| 1 |
BURNS N R, MUSICH D R, MARTIN C, et al. Class Ⅲ camouflage treatment: what are the limits?[J]. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop, 2010, 137(1):9-11.
|
| 2 |
NAKADA T, MOTOYOSHI M, HORINUKI E,et al. Cone-beam computed tomography evaluation of the association of cortical plate proximity and apical root resorption after orthodontic treatment[J]. J Oral Sci, 2016, 58(2): 231-236.
|
| 3 |
刘莉萍, 杨彤彤, 程佳秀. 骨性Ⅱ类上颌磨牙后间隙解剖特征分析[J]. 上海口腔医学, 2021, 30(4): 410-413.
|
| 4 |
田 玲, 周 诺, 宋少华. 下颌第三磨牙倾斜度及磨牙后间隙与骨性Ⅲ类错 畸形的相关性探讨[J]. 临床口腔医学杂志, 2018, 34(9): 533-535. 畸形的相关性探讨[J]. 临床口腔医学杂志, 2018, 34(9): 533-535.
|
| 5 |
KIM S J, CHOI T H, BAIK H S, et al. Mandibular posterior anatomic limit for molar distalization[J]. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop, 2014, 146(2): 190-197.
|
| 6 |
ZHAO Z D, WANG Q Y, YI P, et al. Quantitative evaluation of retromolar space in adults with different vertical facial types[J]. Angle Orthod, 2020, 90(6): 857-865.
|
| 7 |
FAN Z, ZHANG Q, JIANG Y J, et al. Mandibular retromolar space in adults with different sagittal skeletal patterns[J]. Angle Orthod, 2022, 92(5): 606-612.
|
| 8 |
HORNER K A, BEHRENTS R G, KIM K B, et al. Cortical bone and ridge thickness of hyperdivergent and hypodivergent adults[J]. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop, 2012, 142(2): 170-178.
|
| 9 |
MASUMOTO T, HAYASHI I, KAWAMURA A,et al.Relationships among facial type, buccolingual molar inclination, and cortical bone thickness of the mandible[J]. Eur J Orthod, 2001, 23(1): 15-23.
|
| 10 |
郭学强, 刘新强, 王 铮, 等. 成人下颌磨牙后间隙与第三磨牙关系的三维研究[J]. 中华口腔正畸学杂志, 2021, 28(2): 74-79.
|
| 11 |
贺 红. 种植体支抗辅助牙列整体远移的疗效及长期稳定性的研究进展[J]. 中华口腔医学杂志, 2018,53(9): 594-598.
|
| 12 |
RICHARDSON M E. Development of the lower third molar from 10 to 15 years[J].Angle Orthod,1973,43(2): 191-193.
|
| 13 |
乔 峰, 左志刚, 张 健. 不同矢状骨面型患者下颌磨牙后间隙特征分析[J].天津医药,2014,42(3):268-270.
|
| 14 |
CHOI Y T, KIM Y J, YANG K S, et al. Bone availability for mandibular molar distalization in adults with mandibular prognathism[J]. Angle Orthod, 2018, 88(1): 52-57.
|
| 15 |
KIM S H, CHA K S, LEE J W, et al. Mandibular skeletal posterior anatomic limit for molar distalization in patients with Class Ⅲ malocclusion with different vertical facial patterns[J].Korean J Orthod,2021,51(4): 250-259.
|
| 16 |
HUI V L Z, XIE Y X, ZHANG K W, et al. Anatomical limitations and factors influencing molar distalization[J]. Angle Orthod, 2022, 92(5): 598-605.
|
| 17 |
SATO H, KAWAMURA A, YAMAGUCHI M,et al. Relationship between masticatory function and internal structure of the mandible based on computed tomography findings[J]. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop, 2005, 128(6): 766-773.
|
| 18 |
SELLA-TUNIS T, POKHOJAEV A, SARIG R,et al. Human mandibular shape is associated with masticatory muscle force[J]. Sci Rep, 2018, 8(1): 6042.
|
| 19 |
KILIARIDIS S. Masticatory muscle influence on craniofacial growth[J].Acta Odontol Scand,1995,53(3): 196-202.
|
| 20 |
INGERVALL B, MINDER C. Correlation between maximum bite force and facial morphology in children[J].Angle Orthod,1997,67(6):415-422.
|
| 21 |
HWANG S, SONG J, LEE J, et al. Three-dimensional evaluation of dentofacial transverse widths in adults with different sagittal facial patterns[J]. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop, 2018, 154(3): 365-374.
|
 )
)
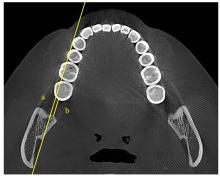
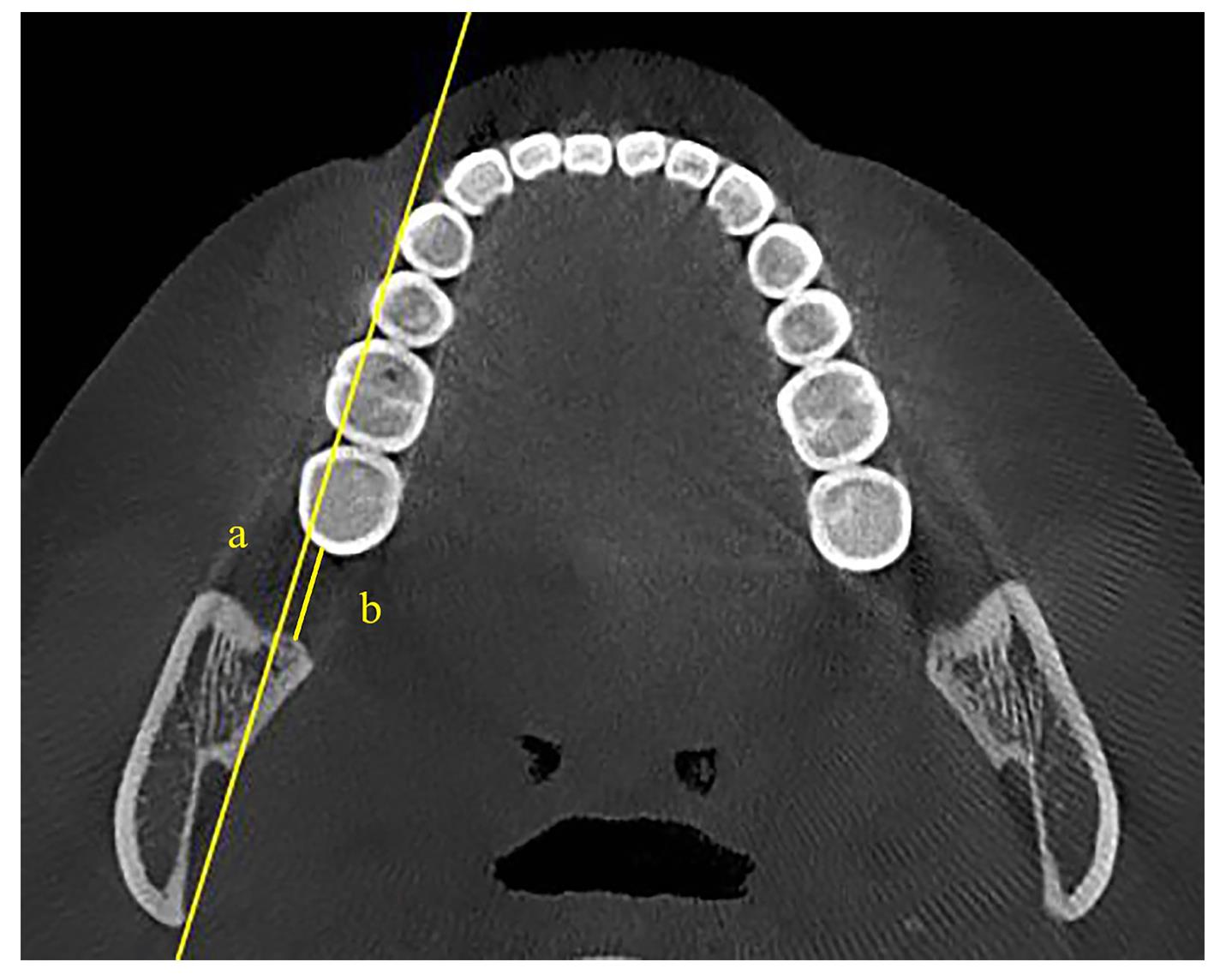
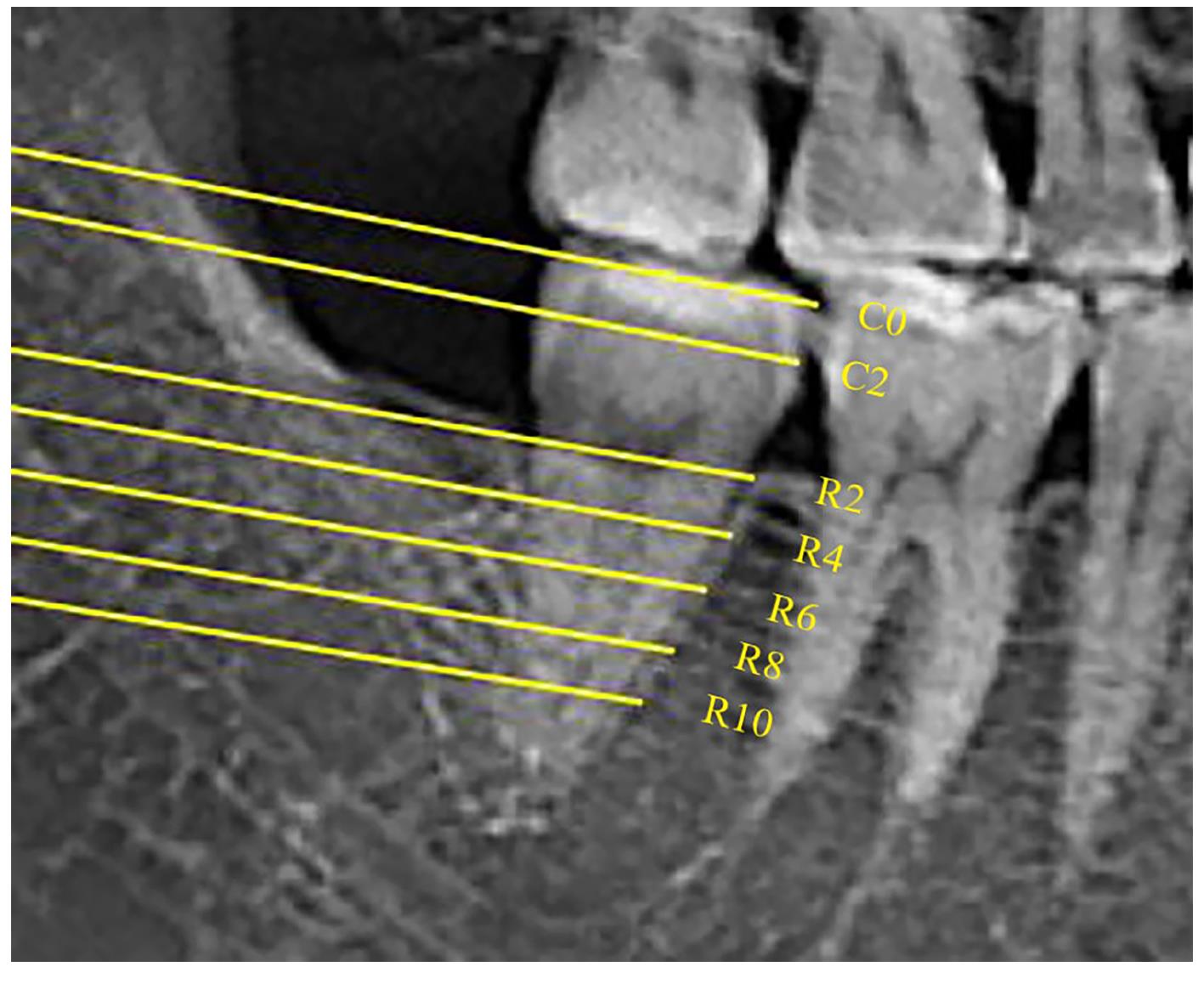
 畸形的相关性探讨[J]. 临床口腔医学杂志, 2018, 34(9): 533-535.
畸形的相关性探讨[J]. 临床口腔医学杂志, 2018, 34(9): 533-535.


