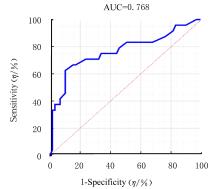
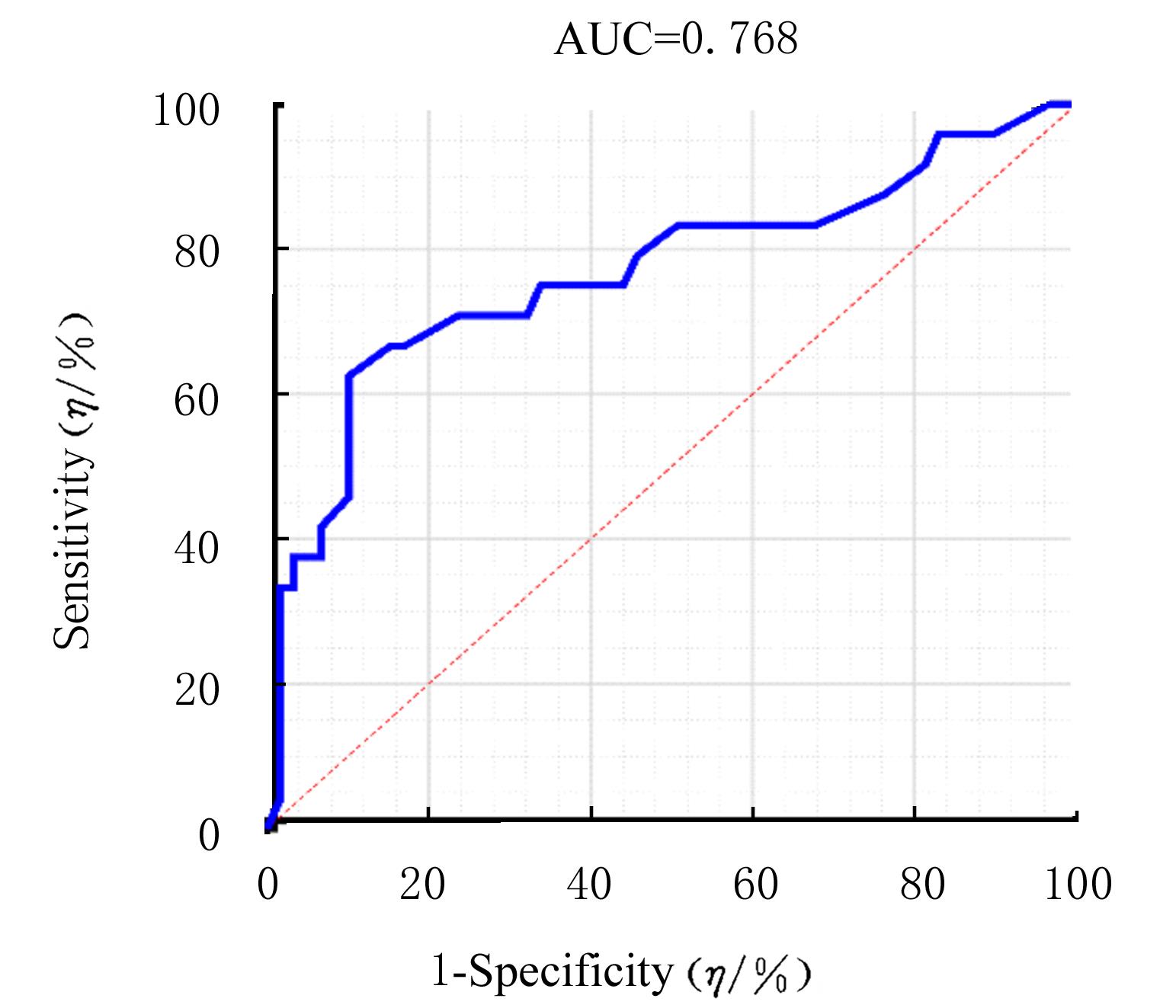
| 1 |
DOIZI S, TRAXER O. Flexible ureteroscopy: technique, tips and tricks[J].Urolithiasis, 2018, 46(1): 47-58.
|
| 2 |
BERARDINELLI F, CINDOLO L, FRANCESCO P, et al. The surgical experience influences the safety of retrograde intrarenal surgery for kidney stones: a propensity score analysis[J]. Urolithiasis, 2017, 45(4): 387-392.
|
| 3 |
MI Q, MENG X, MENG L, et al. Risk factors for systemic inflammatory response syndrome induced by flexible ureteroscope combined with holmium laser lithotripsy[J]. Biomed Res Int, 2020, 2020: 6842479.
|
| 4 |
LI T, SUN X Z, LAI D H, et al. Fever and systemic inflammatory response syndrome after retrograde intrarenal surgery: Risk factors and predictive model[J]. Kaohsiung J Med Sci, 2018, 34(7): 400-408.
|
| 5 |
BHOJANI N, MILLER L E, BHATTACHARYYA S, et al. Risk factors for urosepsis after ureteroscopy for stone disease: a systematic review with meta-analysis[J]. J Endourol, 2021, 35(7): 991-1000.
|
| 6 |
BERRÍOS-TORRES S I, UMSCHEID C A, BRATZLER D W, et al. Centers for disease control and prevention guideline for the prevention of surgical site infection, 2017[J].JAMA Surg,2017,152(8): 784-791.
|
| 7 |
孙颖浩. 吴阶平泌尿外科学[M]. 北京: 人民卫生出版社, 2019.
|
| 8 |
黄健. 中国泌尿外科和男科疾病诊断治疗指南(2019版)[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2019.
|
| 9 |
中国老年 2 型糖尿病防治临床指南编写组,中国老年医学学会老年内分泌代谢分会,中国老年保健医学研究会老年内分泌与代谢分会,等. 中国老年2型糖尿病防治临床指南(2022年版)[J]. 中华内科杂志, 2022, 61(1): 12-50.
|
| 10 |
梅烨, 陈凌武, 高新. 泌尿外科手术学[M]. 3版. 北京: 人民卫生出版社, 2006.
|
| 11 |
胡卫国, 王碧霄, 姬超岳, 等. 上尿路结石合并CRE菌尿行内镜手术后控制感染并发症的经验[J]. 中华泌尿外科杂志, 2020, 41(10): 764-768.
|
| 12 |
SINGER M, DEUTSCHMAN C S, SEYMOUR C W, et al. The Third International Consensus Definitions for Sepsis and Septic Shock (Sepsis-3)[J]. JAMA, 2016, 315(8): 801.
|
| 13 |
杨斌. 糖尿病与肾结石关系的研究进展[J]. 国际泌尿系统杂志, 2021, 41(1): 191-193.
|
| 14 |
HEIN S, PETZOLD R, SCHOENTHALER M, et al. Thermal effects of Ho: YAG laser lithotripsy: real-time evaluation in an in vitro model[J]. World J Urol, 2018, 36(9): 1469-1475.
|
| 15 |
JIAN Z, MA Y, LIU R, et al. Preoperative positive urine nitrite and albumin-globulin ratio are independent risk factors for predicting postoperative fever after retrograde Intrarenal surgery based on a retrospective cohort[J]. BMC Urology, 2020, 20(1): 50.
|
| 16 |
PAINTER J D, AKBARI O. Type 2 innate lymphoid cells: protectors in type 2 diabetes[J]. Front Immunol, 2021, 12: 727008.
|
| 17 |
TONG Z W M, GRANT E, GRAS S, et al. The role of T-cell immunity in COVID-19 severity amongst people living with type Ⅱ diabetes[J]. FEBS J, 2021, 288(17): 5042-5054.
|
| 18 |
BARKAI L J, SIPTER E, CSUKA D, et al. Decreased ficolin-3-mediated complement lectin pathway activation and alternative pathway amplification during bacterial infections in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus[J]. Front Immunol, 2019, 10: 509.
|
| 19 |
申智勇, 钟渠梁, 石家齐,等. 逆行上尿路腔内碎石术后并发急性尿源性感染的相关危险因素分析[J]. 国际泌尿系统杂志, 2020, 40(3): 440-444.
|
| 20 |
GAO X, LU C, XIE F, et al. Risk factors for sepsis in patients with struvite stones following percutaneous nephrolithotomy[J].World J Urol,2020,38(1):219-229.
|
| 21 |
MARTOV A, GRAVAS S, ETEMADIAN M, et al. Postoperative infection rates in patients with a negative baseline urine culture undergoing ureteroscopic stone removal: A matched case-control analysis on antibiotic prophylaxis from the CROES URS Global Study[J]. J Endourol, 2015, 29(2): 171-180.
|
| 22 |
曹金龙,李攀,杨欣,等. 经输尿管镜碎石术后尿源性脓毒性休克的预后影响因素分析[J]. 国际泌尿系统杂志, 2021, 41(1): 44-48.
|
| 23 |
刘肖肖,李书青,张 倩,等.糖尿病合并肾功能不全患者HbA_(1c)估算平均血糖校正模型的建立[J/OL].解放军医学杂志:1-9[2022-06-08]..
|
| 24 |
DEMIR D, DOLUOGLU O, YILDIZ Y, et al. Risk factors for infectious complications in patients undergoing retrograde intrarenal surgery[J]. J Coll Physicians Surg Pak, 2019, 29(6): 558–562.
|
| 25 |
杜浩杰. 上尿路腔镜碎石术中肾盂内压的控制方法和意义[J].国际泌尿系统杂志,2020,40(6):1134-1136.
|
 ),Ranwei LI1(
),Ranwei LI1( )
)