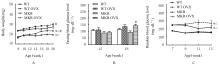
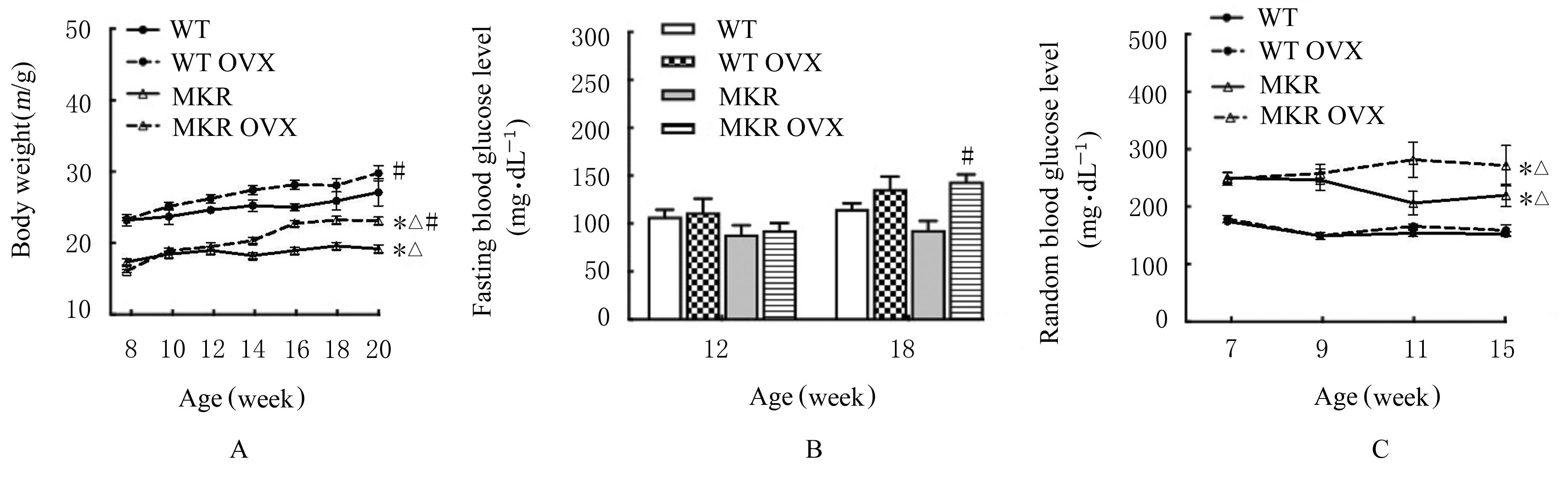
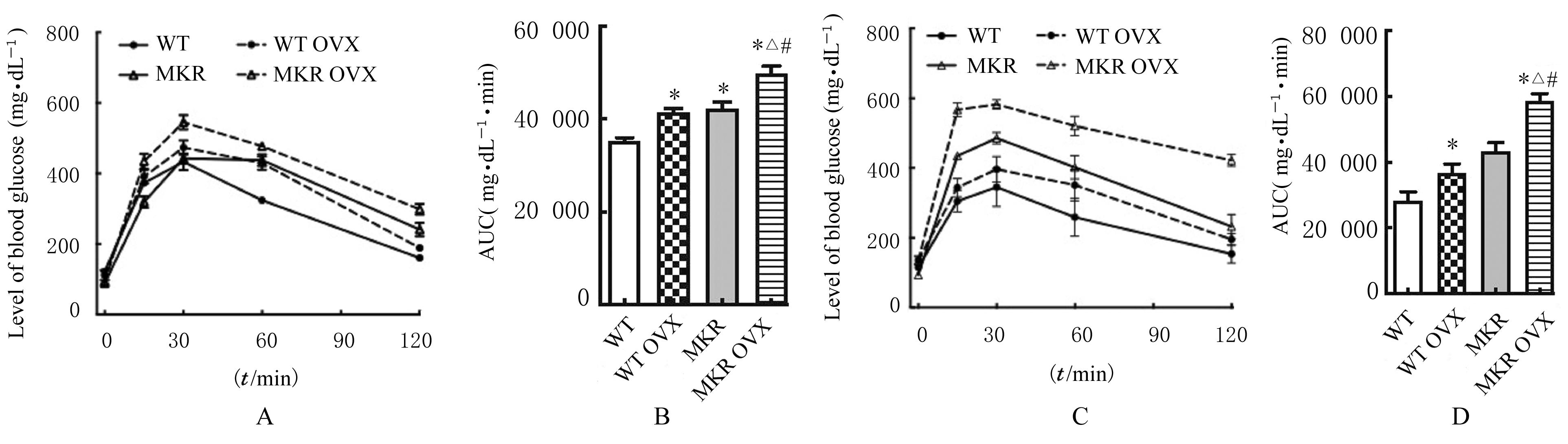
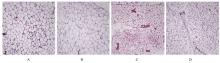
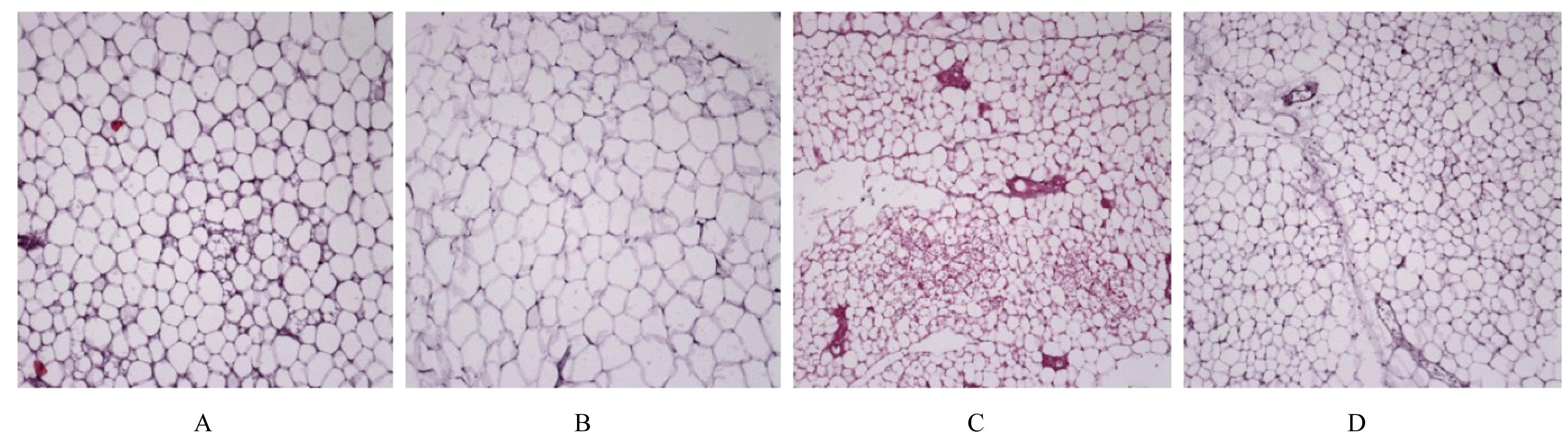
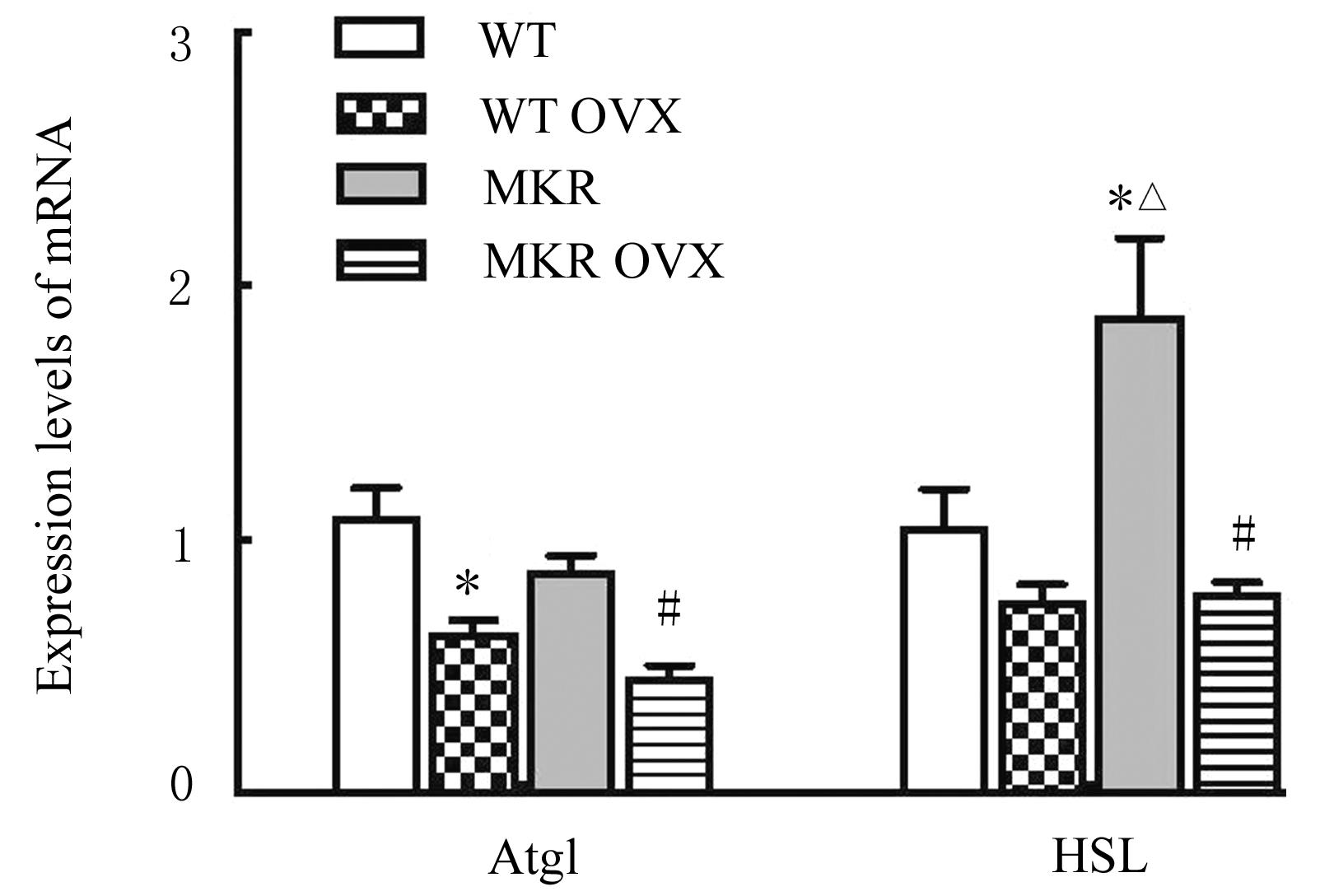
| 1 |
WANG L M, PENG W, ZHAO Z P, et al. Prevalence and treatment of diabetes in China, 2013-2018[J]. JAMA, 2021, 326(24): 2498-2506.
|
| 2 |
LI Y Z, TENG D, SHI X G, et al. Prevalence of diabetes recorded in mainland China using 2018 diagnostic criteria from the American Diabetes Association: national cross sectional study[J]. BMJ, 2020, 369: m997.
|
| 3 |
ALESI S, GHELANI D, RASSIE K, et al. Metabolomic biomarkers in gestational diabetes mellitus: a review of the evidence[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2021, 22(11): 5512.
|
| 4 |
ZHANG N, ZHANG H Q, ZHANG X, et al. The relationship between endogenous testosterone and lipid profile in middle-aged and elderly Chinese men[J]. Eur J Endocrinol, 2014, 170(4): 487-494.
|
| 5 |
MONROE A K, DOBS A S. The effect of androgens on lipids[J]. Curr Opin Endocrinol Diabetes Obes, 2013, 20(2): 132-139.
|
| 6 |
刘 璐, 姜雨佑, 李书书. 性激素及其受体在肝脏脂类代谢中的作用机制研究进展[J]. 中华内分泌代谢杂志, 2020, 36(3): 267-272.
|
| 7 |
常 鑫, 赵 楠, 汤旭磊. 绝经因素与代谢综合征相关性的研究进展[J]. 医学研究杂志, 2019, 48(12): 14-16, 64.
|
| 8 |
黄志英, 丁 岩. 围绝经期女性代谢综合征的相关研究进展[J]. 国际妇产科学杂志, 2020, 47(1): 84-87.
|
| 9 |
STEFANSKA A, BERGMANN K, SYPNIEWSKA G.Metabolic syndrome and menopause: pathophysiology, clinical and diagnostic significance[J]. Adv Clin Chem, 2015, 72: 1-75.
|
| 10 |
FERNÁNDEZ A M, KIM J K, YAKAR S, et al. Functional inactivation of the IGF-I and insulin receptors in skeletal muscle causes type 2 diabetes[J]. Genes Dev, 2001, 15(15): 1926-1934.
|
| 11 |
KIM C H, PENNISI P, ZHAO H, et al. MKR mice are resistant to the metabolic actions of both insulin and adiponectin: discordance between insulin resistance and adiponectin responsiveness[J]. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab, 2006, 291(2): E298-E305.
|
| 12 |
ZHU L, BROWN W C, CAI Q,et al.Estrogen treatment after ovariectomy protects against fatty liver and may improve pathway-selective insulin resistance[J]. Diabetes, 2013, 62(2): 424-434.
|
| 13 |
LIU M L, XU X, RANG W Q, et al. Influence of ovariectomy and 17beta-estradiol treatment on insulin sensitivity, lipid metabolism and post-ischemic cardiac function[J]. Int J Cardiol, 2004, 97(3): 485-493.
|
| 14 |
KO S H, JUNG Y. Energy metabolism changes and dysregulated lipid metabolism in postmenopausal women[J]. Nutrients, 2021, 13(12): 4556.
|
| 15 |
ALEMANY M. Estrogens and the regulation of glucose metabolism[J]. World J Diabetes, 2021, 12(10): 1622-1654.
|
| 16 |
SAMUEL V T, SHULMAN G I. The pathogenesis of insulin resistance: integrating signaling pathways and substrate flux[J]. J Clin Invest, 2016, 126(1): 12-22.
|
| 17 |
RIANT E, WAGET A, COGO H, et al. Estrogens protect against high-fat diet-induced insulin resistance and glucose intolerance in mice[J]. Endocrinology, 2009, 150(5): 2109-2117.
|
| 18 |
SARKAR M, WELLONS M, CEDARS M I, et al. Testosterone levels in pre-menopausal women are associated with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in midlife[J]. Am J Gastroenterol, 2017,112(5): 755-762.
|
| 19 |
BRUNO S, MAISONNEUVE P, CASTELLANA P, et al. Incidence and risk factors for non-alcoholic steatohepatitis: prospective study of 5408 women enrolled in Italian tamoxifen chemoprevention trial[J]. BMJ, 2005, 330(7497): 932.
|
| 20 |
GAO H, BRYZGALOVA G, HEDMAN E, et al. Long-term administration of estradiol decreases expression of hepatic lipogenic genes and improves insulin sensitivity in ob/ob mice: a possible mechanism is through direct regulation of signal transducer and activator of transcription 3[J]. Mol Endocrinol, 2006, 20(6): 1287-1299.
|
| 21 |
BURHANS M S, HAGMAN D K, KUZMA J N,et al. Contribution of adipose tissue inflammation to the development of type 2 diabetes mellitus[J]. Compr Physiol, 2018, 9(1): 1-58.
|
| 22 |
KHOR V K, DHIR R, YIN X Y, et al. Estrogen sulfotransferase regulates body fat and glucose homeostasis in female mice[J]. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab, 2010, 299(4): E657-E664.
|
| 23 |
HEINE P A, TAYLOR J A, IWAMOTO G A, et al. Increased adipose tissue in male and female estrogen receptor-alpha knockout mice[J]. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A, 2000, 97(23): 12729-12734.
|
| 24 |
EATON S A, SETHI J K. Immunometabolic links between estrogen, adipose tissue and female reproductive metabolism[J]. Biology, 2019, 8(1): 8.
|
| 25 |
SANTOSA S, JENSEN M D. Adipocyte fatty acid storage factors enhance subcutaneous fat storage in postmenopausal women[J]. Diabetes, 2013, 62(3): 775-782.
|
| 26 |
BESSESEN D H, COX-YORK K A, HERNANDEZ T L,et al. Postprandial triglycerides and adipose tissue storage of dietary fatty acids: impact of menopause and estradiol[J].Obesity (Silver Spring),2015,23(1): 145-153.
|
 )
)