Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition) ›› 2021, Vol. 47 ›› Issue (1): 82-88.doi: 10.13481/j.1671-587x.20210111
• Research in basic medicine • Previous Articles Next Articles
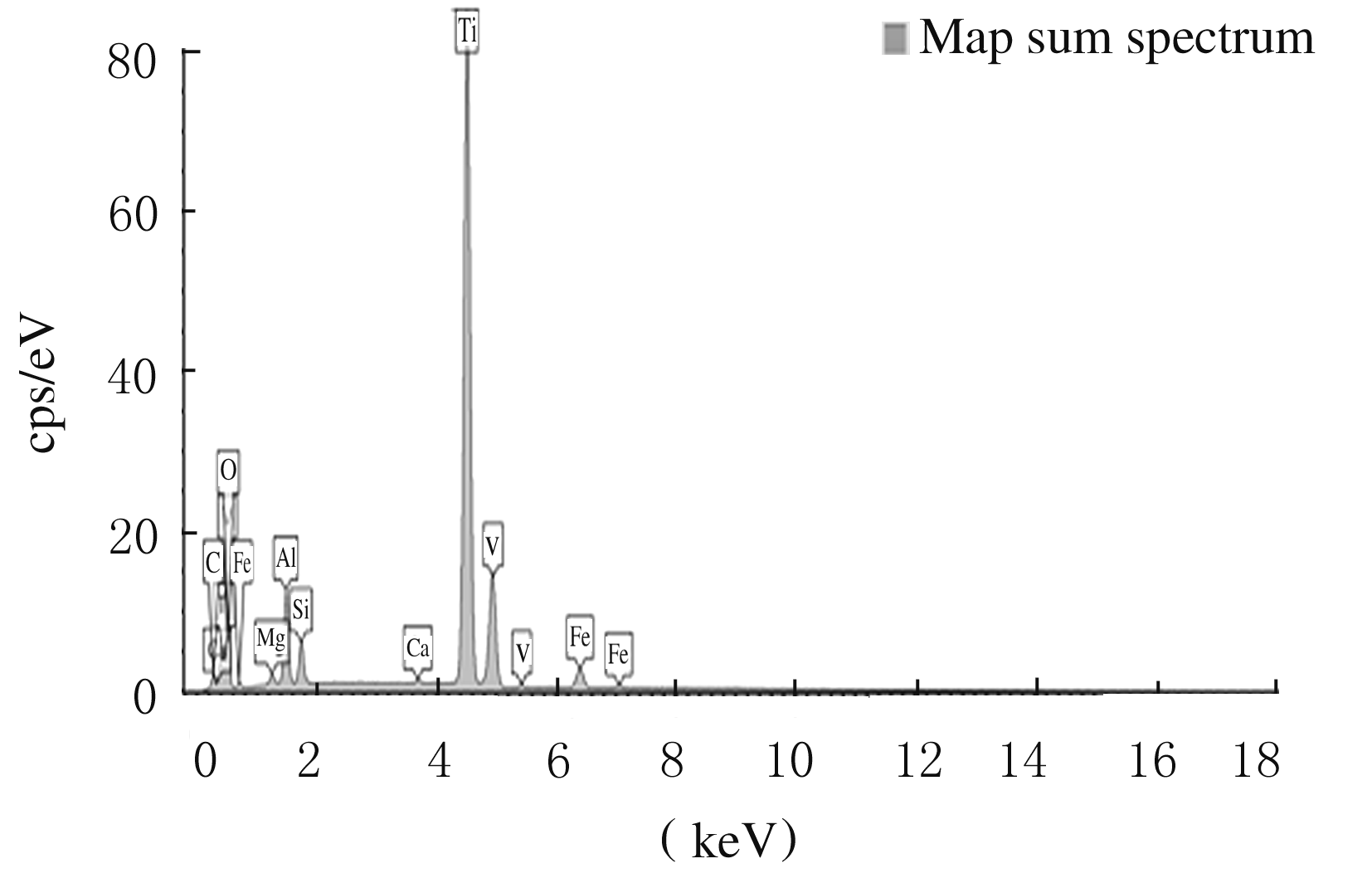
Preparation and bone-binding properties of 3D printed titanium alloy implants
Rui WANG,Meihua LI( ),Wanlin ZHOU
),Wanlin ZHOU
- Department of Stomatology,Second Hospital,Jilin University,Changchun 130041,China
CLC Number:
- R783.1