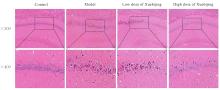
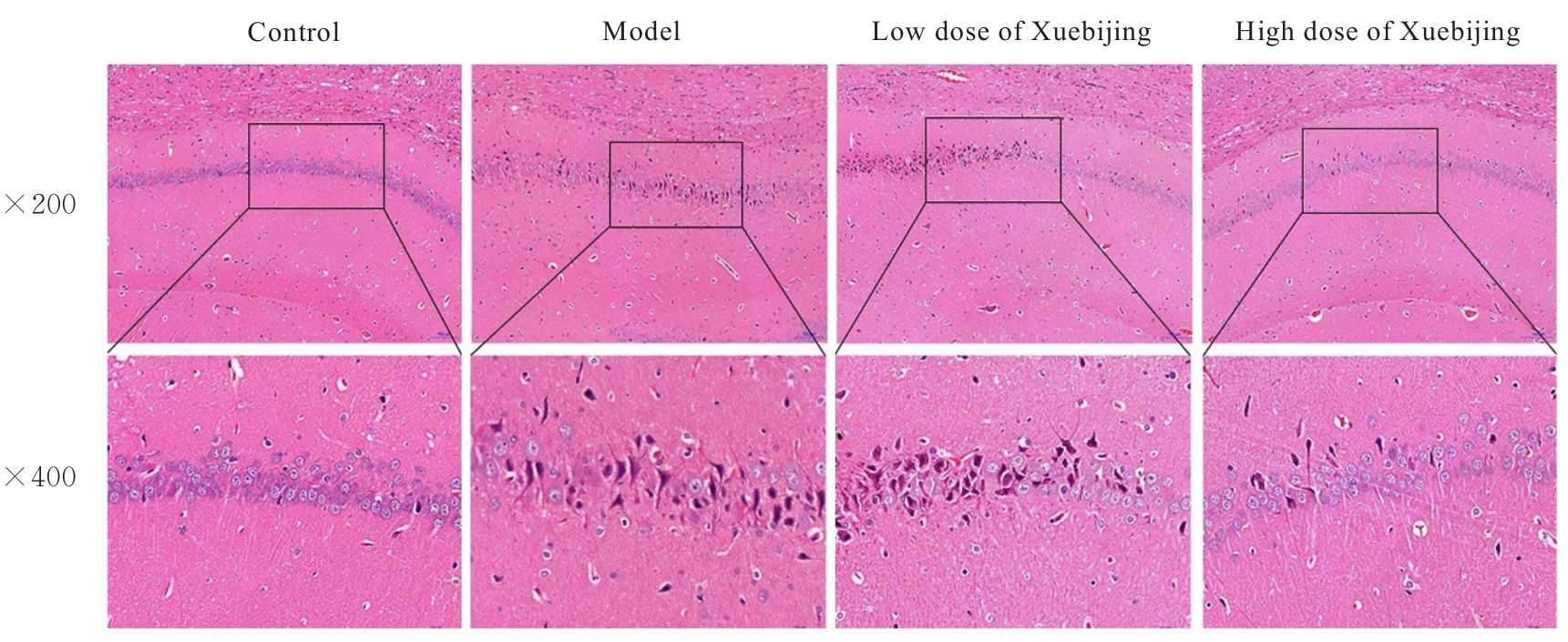
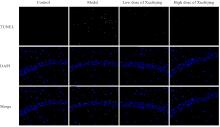
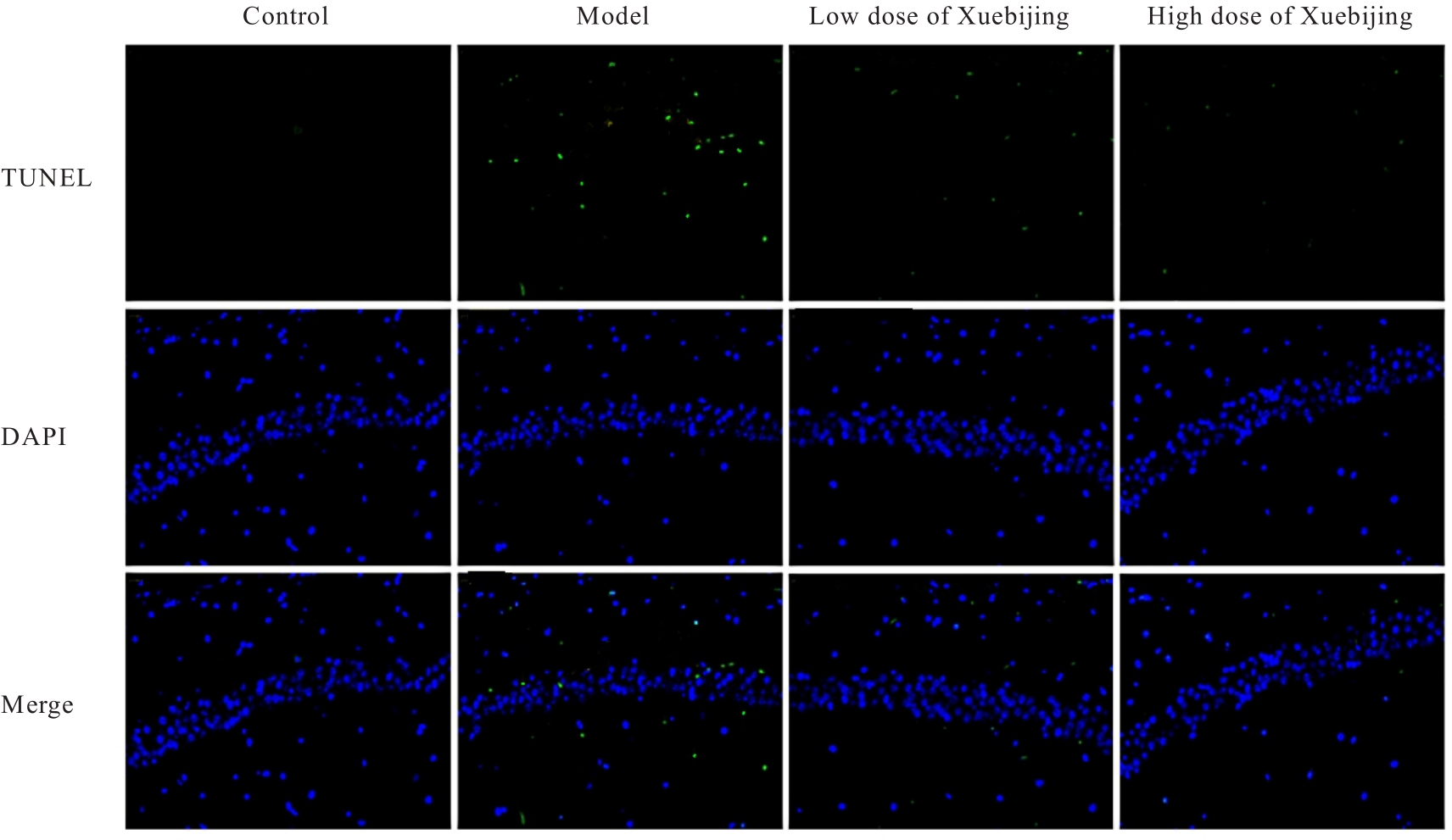
| 1 |
BASSAL F C, HARWOOD M, OH A, et al. Anti-NMDA receptor encephalitis and brain atrophy in children and adults: a quantitative study[J]. Clin Imaging, 2021, 78: 296-300.
|
| 2 |
GU J X, CHEN Q, GU H D, et al. Research progress in teratoma-associated anti-N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor encephalitis: the gynecological perspective[J]. J Obstet Gynaecol Res, 2021, 47(11): 3749-3757.
|
| 3 |
HUANG Q Y, XIE Y, HU Z P, et al. Anti-N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor encephalitis: a review of pathogenic mechanisms, treatment, prognosis[J]. Brain Res, 2020, 1727: 146549.
|
| 4 |
WALKER C A, POULIK J, D’MELLO R J. Anti-NMDA receptor encephalitis in an adolescent with a cryptic ovarian teratoma[J]. BMJ Case Rep, 2021, 14(7): e236340.
|
| 5 |
RAPHAEL I, JOERN R R, FORSTHUBER T G. Memory CD4+ T cells in immunity and autoimmune diseases[J]. Cells, 2020, 9(3): 531.
|
| 6 |
李红岩, 侯振江, 刘建凤, 等. Th17/Treg细胞及其细胞因子在神经系统自身免疫性疾病中的研究进展[J]. 医学综述, 2021, 27(5): 889-895, 900.
|
| 7 |
LEE G R. The balance of Th17 versus Treg cells in autoimmunity[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2018, 19(3): 730.
|
| 8 |
朱 莉, 姜远安, 肖冠华, 等. MiR-125b在病毒性脑炎患儿中的表达水平及其与Th17/Treg平衡及预后的关系[J]. 疑难病杂志, 2021, 20(2): 129-133.
|
| 9 |
李维燕, 张丽平, 董俊刚. 血必净的临床应用研究进展[J]. 实用中医内科杂志, 2022, 36(10): 66-70.
|
| 10 |
CHEN X, FENG Y X, SHEN X Y, et al. Anti-sepsis protection of Xuebijing injection is mediated by differential regulation of pro- and anti-inflammatory Th17 and T regulatory cells in a murine model of polymicrobial sepsis[J]. J Ethnopharmacol, 2018, 211: 358-365.
|
| 11 |
叶 霖, 黄虹蜜, 吴 莹, 等. 抗NMDA受体脑炎相关癫痫小鼠脑组织小胶质细胞及IL-1β、TNF-α表达的变化[J]. 癫痫与神经电生理学杂志, 2022, 31(3): 129-134.
|
| 12 |
CHEN Z Q, ZHOU J T, WU D C, et al. Altered executive control network connectivity in anti-NMDA receptor encephalitis[J]. Ann Clin Transl Neurol, 2022, 9(1): 30-40.
|
| 13 |
WANG B S, ZOU L, ZHOU L. Lipid bilayers regulate allosteric signal of NMDA receptor GluN1 C-terminal domain[J]. Biochem Biophys Res Commun, 2021, 585: 15-21.
|
| 14 |
LIN K L, LIN J J. Neurocritical care for Anti-NMDA receptor encephalitis[J]. Biomed J, 2020, 43(3): 251-258.
|
| 15 |
NOSADINI M, EYRE M, MOLTENI E, et al. Use and safety of immunotherapeutic management of N-methyl-d-aspartate receptor antibody encephalitis: a meta-analysis[J]. JAMA Neurol, 2021, 78(11): 1333-1344.
|
| 16 |
CHEN Y, TONG H S, PAN Z G, et al. Xuebijing injection attenuates pulmonary injury by reducing oxidative stress and proinflammatory damage in rats with heat stroke[J]. Exp Ther Med, 2017, 13(6): 3408-3416.
|
| 17 |
LIU J F, WANG Z Z, LIN J, et al. Xuebijing injection in septic rats mitigates kidney injury, reduces cortical microcirculatory disorders, and suppresses activation of local inflammation[J]. J Ethnopharmacol, 2021, 276: 114199.
|
| 18 |
韩 睿, 李清廉, 刘 锐, 等. 血必净注射液对大鼠缺血性脑损伤的神经保护作用部分通过PI3K/Akt信号通路介导[J]. 中国实验诊断学, 2019, 23(2): 293-297.
|
| 19 |
张美琦, 王浩嘉, 李艺颖, 等. 血必净注射液对多种病毒的抑制作用及机制研究[J]. 药物评价研究, 2022, 45(9): 1697-1705.
|
| 20 |
YANG P, QIAN F Y, ZHANG M F, et al. Th17 cell pathogenicity and plasticity in rheumatoid arthritis[J]. J Leukoc Biol, 2019, 106(6): 1233-1240.
|
| 21 |
YASUDA K, TAKEUCHI Y, HIROTA K. The pathogenicity of Th17 cells in autoimmune diseases[J]. Semin Immunopathol, 2019, 41(3): 283-297.
|
| 22 |
OHKURA N, SAKAGUCHI S. Transcriptional and epigenetic basis of Treg cell development and function: its genetic anomalies or variations in autoimmune diseases[J]. Cell Res, 2020, 30(6): 465-474.
|
| 23 |
KUMAR R, THEISS A L, VENUPRASAD K. RORγt protein modifications and IL-17-mediated inflammation[J]. Trends Immunol, 2021, 42(11): 1037-1050.
|
| 24 |
ONO M. Control of regulatory T-cell differentiation and function by T-cell receptor signalling and Foxp3 transcription factor complexes[J]. Immunology, 2020, 160(1): 24-37.
|
 )
)