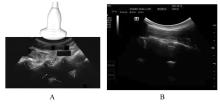
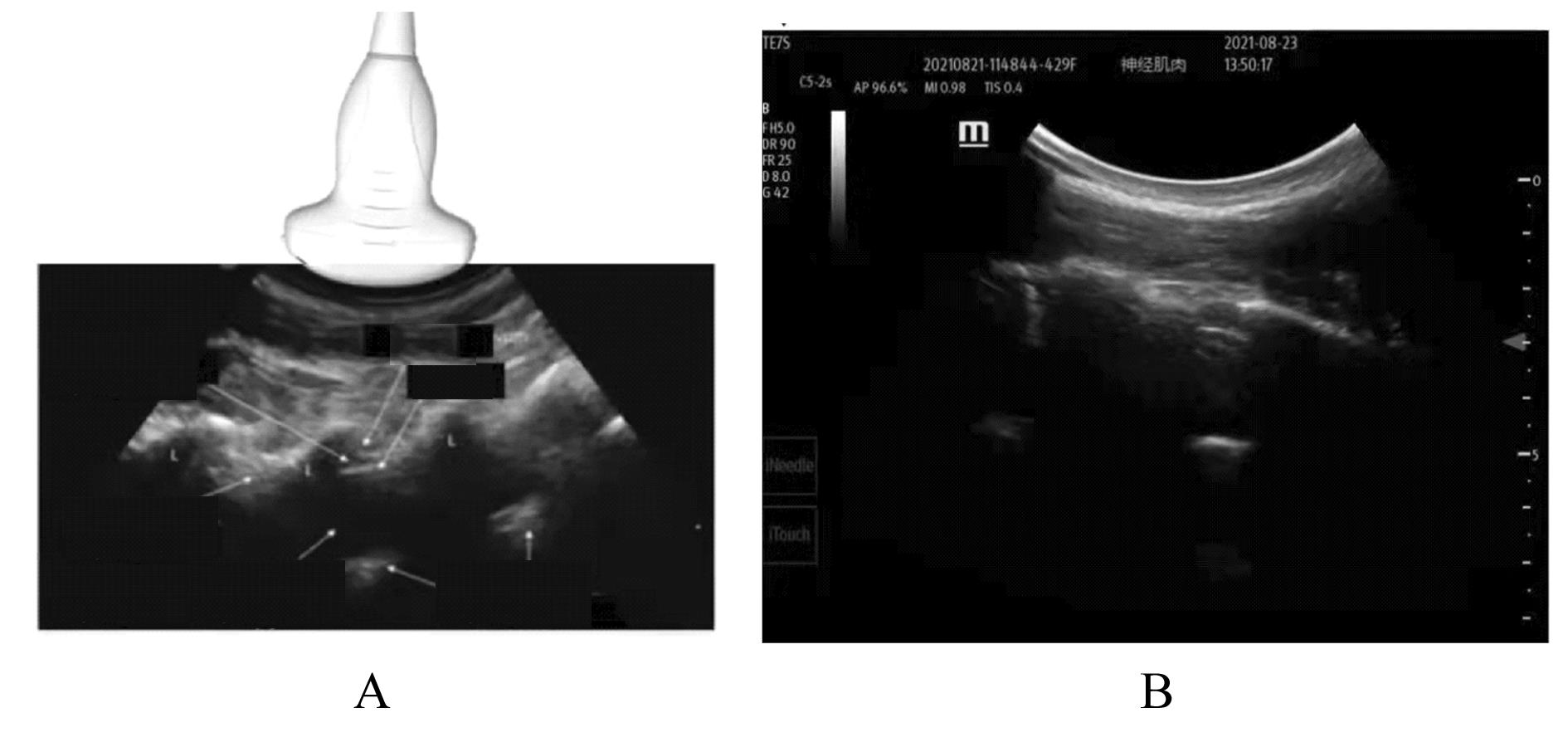
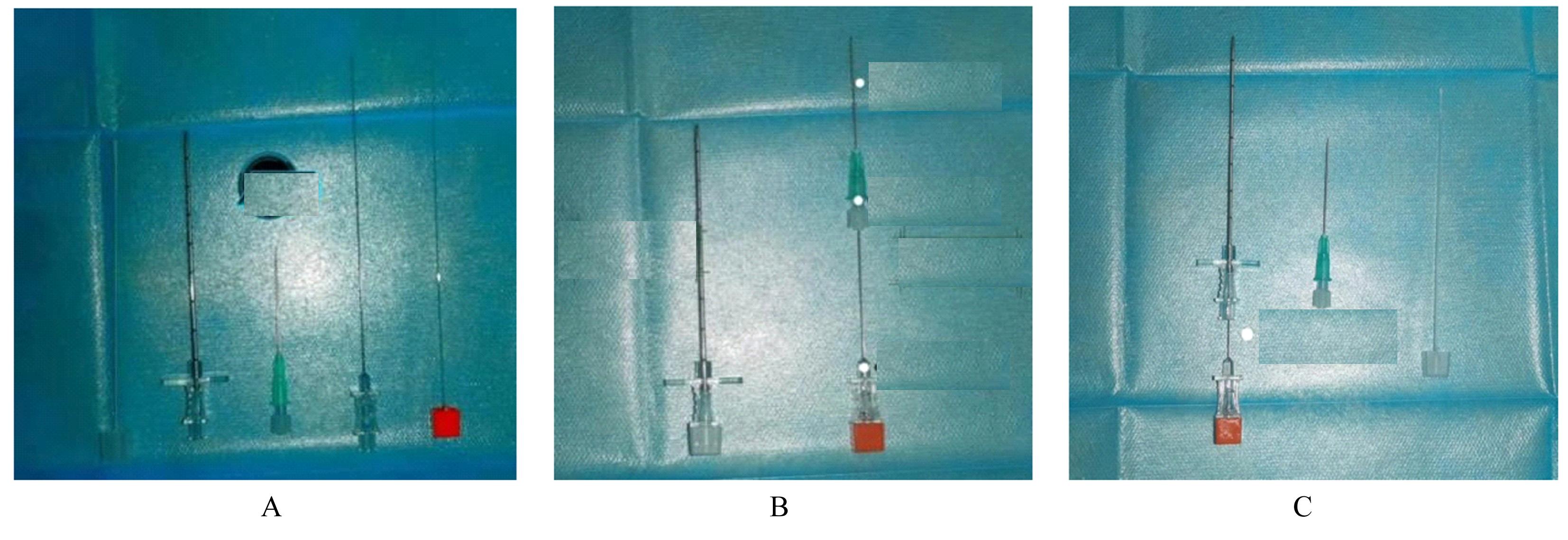
| 1 |
涂学云, 李有武, 万 仑, 等. 全身麻醉与椎管内麻醉对老年髋关节置换术患者凝血功能的影响分析[J]. 中国现代药物应用, 2020, 14(12): 82-84.
|
| 2 |
刘晓师, 马 月. 全身麻醉和椎管内麻醉对老年骨科手术患者术后精神状态及认知功能的影响[J]. 中国伤残医学, 2021, 29(1): 6-8.
|
| 3 |
张丙建. 老年髋关节置换术应用椎管内麻醉对比全身麻醉的优劣势研究[J]. 中国社区医师, 2019, 35(4): 101-102.
|
| 4 |
贾丽玲, 李雁楠, 杨 光, 等. 老年患者髋关节置换术中不同比重罗哌卡因腰麻临床应用比较[J]. 山西医科大学学报, 2018, 49(2): 186-189.
|
| 5 |
CHIN K J, RAMLOGAN R, ARZOLA C, et al. The utility of ultrasound imaging in predicting ease of performance of spinal anesthesia in an orthopedic patient population[J]. Reg Anesth Pain Med, 2013, 38(1): 34-38.
|
| 6 |
SAHOTA J S, CARVALHO J C A, BALKI M, et al. Ultrasound estimates for midline epidural punctures in the obese parturient: paramedian sagittal oblique is comparable to transverse Median plane[J]. Anesth Analg, 2013, 116(4): 829-835.
|
| 7 |
曾庆东, 陈 晨, 唐 浩, 等. 低剂量轻比重脊椎麻醉及神经阻滞麻醉用于髋关节置换术的临床研究[J]. 重庆医学, 2022, 51(17): 2901-2905.
|
| 8 |
王春晓, 李志华, 徐贯杰, 等. 小剂量轻比重布比卡因腰椎麻醉用于老年患者髋部手术的安全性研究[J]. 河北医科大学学报, 2022, 43(9): 1079-1084.
|
| 9 |
林华阳, 饶福东, 林 洁, 等. 改良脊椎-硬膜外联合阻滞法用于高龄患者膝关节置换术的可行性[J]. 中华麻醉学杂志, 2013, 33(12): 1458-1460.
|
| 10 |
耿 姣, 陈宣伶, 王雪冬, 等. 超声辅助定位可提高老年患者椎管内麻醉一次穿刺成功率[J]. 中华医学杂志, 2016, 96(43): 3459-3463.
|
| 11 |
董 慧, 王 云, 利雪阳, 等. 超声脊柱旁正中短轴扫描引导平面内腰段椎管内穿刺的效果: 与脊柱旁正中长轴扫描的比较[J]. 中华麻醉学杂志, 2018(4): 474-476.
|
| 12 |
林华阳. 一种用于超声引导微创腰麻的针内针穿刺装置: CN204106145U[P]. 2015-01-21.
|
| 13 |
林华阳. 一种单次蛛网膜下腔阻滞术中进针设备的控制系统: CN109171899A[P]. 2023-08-01.
|
| 14 |
林华阳. 单次蛛网膜下腔阻滞术中信息收集处理系统及其处理方法: CN109300168A[P]. 2019-02-01.
|
| 15 |
林华阳. 单次蛛网膜下腔阻滞术中进针设备的控制系统及控制方法: CN109190677A[P]. 2019-01-11.
|
| 16 |
夏大卫,李卫平,李宏博,等.穿刺针:CN216221592U[P]. 2022-04-08.
|
| 17 |
唐在荣, 徐知菲, 金 峰, 等. 25G细针侧隐窝入路单次腰麻在老年下肢骨折手术中的应用[J]. 临床麻醉学杂志, 2017, 33(11): 1117-1118.
|
| 18 |
HUANG D, ZHU L J, CHEN J, et al. Minimally invasive spinal anesthesia for cesarean section in maternal anticoagulation therapy: a randomized controlled trial[J]. BMC Anesthesiol, 2019, 19(1): 11.
|
| 19 |
张瑜玲, 陈璐莹, 姜梦婷, 等. 超声辅助定位在老年脊柱侧弯髋部骨折患者腰-硬联合麻醉中的应用[J]. 临床麻醉学杂志, 2021, 37(3): 277-281.
|
| 20 |
耿 姣, 李 民, 郭向阳. 脊柱畸形老年患者超声引导椎管内麻醉成功实施1例[J]. 中华麻醉学杂志, 2018, 38(10): 1273-1274.
|
| 21 |
林华阳, 饶福东, 林 洁, 等. 肌骨超声对改良针内针穿刺技术在单侧全髋关节置换老年人行单次高位腰麻中的应用[J]. 中国伤残医学, 2022, 30(2): 26-28.
|
| 22 |
林华阳, 饶福东, 张 枫, 等. 超声定位下罗哌卡因不同注药方法对单次等比重腰麻在老年单髋置换术中的应用效果[J]. 中国老年学杂志, 2022, 42(20): 4985-4989.
|
| 23 |
刘梦菲,何 龙,田丹丹,等.艾司氯胺酮复合右美托咪定行无阿片麻醉对乳腺癌改良根治术患者术后恢复质量的影响[J].郑州大学学报(医学版),2023,58(3):363-366.
|
| 24 |
PARK S K, YOO S, KIM W H, et al. Ultrasound-assisted vs. landmark-guided paramedian spinal anaesthesia in the elderly: a randomised controlled trial[J]. Eur J Anaesthesiol, 2019, 36(10): 763-771.
|
| 25 |
CHIN K J, PERLAS A, CHAN V, et al. Ultrasound imaging facilitates spinal anesthesia in adults with difficult surface anatomic landmarks[J]. Anesthesiology, 2011, 115(1): 94-101.
|
| 26 |
张保军, 王 凯, 房兰天, 等. 两种多模式镇痛方案在全膝关节置换术中应用效果的比较[J].郑州大学学报(医学版),2023,58(1):103-107.
|
| 27 |
谢淑芳, 管 婷, 俞晨远, 等. 剖宫产术患者三维脊柱超声引导硬膜外穿刺术的效果[J]. 中华麻醉学杂志, 2020, 40(12): 1487-1490.
|
| 28 |
尚若静, 徐建国. 椎管内麻醉的脊神经并发症及防治[J]. 临床麻醉学杂志, 2007, 23(5): 439-440.
|
 ),Fudong RAO2,Jie LIN2,Zhongbiao XIU3,Hong LIU3,Liangzhi ZHANG3,Tingting YANG,Yunxiao QU,Hanbing FANG,He SUN
),Fudong RAO2,Jie LIN2,Zhongbiao XIU3,Hong LIU3,Liangzhi ZHANG3,Tingting YANG,Yunxiao QU,Hanbing FANG,He SUN