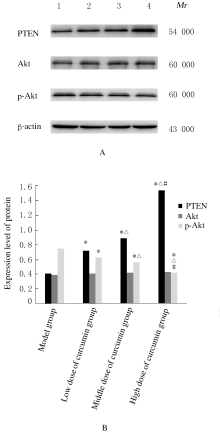
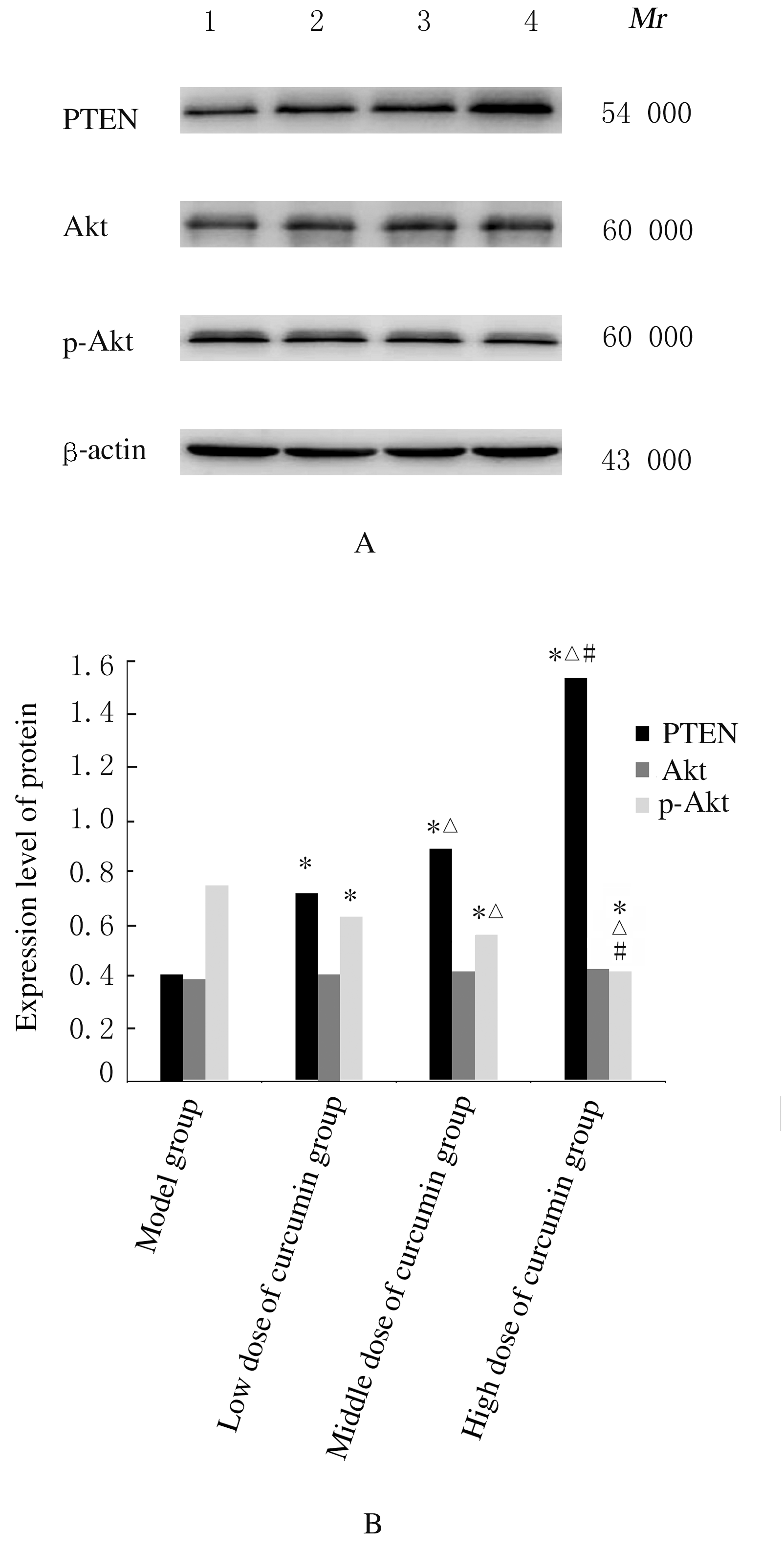
Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition) ›› 2021, Vol. 47 ›› Issue (1): 145-151.doi: 10.13481/j.1671-587x.20210120
• Research in basic medicine • Previous Articles Next Articles
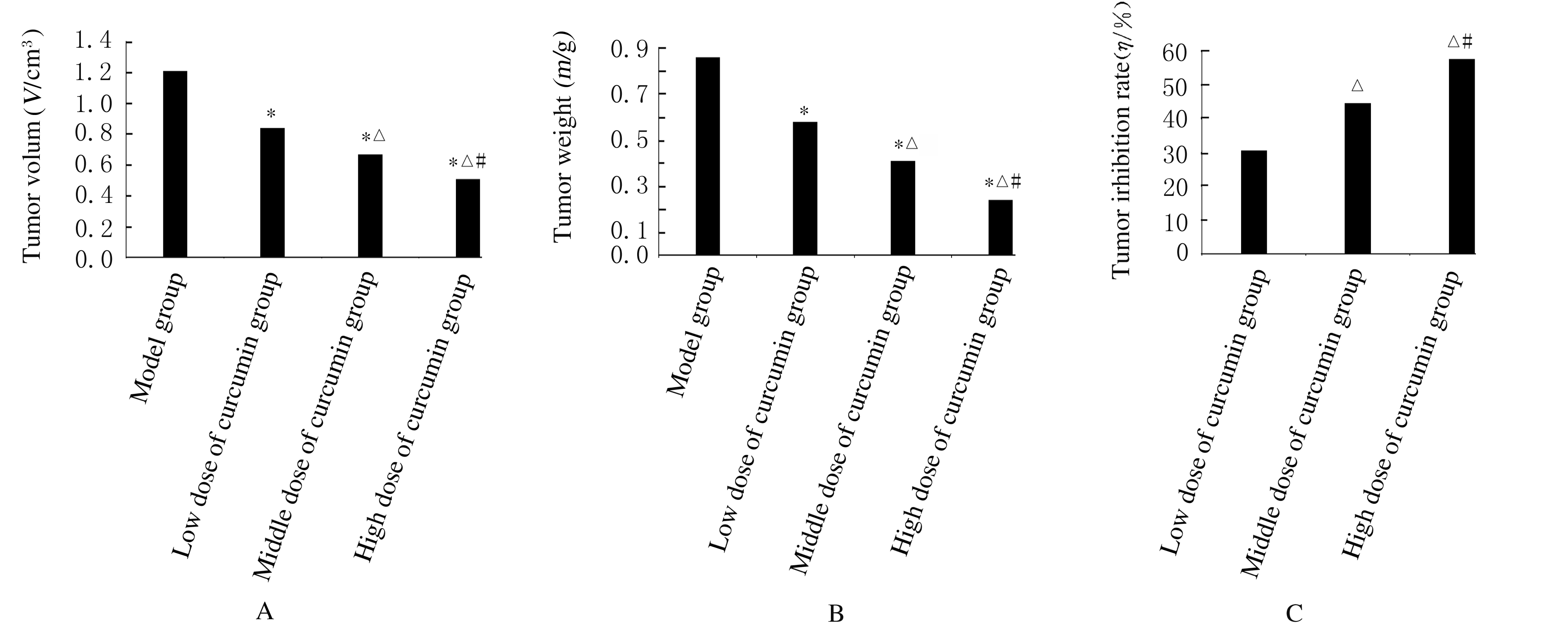
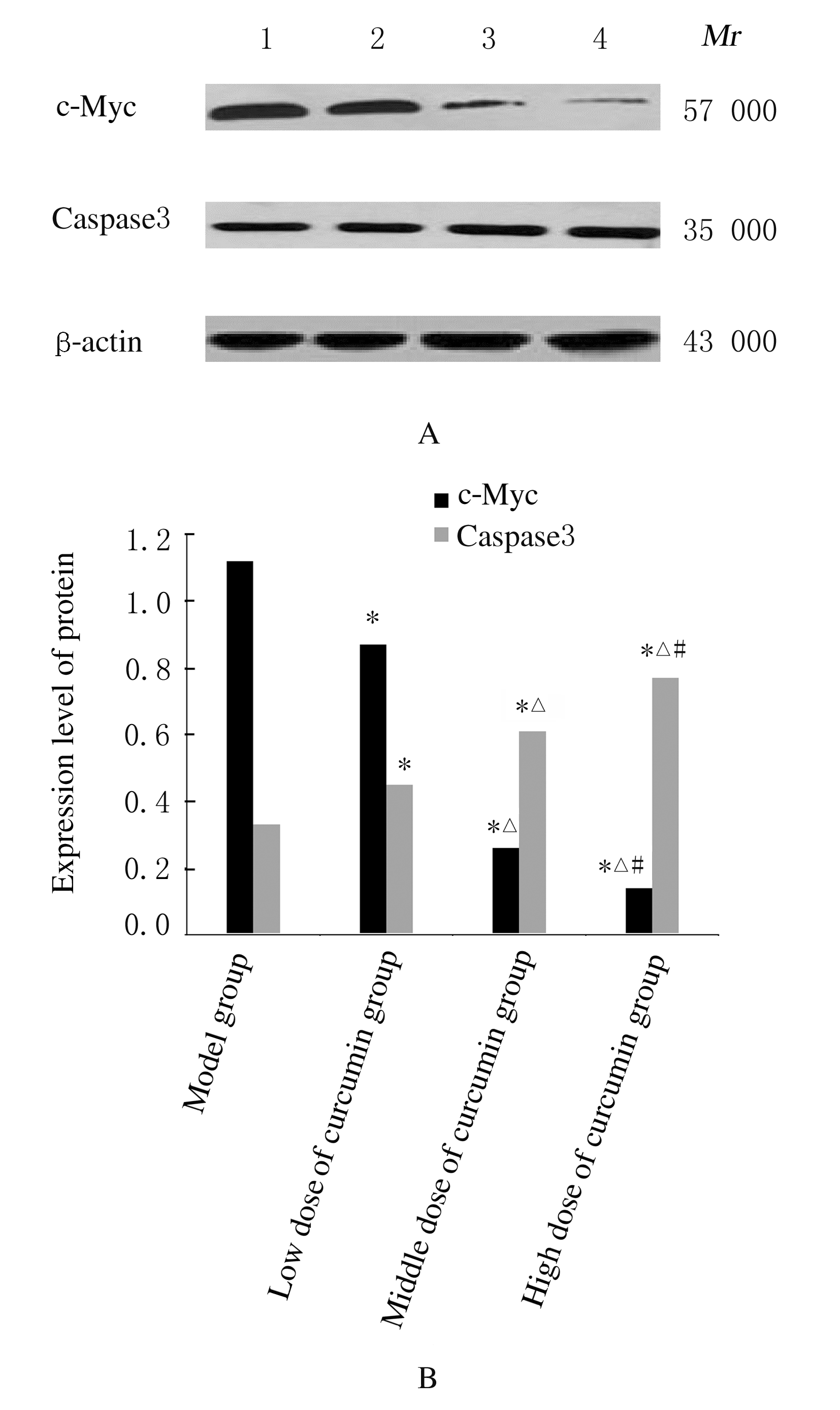
Inhibitory effect of curcumin on tumor growth in colorectal cancer mice and its mechanism of PTEN/PI3K/Akt signaling pathwayPEI Yongbin, WANG Guiqi, LI Wei, JIANG Xia, JIANG Haibo, ZHAO Zengren (Department of General Surgery,First Hospital,Hebei Medical University, Shijiazhuang 050031,China)
-
Received:2020-05-06Online:2021-01-28Published:2021-01-27
CLC Number:
- R735.3
Cite this article
share this article
| 1 | CHANG J, TANG N, FANG Q,et al.Inhibition of COX-2 and 5-LOX regulates the progression of colorectal cancer by promoting PTEN and suppressing PI3K/AKT pathway[J].Biochem Biophys Res Commun,2019,517(1):1-7. |
| 2 | SONG X Q, ZHANG M, DAI E Q, et al.Molecular targets of curcumin in breast cancer (Review)[J].Mol Med Rep,2019,19(1):23-29. |
| 3 | HASSANALILOU T, GHAVAMZADEH S, KHALILI L.Curcumin and gastric cancer: a review on mechanisms of action[J].J Gastrointest Cancer,2019,50(2):185-192. |
| 4 | 李秀娟,罗 强,孙 黎, 等.姜黄素对食管癌Ec109细胞增殖和PTEN/PI3K/Akt信号通路的影响[J].中国应用生理学杂志,2015,31(5):465-468. |
| 5 | 卢晓云,韩树堂,张小琴,等.姜黄素对结肠炎相关结直肠癌上皮-间质转化的影响[J].江苏医药,2019,45(1):1-5,117. |
| 6 | 邢通潮,祝普利,尹超, 等.阿福豆苷对结直肠癌小鼠肿瘤抑制作用及其抗血管生成的影响[J].山东医药,2019,59(23):39-43. |
| 7 | 宋 波,高 波.姜黄素对乳腺癌小鼠肿瘤组织的抑制作用及其机制[J].中华实验外科杂志,2019,36(9):1579-1582. |
| 8 | LIU Y, SUN H, MAKABEL B,et al.The targeting of noncoding RNAs by curcumin: Facts and hopes for cancer therapy (Review)[J].Oncol Rep,2019,42(1):20-34. |
| 9 | WANG M, JIANG S, ZHOU L,et al.Potential mechanisms of action of curcumin for cancer prevention: Focus on cellular signaling pathways and miRNAs[J].Int J Biol Sci,2019,15(6):1200-1214. |
| 10 | CALIBASI-KOCAL G, PAKDEMIRLI A, BAYRAK S,et al.Curcumin effects on cell proliferation, angiogenesis and metastasis in colorectal cancer[J].J BUON,2019,24(4):1482-1487. |
| 11 | 张生军,刘敏丽,常 琦,等.姜黄素通过靶向PBK对结直肠癌HCT116细胞增殖的抑制作用[J].上海交通大学学报(医学版),2016,36(7):980-985. |
| 12 | 李 倩,徐春燕,彭 鹏,等.姜黄素对 TNF-α诱导人结直肠癌细胞上皮间充质转化、迁移的影响[J].山东医药,2016,56(34):1-3. |
| 13 | PENG K, KOU L, YU L,et al.Histone demethylase JMJD2D interacts with β-catenin to induce transcription and activate colorectalcancer cell proliferation and tumor growth in mice[J].Gastroenterology,2019,156(4):1112-1126. |
| 14 | SCHMIDT S, GAY D, UTHE F W,et al.A MYC-GCN2-eIF2α negative feedback loop limits protein synthesis to prevent MYC-dependent apoptosis in colorectal cancer[J].Nat Cell Biol,2019,21(11):1413-1424. |
| 15 | ZHANG P, LI R, XIAO H,et al.BRD4 inhibitor AZD5153 suppresses the proliferation of colorectal cancer cells and sensitizes the anticancer effect of PARP inhibitor[J].Int J Biol Sci,2019,15(9):1942-1954. |
| 16 | LI Q, WEI L, LIN S,et al.Synergistic effect of kaempferol and 5-fluorouracil on the growth of colorectal cancer cells by regulating the PI3K/Akt signaling pathway[J].Mol Med Rep,2019,20(1):728-734. |
| 17 | LI Q Y, LAI Z J, YAN Z K,et al.Hedyotis diffusa Willd inhibits proliferation and induces apoptosis of 5-FU resistant colorectal cancer cells by regulating the PI3K/AKT signaling pathway[J].Mol Med Rep,2018,17(1):358-365. |
| 18 | QIN Y, HUO Z B, SONG X,et al.Mir-106a regulates cell proliferation and apoptosis of colon cancer cells through targeting the PTEN/PI3K/AKT signaling pathway[J].Oncol Lett,2018,15(3):3197-3201. |
| 19 | GEHRINGER F, WEISSINGER S E, MÖLLER P,et al.Physiological levels of the PTEN-PI3K-AKT axis activity are required for maintenance of Burkitt lymphoma[J].Leukemia,2020,34(3):857-871. |
| 20 | MENG J, LIU G J, SONG J Y,et al.Preliminary results indicate resveratrol affects proliferation and apoptosis of leukemia cells by regulating PTEN/PI3K/AKT pathway[J].Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci,2019,23(10):4285-4292. |
| 21 | SHANG H, WANG T, SHANG F,et al.Over-expression of DJ-1 attenuates effects of curcumin on colorectal cancer cell proliferation and apoptosis[J].Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci,2020,24(14):7567. |
| 22 | LIU W W, HUANG M X, ZOU Q Q,et al.Curcumin suppresses gastric cancer biological activity by regulation of miRNA-21: an in vitro study[J].Int J Clin Exp Pathol,2018,11(12):5820-5829. |
| [1] | Xue LUAN,Guanghai YAN,Haibo LI,Bo ZHANG,Wei ZHANG,Yuanyuan HUANG. Effect of salidroside on airway inflammation in mice with asthma and its mechanism [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2021, 47(3): 537-544. |
| [2] | Runhong MU,Xinzhu LIU,Rui LIN,Yupeng LI,Luyao WANG,Chunyu WANG,Xiao GUO. Effect of PRDX6 over-expression of proliferation, invasion and migration of liver cancer cells and its molecular mechanism [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2021, 47(3): 559-565. |
| [3] | Cuilan LIU,Jianjun LI,He JIANG,Jing LIU,Dan WANG,Chen LI,Di ZHAO. Effect of urolithin B on biological behaviors of human glioblastome U118 MG cells and its mechanism [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2021, 47(3): 566-574. |
| [4] | Xining LI,Wei WENG,Zheyuan SHEN,Xiaojie DOU,Yu ZHAO,Jikang MIN. Effect of mTOR phosphorylation level on proliferation,autophagy,and differentiation of MC3T3-E1 osteoblasts and its mechanism [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2021, 47(3): 575-586. |
| [5] | Yingjun REN,Hui ZHANG,Ying ZHOU. Inhibitory effects of centromere protein U knockdown on self-renewal, cisplatin resistance and Wnt/β-catenin signaling activity in cisplatin resistant ovarian cancer cells [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2021, 47(3): 608-614. |
| [6] | Jia FENG,Haichan XU,Jian WEN,Zehua WU,Yi CHEN. Effect of betulinic acid on proliferation and apoptosis of myeloma cells by regulating JAK2/STAT3 signaling pathway and its mechanism [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2021, 47(3): 615-622. |
| [7] | Chunqing MU,Lei ZHOU,Nan ZHAO,Hong WANG,Zhi LI. Effect of metformin on proliferation of lung cancer A549 cells through PI3K/AKT/GSK3β signaling pathway [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2021, 47(3): 637-643. |
| [8] | Pei GONG,Jingran LIU,Shimin ZHAO,Yuzhen WANG,Jiming XIE. Inhibitory effect of MCM10 silencing on proliferation of breast cancer MDA-MB-231 cells and its mechanism [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2021, 47(3): 652-659. |
| [9] | Xiaohui LI,Ziwei QU,Xin LU,Qingbin MENG,Huatao CHEN,Jun REN,Chengpei TAN. Regulatory effect of exosomes carrying miR-196b-5p derived from bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells on biological characteristics of colon cancer cells [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2021, 47(3): 660-668. |
| [10] | Ying YANG,Wei ZHAO,Dan LYU. Effect of C19ORF12 on proliferation and chemo-sensitivity of gastric cancer MKN45 cells and its mechanism [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2021, 47(3): 687-693. |
| [11] | Tianqi ZOU,Lin BAI,Zhengxu ZHANG,He LI,Chunmei WANG,Jinghui SUN,Jianguang CHEN,Xi CHEN,Chengyi ZHANG. Inhibitory effect of prunus tomentosa thunb total flavonoids on skin hypertrophic scar in mice and its mechanism [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2021, 47(2): 265-274. |
| [12] | Bingxue QI,Yan MA,Yixian ZHANG,Yadong SUN,Lining MIAO. Effect of liraglutide on expressions of mRNA and protein of related proteins after podocyte injury induced by high glucose and its mechanism [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2021, 47(2): 275-283. |
| [13] | Zhanqi ZHAO,Chengjin ZHANG,Juan TIAN. Inhibitory effect of Ndfip1 on ferrion-induced neuronal apoptosis and its neuroprotective mechanism [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2021, 47(2): 338-343. |
| [14] | Haoxuan TANG,Nanfeng MENG,Meiling DU,Wei WANG,Tao HE. Inhibitory effect of new VEGF monoclonal antibody combined with all-trans retinoic acid on proliferation of breast cancer MCF-7 cells [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2021, 47(2): 344-351. |
| [15] | Nuan WANG,Lijuan YANG,Juanjuan DAI,Aili WANG,Yan WU,Chengxia LIU. Promotion effects of MARCH1 on migration and invasion of human gastric cancer cells through PI3K/AKT signaling pathway [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2021, 47(2): 352-359. |