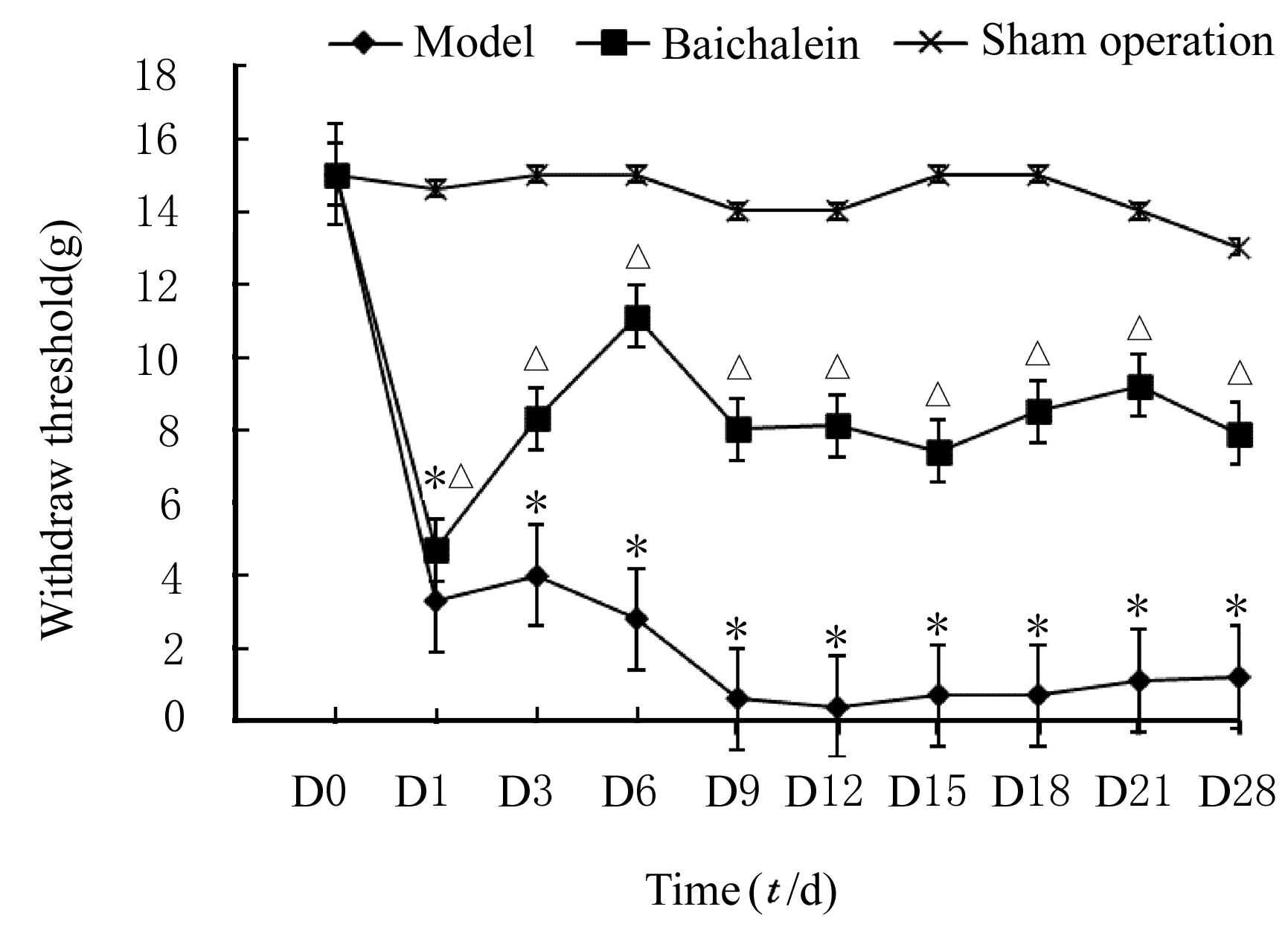
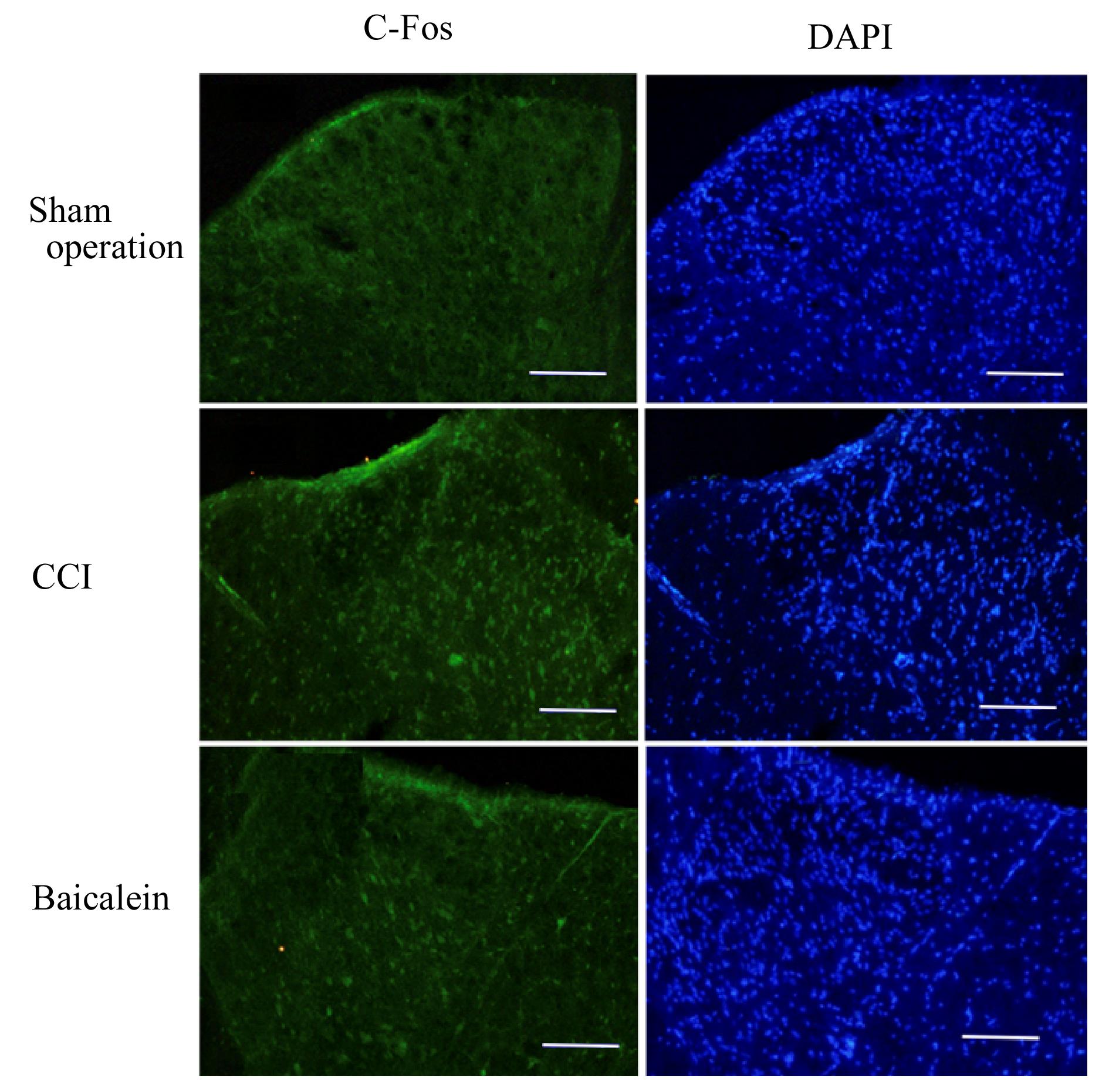
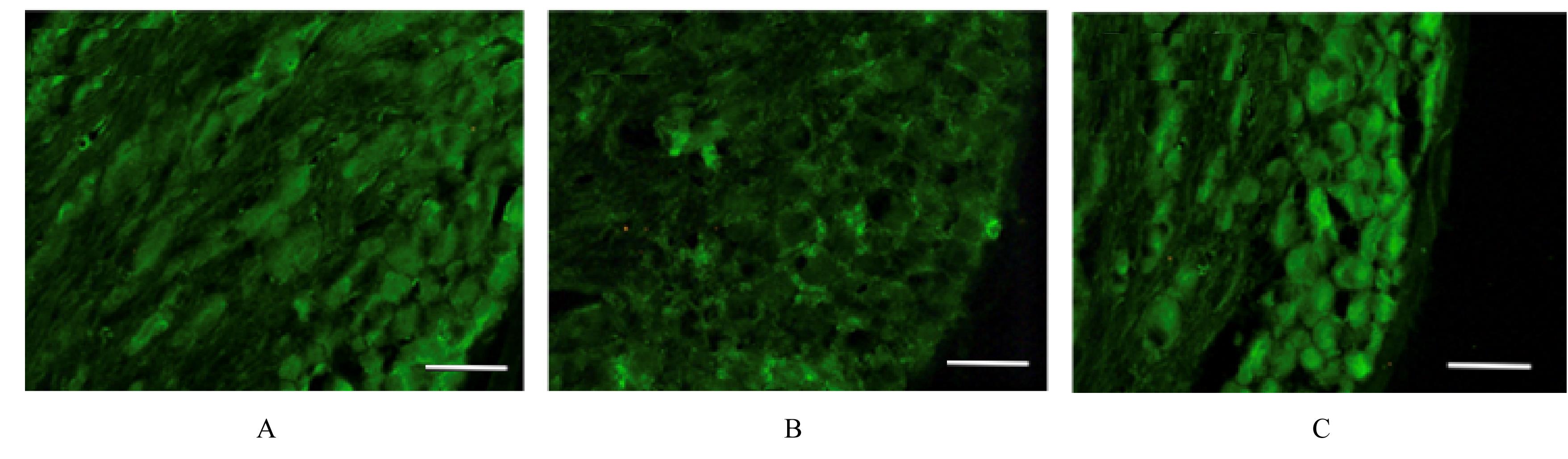
| 1 |
TREEDE R D, RIEF W, BARKE A, et al. Chronic pain as a symptom or a disease: the IASP Classification of Chronic Pain for the International Classification of Diseases (ICD-11)[J]. Pain, 2019, 160(1): 19-27.
|
| 2 |
TULI H S, AGGARWAL V, KAUR J, et al. Baicalein: a metabolite with promising antineoplastic activity[J]. Life Sci, 2020, 259: 118183.
|
| 3 |
HU S, CHEN Y, WANG Z F, et al. The analgesic and antineuroinflammatory effect of baicalein in cancer-induced bone pain[J]. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med, 2015, 2015: 973524.
|
| 4 |
LAI H C, LU C H, WONG C S, et al. Baicalein attenuates neuropathic pain and improves sciatic nerve function recovery in rats with partial sciatic nerve transection[J].J Chin Med Assoc,2018,81(11): 955-963.
|
| 5 |
CORTÉS D, CARBALLO-MOLINA O A, CASTELLANOS-MONTIEL M J, et al. The non-survival effects of glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor on neural cells[J]. Front Mol Neurosci, 2017, 10: 258.
|
| 6 |
王晓东, 薛朝霞. 胶质细胞源性神经营养因子在神经病理性疼痛中的研究进展[J]. 中国疼痛医学杂志, 2018, 24(3): 210-214.
|
| 7 |
NAM J H, LEEM E, JEON M T, et al. Induction of GDNF and BDNF by hRheb(S16H) transduction of SNpc neurons: neuroprotective mechanisms of hRheb(S16H) in a model of Parkinson’s disease[J]. Mol Neurobiol, 2015, 51(2): 487-499.
|
| 8 |
ZHANG X, DU L D, ZHANG W, et al. Therapeutic effects of baicalein on rotenone-induced Parkinson’s disease through protecting mitochondrial function and biogenesis[J]. Sci Rep, 2017, 7(1): 9968.
|
| 9 |
CHENG H M, QI Y B, LAI N X, et al. Inhibition of hyperactivity of the dorsal raphe 5-HTergic neurons ameliorates hippocampal seizure[J]. CNS Neurosci Ther, 2021, 27(8): 963-972.
|
| 10 |
SALIO C, FERRINI F, MUTHURAJU S, et al. Presynaptic modulation of spinal nociceptive transmission by glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor (GDNF)[J]. J Neurosci, 2014, 34(41): 13819-13833.
|
| 11 |
查磊琼, 彭志友, 冯智英. 神经病理性疼痛药物治疗新靶点研究进展[J]. 中国疼痛医学杂志, 2018, 24(6): 402-406.
|
| 12 |
GOSSRAU G, SABATOWSKI R. Diagnostics and therapy of neuropathic pain[J]. Anaesthesist,2021,70(12): 993-1002.
|
| 13 |
LIU X H, GREEN K J, FORD Z K, et al. Growth hormone regulates the sensitization of developing peripheral nociceptors during cutaneous inflammation[J]. Pain, 2017, 158(2): 333-346.
|
| 14 |
MERIGHI A. Targeting the glial-derived neurotrophic factor and related molecules for controlling normal and pathologic pain[J]. Expert Opin Ther Targets, 2016, 20(2): 193-208.
|
| 15 |
TIAN W, HAN X G, LIU Y J, et al. Intrathecal epigallocatechin gallate treatment improves functional recovery after spinal cord injury by upregulating the expression of BDNF and GDNF[J]. Neurochem Res, 2013, 38(4): 772-779.
|
| 16 |
HIRAI T, NOMURA K, IKAI R, et al. Baicalein stimulates fibroblast growth factor 21 expression by up-regulating retinoic acid receptor-related orphan receptor α in C2C12 myotubes[J]. Biomed Pharmacother, 2019, 109: 503-510.
|
| 17 |
LEE J, AHN E, KIM S Y, et al. Inclusion complexes of cysteinyl β-cyclodextrin with baicalein restore collagen synthesis in fibroblast cells following ultraviolet exposure[J]. J Cell Biochem, 2019, 120(3):4032-4043.
|
| 18 |
PARK C, CHOI E O, KIM G Y, et al. Protective effect of baicalein on oxidative stress-induced DNA damage and apoptosis in RT4-D6P2T schwann cells[J]. Int J Med Sci, 2019, 16(1): 8-16.
|
| 19 |
PURUSHOTHAMAN B, SUMATHI T.5,6,7 trihydroxy flavone armoured neurodegeneration caused by Quinolinic acid induced huntington’s like disease in rat striatum-reinstating the level of brain neurotrophins with special reference to cognitive-socio behavior,biochemical and histopathological aspects [J]. Neurosci Res,2022,174:25-35.
|
 ),Bingying FANG1,Man HAN1,Haifa QIAO2,Yuanwang YU1
),Bingying FANG1,Man HAN1,Haifa QIAO2,Yuanwang YU1