Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition) ›› 2021, Vol. 47 ›› Issue (5): 1116-1123.doi: 10.13481/j.1671-587X.20210506
• Research in basic medicine • Previous Articles Next Articles
Preparation of cinnamaldehyde antibacterial adhesive and evaluation on its antibacterial property
Han WANG,Zilu TIAN,Xuanyan ZHU,Yubin YANG,Song ZHU( )
)
- Department of Prosthodontics,Stomatology Hospital,Jilin University,Changchun 130021,China
-
Received:2020-12-29Online:2021-09-28Published:2021-10-26 -
Contact:Song ZHU E-mail:zhusong1965@163.com
CLC Number:
- R783.1
Cite this article
Han WANG,Zilu TIAN,Xuanyan ZHU,Yubin YANG,Song ZHU. Preparation of cinnamaldehyde antibacterial adhesive and evaluation on its antibacterial property[J].Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2021, 47(5): 1116-1123.
share this article
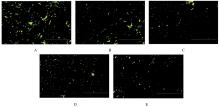
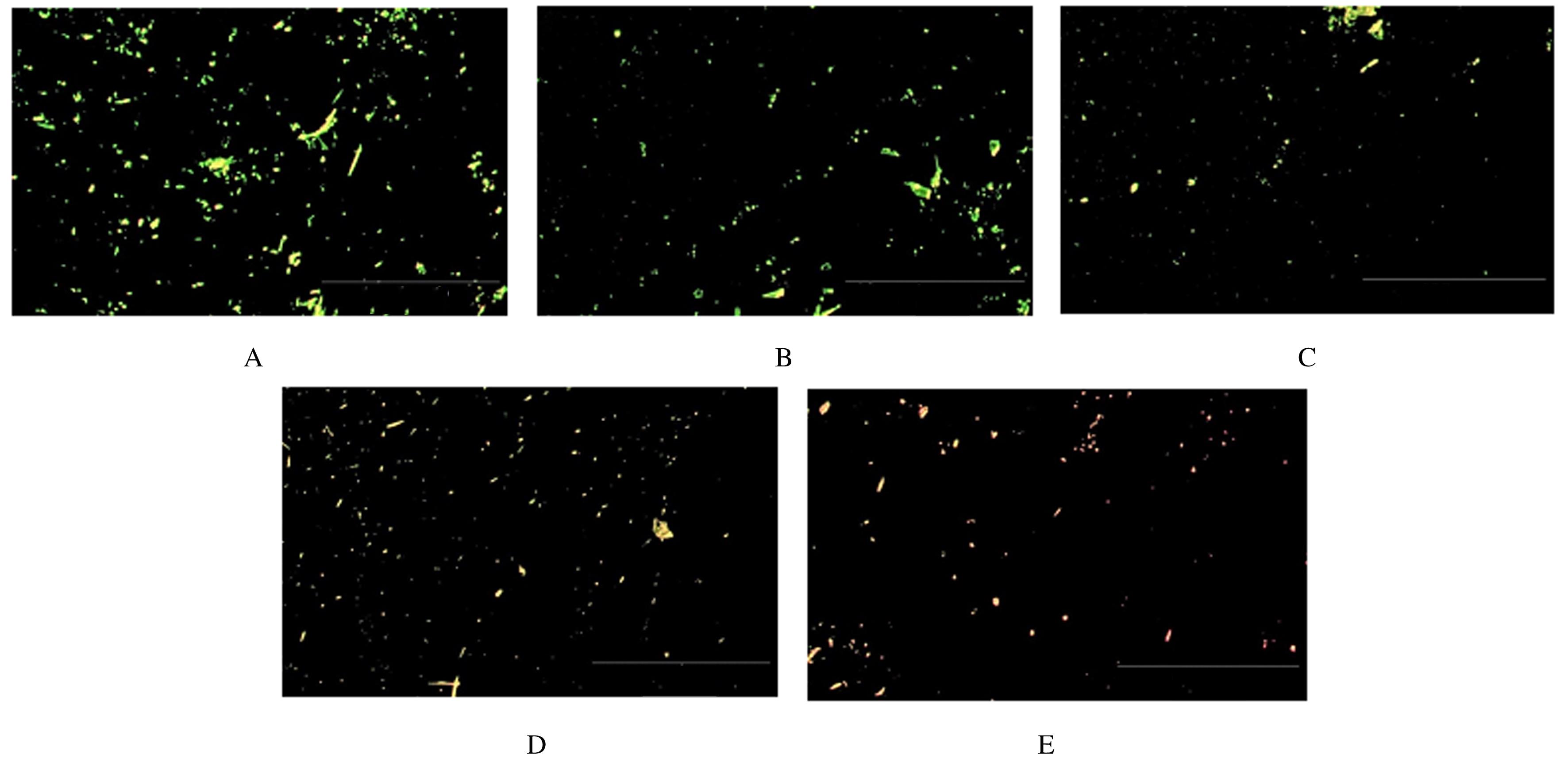
Tab. 2
Cell survival rates and cytotoxicity grades of adhesives in various groups"
| Group | Cell survival rate(η/%) | Cytotoxicity grade | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 000 times | 2 000 times | 4 000 times | 1 000 times | 2 000 times | 4 000 times | |
| Control | 70.49 | 95.25 | 99.68 | 2 | 1 | 1 |
| Cinnamaldenhyde | ||||||
| 2% | 79.32 | 114.93 | 113.93 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| 4% | 75.16 | 95.60 | 96.89 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| 6% | 75.41 | 104.13 | 108.91 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| 8% | 72.55 | 99.22 | 108.58 | 2 | 1 | 0 |
| 1 | SU M X, YAO S Y, GU L S, et al. Antibacterial effect and bond strength of a modified dental adhesive containing the peptide nisin[J]. Peptides, 2018, 99: 189-194. |
| 2 | CHRYSANTHAKOPOULOS N A. Placement, replacement and longevity of composite resin-based restorations in permanent teeth in Greece[J]. Int Dent J, 2012, 62(3): 161-166. |
| 3 | ZHANG N, MELO M A, BAI Y, et al. Novel protein-repellent dental adhesive containing 2-methacryloyloxyethyl phosphorylcholine[J]. J Dent, 2014, 42(10): 1284-1291. |
| 4 | ZHANG N, ZHANG K, WEIR M D, et al. Effects of water-aging for 6 months on the durability of a novel antimicrobial and protein-repellent dental bonding agent[J]. Int J Oral Sci, 2018, 10(2): 18. |
| 5 | 许晓虎,戴杏竹,赵望泓. 纳米防龋材料的研究进展[J]. 口腔疾病防治, 2018, 26(7): 472-476. |
| 6 | BOUTSIOUKI C, FRANKENBERGER R, LÜCKER S, et al. Inhibition of secondary caries in vitro by addition of chlorhexidine to adhesive components[J]. Dent Mater, 2019, 35(3): 422-433. |
| 7 | MACHADO A H S, GARCIA I M, MOTTA A S D, et al. Triclosan-loaded chitosan as antibacterial agent for adhesive resin[J]. J Dent, 2019, 83: 33-39. |
| 8 | FEITOSA S A, PALASUK J, KAMOCKI K, et al. Doxycycline-encapsulated nanotube-modified dentin adhesives[J]. J Dent Res, 2014, 93(12): 1270-1276. |
| 9 | DELAVIZ Y, LIU T W, DEONARAIN A R, et al. Physical properties and cytotoxicity of antimicrobial dental resin adhesives containing dimethacrylate oligomers of Ciprofloxacin and Metronidazole[J]. Dent Mater, 2019, 35(2): 229-243. |
| 10 | 陈 慧, 程 磊. 防龋粘接材料的研究进展[J]. 国际口腔医学杂志, 2017, 44(1): 92-97. |
| 11 | NABAVI S M, MARCHESE A, IZADI M, et al. Plants belonging to the genus Thymus as antibacterial agents: from farm to pharmacy[J]. Food Chem, 2015, 173: 339-347. |
| 12 | NABAVI S F, DI LORENZO A, IZADI M, et al. Antibacterial effects of cinnamon: from farm to food, cosmetic and pharmaceutical industries[J]. Nutrients, 2015, 7(9): 7729-7748. |
| 13 | COCCO A R, ROSA W L, SILVA A F, et al. A systematic review about antibacterial monomers used in dental adhesive systems: Current status and further prospects[J]. Dent Mater, 2015, 31(11): 1345-1362. |
| 14 | ESTEBAN FLOREZ F L, HIERS R D, LARSON P, et al. Antibacterial dental adhesive resins containing nitrogen-doped titanium dioxide nanoparticles[J]. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl, 2018, 93: 931-943. |
| 15 | YAN H Y, WANG S L, HAN L, et al. Chlorhexidine-encapsulated mesoporous silica-modified dentin adhesive[J]. J Dent, 2018, 78:83-90. |
| 16 | GUO X, CHENG Q, YU G, et al. The functions of hydrophobic elastic polyurethane combined with an antibacterial triclosan derivative in the dentin restoration interface[J]. J Mech Behav Biomed Mater, 2020, 102: 103471. |
| 17 | SHREAZ S, WANI W A, BEHBEHANI J M,et al. Cinnamaldehyde and its derivatives, a novel class of antifungal agents[J]. Fitoterapia, 2016, 112: 116-131. |
| 18 | 中华人民共和国国家卫生和计划生育委员会. 食品安全国家标准 食品添加剂使用标准: [S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2015. |
| 19 | HE T F, WANG L H, NIU D B, et al. Cinnamaldehyde inhibit Escherichia coli associated with membrane disruption and oxidative damage[J]. Arch Microbiol, 2019, 201(4): 451-458. |
| 20 | ELGAMILY H, SAFY R, MAKHARITA R. Influence of medicinal plant extracts on the growth of oral pathogens Streptococcus mutans and Lactobacillus acidophilus: an In-vitro study[J]. Open Access Maced J Med Sci, 2019, 7(14): 2328-2334. |
| 21 | HE T F, ZHANG Z H, ZENG X A, et al. Determination of membrane disruption and genomic DNA binding of cinnamaldehyde to Escherichia coli by use of microbiological and spectroscopic techniques[J]. J Photochem Photobiol B, 2018, 178: 623-630. |
| 22 | LIU S, HOU Y, LIU W, et al. Components of the calcium-calcineurin signaling pathway in fungal cells and their potential as antifungal targets[J]. Eukaryot Cell, 2015, 14(4): 324-334. |
| 23 | WANG S Y, CHEN P F, CHANG S T. Antifungal activities of essential oils and their constituents from indigenous cinnamon (Cinnamomum osmophloeum) leaves against wood decay fungi[J]. Bioresour Technol, 2005, 96(7): 813-818. |
| 24 | FILHO J G, VIZOTO N L, LUIZA DE AGUIAR LOESCH M, et al. Genetic and physiological effects of subinhibitory concentrations of oral antimicrobial agents on Streptococcus mutans biofilms[J]. Microb Pathog, 2021, 150: 104669. |
| 25 | SONG Y M, ZHOU H Y, WU Y, et al. In vitro evaluation of the antibacterial properties of tea tree oil on planktonic and biofilm-forming Streptococcus mutans [J]. AAPS PharmSciTech, 2020, 21(6): 227. |
| 26 | AKHLAGHI N, SADEGHI M, FAZELI F, et al. The antibacterial effects of coffee extract, chlorhexidine, and fluoride against Streptococcus mutans and Lactobacillus plantarum: an in vitro study[J]. Dent Res J (Isfahan), 2019, 16(5): 346-353. |
| 27 | MARTINS M L, LEITE K L F, PACHECO-FILHO E F, et al. Efficacy of red propolis hydro-alcoholic extract in controlling Streptococcus mutans biofilm build-up and dental enamel demineralization[J]. Arch Oral Biol, 2018, 93: 56-65. |
| 28 | LI F, CHEN J, CHAI Z, et al. Effects of a dental adhesive incorporating antibacterial monomer on the growth, adherence and membrane integrity of Streptococcus mutans[J]. J Dent,2009,37(4): 289-296. |
| 29 | GONG H, GUO X, CAO D, et al. Photopolymerizable and moisture-curable polyurethanes for dental adhesive applications to increase restoration durability[J]. J Mater Chem B, 2019, 7(5): 744-754. |
| [1] | Linlin YAN,Lin ZHU,Yuanhang ZHAO,Jiazhuo SONG,Xinying ZOU,Xin LIU,Hong ZHAO,Zhimin ZHANG,Hong ZHANG. Inhibitory effect of Streptococcus mutans by titanium dioxide nanoparticles combined with LED light irradiation and its mechanism [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2022, 48(4): 929-937. |
| [2] | ZHAO Mengming, ZHANG Xin, WANG Feifei, LI Rui, LIU Dayong, HU Meilin, JIA Zhi. Comparison of marginal closure effects among 4 kinds of resinmaterials in filling simulated Ⅴ-type cavity of permanent malars in vitro [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2020, 46(02): 389-393. |
| [3] | ZHANG Xiaomeng, WANG Huimin, YANG Yubin, ZHU Xuanyan, TIAN Zilu, ZHU Song. Preparation of light-curable polyurethane adhesive and its effect on properties of traditional acrylic resin adhesives [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2020, 46(02): 365-371. |
| [4] | WANG Shoudong, YANG Luyi, NING Lei, MU Qili, YAN Jing, ZHAO Xuejiao, YU Miao, SUN Shufen. Comparison of bond strengths of three kinds of metal bottom plate brackets before and after sandblasting and its significance [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2018, 44(05): 949-954. |
| [5] | YU Shiyang, QI Pengpeng, WANG Honghong, LI Yushan, WANG Jingyun. Effects of different surface treatment methods on bond strength of zirconia prosthesis [J]. Journal of Jilin University Medicine Edition, 2017, 43(03): 588-592. |
| [6] | MOU Yinhe, YANG Luyi, WU Yanran, TENG Rong, XIA Xiaoxue, NING Lei, WANG Shoudong. Comparison among bonding strenghs of three kinds of orthodontic adhesives under different conditions and their significances [J]. Journal of Jilin University Medicine Edition, 2016, 42(03): 512-516. |
| [7] | LIU Chao, GE Jiuyu, YIN Shuo, LI Wen, MIAO Leiying. Comparison of VAS score and morphology of teeth of elder patients with secondary dentin sensitivity following tooth abrasion before and after penetrating resin treatment [J]. Journal of Jilin University Medicine Edition, 2015, 41(05): 1008-1011. |
| [8] | SHI Rui-xin,ZHU Xian-chun,CHEN Yuan-ping,ZHOU Yan-min. Effects of different etching methods on losing ratio of bond orthodontic brackets in fluorotic teeth [J]. J4, 2011, 37(2): 319-322. |
| [9] | JIANG Hong-yu,SUI Da-yuan,YU Xiao-feng,QU Shao-chun,XU Hua-li,WANG Zhi-cai,CHEN Yan-ping. Effects of Acanthopanax senticosus saponins(ASS) on hemorrheologyand platelet function in experimental cerebral ischemia rats [J]. J4, 2004, 30(3): 384-386. |
| [10] | ZHAO Hong-mei,YU Xiao-feng,QU Shao-chun, XU Hua-li,SUI Da-yuan. Effects of SATP on platelet function and blood viscosityin experimental cerebral ischemia rats [J]. J4, 2004, 30(3): 393-395. |