Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition) ›› 2021, Vol. 47 ›› Issue (1): 44-52.doi: 10.13481/j.1671-587x.20210106
• Research in basic medicine • Previous Articles Next Articles
Activity and stability of reductase of Mesonia sp. S52 Cr(Ⅵ) and its optimization of Cr(Ⅵ) reduction conditions
Jiayao LI1,Xiaoxia LI2,Qiuying AN1,Chun FAN1,Dongbei GUO1,Chen TANG1,Min ZHANG1,Xieryazdan SANGDUHAX1,Ran ZHAO1( )
)
- 1.State Key Laboratory of Molecular Vaccinology and Molecular Diagnostics,Department of Preventive Medicine,School of Public Health,Xiamen University,Xiamen 361102,China
2.Office Department,Qionglai Health Bureau,Chengdu 611530,China
-
Received:2020-07-21Online:2021-01-28Published:2021-01-27 -
Contact:Ran ZHAO E-mail:zhaoran@xmu.edu.cn
CLC Number:
- R123
Cite this article
Jiayao LI,Xiaoxia LI,Qiuying AN,Chun FAN,Dongbei GUO,Chen TANG,Min ZHANG,Xieryazdan SANGDUHAX,Ran ZHAO. Activity and stability of reductase of Mesonia sp. S52 Cr(Ⅵ) and its optimization of Cr(Ⅵ) reduction conditions[J].Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2021, 47(1): 44-52.
share this article
Tab.1
Reduction rates of Cr(Ⅵ) by intracellular and extracellular enzymes in S52 strain at different time points (n=3,x±s,η/%)"
| Group | Reduction rate of Cr(Ⅵ) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (t/h) 3 | 6 | 12 | 24 | 48 | |
| Control | 1.8±0.5 | 6.1±1.2 | 11.8±1.9 | 26.9±3.1 | 73.1±4.3 |
| Intracellular enzyme | 18.1±1.3*△ | 3.2±0.9* | 0.2±0.1* | 0.0±0.0* | 0.6±0.1* |
| Extracellular enzyme | 10.8±1.5* | 2.7±0.5* | 0.1±0.2* | 0.8±0.1* | 0.0±0.0* |
Tab.2
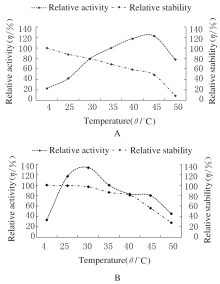
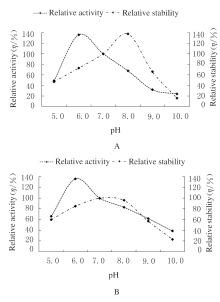
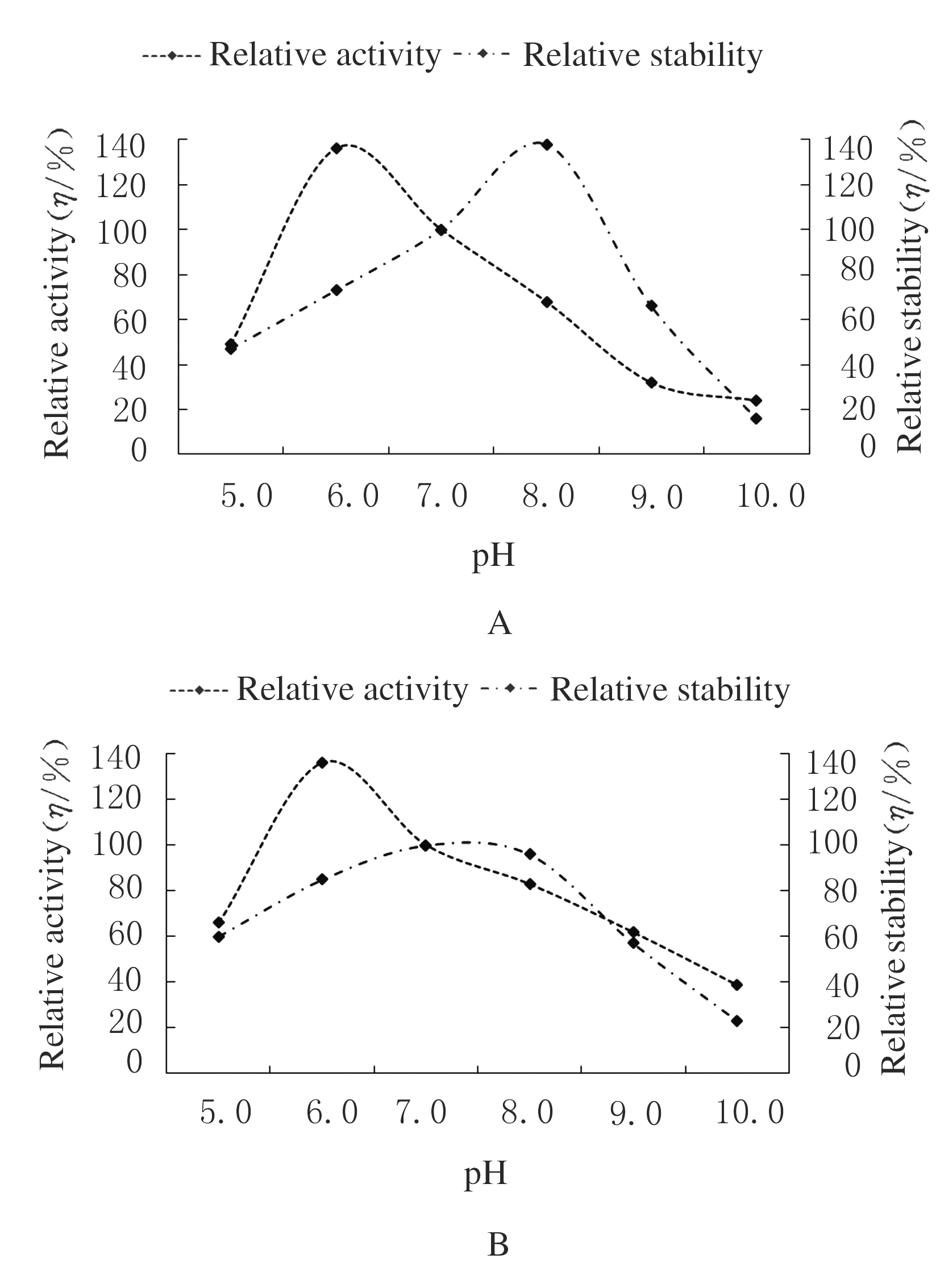
Reduction rates of Cr(Ⅵ) by intracellular enzymes under conditions of different temperatures and pH values at 3 h after treatment (n=3,x±s,η/%)"
| pH | Reduction rate of Cr(Ⅵ) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (θ/℃) 25 | 30 | 35 | 40 | 45 | 50 | ||
| 5.0 | 6.2±0.9*?# | 7.9±1.1*?# | 8.3±1.0*?# | 12.9±1.8* | 14.4±4.0* | 10.0±1.1*?# | |
| 6.0 | 12.3±1.4?# | 24.5±2.1?# | 30.6±3.2?# | 38.2±3.3 | 39.7±4.2 | 33.4±3.3?# | |
| 7.0 | 12.3±1.9*?# | 23.0±3.0*?# | 29.2±2.3*?# | 33.6±4.1* | 36.0±5.1* | 28.6±4.3*?# | |
| 8.0 | 7.4±0.4*?# | 11.6±2.4*?# | 17.4±3.6*?# | 19.2±3.5* | 19.9±1.9* | 16.1±5.5*?# | |
| 9.0 | 5.8±1.1*?# | 6.0±1.3*?# | 8.0±1.5*?# | 9.1±3.0* | 9.3±1.1* | 6.1±1.2*?# | |
| 10.0 | 3.4±0.1*?# | 4.3±0.2*?# | 5.8±0.8*?# | 6.8±0.9* | 7.1±0.8* | 5.2±0.9*?# | |
Tab.3
Reduction rates of Cr (Ⅵ) by extracellular enzymes at different temperatures and pH values at 3 h after treatment (n=3,x±s,η/%)"
| pH | Reduction rates of Cr (Ⅵ) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (θ/℃) 25 | 30 | 35 | 40 | 45 | 50 | ||
| 5.0 | 8.0±0.5*?# | 9.6±1.8*? | 5.8±1.5*?# | 4.4±1.5*?# | 4.5±1.1*?# | 2.7±0.9*?# | |
| 6.0 | 17.6±3.1# | 19.8±2.2 | 16.1±1.2# | 15.7±4.9# | 12.0±2.6# | 6.6±2.2# | |
| 7.0 | 17.0±2.2# | 19.5±3.6 | 14.6±2.5# | 11.6±2.1# | 9.9±2.1# | 5.7±1.4# | |
| 8.0 | 11.6±3.1*?# | 12.0±1.4*? | 11.2±3.3*?# | 10.4±3.2*?# | 8.4±1.2*?# | 2.5±0.8*?# | |
| 9.0 | 8.1±1.4*?# | 9.0±1.0*? | 3.8±0.7*?# | 3.8±0.4*?# | 2.4±1.0*?# | 1.0±0.2*?# | |
| 10.0 | 5.8±0.9*?# | 5.7±1.1*? | 3.7±0.6*?# | 2.3±0.1*?# | 1.1±0.9*?# | 0.7±0.5*?# | |
Tab.5
Reduction rates of Cr(Ⅵ) by Cr(Ⅵ) redutases after treated with different small molecules for 3 h in various groups (n=3,x±s,η/%)"
| Group | Reduction rate of Cr(Ⅵ) | |
|---|---|---|
| Intracellular enzyme | Extracellular enzyme | |
| Control | 37.9±3.8 | 18.2±1.8 |
| EDTA | 19.8±3.2* | 11.7±3.4* |
| Triton X-100 | 36.3±2.5 | 17.7±2.0 |
| Tween 80 | 24.2±3.9* | 13.5±0.8* |
| SDS | 25.6±1.0* | 10.2±2.1* |
| 1 | STURM G, BRUNNER S, SUVOROVA E, et al. Chromate resistance mechanisms in Leucobacter chromiiresistens [J]. Appl Environ Microbiol, 2018, 84(23): e02208-e02218. |
| 2 | KABIR M M, FAKHRUDDIN A N M, CHOWDHURY M A Z, et al. Isolation and characterization of chromium(Ⅵ)-reducing bacteria from tannery effluents and solid wastes [J]. World J Microbiol Biotechnol, 2018, 34(9): 126. |
| 3 | FERNÁNDEZ P M, VIÑARTA S C, BERNAL A R, et al. Bioremediation strategies for chromium removal: Current research, scale-up approach and future perspectives [J]. Chemosphere, 2018, 208: 139‐148. |
| 4 | 张云江,何杨,张瑶瑶,等.辽宁省一般人群全血和尿液中铬水平分析[J].中国公共卫生,2016,32(5): 639-642. |
| 5 | FERREIRA L M R, CUNHA-OLIVEIRA T, SOBRAL M C, et al. Impact of carcinogenic chromium on the cellular response to proteotoxic stress [J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2019, 20(19):E4901. |
| 6 | ZHAO R, YAN S S, LIU M, et al. Seafood consumption among Chinese coastal residents and health risk assessment of heavy metals in seafood [J]. Environ Sci Pollut Res, 2016, 23(16): 16834-16844. |
| 7 | RAINBOW P S, LUOMA S N. Metal toxicity, uptake and bioaccumulation in aquatic invertebrates--modelling zinc in crustaceans [J]. Aquat Toxicol, 2011, 105(3/4): 455‐465. |
| 8 | 陆秋艳,吕华东,邱秀玉,等.福建省水产品中铅镉铬蓄积量检测[J].中国公共卫生,2009,25(1): 67-68. |
| 9 | 寇 琰,于素芳,易 超,等.6 价铬对人胚肺细胞P53和Bcl-2蛋白表达影响[J].中国公共卫生,2006,22(9): 1119. |
| 10 | JOBBY R, JHA P, GUPTA A, et al. Biotransformation of chromium by root nodule bacteria Sinorhizobium sp. SAR1 [J]. PLoS One, 2019, 14(7): e0219387. |
| 11 | JOBBY R, JHA P, YADAV A K, et al. Biosorption and biotransformation of hexavalent chromium[Cr(Ⅵ)]: A comprehensive review [J]. Chemosphere, 2018, 207: 255‐266. |
| 12 | WANG Y T, XIAO C S. Factors affecting hexavalent chromium reduction in pure cultures of bacteria [J]. Water Res, 1995, 29(11): 2467-2474. |
| 13 | TAHRI JOUTEY N, BAHAFID W, SAYEL H, et al. Hexavalent chromium removal by a novel Serratia proteamaculans isolated from the bank of Sebou River (Morocco) [J]. Environ Sci Pollut Res, 2014,21 (4), 3060-3072. |
| 14 | 郭东北,唐 晨,张 敏,等.金属离子和小分子物质对耐铬(Ⅵ)菌株M52还原能力的影响[J].吉林大学学报(医学版),2019,45(5):1003-1008. |
| 15 | 肖伟,王磊,李倬锴,等.六价铬还原细菌Bacillus cereus S5.4还原机理及酶学性质研究[J].环境科学,2008,29(3):751-755. |
| 16 | 夏险,李明顺,武士娟,等.微生物铬转化和抗性机制与生物修复研究进展[J].微生物学通报,2017,44(7):1668-1675. |
| 17 | 焦仕林,朱培蕾,姜 朴,等.蜡样芽孢杆菌还原六价铬效果分析[J].中国公共卫生,2016,32(10): 1326-1329. |
| 18 | THATOI H, DAS S, MISHRA J, et al. Bacterial chromate reductase, a potential enzyme for bioremediation of hexavalent chromium: a review[J]. J Environ Manage, 2014, 146: 383-399. |
| 19 | ZHAO X L, DRLICA K. Reactive oxygen species and the bacterial response to lethal stress [J]. Curr Opin Microbiol, 2014, 21: 1‐6. |
| 20 |
BALDIRIS R, ACOSTA-TAPIA N, MONTES A, et al. Reduction of hexavalent chromium and detection of chromate reductase (ChrR) in Stenotrophomonas maltophilia [J]. Molecules, 2018.DOI:10.3390/molecules 23020406.
doi: 10.3390/molecules 23020406 |
| 21 | MYERS C R. The effects of chromium(Ⅵ) on the thioredoxin system: implications for redox regulation[J]. Free Radic Biol Med, 2012, 52(10): 2091‐2107. |
| 22 | ELANGOVAN R, ABHIPSA S, ROHIT B, et al. Reduction of Cr(Ⅵ) by a Bacillus sp. [J].Biotechnol Lett, 2006, 28: 247-252 |
| 23 | BAE W C,LEE H K,CHOE Y C, et al. Purification and characterization of NADPH-dependent Cr(Ⅵ) reductase from Escherichia coli ATCC 33456 [J].J Microbiol, 2005, 43 (1): 21-27. |
| 24 | 魏 斐,杨丽荣,薛保国,等.还原六价铬细菌及其还原酶的研究[J].中国生物工程杂志,2012,32(4):53-59. |
| 25 | 杨胜男, 刘 娜, 宋东辉. 菌藻混合体系去除Cr(Ⅵ)的条件优化及Cr(Ⅵ)还原酶活性的测定[J].生物技术通报,2019,35(9):83-92. |
| 26 | TANRIKULU A C,ABAKAY A,EVLIYAOGLU O,et al. Coenzyme Q10,copper, zinc, and lipid peroxidation levels in serum of patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease [J]. Biol Trace Elem Res, 2011, 143(2): 659-667. |
| 27 | XU W H, JIAN H, LIU Y G, et al. Bioreduction of chromate by an isolated bacillus anthracis Cr-4 with soluble Cr(Ⅲ) product [J]. Water Air Soil Pollut, 2015, 226 (3) : 82. |
| 28 | TAN H, WANG C,ZENG G Q, et al. Bioreduction and biosorption of Cr(Ⅵ) by a novel Bacillus sp. CRB-B1 strain [J]. J Hazard Mater, 2020, 386:121628 |
| 29 | 刘玉沛. 赤红球菌与小球藻互生关系对苯酚降解影响的研究[D].秦皇岛:燕山大学, 2015. |
| 30 | SAFONOVA E, KVITKO K V, IANKEVITCH M I, et al. Biotreatment of industrial wastewater by selected algal-bacterial consortia [J]. Engineer Life Sci, 2010, 4(4): 347-353. |
| 31 | PRADHAN D, SUKLA L B, MISHRA B B, et al. Biosorption for removal of hexavalent chromium using microalgae Scenedesmus sp. [J]. Cleaner Production, 2019, 209: 617-629. |
| [1] | GUO Dongbei, TANG Chen, ZHANG Min, FAN Chun, YUE Ziyu, LI Jiayao, CHEN Qun, ZHAO Ran. Effects of metal ions and small molecules on reduction of Cr(Ⅵ) resistant strain M52 [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2019, 45(05): 1003-1008. |
| [2] | YANG Wei, LI Mingcheng. Analysis on gene profile of over-expression WWOX gene in human oral squamous cell carcinoma Tca8113 cells and tumor inhibition mechanism of WWOX gene [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2018, 44(06): 1169-1173. |
| [3] | LI Baoquan, LIU Luyao, ZHANG Wenwen, LIU Keke, JIANG Ting, BU Wenhuan, LI Bo, SUN Hongchen. Influence of α-Si3N4 and SP1SiO2 fusing conditions and filler ratios in properities of dental resin composites [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2018, 44(05): 968-973. |
| [4] | LIU Danqing, YE Shufeng, TONG Weifang, TENG Bo, WANG Sanchun, FENG Qingjie. Renal clear cell carcinoma transferred to nasal cavity and sinuses:A case reportand literature review [J]. Journal of Jilin University Medicine Edition, 2017, 43(04): 829-831. |
| [5] | CHEN Xin, LIU Te, WANG Shuyue, ZHANG Wenjing, XIE Jingfang, QIN Yuanming, QIAN Donghua, YE Lin. Effect of daily mean temperature on hospital admissions of patients with acute exacerbation of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease [J]. Journal of Jilin University Medicine Edition, 2015, 41(02): 389-392. |
| [6] | YU Wei-xian,LIU Xin-chan,WANG Wen-tian,ZHANG Yu-feng,GAO Ai-chao. Effects of C-terminal and N-terminal deletions of FtsZ in Porphyromonas Gingivalis on GTPase activity [J]. Journal of Jilin University Medicine Edition, 2013, 39(5): 898-902. |
| [7] | ZHANG Xue,CHEN Ping,BI Yun-feng,QU Ning-ning,LIU Qiong,SUN Xin-ze. Cloning and expression of nitrite reductase gene from Alcaligenes xylosoxidans [J]. Journal of Jilin University Medicine Edition, 2013, 39(4): 690-693. |
| [8] | YANG Yun,WANG Xiao-rong,HAN Ling-yu,ZHANG Ying-xin,YAN Tong-tong,LIU Tong-bin,SHEN Zheng-xuan. Effect of radio frequency low temperature plasma treatment on concentration of residual MMA in antibacterial room temperature curing PMMA material [J]. Journal of Jilin University Medicine Edition, 2013, 39(3): 482-487. |
| [9] |
JIA Chun-li,WANG Xiao-rong,ZHANG Ci-tong,SUN Shi-qun,YANG Yun.
Evaluation on in vitro antibacterial effect |of room curing polymethylmethacrylate material adding nano-silver base inorganic antibacterial agents [J]. J4, 2012, 38(5): 899-903. |
| [10] | YU Wei-xian,WANG Wen-tian,LIU Xin-chan,ZHANG Yu-feng. Thermostability of GTPase activity of cell division protein FtsZ in Porphyromonas gingivalis [J]. J4, 2012, 38(3): 551-554. |
| [11] | . Enzyme properties and classification of Neanthes japonica (Iznka) fibrinolytic enzyme [J]. J4, 2011, 37(2): 267-270. |
| [12] | ZHANG Jia-Ying, ZUO Wen-Jing, WU Guang-Heng, SUN He-Tong. Association between MTHFR gene C677T polymorphism and habitual abortion [J]. J4, 2009, 35(4): 698-701. |
| [13] | JIANG Yan-fang,ZHAO Ping-wei,TAN Yan,FANG Yan-qiu,YASUSHI Matsuzaki. Anti-proliferative effect of dehydroepiandrosterone and its metabolites on human tumor lines [J]. J4, 2008, 34(6): 985-989. |
| [14] | FANG Le, WANG Tian-wei,SHAO Yan-kun, YANG Hong. Association between MTHFRC677T, CBS844ins68 polymorphism and young ischemic stroke [J]. J4, 2007, 33(2): 310-313. |
| [15] | ZHANG Wen-song,ZHOU Hong-yan,GU Shu-yan,ZHENG Ya-juan,XU Shao-lin. Inhibitory effects of cyclooxygenase-2-selectiveinhibitor on angiogenesis postkeratoplasty [J]. J4, 2005, 31(5): 713-716. |
|