIU,Shuang JIANG. Protective effect of Modified Xiao-Xian-Xiong Decoction on liver injury in rats with type 2 diabete mellitus and its mechanism [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2023, 49(3): 608-616. |
| [2] | Rui WANG,Ding ZHANG,Ruijian ZHUGE,Qian XUE,Li GUO. Bioinformatics analysis on mechanism of liver injury induced by hexavalent chromium [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2023, 49(2): 452-459. |
| [3] | Junxiong ZHAO,Qian WU,Liangui NIE,Shengquan LIU,Zhentao JIANG,Jian CHEN,Ting XIAO,Jun YANG. Ameliorative effect of SO2 on myocardial fibrosis in type 2 diabetes mellitus rats and its mechanism [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2023, 49(1): 8-14. |
| [4] | Xiaoyan WANG,Qiuyue ZHANG,Yujie HU,Zhijing MO. Bioinformatics analysis based on molecular characteristics and mechanism of cystic fibrosis [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2022, 48(5): 1290-1297. |
| [5] | Yongxin ZHAI,Huaifeng TA,Yi ZHANG,Qijia SUN,Ming ZHANG,Shuqiang FENG,Ranwei LI. Effect of preoperative glycemic level on infection-related complications of diabetic patients after flexible ureteroscopic lithotripsy [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2022, 48(3): 766-772. |
| [6] | Zhijuan ZHAO,Lian MENG,Chunxia LIU. Bioinformatics analysis on miRNA-mRNA regulatory networks based on fusion genes acting in rhabdomyosarcoma [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2022, 48(1): 154-162. |
| [7] | LIU Donghui, FU Wenliang, FU Xiumei, SONG Chengjun, CHEN Zhihong. Regulatory effect of sericin on liver insulin PI3K/Akt signaling pathway in rats of type 2 diabetes mellitus and its mechanism [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2020, 46(02): 228-232. |
| [8] | QI Bingxue, SUN Yadong. A prospective study on primary prevention of major vascular lesions of type 2 diabetes mellitus patients in Han population in Northeast China [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2018, 44(06): 1243-1248. |
| [9] | QI Lu, BAI Wei, YU Weiying, LI Yuanyuan, HUA Wanqing, KOU Changgui. Randomized controlled trials for curative effect of saxagliptin combined with insulin in treatment of patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: Meta-analysis [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2018, 44(06): 1235-1242. |
| [10] | SUN Zhumei, LIANG Weishi, KANG Jiali, MENG Xubing, WANG Jianxing, HAN Shuying. Dynamic pathological characteristics of kidney in db/db mice with type 2 diabetes mellitus [J]. Journal of Jilin University Medicine Edition, 2018, 44(03): 499-503. |
| [11] | LI Chunhua, GUO Xin, DOU Jing, DING Mingxuan, YAO Yan, ZHANG Yanqiu. Survey analysis on cognitive dysfunction in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus and its influecing factors [J]. Journal of Jilin University Medicine Edition, 2018, 44(02): 431-437. |
| [12] | LIU Xiaojie, MEI Tao, MA Hongyan, YE Shandong. Analysis of influencing factors of carotid atherosclerosis plaque formation and stability in simple type 2 diabetic patients [J]. Journal of Jilin University Medicine Edition, 2018, 44(02): 350-355. |
| [13] | WANG Jianxing, JIANG Yan, WANG Yan, WU Lei, MU Yu, HAN Shuying. Influence of extract from fermented buckwheat flower and leaf in kidney injury in type 2 diabetic db/db mice [J]. Journal of Jilin University Medicine Edition, 2018, 44(01): 95-100. |
| [14] | GOU Xiangbo, GUO Jing, BAI Jing. Protective effect of total flavones of buckwheat flowers and leaves on myocardial fibrosis of type 2 diabetic ratsand its mechanism [J]. Journal of Jilin University Medicine Edition, 2016, 42(04): 694-698. |
| [15] | TU Peipei, LI Xiaodan, MA Baicheng, ZHANG Yaofang, DUAN Huikun, NI Zaizhong, WANG Haisong, JIANG Pingzhe, LI Miao, WU Ri, LI Minggang. Changes and significance of hepatic histone H3 epigenetic modification in type 2 diabetic mice [J]. Journal of Jilin University Medicine Edition, 2015, 41(04): 756-762. |