Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition) ›› 2024, Vol. 50 ›› Issue (5): 1243-1249.doi: 10.13481/j.1671-587X.20240507
• Research in basic medicine • Previous Articles
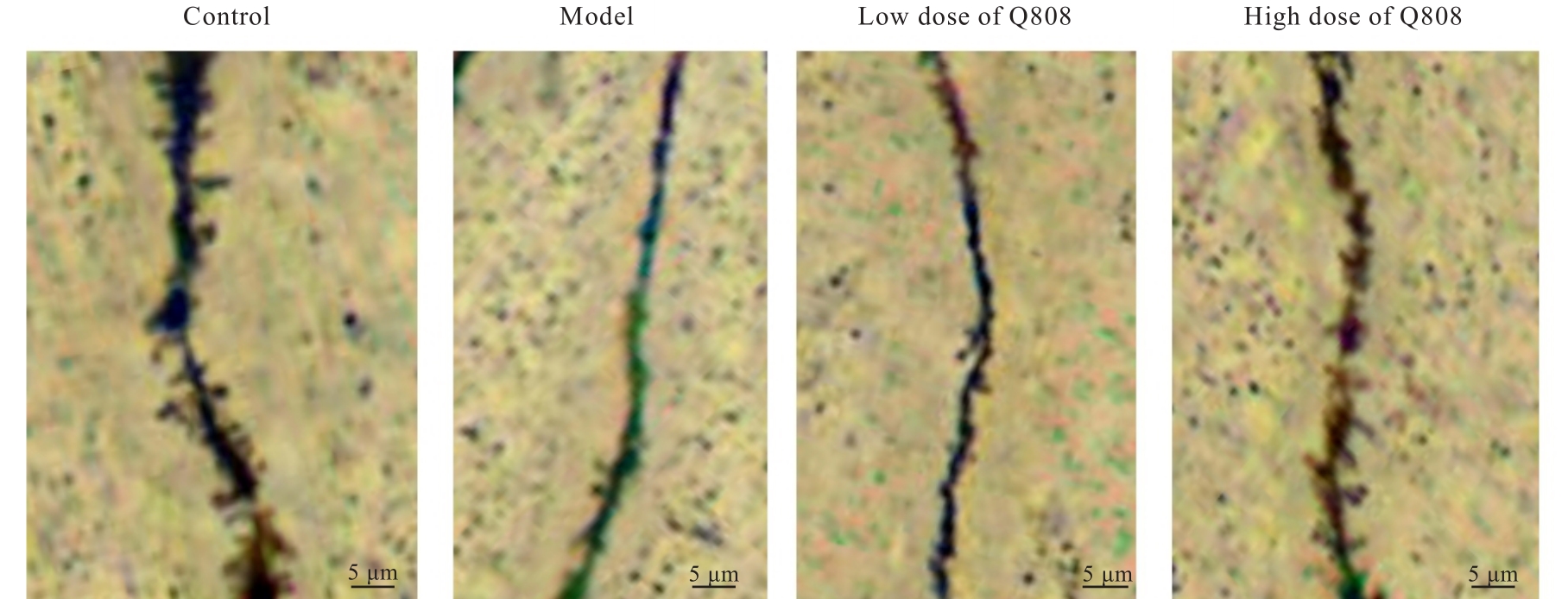
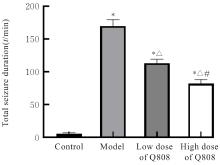
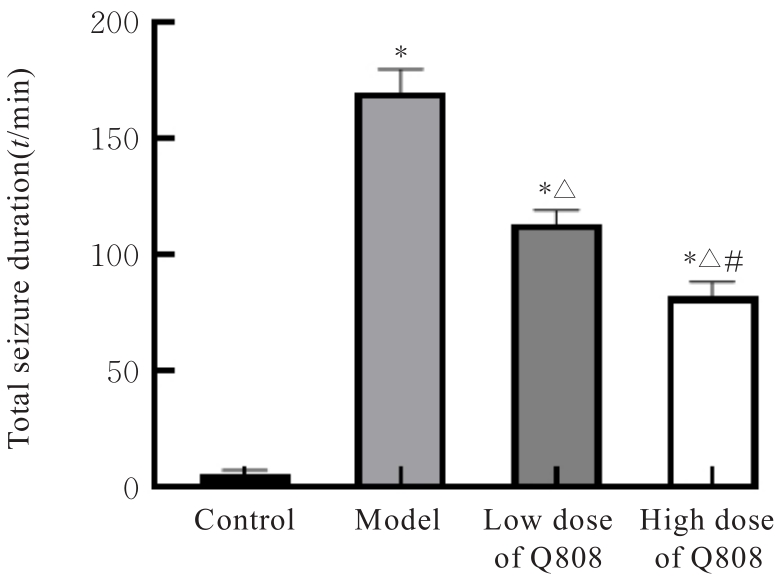
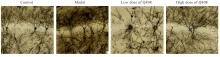
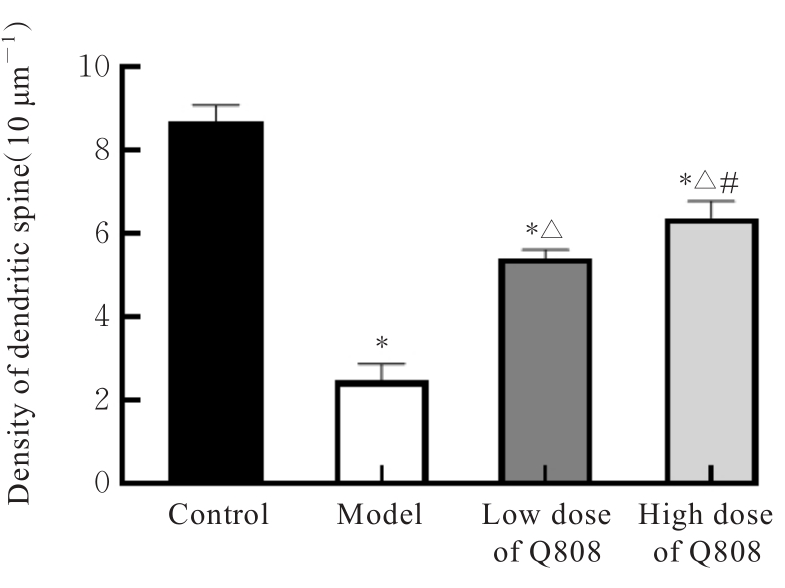
Ameliorative effect of novel antiepileptic drug Q808 on rats with temporal lobe epilepsy and its mechanism
Weiwei ZHENG,Fan GAO,Zhenlin YANG,Jiarui LI,Jingjing GUO,Jinzi LI( )
)
- Department of Pediatrics,Affiliated Hospital,Yanbian University,Yanji 133000,China
CLC Number:
- R742.1