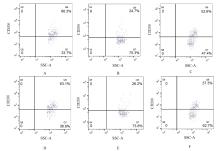
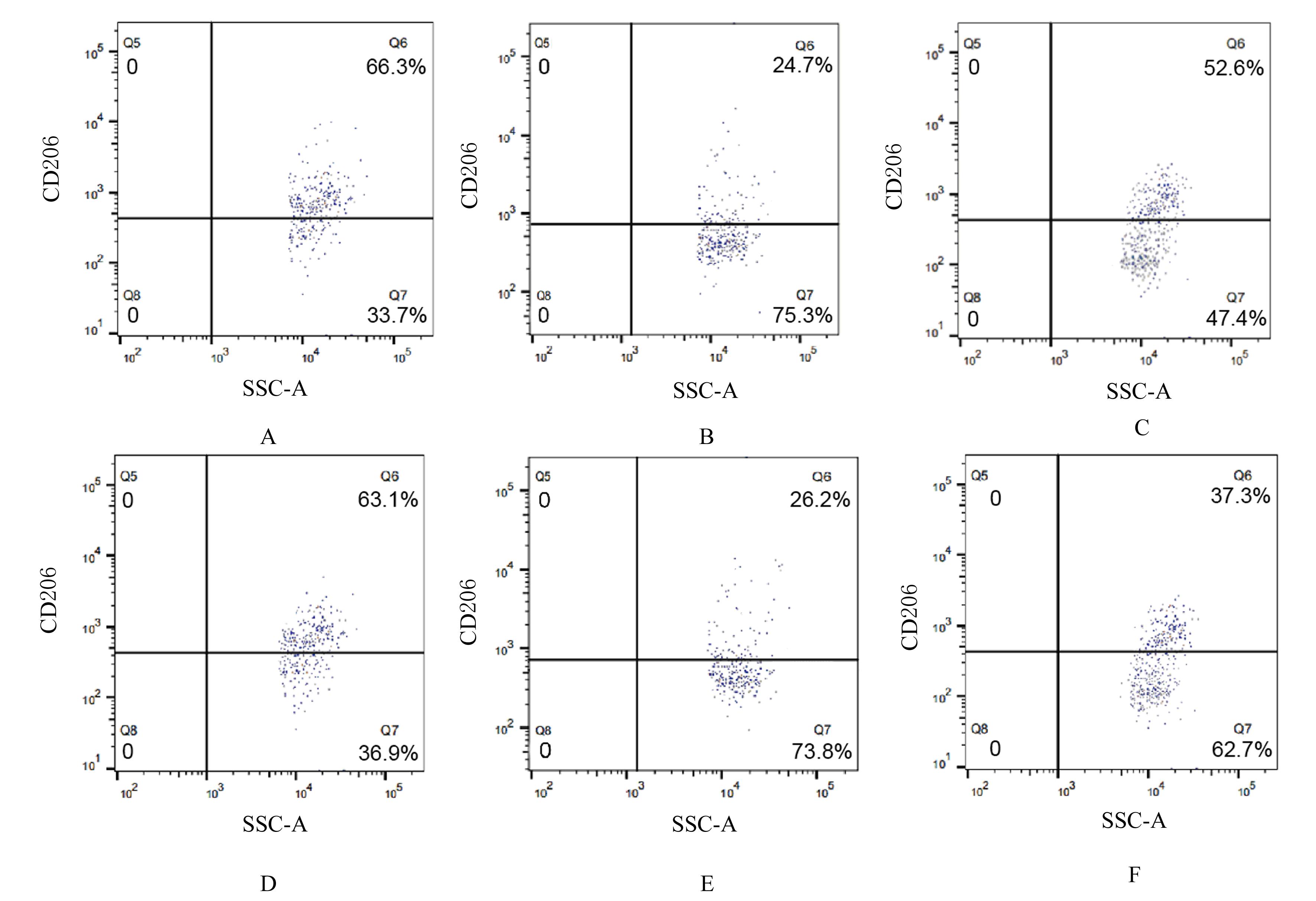
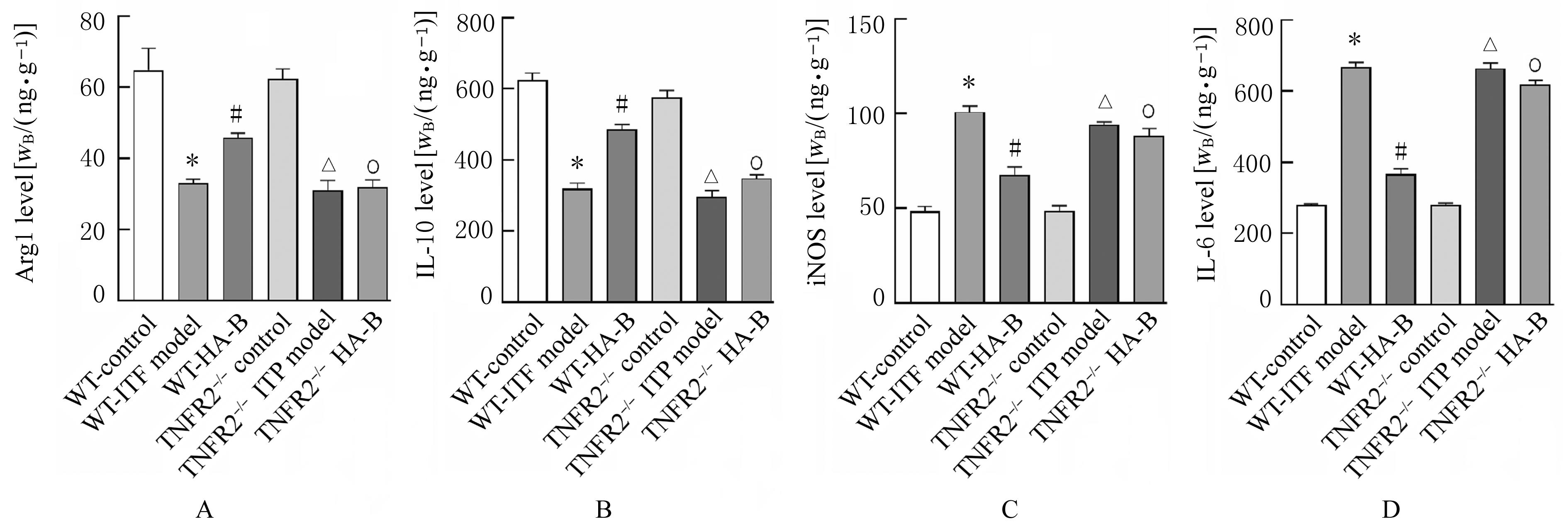
| 1 |
AUDIA S, MAHÉVAS M, SAMSON M, et al. Pathogenesis of immune thrombocytopenia[J]. Autoimmun Rev, 2017, 16(6): 620-632.
|
| 2 |
KOHLI R, CHATURVEDI S. Epidemiology and clinical manifestations of immune thrombocytopenia[J]. Hamostaseologie, 2019, 39(3): 238-249.
|
| 3 |
SILVA E DDA, CANCELA M, MONTEIRO K M, et al. Antigen B from Echinococcus granulosus enters mammalian cells by endocytic pathways[J]. PLoS Negl Trop Dis, 2018, 12(5): e0006473.
|
| 4 |
NOUIR NBEN, NUÑEZ S, GIANINAZZI C, et al. Assessment of Echinococcus granulosus somatic protoscolex antigens for serological follow-up of young patients surgically treated for cystic echinococcosis[J]. J Clin Microbiol, 2008, 46(5): 1631-1640.
|
| 5 |
RIGANÒ R, BUTTARI B, PROFUMO E, et al. Echinococcus granulosus antigen B impairs human dendritic cell differentiation and polarizes immature dendritic cell maturation towards a Th2 cell response[J]. Infect Immun, 2007, 75(4): 1667-1678.
|
| 6 |
ORECCHIONI M, GHOSHEH Y, PRAMOD A B, et al. Macrophage polarization: different gene signatures in M1(LPS+) vs. classically and M2(LPS-) vs. alternatively activated macrophages[J]. Front Immunol, 2019, 10: 1084.
|
| 7 |
LIU L L, GUO H M, SONG A M, et al. Progranulin inhibits LPS-induced macrophage M1 polarization via NF-κB and MAPK pathways[J]. BMC Immunol,2020,21(1): 32.
|
| 8 |
MEDLER J, WAJANT H. Tumor necrosis factor receptor-2 (TNFR2): an overview of an emerging drug target[J].Expert Opin Ther Targets,2019,23(4):295-307.
|
| 9 |
FU W Y, HU W H, YI Y S, et al. TNFR2/14-3-3ε signaling complex instructs macrophage plasticity in inflammation and autoimmunity[J]. J Clin Invest, 2021, 131(16): e144016.
|
| 10 |
ORIOL R, WILLIAMS J F, PÉREZ ESANDI M V, et al. Purification of lipoprotein antigens of Echinococcus granulosus from sheep hydatid fluid[J]. Am J Trop Med Hyg, 1971, 20(4): 569-574.
|
| 11 |
JAHANI Z, MESHGI B, RAJABI-BZL M, et al. Improved serodiagnosis of hydatid cyst disease using gold nanoparticle labeled antigen B in naturally infected sheep[J]. Iran J Parasitol, 2014, 9(2): 218-225.
|
| 12 |
FU A K, WANG Y, WU Y P, et al. Echinacea purpurea extract polarizes M1 macrophages in murine bone marrow-derived macrophages through the activation of JNK[J]. J Cell Biochem, 2017, 118(9): 2664-2671.
|
| 13 |
PROVAN D, ARNOLD D M, BUSSEL J B, et al. Updated international consensus report on the investigation and management of primary immune thrombocytopenia[J].Blood Adv,2019,3(22):3780-3817.
|
| 14 |
AUDIA S, BONNOTTE B.Emerging therapies in immune thrombocytopenia[J].J Clin Med,2021,10(5):1004.
|
| 15 |
MILES S, MOURGLIA-ETTLIN G, FERNÁNDEZ V.Expanding the family of Mu-class glutathione transferases in the cestode parasite Echinococcus granulosus sensu lato[J]. Gene, 2022, 835: 146659.
|
| 16 |
MAGLIOCO A, AGÜERO F A, VALACCO M P,et al.Characterization of the B-cell epitopes of Echinococcus granulosus histones H4 and H2A recognized by sera from patients with liver cysts[J]. Front Cell Infect Microbiol, 2022, 12: 901994.
|
| 17 |
DÍAZ A, ALLEN J E. Mapping immune response profiles: the emerging scenario from helminth immunology[J].Eur J Immunol,2007,37(12):3319-3326.
|
| 18 |
SHEPHERD J C, AITKEN A, MCMANUS D P. A protein secreted in vivo by Echinococcus granulosus inhibits elastase activity and neutrophil chemotaxis[J]. Mol Biochem Parasitol, 1991, 44(1): 81-90.
|
| 19 |
ALSHEVSKAYA A, ZHUKOVA J, KIREEV F,et al. Redistribution of TNF receptor 1 and 2 expression on immune cells in patients with bronchial asthma[J]. Cells, 2022, 11(11): 1736.
|
| 20 |
BEN-BARUCH A. Tumor necrosis factor α: taking a personalized road in cancer therapy[J]. Front Immunol, 2022, 13: 903679.
|
| 21 |
MALINOWSKA I, OBITKO-PŁUDOWSKA A, BUESCHER E S, et al. Release of cytokines and soluble cytokine receptors after intravenous anti-D treatment in children with chronic thrombocytopenic purpura[J]. Hematol J, 2001, 2(4): 242-249.
|
| 22 |
LIBRATY D H, ENDY T P, HOUNG H S, et al. Differing influences of virus burden and immune activation on disease severity in secondary dengue-3 virus infections[J]. J Infect Dis, 2002, 185(9): 1213-1221.
|
| 23 |
SHAPOURI-MOGHADDAM A, MOHAMMADIAN S, VAZINI H, et al. Macrophage plasticity, polarization, and function in health and disease[J]. J Cell Physiol, 2018, 233(9): 6425-6440.
|
 )
)