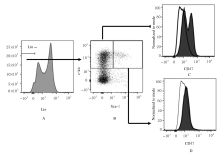
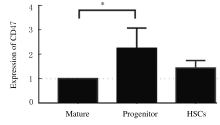
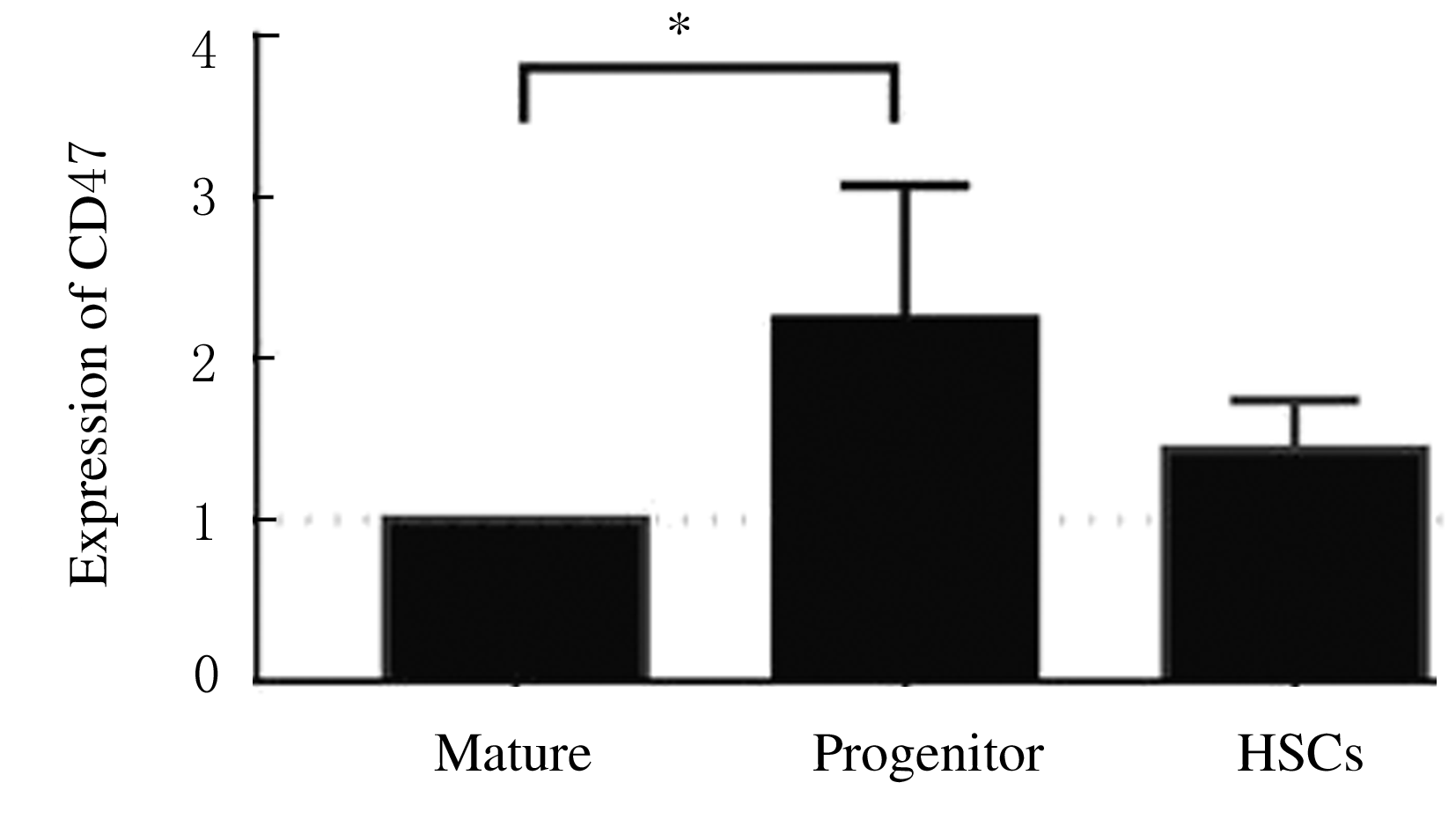
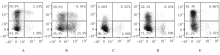
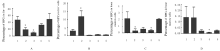
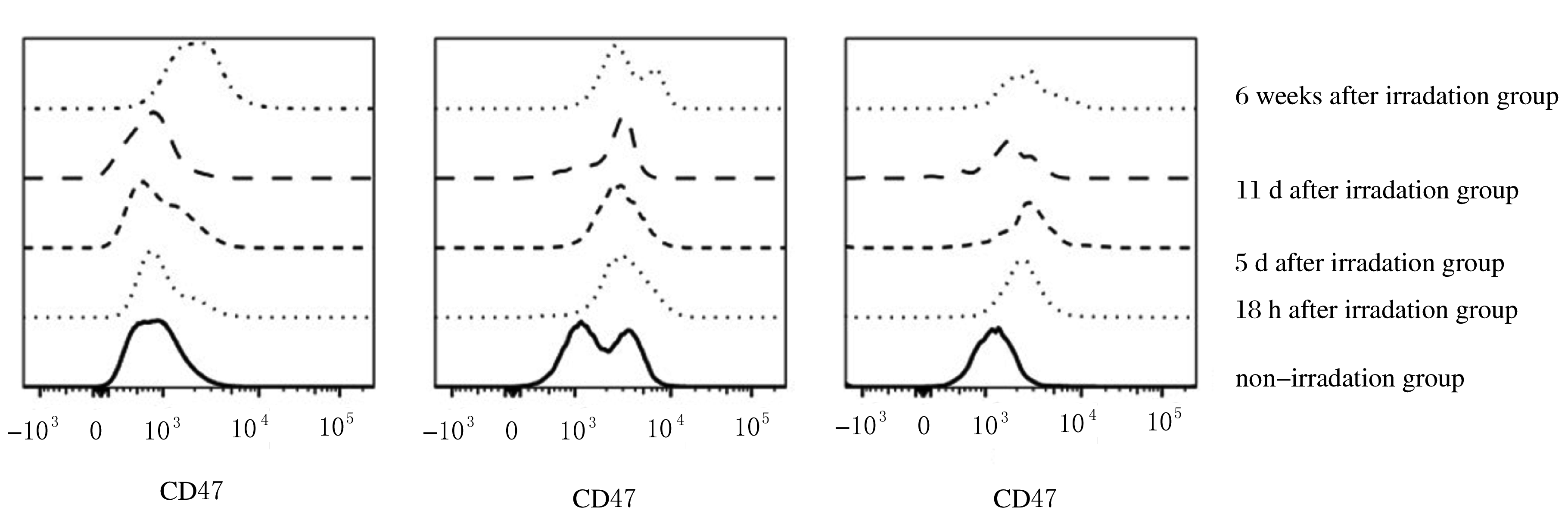
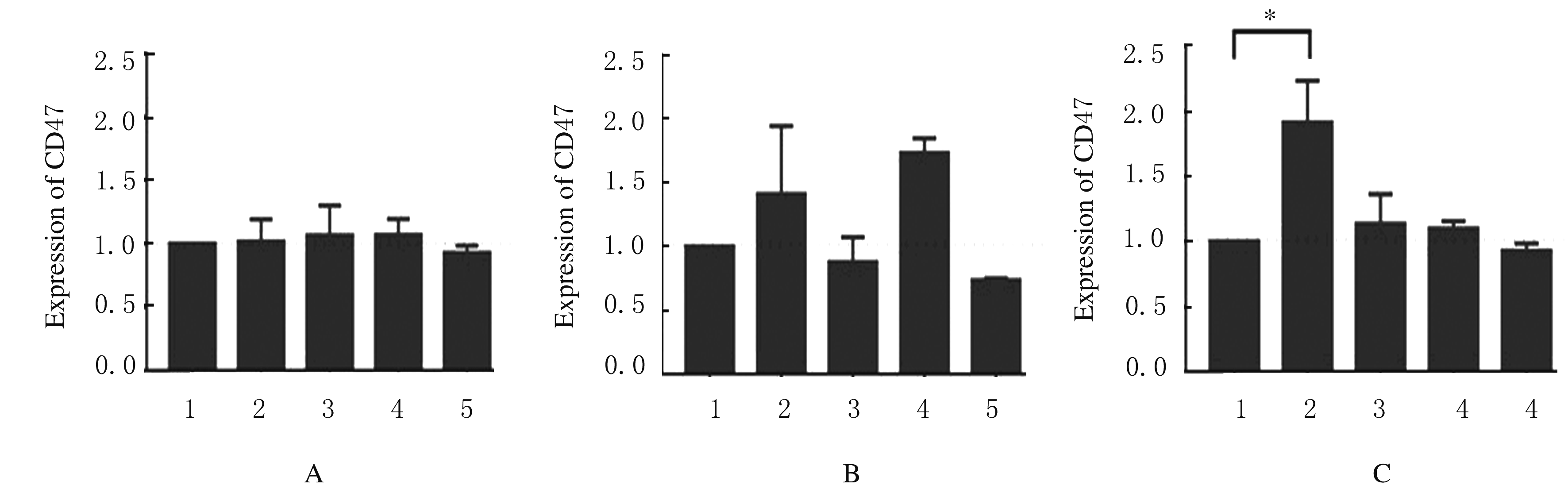
| [1] |
TANG Geng, SHI Yaoting, KONG Weixuan, KE Xiyang, LI Chengxiang, QIU Yuqi, YU Lei, YANG Yanming, WANG Zhicheng.
Effect of ionizing radiation on DNA damage repair in HeLa cells silencing ATRX
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2019, 45(05): 981-985.
|
| [2] |
REN Ming, ZHANG Yan, LI Ronghang, LI Qiuju.
Effect of Ginkgo biloba L. extract on oxidative stress and activity of protein kinase C in spleen tissue of mice with irradiation damage
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2019, 45(02): 223-227.
|
| [3] |
QUAN Xiaoyue, LIU Bailong, LIU Min, DONG Lihua.
Treatment of lung squamous cell carcinoma with apatinib in patient who couldn't tolerate chemotherapy: A case report and literature review
[J]. Journal of Jilin University Medicine Edition, 2018, 44(03): 624-627.
|
| [4] |
YU Lei, WANG Yunlong, CHEN Zhishen, WANG Xinchun, GAO Yugang, JIA Xiaojing.
Influence of antlerbase on Notch2 gene expression and immune functionof mice with thymic lymphomas induced by ionizing radiation
[J]. Journal of Jilin University Medicine Edition, 2016, 42(05): 887-891.
|
| [5] |
HU Zhihong, ZHAO Dali, XIE Zhongwei, WANG Mengying, HU Jingkun, GONG Shouliang, LIU Yang, QI Yali.
Effects of pEgr1-TRAIL recombinant plasmid combined with ionizing radiation on related gene and protein expressions of death receptor pathway in breast cancer MCF-7 cells
[J]. Journal of Jilin University Medicine Edition, 2016, 42(03): 419-423.
|
| [6] |
ZHANG Jing, ZHAO Dali, XIE Zhongwei, LIU Yanjun, LI Zhijun, LI Yan, GONG Shouliang, QI Yali.
Effects of ionizing radiation on autophagy and apoptosis in MCF-7 cells with Beclin 1 over-and low-expressions and their regulating mechanisms
[J]. Journal of Jilin University Medicine Edition, 2015, 41(06): 1139-1143.
|
| [7] |
QI Yali, ZHAO Dali, LIU Yanjun, GONG Shouliang, WANG Zhicheng.
Effects of Akt combined with ionizing radiation onapoptosis, autophagy and proliferation in breast cancer MCF-7 cells
[J]. Journal of Jilin University Medicine Edition, 2015, 41(01): 1-5.
|
| [8] |
FANG Fang,ZHAO Xue-lian,LI Dan-li,BAI Yang,GONG Shou-liang,LIU Yang,WANG Zhi-cheng.
Effects of ionizing radiation on ROS,apoptosis and cell cycle in breast cancer stem cells
[J]. Journal of Jilin University Medicine Edition, 2014, 40(06): 1132-1137.
|
| [9] |
QI Ya-li1,2, LIU Hong-bin3, XIE Zhong-wei3, LIU Yan-jun4, WANG Jian-feng2,5.
Effects of ionizing radiation on proliferation and invasion of MCF-7 cells transfected with pcDNA3.1-Egr-1-AIF△1-480 plasmid
[J]. Journal of Jilin University Medicine Edition, 2014, 40(05): 929-932.
|
| [10] |
ZHOU Hui,YANG Bing,TANG Quan,SUN Yuan-ming,HAN Yin,FAN Fei-yue,LIU Xiao-dong,JIA Li-li.
Effect of ionizing radiation on expression of RANK in differentiation process of osteoclasts and its molecular mechanism of bone injury
[J]. Journal of Jilin University Medicine Edition, 2013, 39(6): 1127-1131.
|
| [11] |
SUN Bao-Wa, DONG Juan-Cong, WANG Jin-Hu, JIN Shun-Zi, TUN Cong-Mei.
Effects of ionizing radiation on regulatory factors in different subsets of T lymphocytes of immune organs in mice
[J]. J4, 2011, 37(6): 985-988.
|
| [12] |
MENG Fan-Xu, CHAN Yu-Xin, DONG Juan-Cong, JIN Shun-Zi.
Effects of ionizing radiation with different doses on |regulatory T cells and |expression of TGF-β1 in mouse spleen
[J]. J4, 2011, 37(3): 398-402.
|
| [13] |
JI E-Chi, ZHANG Shen-Yu, WANG Hong-Yan, LI Jin-Hua, GONG Shou-Liang.
Relationship between autophagy and apoptosis of MCF-7 cells induced
by ionizing radiation
[J]. J4, 2009, 35(6): 1007-1010.
|
| [14] |
YU Lei, LIU Yong-Zhe, SUN Shi-Long, FANG Fang, GONG Hong-Wei, CHEN Qiang, JU Gui-Zhi.
Analysis on relevance between c-myc gene and thymic lymphomas of mice induced by ionizing radiation
[J]. J4, 2009, 35(6): 971-974.
|
| [15] |
LIU Shu-chun,ZHAO Wen-ju,SUN Li-guang,LI Peng-wu,LU Zhe,GONG Shou-liang .
Time effect of adaptive response of apoptosis and cell cycle progression induced by low-dose ionizing radiation in EL-4 lymphoma cells in vitro
[J]. J4, 2008, 34(4): 543-546.
|
 ),Yongguang YANG(
),Yongguang YANG( )
)