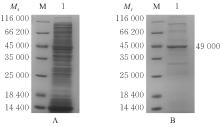
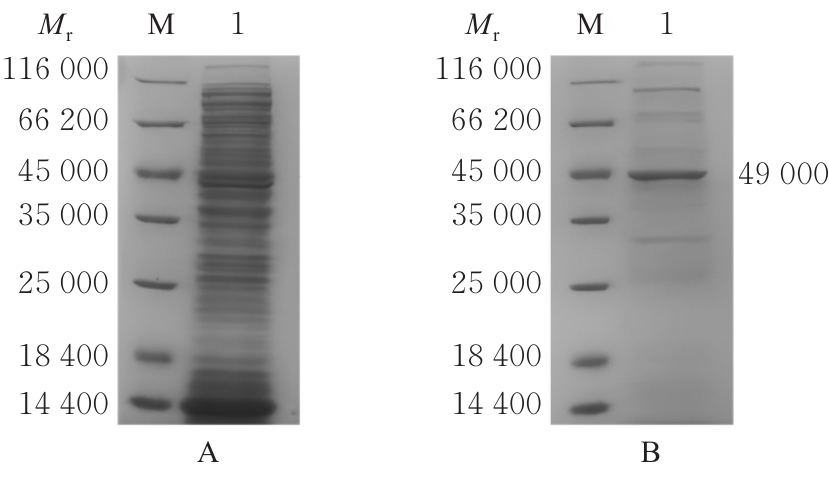
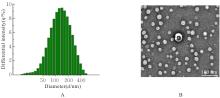
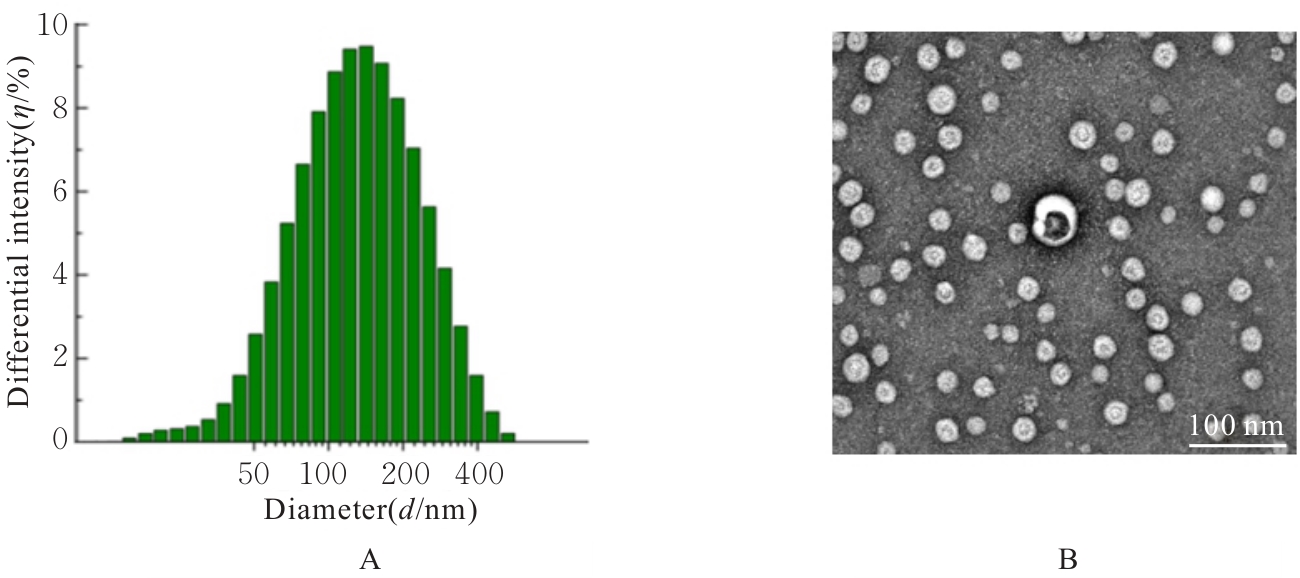
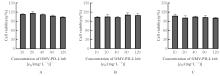
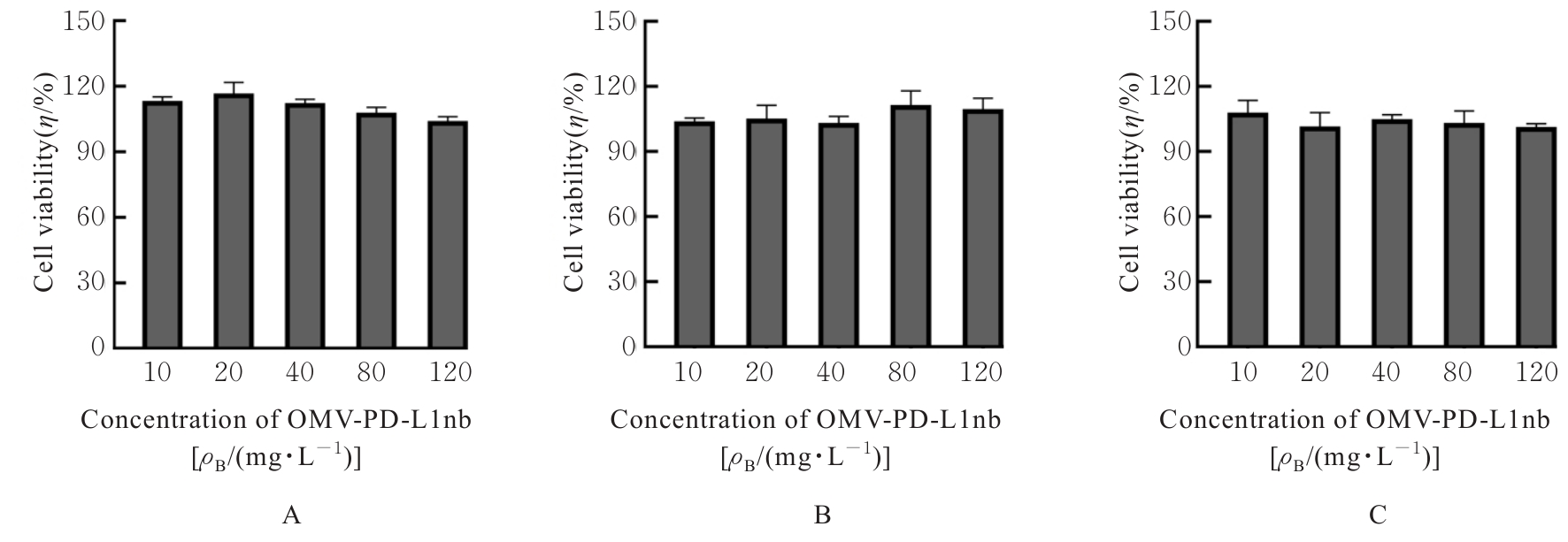
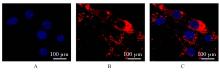
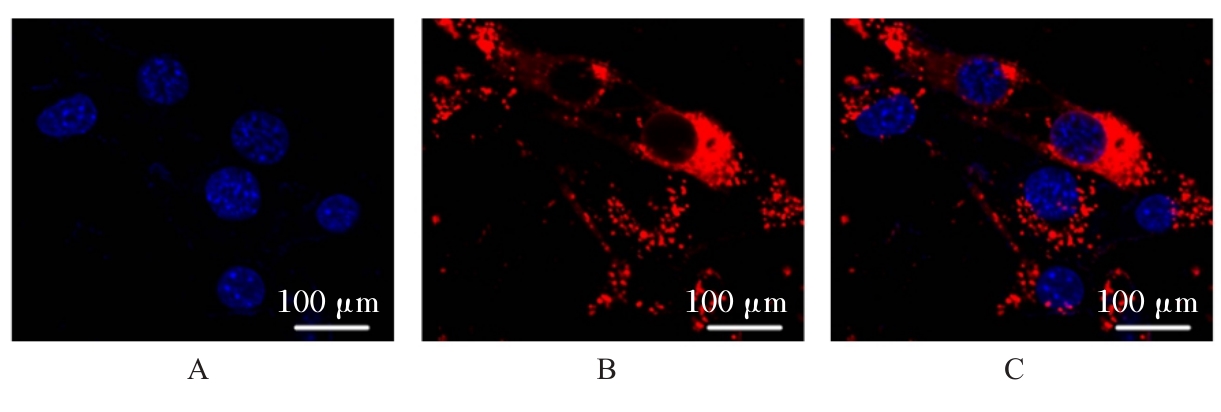
| [1] |
PATWEKAR M, SEHAR N, PATWEKAR F, et al. Novel immune checkpoint targets: a promising therapy for cancer treatments[J]. Int Immunopharmacol, 2024, 126: 111186.
|
| [2] |
SHARMA P, GOSWAMI S, RAYCHAUDHURI D, et al. Immune checkpoint therapy-current perspectives and future directions[J]. Cell, 2023, 186(8): 1652-1669.
|
| [3] |
GE W F, SONG S Y, QI X C, et al. Review and prospect of immune checkpoint blockade therapy represented by PD-1/PD-L1 in the treatment of clear cell renal cell carcinoma[J]. Oncol Res, 2023, 31(3): 255-270.
|
| [4] |
ZHANG Q, YANG C Y, GAO X S, et al. Phytochemicals in regulating PD-1/PD-L1 and immune checkpoint blockade therapy[J]. Phytother Res, 2024, 38(2): 776-796.
|
| [5] |
张蓝方, 张明娟, 许进秀, 等. PD-1/PD-L1通路、Th17和Tregs细胞在肿瘤免疫中的作用[J]. 现代肿瘤医学, 2023, 31(18): 3519-3523.
|
| [6] |
罗丽波, 任胜祥. KRAS和TP53共突变对肺腺癌生物学行为的影响[J]. 同济大学学报(医学版), 2024, 45(03): 345-353.
|
| [7] |
THOMMEN D S, PEEPER D S. Rational combination of cancer therapies with PD1 axis blockade[J]. Nat Rev Cancer, 2024. DOI: 10.1038/s41568-024-00727-1 .
doi: 10.1038/s41568-024-00727-1
|
| [8] |
ZHANG H, LIU L, LIU J B, et al. Roles of tumor-associated macrophages in anti-PD-1/PD-L1 immunotherapy for solid cancers[J]. Mol Cancer, 2023, 22(1): 58.
|
| [9] |
ZHOU Y J, LI G L, WANG J Y, et al. PD-L1: expression regulation[J]. Blood Sci, 2023, 5(2): 77-91.
|
| [10] |
LI W, WU F L, ZHAO S L, et al. Correlation between PD-1/PD-L1 expression and polarization in tumor-associated macrophages: a key player in tumor immunotherapy[J]. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev, 2022, 67: 49-57.
|
| [11] |
YIN S N, CHEN Z J, CHEN D G, et al. Strategies targeting PD-L1 expression and associated opportunities for cancer combination therapy[J]. Theranostics, 2023, 13(5): 1520-1544.
|
| [12] |
AGOSTINI M, TRALDI P, HAMDAN M. Proteomic investigation of immune checkpoints and some of their inhibitors[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2024, 25(17): 9276.
|
| [13] |
XUE F X, REN X T, KONG C Y, et al. Polymeric PD1/PDL1 bispecific antibody enhances immune checkpoint blockade therapy[J]. Mater Today Bio, 2024, 28: 101239.
|
| [14] |
FODA B M, MISEK S A, GALLO K A, et al. Inhibition of the Rho/MRTF pathway improves the response of BRAF-resistant melanoma to PD1/PDL1 blockade[J]. Int J Cancer, 2024, 155(7): 1303-1315.
|
| [15] |
钟丰羽, 王 婷, 古文姝, 等. Pembrolizumab联合曲妥珠单抗治疗HER2阳性胃癌研究进展[J]. 现代医药卫生, 2023, 39(21): 3730-3735.
|
| [16] |
曹佳丽, 熊枝繁, 靳 泽, 等. 免疫检查点抑制剂在肝细胞癌治疗中的研究进展[J]. 肿瘤防治研究, 2023, 50(5): 525-530.
|
| [17] |
NASEER F, AHMAD T, KOUSAR K, et al. Formulation for the targeted delivery of a vaccine strain of oncolytic measles virus (OMV) in hyaluronic acid coated thiolated chitosan as a green nanoformulation for the treatment of prostate cancer: a viro-immunotherapeutic approach[J]. Int J Nanomedicine, 2023, 18: 185-205.
|
| [18] |
JI P P, WU P Y, WANG L T, et al. Lysosome-targeting bacterial outer membrane vesicles for tumor specific degradation of PD-L1[J]. Small, 2024, 20(43): e2400770.
|
| [19] |
LI Y C, ZHU T C, CHEN J, et al. Dual-targeted engineered bacterial outer membrane vesicles for hepatocellular carcinoma immunotherapy[J]. Adv Funct Mater, 2024, 34(41): 2401355.
|
| [20] |
JIN M L, HUO D, SUN J J, et al. Enhancing immune responses of ESC-based TAA cancer vaccines with a novel OMV delivery system[J]. J Nanobiotechnology, 2024, 22(1): 15.
|
| [21] |
CUI C Y, HE Q, WANG J J, et al. Targeted miR-34a delivery with PD1 displayed bacterial outer membrane vesicles-coated zeolitic imidazolate framework nanoparticles for enhanced tumor therapy[J]. Int J Biol Macromol, 2023, 247: 125692.
|
| [22] |
SU L Y, TIAN Y, ZHENG Q, et al. Anti-tumor immunotherapy using engineered bacterial outer membrane vesicles fused to lysosome-targeting chimeras mediated by transferrin receptor[J]. Cell Chem Biol, 2024, 31(6): 1219-1230.e5.
|
| [23] |
CHEN X, LI P Z, LUO B, et al. Surface mineralization of engineered bacterial outer membrane vesicles to enhance tumor photothermal/immunotherapy[J]. ACS Nano, 2024, 18(2): 1357-1370.
|
| [24] |
ZHENG K S, FENG Y P, LI L, et al. Engineered bacterial outer membrane vesicles: a versatile bacteria-based weapon against gastrointestinal tumors[J]. Theranostics, 2024, 14(2): 761-787.
|
 ),Xingang GUAN2(
),Xingang GUAN2( )
)