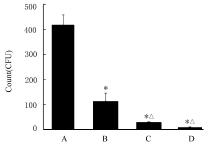
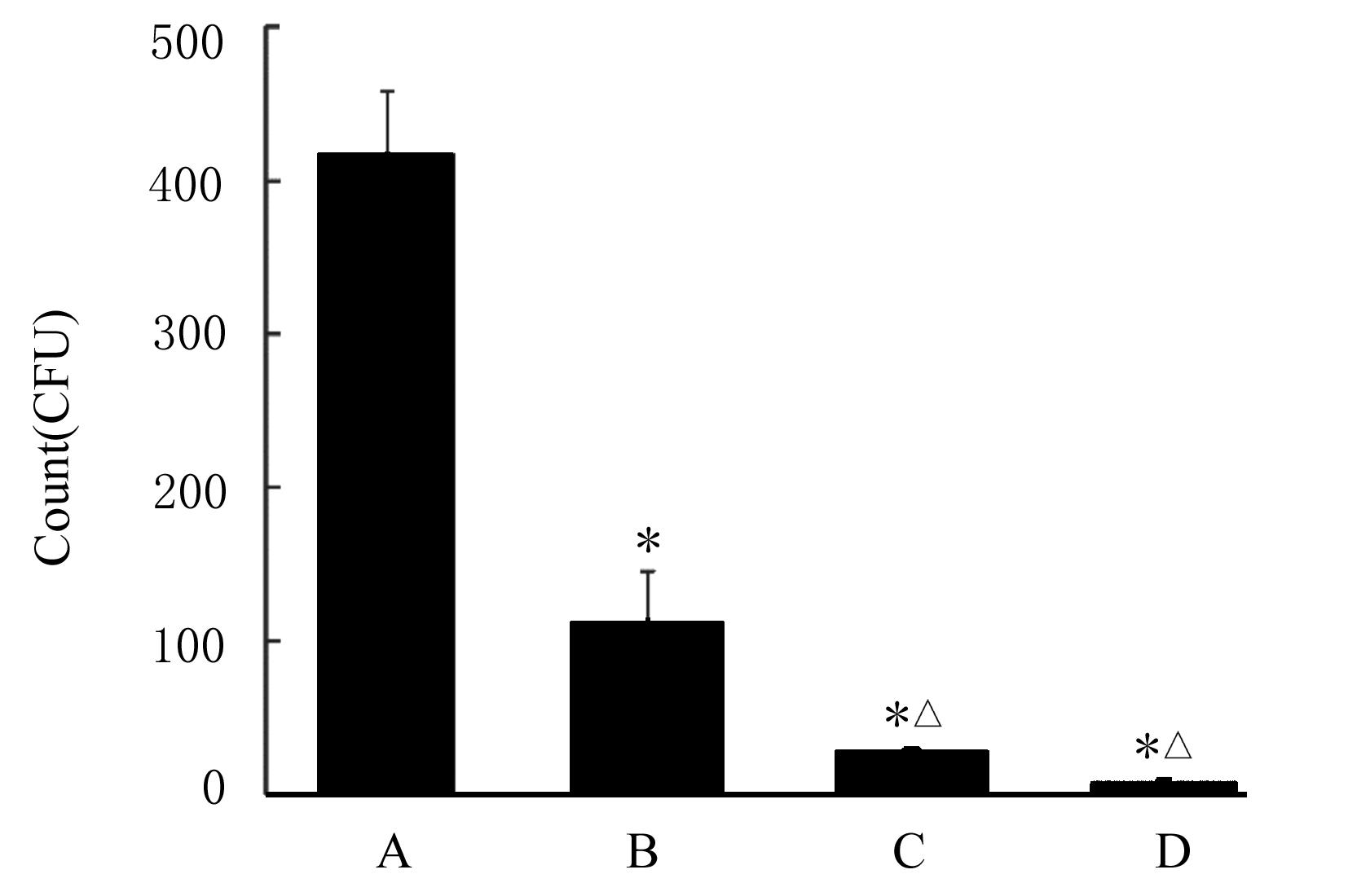
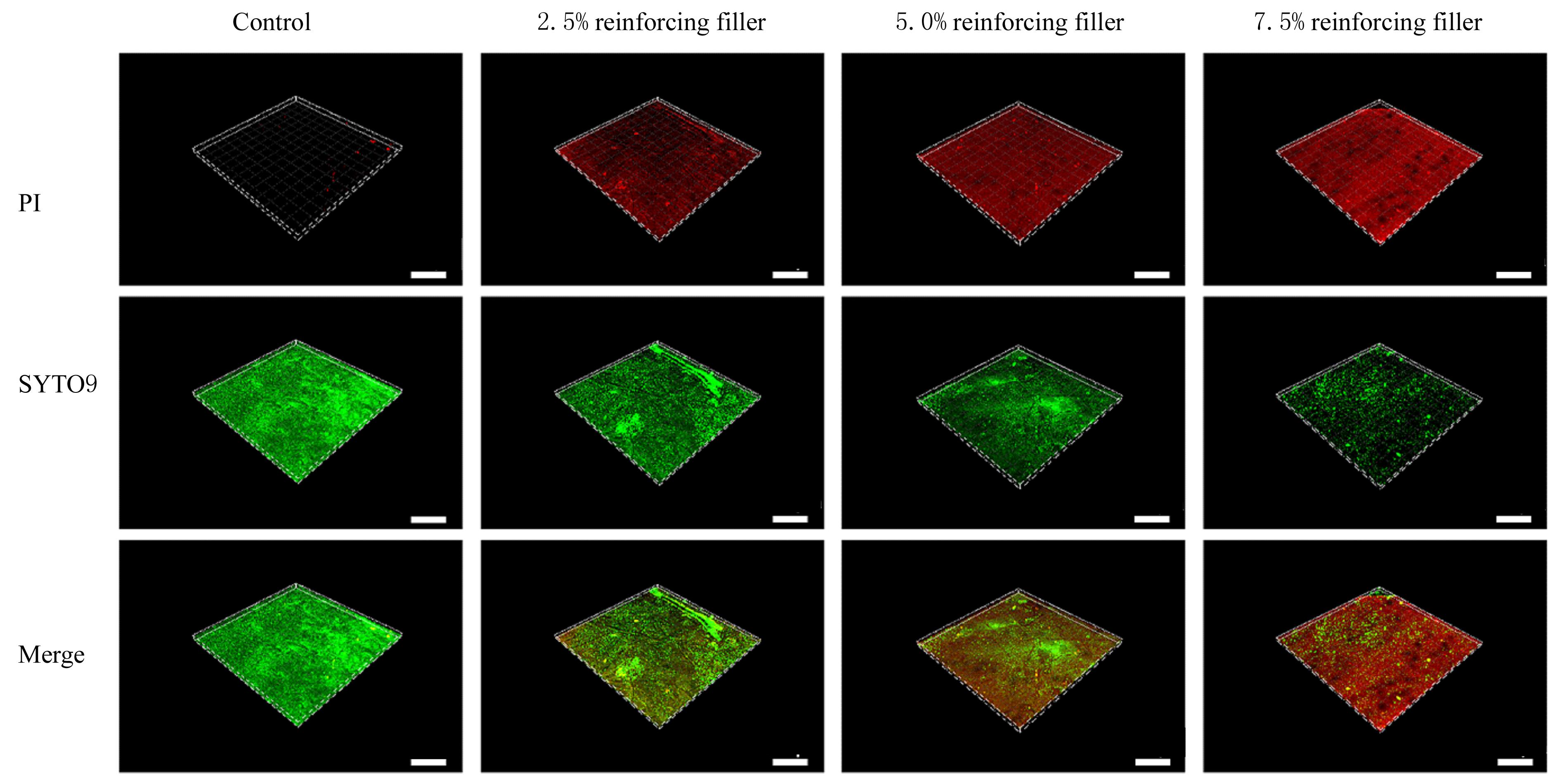
| 1 |
FERRACANE J L. Resin composite—state of the art[J]. Dent Mater, 2011, 27(1): 29-38.
|
| 2 |
SU M X, YAO S Y, GU L S, et al. Antibacterial effect and bond strength of a modified dental adhesive containing the peptide nisin[J]. Peptides, 2018, 99: 189-194.
|
| 3 |
WANG Y Z, ZHU M F, ZHU X X. Functional fillers for dental resin composites[J]. Acta Biomater, 2021, 122: 50-65.
|
| 4 |
ARDESTANI S S, BONAN R F, MOTA M F, et al. Effect of the incorporation of silica blow spun nanofibers containing silver nanoparticles (SiO2/Ag) on the mechanical, physicochemical, and biological properties of a low-viscosity bulk-fill composite resin[J]. Dent Mater, 2021, 37(10): 1615-1629.
|
| 5 |
SILVESTRIN L B, GARCIA I M, VISIOLI F, et al. Physicochemical and biological properties of experimental dental adhesives doped with a guanidine-based polymer: an in vitro study[J]. Clin Oral Investig, 2022, 26(4): 3627-3636.
|
| 6 |
YANG D L, CUI Y N, SUN Q, et al. Antibacterial activity and reinforcing effect of SiO2-ZnO complex cluster fillers for dental resin composites[J]. Biomater Sci, 2021, 9(5): 1795-1804.
|
| 7 |
BAROT T, RAWTANI D, KULKARNI P. Physicochemical and biological assessment of silver nanoparticles immobilized Halloysite nanotubes-based resin composite for dental applications[J]. Heliyon, 2020, 6(3): e03601.
|
| 8 |
SORKHDINI P, GREGORY R L, CRYSTAL Y O, et al. Effectiveness of in vitro primary coronal caries prevention with silver diamine fluoride-Chemical vs biofilm models[J]. J Dent, 2020, 99: 103418.
|
| 9 |
YIN I X, ZHANG J, ZHAO I S, et al. The antibacterial mechanism of silver nanoparticles and its application in dentistry[J]. Int J Nanomedicine, 2020, 15: 2555-2562.
|
| 10 |
WANG Q Y, ZHANG Y, LI Q, et al. Therapeutic applications of antimicrobial silver-based biomaterials in dentistry[J]. Int J Nanomedicine, 2022, 17: 443-462.
|
| 11 |
ZHANG X Y, ZHANG G N, CHAI M Z, et al. Synergistic antibacterial activity of physical-chemical multi-mechanism by TiO2 nanorod arrays for safe biofilm eradication on implant[J]. Bioact Mater, 2021, 6(1): 12-25.
|
| 12 |
KUROIWA A, NOMURA Y, OCHIAI T, et al. Antibacterial, hydrophilic effect and mechanical properties of orthodontic resin coated with UV-responsive photocatalyst[J]. Materials, 2018, 11(6): 889.
|
| 13 |
ESTEBAN FLOREZ F L, TROFIMOV A A, IEVLEV A, et al. Advanced characterization of surface-modified nanoparticles and nanofilled antibacterial dental adhesive resins[J]. Sci Rep, 2020, 10(1): 9811.
|
| 14 |
KAWASHITA M, ENDO N, WATANABE T, et al. Formation of bioactive N-doped TiO2 on Ti with visible light-induced antibacterial activity using NaOH, hot water, and subsequent ammonia atmospheric heat treatment[J]. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces, 2016, 145: 285-290.
|
| 15 |
ANANPATTARACHAI J, BOONTO Y, KAJITVICHYANUKUL P. Visible light photocatalytic antibacterial activity of Ni-doped and N-doped TiO2 on Staphylococcus aureus and Escherichia coli bacteria[J]. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int, 2016, 23(5): 4111-4119.
|
| 16 |
COSTA A I, GEMINI-PIPERNI S, ALVES A C, et al. TiO2 bioactive implant surfaces doped with specific amount of Sr modulate mineralization[J]. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl, 2021, 120: 111735.
|
| 17 |
ZHAO Z H, OMER A A, QIN Z R,et al.Cu/N-codoped TiO2 prepared by the sol-gel method for phenanthrene removal under visible light irradiation[J]. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int, 2020, 27(15): 17530-17540.
|
| 18 |
WANG X P, TANG Y X, LEIW M Y, et al. Solvothermal synthesis of Fe-C codoped TiO2 nanoparticles for visible-light photocatalytic removal of emerging organic contaminants in water[J]. Appl Catal A, 2011, 409/410: 257-266.
|
| 19 |
KUVAREGA A T, KRAUSE R W M, MAMBA B B. Nitrogen/palladium-codoped TiO2 for efficient visible light photocatalytic dye degradation[J]. J Phys Chem C, 2011, 115(45): 22110-22120.
|
| 20 |
MURGOLO S, MOREIRA I S, PICCIRILLO C,et al. Photocatalytic degradation of diclofenac by Hydroxyapatite-TiO₂ composite material: identification of transformation products and assessment of toxicity[J]. Materials, 2018, 11(9): 1779.
|
| 21 |
MÁRQUEZ BRAZÓN E, PICCIRILLO C, MOREIRA I S, et al. Photodegradation of pharmaceutical persistent pollutants using hydroxyapatite-based materials[J]. J Environ Manage, 2016, 182: 486-495.
|
| 22 |
GEORGE S M, NAYAK C, SINGH I, et al. Multifunctional hydroxyapatite composites for orthopedic applications: a review[J]. ACS Biomater Sci Eng, 2022, 8(8): 3162-3186.
|
| 23 |
LI Y C, ZHANG D X, WAN Z, et al. Dental resin composites with improved antibacterial and mineralization properties via incorporating zinc/strontium-doped hydroxyapatite as functional fillers[J]. Biomed Mater, 2022, 17(4): 45002.
|
| 24 |
ALGHANNAM M I, ALABBAS M S, ALJISHI J A, et al. Remineralizing effects of resin-based dental sealants: a systematic review of in vitro studies[J]. Polymers, 2022, 14(4): 779.
|
| 25 |
ESTEBAN FLOREZ F L, KRAEMER H, HIERS R D,et al. Sorption, solubility and cytotoxicity of novel antibacterial nanofilled dental adhesive resins[J]. Sci Rep, 2020, 10(1): 13503.
|
| 26 |
ZHANG J H, HE X, YU S Y, et al. A novel dental adhesive containing Ag/polydopamine-modified HA fillers with both antibacterial and mineralization properties[J]. J Dent, 2021, 111: 103710.
|
| 27 |
ANDRZEJEWSKA E. Photopolymerization kinetics of multifunctional monomers[J]. Prog Polym Sci, 2001, 26(4): 605-665.
|
| 28 |
COLLARES F M, OGLIARI F A, ZANCHI C H,et al. Influence of 2-hydroxyethyl methacrylate concentration on polymer network of adhesive resin[J]. J Adhes Dent, 2011, 13(2): 125-129.
|
| 29 |
SIDERIDOU I, TSERKI V, PAPANASTASIOU G. Effect of chemical structure on degree of conversion in light-cured dimethacrylate-based dental resins[J]. Biomaterials, 2002, 23(8): 1819-1829.
|
| 30 |
FLURY S, HAYOZ S, PEUTZFELDT A, et al. Depth of cure of resin composites: is the ISO 4049 method suitable for bulk fill materials?[J]. Dent Mater, 2012, 28(5): 521-528.
|
| 31 |
VIJAYAKUMAR A, SARVESWARI H B, VASUDEVAN S, et al. Baicalein inhibits Streptococcus mutans biofilms and dental caries-related virulence phenotypes[J]. Antibiotics, 2021, 10(2): 215.
|
| 32 |
WU Y F, ZANG Y, XU L, et al. Synthesis of high-performance conjugated microporous polymer/TiO2 photocatalytic antibacterial nanocomposites[J]. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl, 2021, 126: 112121.
|
| 33 |
ZIENTAL D, CZARCZYNSKA-GOSLINSKA B, MLYNARCZYK D T, et al. Titanium dioxide nanoparticles: prospects and applications in medicine[J]. Nanomaterials (Basel), 2020, 10(2): E387.
|
| 34 |
MALEKI-GHALEH H, SIADATI M H, FALLAH A, et al. Antibacterial and cellular behaviors of novel zinc-doped hydroxyapatite/graphene nanocomposite for bone tissue engineering[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2021, 22(17): 9564.
|
 ),Hong ZHANG1(
),Hong ZHANG1( )
)