| 1 |
BRAY F, FERLAY J, SOERJOMATARAM I, et al. Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries[J].CA Cancer J Clin,2018,68(6):394-424.
|
| 2 |
YAN B, SU B B, BAI D S, et al. A practical nomogram and risk stratification system predicting the cancer-specific survival for patients with early hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. Cancer Med, 2021,10(2): 496-506.
|
| 3 |
GALLE P R, FOERSTER F, KUDO M, et al. Biology and significance of alpha-fetoprotein in hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. Liver Int, 2019, 39(12): 2214-2229.
|
| 4 |
YANG D S, ZHU M Q, XIONG X Y, et al. Clinical features and prognostic factors in patients with microvascular infiltration of hepatocellular carcinoma: development and validation of a nomogram and risk stratification based on the SEER database[J]. Front Oncol, 2022, 12: 987603.
|
| 5 |
中华人民共和国国家卫生健康委员会.原发性肝癌诊疗指南(2022年版)[J]. 肿瘤综合治疗电子杂志, 2022,8(2): 16-53.
|
| 6 |
CUCCHETTI A, PISCAGLIA F, GRIGIONI A D, et al. Preoperative prediction of hepatocellular carcinoma tumour grade and micro-vascular invasion by means of artificial neural network: a pilot study[J]. J Hepatol, 2010, 52(6): 880-888.
|
| 7 |
WANG M J, DEVARAJAN K, SINGAL A G, et al. The doylestown algorithm: a test to improve the performance of AFP in the detection of hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. Cancer Prev Res, 2016, 9(2): 172-179.
|
| 8 |
GIANNINI E G, MARENCO S, BORGONOVO G, et al. Alpha-fetoprotein has no prognostic role in small hepatocellular carcinoma identified during surveillance in compensated cirrhosis[J]. Hepatology, 2012, 56(4): 1371-1379.
|
| 9 |
BAI D S, ZHANG C, CHEN P, et al. The prognostic correlation of AFP level at diagnosis with pathological grade, progression, and survival of patients with hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. Sci Rep,2017,7(1):12870.
|
| 10 |
FARINATI F, MARINO D, DE GIORGIO M, et al. Diagnostic and prognostic role of alpha-fetoprotein in hepatocellular carcinoma: both or neither?[J]. Am J Gastroenterol, 2006, 101(3): 524-532.
|
| 11 |
JIANG S J, ZHAO R J, LI Y R, et al. Prognosis and nomogram for predicting postoperative survival of duodenal adenocarcinoma: a retrospective study in China and the SEER database[J]. Sci Rep, 2018, 8(1): 7940.
|
| 12 |
WU J, ZHANG H B, LI L, et al. A nomogram for predicting overall survival in patients with low-grade endometrial stromal sarcoma: a population-based analysis[J]. Cancer Commun, 2020, 40(7): 301-312.
|
| 13 |
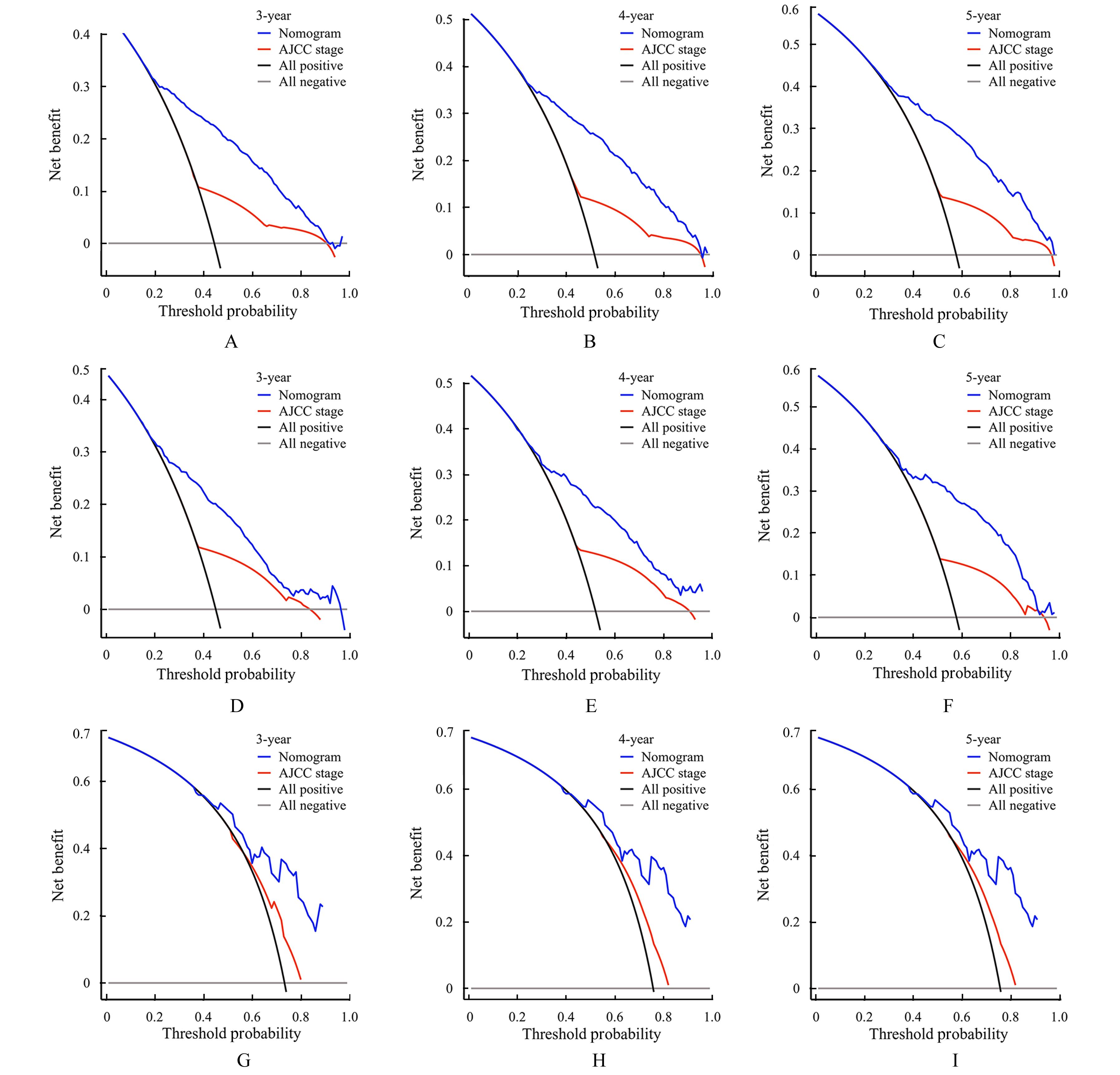
VICKERS A J, ELKIN E B. Decision curve analysis: a novel method for evaluating prediction models[J]. Med Decis Making, 2006, 26(6): 565-574.
|
| 14 |
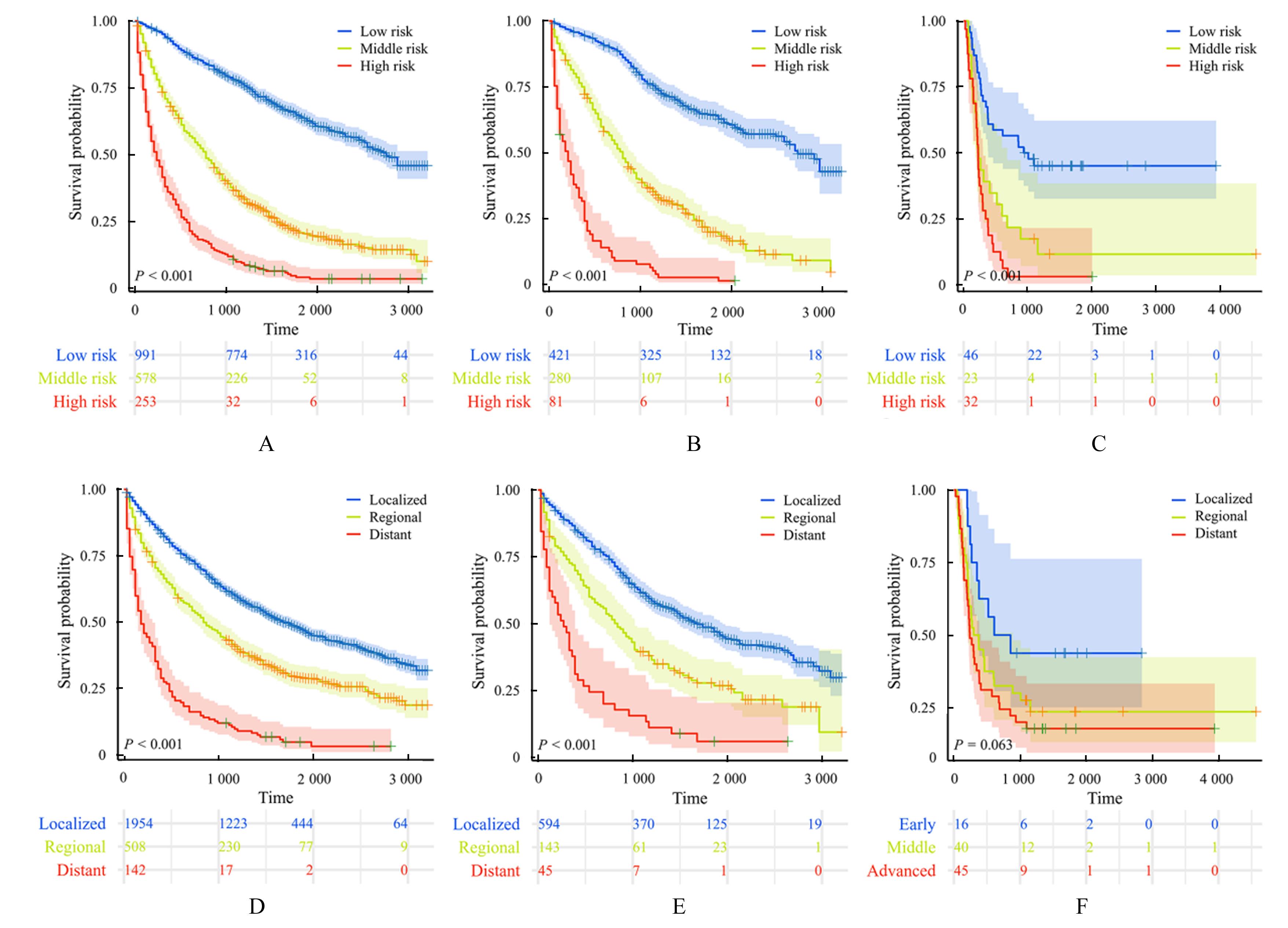
CAMP R L, DOLLED-FILHART M, RIMM D L. X-tile:a new bio-informatics tool for biomarker assessment and outcome-based cut-point optimization[J]. Clin Cancer Res, 2004, 10(21): 7252-7259.
|
| 15 |
TAN X J, WANG J K, TANG J, et al. A nomogram for predicting cancer-specific survival in children with wilms tumor: a study based on SEER database and external validation in China[J]. Front Public Health, 2022, 10: 829840.
|
| 16 |
HUANG X, LUO Z, LIANG W, et al. Survival nomogram for young breast cancer patients based on the SEER database and an external validation cohort[J]. Ann Surg Oncol, 2022, 29(9): 5772-5781.
|
| 17 |
LIU K, HUANG G B, CHANG P K, et al. Construction and validation of a nomogram for predicting cancer-specific survival in hepatocellular carcinoma patients[J]. Sci Rep, 2020, 10(1): 21376.
|
| 18 |
TERENTIEV A A, MOLDOGAZIEVA N T. Alpha-fetoprotein: a renaissance[J].Tumour Biol,2013,34(4): 2075-2091.
|
| 19 |
TOYODA H, KUMADA T, TADA T, et al. Clinical utility of highly sensitive Lens culinaris agglutinin-reactive alpha-fetoprotein in hepatocellular carcinoma patients with alpha-fetoprotein <20 ng/mL[J]. Cancer Sci, 2011, 102(5): 1025-1031.
|
| 20 |
XU Y Y, LU X, MAO Y L, et al. Clinical diagnosis and treatment of alpha-fetoprotein-negative small hepatic lesions[J]. Chung Kuo Yen Cheng Yen Chiu, 2013, 25(4): 382-388.
|
| 21 |
ZHANG X F, QI X, MENG B, et al. Prognosis evaluation in alpha-fetoprotein negative hepatocellular carcinoma after hepatectomy: comparison of five staging systems[J]. Eur J Surg Oncol, 2010, 36(8): 718-724.
|
| 22 |
GÓMEZ-RODRÍGUEZ R, ROMERO-GUTIÉRREZ M, ARTAZA-VARASA T, et al. The value of the Barcelona Clinic Liver Cancer and alpha-fetoprotein in the prognosis of hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. Rev Esp Enferm Dig, 2012, 104(6): 298-304.
|
| 23 |
GAN W, HUANG J L, ZHANG M X, et al. New nomogram predicts the recurrence of hepatocellular carcinoma in patients with negative preoperative serum AFP subjected to curative resection[J]. J Surg Oncol, 2018, 117(7): 1540-1547.
|
| 24 |
REN N, QIN L X, TU H, et al. The prognostic value of circulating plasma DNA level and its allelic imbalance on chromosome 8p in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol, 2006, 132(6): 399-407.
|
| 25 |
WANG X P, MAO M J, HE Z L, et al. Development and validation of a prognostic nomogram in AFP-negative hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. Int J Biol Sci, 2019, 15(1): 221-228.
|
| 26 |
ZHAN H, ZHAO X, LU Z X, et al. Correlation and survival analysis of distant metastasis site and prognosis in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. Front Oncol, 2021, 11: 652768.
|
| 27 |
ZHANG W, JI L C, WANG X J, et al. Nomogram predicts risk and prognostic factors for bone metastasis of pancreatic cancer: a population-based analysis[J]. Front Endocrinol, 2021, 12: 752176.
|
| 28 |
WANG H M, SHAN X F, ZHANG M, et al. Homogeneous and heterogeneous risk and prognostic factors for lung metastasis in colorectal cancer patients[J]. BMC Gastroenterol, 2022, 22(1): 193.
|
| 29 |
TONG Y X, HUANG Z H, HU C, et al. Independent risk factors evaluation for overall survival and cancer-specific survival in thyroid cancer patients with bone metastasis: a study for construction and validation of the predictive nomogram[J].Medicine,2020,99(36):e21802.
|
| 30 |
HUANG Z H, HU C, LIU K W, et al. Risk factors, prognostic factors, and nomograms for bone metastasis in patients with newly diagnosed infiltrating duct carcinoma of the breast: a population-based study[J]. BMC Cancer, 2020, 20(1): 1145.
|
 ),Puhua ZENG2,3(
),Puhua ZENG2,3( )
)