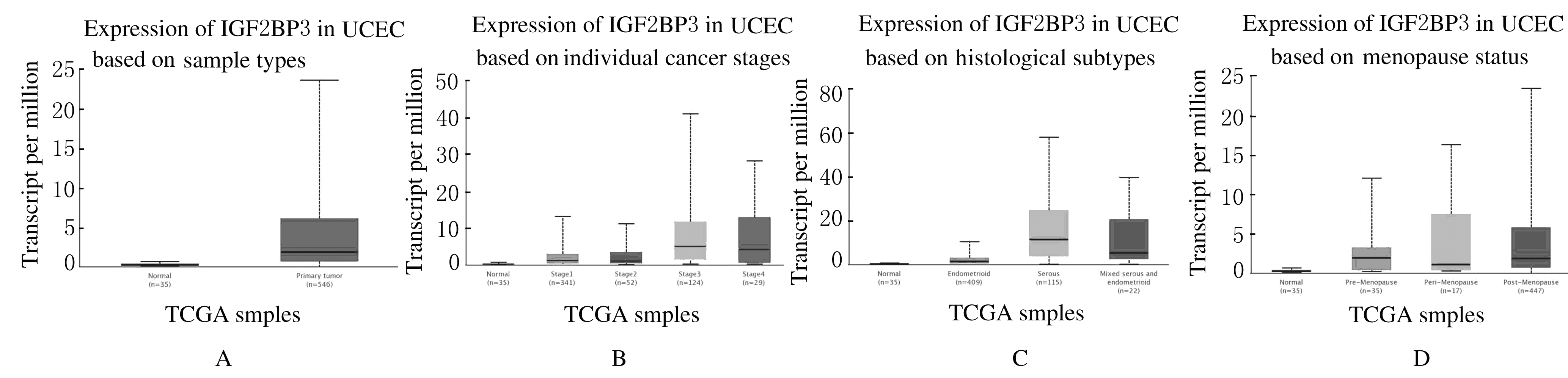
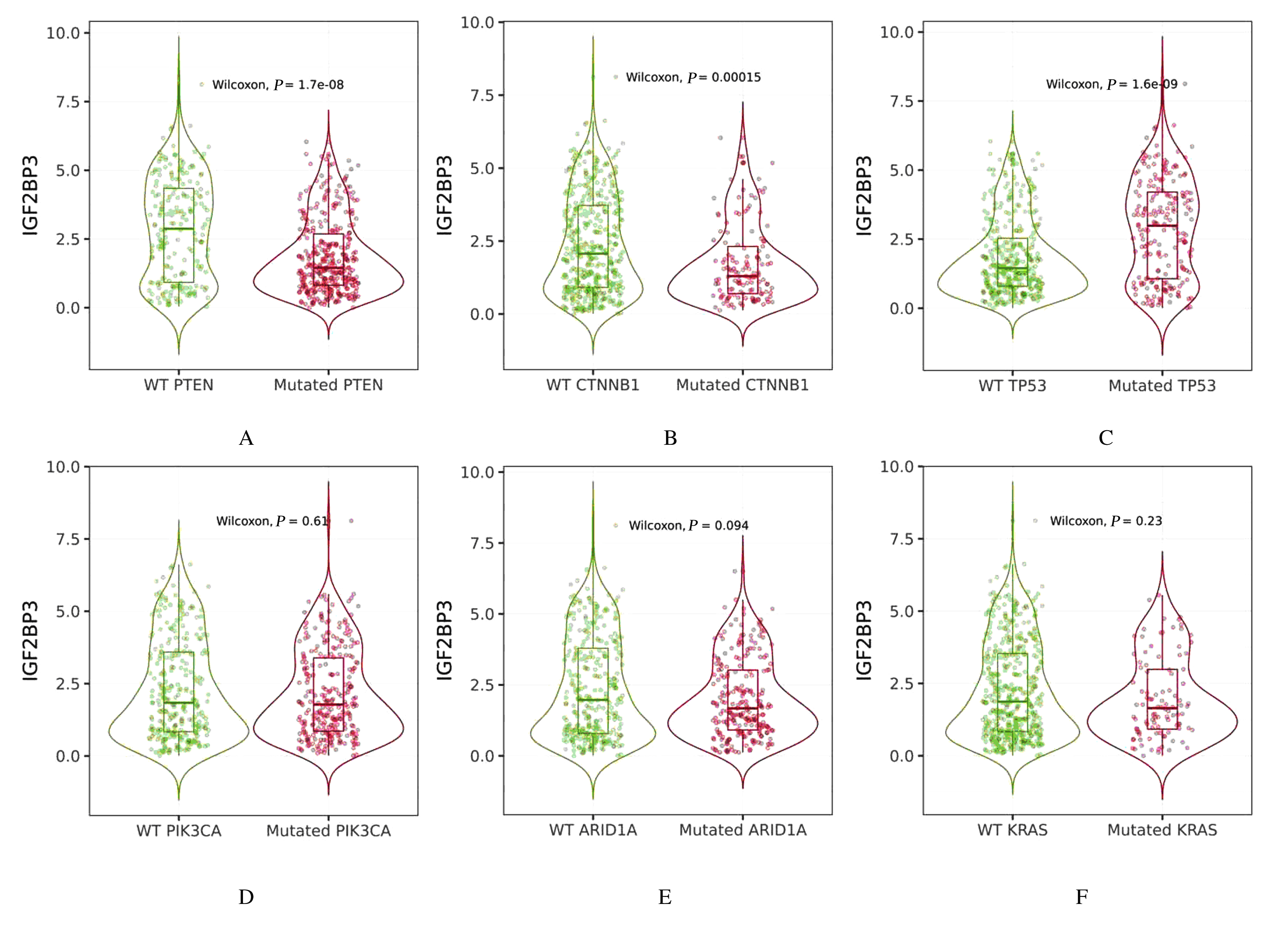
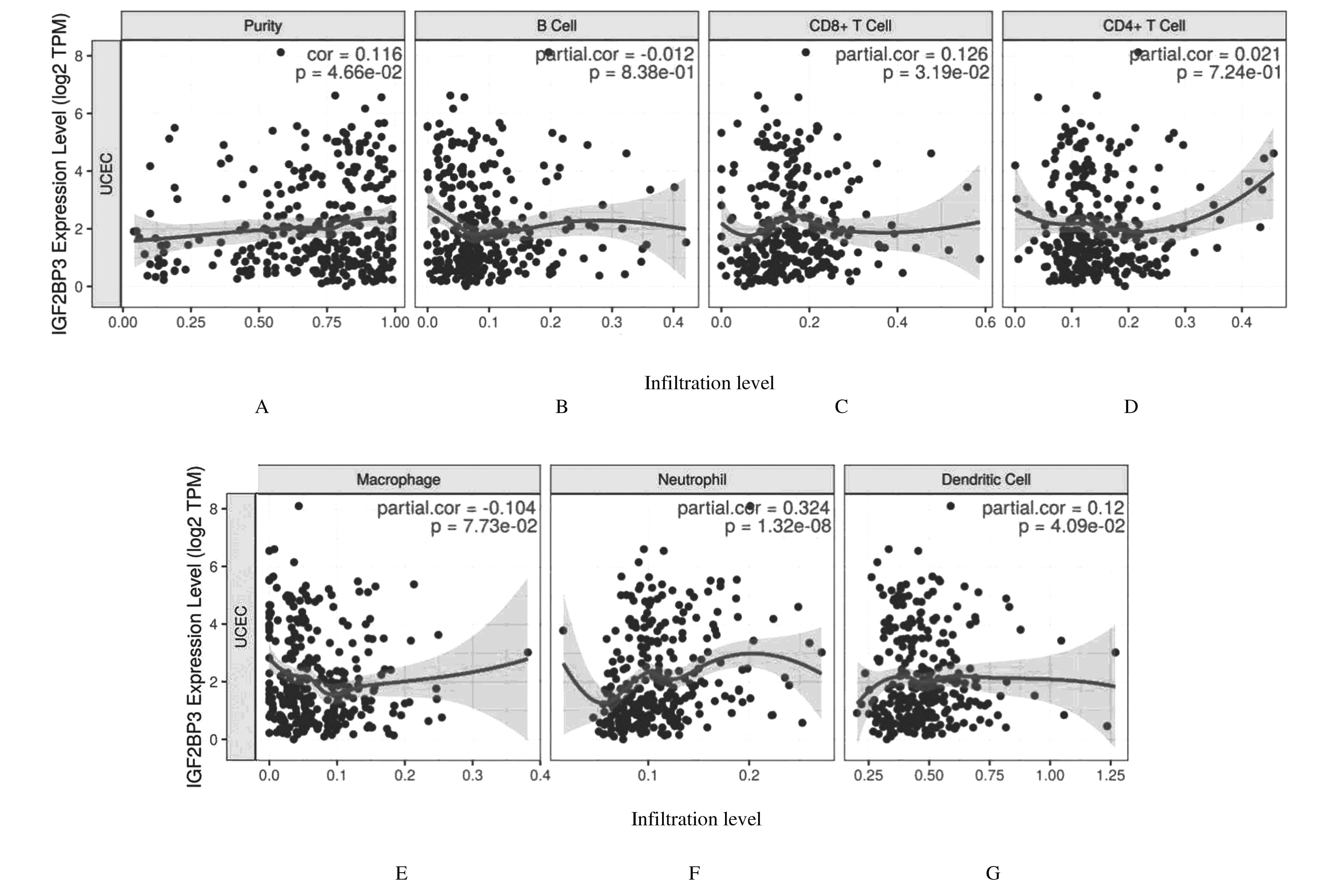
Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition) ›› 2021, Vol. 47 ›› Issue (2): 438-452.doi: 10.13481/j.1671-587X.20210225
• Research in clinical medicine • Previous Articles Next Articles
Bioinformatics analysis based on effect of expression levels of m6A regulators on immune infiltration and prognosis of uterine corpus endometrial carcinoma
Lan ZHENG1,2,Songzhe PIAO3,Ran XU1,Xinyue WANG1,Yixuan WANG1,Zhenhua LIN1( ),Yang YANG1(
),Yang YANG1( )
)
- 1.Department of Pathology,Key Laboratory of Gynecologic Tumor Bioinformatics,Jilin Provincial Science and Technology Department,College of Medical Sciences,Yanbian University,Yanji 133002,China
2.Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology,Affiliated Taizhou Hospital,Wenzhou Medical University,Linhai 317005,China
3.Department of Urology,Affiliated Taizhou Hospital,Wenzhou Medical University,Linhai 317005,China
-
Received:2020-10-14Online:2021-03-28Published:2021-03-25 -
Contact:Zhenhua LIN,Yang YANG E-mail:zhlin720@ybu.edu.cn;yangyang@ybu.edu.cn
CLC Number:
- R737.33
Cite this article
Lan ZHENG,Songzhe PIAO,Ran XU,Xinyue WANG,Yixuan WANG,Zhenhua LIN,Yang YANG. Bioinformatics analysis based on effect of expression levels of m6A regulators on immune infiltration and prognosis of uterine corpus endometrial carcinoma[J].Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2021, 47(2): 438-452.
share this article
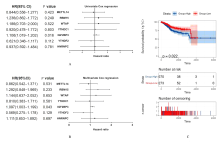
Tab.1
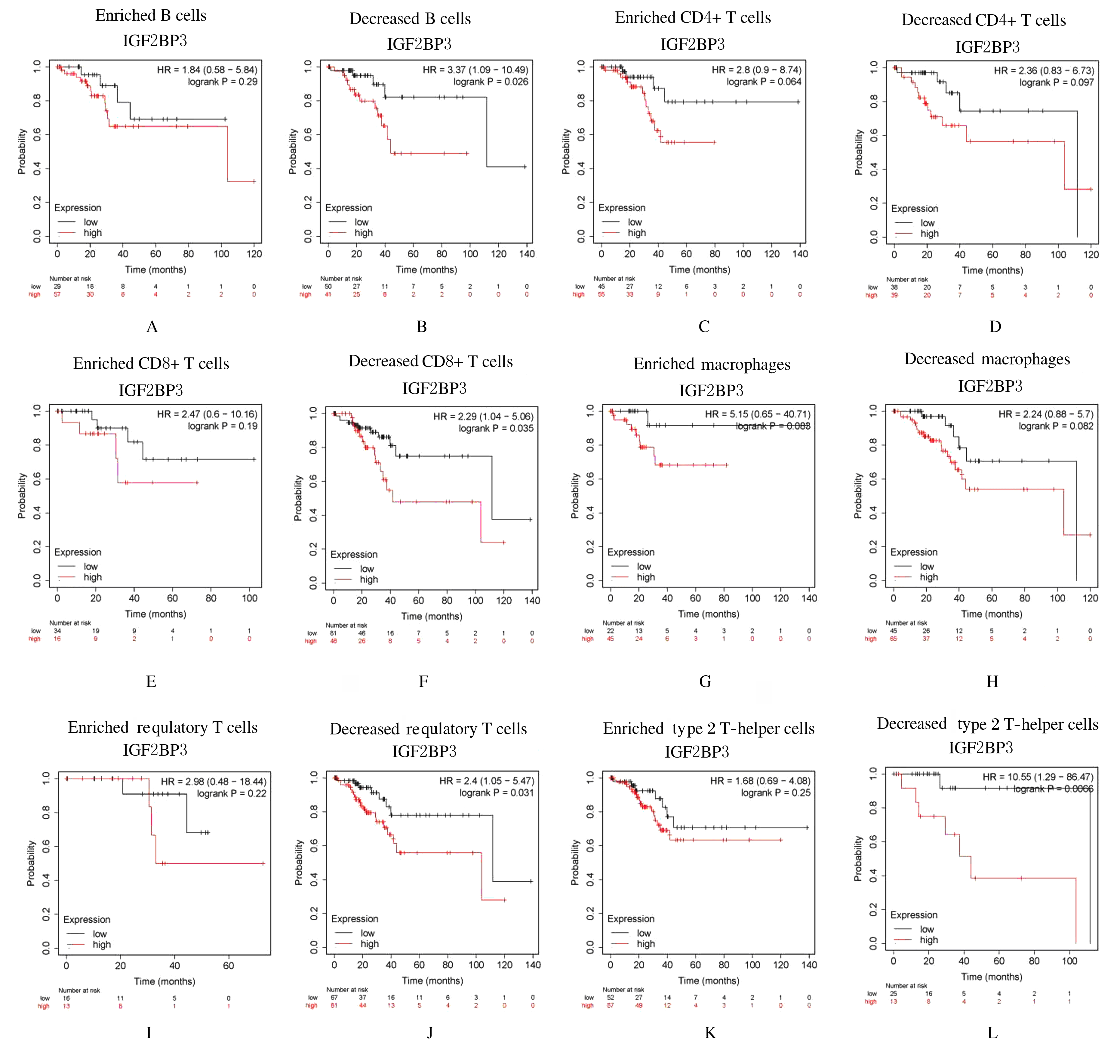
Correlations between IGF2BP3 mRNA expression level and biological markers of immune cells analyzed with TIMER database"
| UCEC | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Description | Gene marker | None | Purity | |||
| r | P | r | P | |||
| CD8+T cells | CD8A | 0.061 | 1.53E-01 | 0.133 | 2.25E-02 | |
| CD8B | -0.095 | 2.66E-02 | -0.053 | 3.68E-01 | ||
| T cells (general) | CD3D | -0.079 | 6.62E-02 | 0.009 | 8.83E-01 | |
| CD3E | -0.066 | 1.24E-01 | 0.016 | 7.80E-01 | ||
| CD2 | -0.019 | 6.50E-01 | 0.068 | 2.45E-01 | ||
| B cell | CD19 | 0.114 | 7.90E-03 | 0.188 | 1.25E-03 | |
| CD79A | -0.003 | 9.53E-01 | 0.106 | 7.03E-02 | ||
| FCRL2 | -0.166 | 1.00E-04 | 0.107 | 6.63E-02 | ||
| MS4A1 | 0.035 | 4.13E-01 | 0.113 | 5.40E-02 | ||
| Monocytes | CD86 | 0.033 | 4.41E-01 | 0.074 | 2.09E-01 | |
| CD115(CSF1R) | -0.094 | 2.74E-02 | -0.027 | 6.43E-01 | ||
| C3AR1 | 0.027 | 5.30E-01 | 0.085 | 1.48E-01 | ||
| CD86 | 0.033 | 4.41E-01 | 0.074 | 2.09E-01 | ||
| TAM | CCL2 | -0.007 | 8.62E-01 | 0.018 | 7.65E-01 | |
| CD68 | 0.069 | 1.07E-01 | 0.131 | 2.52E-02 | ||
| IL10 | 0.070 | 1.02E-01 | 0.117 | 4.53E-02 | ||
| CD84 | 0.089 | 3.88E-02 | 0.129 | 2.73E-02 | ||
| M1 macrophages | INOS(NOS2) | 0.090 | 3.55E-02 | 0.127 | 2.95E-02 | |
| IRF5 | 0.217 | 3.13E-07 | 0.221 | 1.40E-04 | ||
| M2 macrophages | CD163 | 0.153 | 3.49E-04 | 0.206 | 3.90E-04 | |
| VSIG4 | 0.074 | 8.34E-02 | 0.118 | 4.37E-02 | ||
| MS4A4A | 0.056 | 1.90E-01 | 0.095 | 1.05E-01 | ||
| Neutrophils | CD66b(CEACAM8) | -0.008 | 8.53E-01 | -0.005 | 9.26E-01 | |
| CD11b(ITGAM) | -0.052 | 2.27E-01 | -0.04 | 4.93E-01 | ||
| CCR7 | -0.002 | 9.65E-01 | 0.102 | 8.19E-02 | ||
| KIR2DL1 | 0.002 | 9.57E-01 | -0.040 | 5.00E-01 | ||
| KIR2DL3 | 0.051 | 2.38E-01 | 0.006 | 9.18E-01 | ||
| KIR2DL4 | 0.064 | 1.34E-01 | 0.129 | 2.70E-02 | ||
| CSF3R | 0.078 | 7.04E-02 | 0.159 | 6.24E-03 | ||
| S100A12 | -0.024 | 5.80E-01 | 0.065 | 2.69E-01 | ||
| DC | HLA?DPB1 | -0.106 | 1.30E-02 | -0.016 | 7.90E-01 | |
| HLA?DQB1 | -0.105 | 1.39E-02 | -0.038 | 5.13E-01 | ||
| HLA?DRA | -0.047 | 2.72E-01 | 0.027 | 6.40E-01 | ||
| HLA?DPA1 | -0.040 | 3.56E-01 | 0.022 | 7.02E-01 | ||
| BDCA?1(CD1C) | -0.113 | 8.08E-03 | -0.075 | 2.03E-01 | ||
| BDCA?4(NRP1) | 0.055 | 2.03E-01 | 0.123 | 3.50E-02 | ||
| CD11c(ITGAX) | -0.004 | 9.21E-01 | -0.003 | 9.65E-01 | ||
| CD209 | 0.104 | 1.48E-02 | 0.159 | 1.54E-02 | ||
| Th1 | T?bet(TBX21) | 0.019 | 6.64E-01 | 0.093 | 1.12E-01 | |
| STAT4 | 0.052 | 2.29E-01 | 0.114 | 5.22E-02 | ||
| STAT1 | 0.389 | 3.92E-21 | 0.455 | 2.10E-16 | ||
| Description | Gene marker | None Purity | ||||
| r | P | r | P | |||
| IFN?γ(IFNG) | 0.074 | 8.23E-02 | 0.104 | 7.63E-02 | ||
| TNF?α(TNF) | 0.043 | 3.11E-01 | 0.089 | 1.27E-01 | ||
| Th2 | GATA3 | 0.012 | 7.73E-01 | -0.002 | 9.72E-01 | |
| STAT6 | 0.085 | 4.64E-02 | 0.118 | 4.30E-02 | ||
| STAT5A | 0.065 | 1.32E-01 | 0.160 | 6.00E-03 | ||
| IL13 | -0.076 | 7.58E-02 | -0.037 | 5.25E-01 | ||
| Tfh | BCL6 | -0.007 | 8.76E-01 | -0.044 | 4.49E-01 | |
| IL21 | 0.051 | 2.32E-01 | 0.113 | 5.36E-02 | ||
| Th17 | STAT3 | 0.119 | 5.31E-03 | 0.161 | 5.84E-03 | |
| IL17A | 0.063 | 1.41E-01 | 0.035 | 5.48E-01 | ||
| Treg | FOXP3 | 0.007 | 8.69E-01 | 0.091 | 1.20E-01 | |
| CCR8 | 0.083 | 5.28E-02 | 0.089 | 1.30E-01 | ||
| STAT5B | 0.171 | 6.08E-05 | 0.232 | 6.07E-05 | ||
| TGFβ(TGFβ1) | 0.077 | 7.06E-02 | 0.115 | 4.86E-02 | ||
| T cell exhaustion | PD?1(PDCD1) | -0.016 | 7.04E-01 | 0.056 | 3.41E-01 | |
| CTLA4 | -0.040 | 3.47E-01 | 0.041 | 4.88E-01 | ||
| LAG3 | 0.079 | 6.40E-02 | 0.152 | 8.96E-03 | ||
| TIM?3(HAVCR2) | 0.046 | 2.83E-01 | 0.112 | 5.46E-02 | ||
| GZMB | 0.025 | 5.59E-01 | 0.074 | 2.04E-01 | ||
| NK cells | KIR3DL3 | 0.067 | 1.20E-01 | 0.055 | 3.52E-01 | |
| NCR1 | 0.010 | 8.13E-01 | 0.038 | 5.16E-01 | ||
Tab. 2
Correlations between IGF2BP3 mRNA expression level and markers of immune cells analyzed with GEPIA database"
| UCEC | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Description | Gene marker | Tumor | Normal | ||
| r | P | r | P | ||
| B cells | CD19 | 0.140 | 0.072 | -0.280 | 0.360 |
| CD79A | 0.069 | 0.360 | -0.066 | 0.830 | |
| TAM | CCL2 | 0.028 | 0.710 | 0.450 | 0.130 |
| CD68 | 0.190 | 0.014 | -0.063 | 0.840 | |
| IL?10 | 0.170 | 0.026 | -0.120 | 0.700 | |
| CD84 | 0.100 | 0.190 | -0.170 | 0.580 | |
| M1 macrophages | INOS(NOS2) | 0.320 | 1.60E-05 | 0.085 | 0.780 |
| IRF5 | 0.250 | 9.50E-04 | 0.660 | 0.014 | |
| M2 macrophages | CD163 | -0.014 | 0.860 | -0.200 | 0.510 |
| VSIG4 | 0.050 | 0.510 | -0.094 | 0.760 | |
| MS4A4A | 0.068 | 0.370 | -0.160 | 0.600 | |
| DC | HLA?DPB1 | -0.002 | 0.980 | 0.130 | 0.670 |
| HLA?DQB1 | -0.170 | 0.029 | 0.028 | 0.930 | |
| HLA?DRA | 0.110 | 0.140 | 0.280 | 0.350 | |
| HLA?DPA1 | 0.096 | 0.210 | 0.250 | 0.410 | |
| BDCA?1(CD1C) | -0.054 | 0.480 | -0.260 | 0.390 | |
| BDCA?4(NRP1) | 0.130 | 0.097 | -0.410 | 0.170 | |
| CD11c(ITGAX) | 0.051 | 0.500 | 0.540 | 0.054 | |
| CD209 | -0.015 | 0.850 | -0.250 | 0.410 | |
| Th1 | T?bet(TBX21) | 0.009 | 0.910 | 0.290 | 0.330 |
| STAT4 | 0.130 | 0.098 | 0.140 | 0.430 | |
| STAT1 | 0.450 | 5.50E-10 | -0.094 | 0.760 | |
| IFN?γ(IFNG) | 0.100 | 0.170 | 0.140 | 0.640 | |
| TNF?α(TNF) | 0.019 | 0.800 | 0.330 | 0.270 | |
| Th2 | GATA3 | 0.054 | 0.480 | 0.091 | 0.770 |
| STAT6 | 0.370 | 4.70E-07 | -0.320 | 0.290 | |
| STAT5A | 0.130 | 0.083 | -0.230 | 0.450 | |
| IL?13 | -0.024 | 0.750 | 0.600 | 0.029 | |
| Th17 | STAT3 | 0.430 | 3.20E-09 | 0.091 | 0.770 |
| IL?17A | 0.180 | 0.018 | 0.200 | 0.510 | |
| Treg | FOXP3 | -0.005 | 0.950 | 0.180 | 0.550 |
| CCR8 | 0.320 | 2.10E-05 | 0.240 | 0.430 | |
| STAT5β | 0.490 | 7.30E-12 | -0.300 | 0.310 | |
| TGFβ(TGFβ1) | 0.180 | 0.020 | -0.110 | 0.710 | |
| 1 | LU K, BROADDUS R. Endometrial cancer [J]. N Engl Med, 2020, 383(21): 2053-2064. |
| 2 | DANAHER P, WARREN S, LU R, et al. Pan-cancer adaptive immune resistance as defined by the Tumor Inflammation Signature (TIS): results from The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA) [J]. Immunother Cancer, 2018, 6(1): 63. |
| 3 | VANDERSTRAETEN A, TUYAERTS S, AMANT F. The immune system in the normal endometrium and implications for endometrial cancer development [J]. Reproductive Immunol, 2015, 109: 7-16. |
| 4 | GUO F, DONG Y, TAN Q, et al. Tissue infiltrating immune cells as prognostic biomarkers in endometrial cancer: A Meta-analysis [J]. Dis Markers, 2020, 2020: 1805764. |
| 5 | DE FELICE F, MARCHETTI C, TOMBOLINI V, et al. Immune check-point in endometrial cancer [J]. Int J Clin Oncol, 2019, 24(8): 910-916. |
| 6 | VERSLUIS M, MARCHAL S, PLAT A, et al. The prognostic benefit of tumour-infiltrating Natural Killer cells in endometrial cancer is dependent on concurrent overexpression of human leucocyte antigen-E in the tumour microenvironment [J]. Eur J Cancer, 2017, 86: 285-295. |
| 7 | WORKEL H, KOMDEUR F, WOUTERS M, et al. CD103 defines intraepithelial CD8+ PD1+ tumour-infiltrating lymphocytes of prognostic significance in endometrial adenocarcinoma [J]. Eur J Cancer, 2016, 60: 1-11. |
| 8 | LAN Q, LIU P, HAASE J, et al. The critical role of RNA m6A methylation in cancer [J]. Cancer Res, 2019, 79(7): 1285-1292. |
| 9 | WANG Y Z, REN F, SONG Z X, et al. Multiomics profile and prognostic gene signature of m6A regulators in uterine corpus endometrial carcinoma [J]. Cancer, 2020, 11(21): 6390-6401. |
| 10 | SHULMAN Z, STERN-GINOSSAR N. The RNA modification N6-methyladenosine as a novel regulator of the immune system [J]. Nat Immunol, 2020, 21(5): 501-512. |
| 11 | YI L, WU G, GUO L, et al. Comprehensive analysis of the PD-L1 and immune infiltrates of mA RNA methylation regulators in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma [J]. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids, 2020, 21: 299-314. |
| 12 | WU H, DONG H, FU Y, et al. Expressions of m6A RNA methylation regulators and their clinical predictive value in cervical squamous cell carcinoma and endometrial adenocarcinoma [J]. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol, 2021, 48(2): 270-278. |
| 13 | DANAHER P, WARREN S, DENNIS L, et al. Gene expression markers of tumor infiltrating leukocytes [J]. Immunother Cancer, 2017, 5: 18. |
| 14 | SOUSA S, MÄÄTTÄ J. The role of tumour-associated macrophages in bone metastasis [J]. Bone Oncol, 2016, 5(3): 135-138. |
| 15 | SIEMERS N, HOLLOWAY J, CHANG H, et al. Genome-wide association analysis identifies genetic correlates of immune infiltrates in solid tumors [J]. PLoS One, 2017, 12(7): e0179726. |
| 16 | YANG J, LI H X, HU S D, et al. ACE2 correlated with immune infiltration serves as a prognostic biomarker in endometrial carcinoma and renal papillary cell carcinoma: implication for COVID-19 [J]. Aging, 2020, 12(8): 6518-6535. |
| 17 | SCHOBER P, BOER C, SCHWARTE L. Correlation coefficients: appropriate use and interpretation [J]. Anesth Analg, 2018, 126(5): 1763-1768. |
| 18 | NETWORK C G A R, KANDOTH C,SCHULTZ N, et al. Integrated genomic characterization of endometrial carcinoma [J]. Nature, 2013, 497(7447): 67-73. |
| 19 | PAKISH J B, ZHANG Q, CHEN Z Y, et al. Immune microenvironment in microsatellite-instable endometrial cancers: hereditary or sporadic origin matters [J]. Clin Cancer Res, 2017, 23(15): 4473-4481. |
| 20 | LI C, ZOTA V, WODA B, et al. Expression of a novel oncofetal mRNA-binding protein IMP3 in endometrial carcinomas: diagnostic significance and clinicopathologic correlations [J]. Mod Pathol, 2007, 20(12): 1263-1268. |
| 21 | ZHENG W X, YI X F, FADARE O, et al. The oncofetal protein IMP3: a novel biomarker for endometrial serous carcinoma [J]. Am Surg Pathol, 2008, 32(2): 304-315. |
| 22 | VISSER N, PUTTEN LVAN D E R, EGERSCHOT A V A N, et al. Addition of IMP3 to L1CAM for discrimination between low- and high-grade endometrial carcinomas: a European Network for Individualised Treatment of Endometrial Cancer collaboration study[J]. Hum Pathol, 2019, 89(7): 90-98. |
| 23 | MHAWECH-FAUCEGLIA P, HERRMANN F R, RAI H, et al. IMP3 distinguishes uterine serous carcinoma from endometrial endometrioid adenocarcinoma [J]. Am J Clin Pathol, 2010, 133(6): 899-908. |
| 24 | LI W, LIU D, CHANG W, et al. Role of IGF2BP3 in trophoblast cell invasion and migration [J]. Cell Death Dis, 2014, 5: e1025. |
| 25 | HAN D L, LIU J Y, CHEN C, et al. Anti-tumour immunity controlled through mRNA m6A methylation and YTHDF1 in dendritic cells [J].Nature, 2019,566(7743): 270-274. |
| 26 | ZHANG B, WU Q, LI B, et al. m6A regulator-mediated methylation modification patterns and tumor microenvironment infiltration characterization in gastric cancer [J]. Mol Cancer, 2020, 19(1): 53. |
| 27 | ZHENG Q, HOU J, ZHOU Y, et al. The RNA helicase DDX46 inhibits innate immunity by entrapping mA-demethylated antiviral transcripts in the nucleus [J]. Nat Immunol, 2017, 18(10): 1094-1103. |
| 28 | WINKLER R, GILLIS E, LASMAN L, et al. m6A modification controls the innate immune response to infection by targeting type Ⅰ interferons [J]. Nat Immunol, 2019, 20(2): 173-182. |
| 29 | RUBIO R M, DEPLEDGE D P, BIANCO C, et al. RNA m6A modification enzymes shape innate responses to DNA by regulating interferon B [J]. Genes Develop, 2018, 32: 1472-1484. |
| 30 | LI H B, TONG J Y, ZHU S, et al. m6A mRNA methylation controls T cell homeostasis by targeting the IL-7/STAT5/SOCS pathways [J]. Nature, 2017, 548(7667): 338-342. |
| [1] | Yuqing PAN,Yunyan SUN,Yixun LI,Liying WANG,Zhuoma SINAN,Rui CHEN,Xi ZHANG,Yan DU. Construction and analysis of competitive endogenous RNA networks in acute myeloid leukemia based on high-throughput microarray [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2021, 47(3): 669-676. |
| [2] | Yao LIN,Chunlin LIN,Qin WANG,Bin ZHANG,Shaoyu WANG,Guangwei ZHU. Expressions of minichromosome maintenance proteins and structural maintenance of chromosomes 4 genes in cervical squamous cell carcinoma tissue and bioinformation analysis [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2021, 47(2): 430-437. |
| [3] | Jing WANG,Jing LIU,Xujing WEI,Yafei DU,Guiying FANG,Lin LI. Effects of oridonin on proliferation, migration, invasion and expression of lncRNA CCAT1 of endometrial carcinoma HEC-1B cells [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2021, 47(2): 384-389. |
| [4] | ZHANG Xi, ZHAI Li, SUN Yunyan, YANG Wei, GAO Yanzhang, LEI Ming, PAN Yuqing. Bioinformatics analysis of pediatric acute myeloid leukemia based on high-throughput microarray [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2020, 46(05): 1036-1042. |
| [5] | WEI Xujing, LI Lin, ZHANG Hongzhen, WANG Jing, XU Jing. Effects of LncRNA CCAT1 on proliferation,invasion and migration of endometrial cancer cells through TGF-β1/smad signaling pathway [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2020, 46(05): 1016-1022. |
| [6] | WANG Zhi, HONG Li, LI Suting, ZENG Wanling. Analysis on endometrial cancer-related genes and candidate pathways based on GEO database bioinformatics methods [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2020, 46(04): 804-809. |
| [7] | TAN Qi, REN Liqun, ZHANG Yibing, WANG Yadi, GU Zehui, HUANG Peng, CHEN Suxian. Application of bioinformatics in screening of miRNA biomarkers in triple-negative breast cancer [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2019, 45(05): 1098-1105. |
| [8] | DU Yayan, LIU Yang, LU Mu, HUAI Shitao, LYU Zuoli, WEI Yutao. Expressions of adiponectin-related miR-371b-5p in epicardial adipose tissue and plasma of patients with coronary heart disease and its effect on secretion of adipocytokines [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2019, 45(03): 643-650. |
| [9] | HUO Yanwei, XIE Bing, JIANG Lei, ZHANG Rui, SONG Mei, WANG Lan, WANG Xueyi, XU Shunjiang. Expressions of miRNAs related to accelerating senescence in serum of patients with amnestic mild cognitive impairment and analysison their biological information [J]. Journal of Jilin University Medicine Edition, 2017, 43(02): 322-327. |