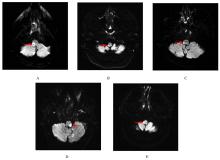
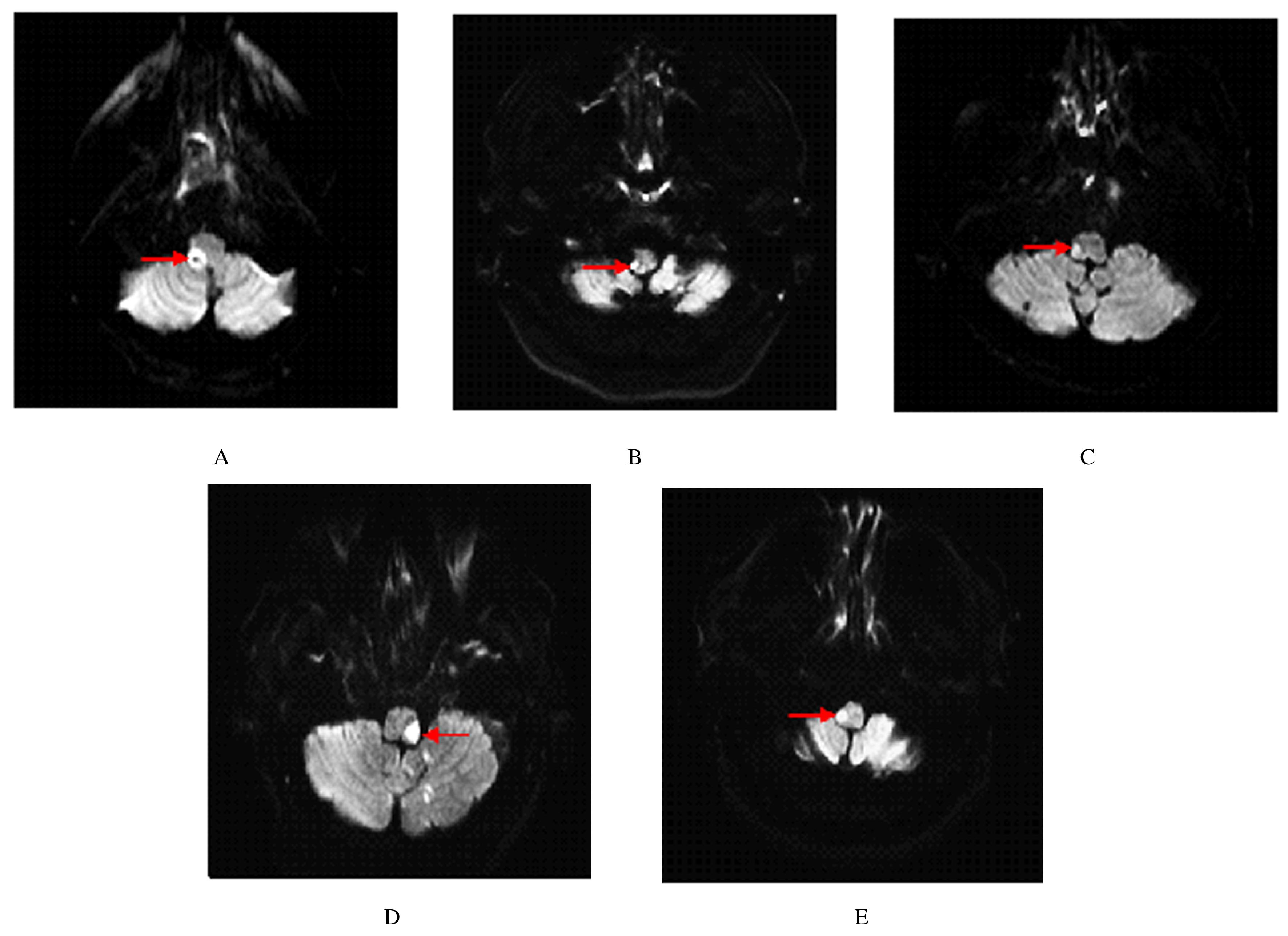
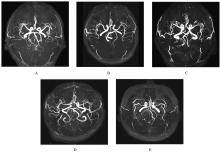
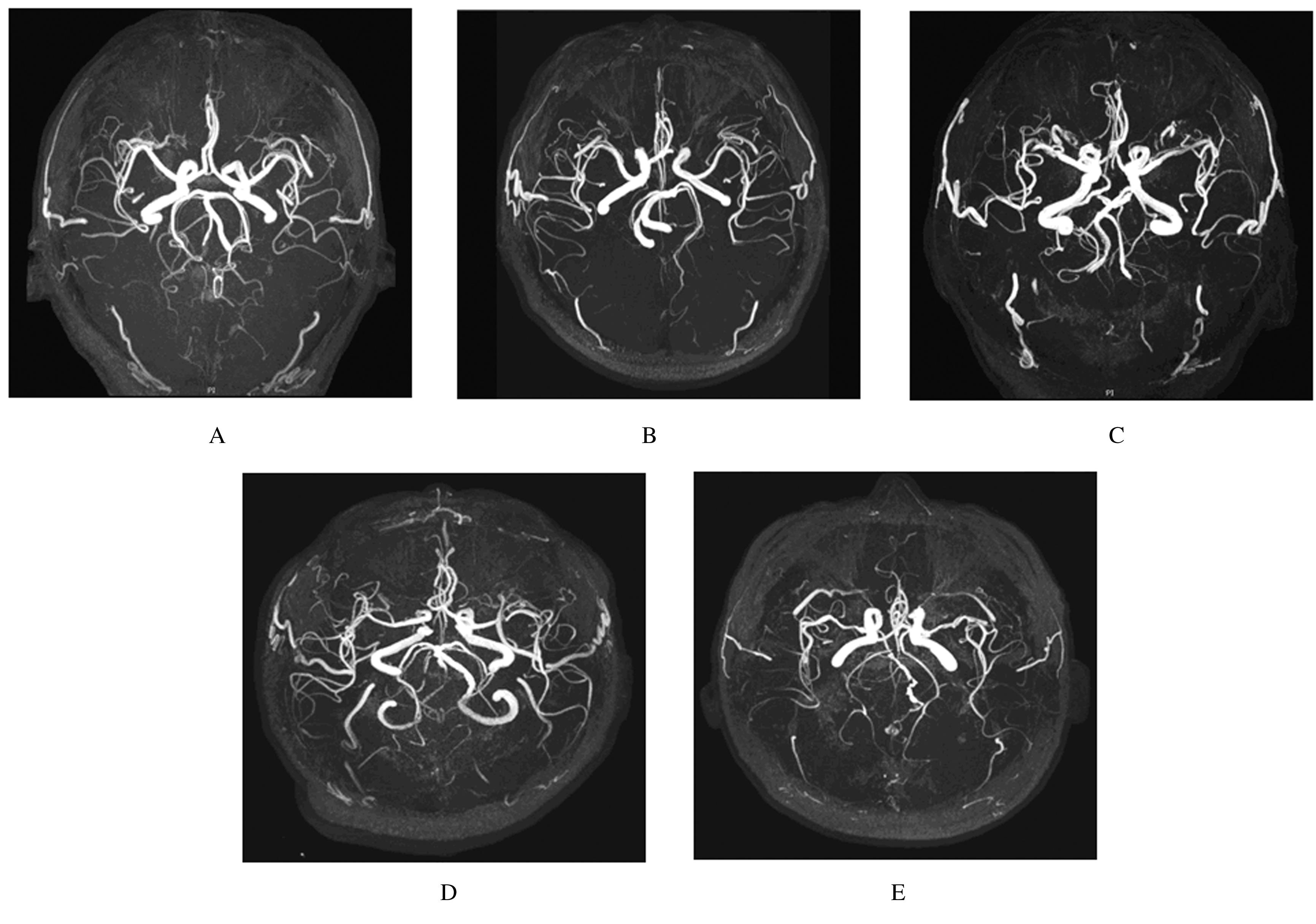
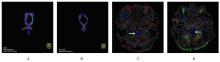
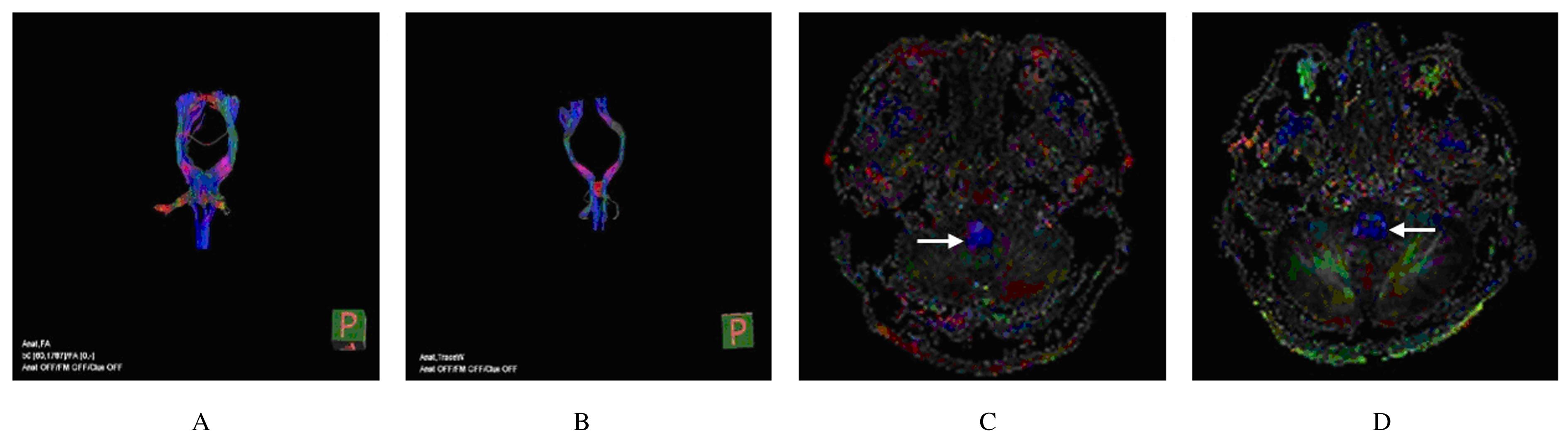
| 1 |
吴海香, 杨清成, 张向东. Opalski综合征临床特征分析[J]. 中国实用神经疾病杂志,2011,14(13): 39-41.
|
| 2 |
UEMURA M, NARITOMI H, UNO H, et al. Ipsilateral hemiparesis in lateral medullary infarction: Clinical investigation of the lesion location on magnetic resonance imaging[J]. J Neurol Sci, 2016, 365: 40-45.
|
| 3 |
苏 琪, 孙洪扬, 解忠祥, 等. Opalski综合征1例报告[J]. 中国神经精神疾病杂志, 2019, 45(4): 235-236.
|
| 4 |
OGAWA T, SHOJIMA Y, KUROKI T, et al. Cervico-shoulder dystonia following lateral medullary infarction: a case report and review of the literature[J]. J Med Case Rep, 2018, 12(1): 34.
|
| 5 |
KON T, FUNAMIZU Y, UENO T, et al. Dermatomal sensory manifestations in Opalski syndrome[J]. J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis, 2017, 26(1): e18-e19.
|
| 6 |
AYNACI O, GOK F, YOSUNKAYA A. Management of a patient with Opalski’s syndrome in intensive care unit[J]. Clin Case Rep, 2017, 5(9): 1518-1522.
|
| 7 |
KK P, R K, P C, et al. A rare variant of Wallenberg’s syndrome: Opalski syndrome[J]. J Clin Diagn Res, 2014, 8(7): MD05-MD06.
|
| 8 |
LEVY M, LEVY E, MAIMON S. Atypical postpartum stroke presenting as Opalski syndrome: case report and review of the literature[J]. Case Rep Neurol, 2011, 3(2): 191-198.
|
| 9 |
YANG S S, JIA J P. Differences in risk factors between anterior and posterior circulation affecting young ischemic stroke onset and prognosis[J]. Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi, 2013, 93(5): 348-351.
|
| 10 |
LEE G, ARCASOY M O.The clinical and laboratory evaluation of the patient with erythrocytosis[J]. Eur J Intern Med,2015,26(5): 297-302.
|
| 11 |
DEMBO T, TANAHASHI N. Opalski syndrome caused by vertebral artery compression of the lateral surface of the medulla oblongata[J]. Intern Med Tokyo Jpn, 2013, 52(10): 1115-1120.
|
| 12 |
DESHPANDE A, SHETTY A, PAI A R, et al. Abnormal brain MRI diffusion-weighted imaging in a case of Opalski syndrome[J].Case Rep,2014,2014(feb05 1): bcr2013201695.
|
| 13 |
KIM H Y, KOH S H, LEE K Y, et al. Opalski’s syndrome with cerebellar infarction[J]. J Clin Neurol, 2006, 2(4): 276-278.
|
| 14 |
BAILON O, GARCIA P Y, LOGAK M, et al. Opalski syndrome detected on DWI MRI: a rare lateral medullary infarction. Case report and review[J]. Rev Neurol (Paris), 2011, 167(2): 177-180.
|
| 15 |
MAHALE R R, MEHTA A, MIRYALA A, et al. A probable cavernoma in the medulla oblongata presenting as Opalski syndrome: a rare entity[J]. Neurol India, 2016, 64(): S113-S114.
|
| 16 |
KIM J S. Pure lateral medullary infarction: clinical-radiological correlation of 130 acute, consecutive patients[J]. Brain, 2003, 126(pt 8): 1864-1872.
|
| 17 |
韩艺华, 王心慧, 陈嘉峰. Opalski综合征3例报告[J]. 中风与神经疾病杂志, 2014, 31(8): 737.
|
| 18 |
HARA D, AKAMATSU M, MIZUKAMI H, et al. Opalski syndrome treated with intravenous recombinant tissue type plasminogen activator-case report and review of literature[J].J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis,2020,29(8):104806.
|
| 19 |
LEI Q, LV J, KANG B, et al. Comorbid SUNCT syndrome and opalski syndrome caused by dorsolateral medullary infarction[J]. Front Neurol, 2020, 11: 52.
|
| 20 |
NAKAMURA S, KITAMI M, FURUKAWA Y. Opalski syndrome: ipsilateral hemiplegia due to a lateral-medullary infarction[J]. Neurology, 2010, 75(18): 1658.
|
| 21 |
张 婧,赵志勇,张国晋,等.微囊型脑膜瘤与脑膜尤文肉瘤/外周原始神经外胚层肿瘤的MRI鉴别诊断[J].中国医学物理学杂志,2021,38(5):561-565.
|
| 22 |
KAMEDA W, KAWANAMI T, KURITA K, et al. Lateral and medial medullary infarction: a comparative analysis of 214 patients[J]. Stroke, 2004, 35(3): 694-699.
|
 ),Jinting HE1(
),Jinting HE1( )
)