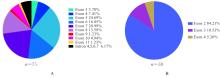
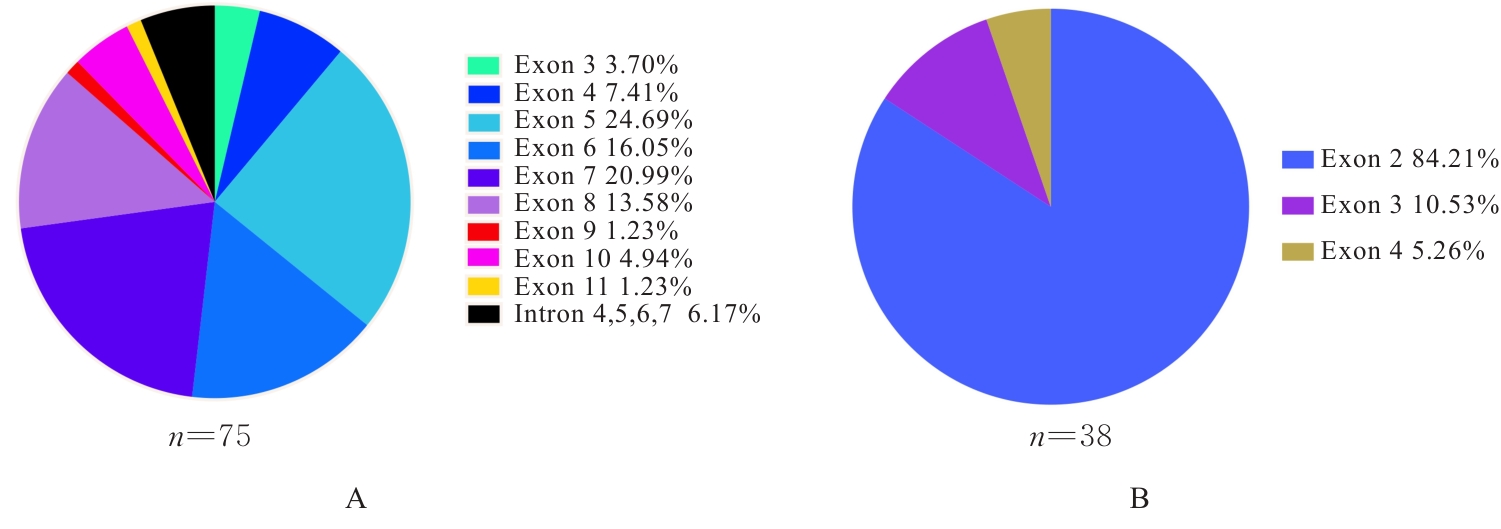
| 1 |
曹毛毛, 陈万青. GLOBOCAN 2020全球癌症统计数据解读[J/OL]. 中国医学前沿杂志(电子版), 2021, 13(3): 63-69.
|
| 2 |
SUNG H, FERLAY J, SIEGEL R L, et al. Global cancer statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries[J]. CA Cancer J Clin, 2021, 71(3): 209-249.
|
| 3 |
ZHENG R S, CHEN R, HAN B F, et al. Cancer incidence and mortality in China, 2022[J]. Zhonghua Zhong Liu Za Zhi, 2024, 46(3): 221-231.
|
| 4 |
ZHENG R S, ZHANG S W, SUN K X, et al. Cancer statistics in China, 2016[J]. Zhonghua Zhong Liu Za Zhi, 2023, 45(3): 212-220.
|
| 5 |
OLIVIER M, HOLLSTEIN M, HAINAUT P. TP53 mutations in human cancers: origins, consequences, and clinical use[J]. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol, 2010, 2(1): a001008.
|
| 6 |
陈 奇, 曾照芳. p53基因突变与消化系统恶性肿瘤的关联[J]. 激光杂志, 2012, 33(2): 79-80.
|
| 7 |
沈 琳. 二代测序技术在消化系统肿瘤临床应用的中国专家共识[J]. 肿瘤综合治疗电子杂志, 2024, 10(1): 69-92.
|
| 8 |
雷 静, 张珲娉, 韩 伟, 等. 消化道恶性肿瘤高通量基因测序的生物统计分析[J]. 现代肿瘤医学, 2021, 29(23): 4118-4121.
|
| 9 |
罗喜顺, 王海鹏, 朱袭嘉, 等. 结直肠癌KRAS基因突变阳性与P53及MCC基因的相关性研究[J/OL]. 消化肿瘤杂志(电子版), 2021, 13(2): 125-129.
|
| 10 |
季晓君, 苗 雷, 马昌友, 等. 消化系统常见肿瘤突变基因分析及新靶点成药性评估[J]. 肿瘤防治研究, 2022, 49(4): 340-346.
|
| 11 |
罗丽波, 任胜祥. KRAS和TP53共突变对肺腺癌生物学行为的影响[J]. 同济大学学报(医学版), 2024, 45(3): 345-353.
|
| 12 |
ANDO K, NAKAMURA Y, KITAO H, et al. Mutational spectrum of TP53 gene correlates with nivolumab treatment efficacy in advanced gastric cancer (TP53MUT study)[J]. Br J Cancer, 2023, 129(6): 1032-1039.
|
| 13 |
WEN X J, LU F M, LIU S. Prognostic value of p53 mutation for poor outcome of Asian primary liver cancer patients: evidence from a cohort study and meta-analysis of 988 patients[J]. Onco Targets Ther, 2016, 9: 7425-7433.
|
| 14 |
HU S S, CHEN X, XU X X, et al. STRAP as a new therapeutic target for poor prognosis of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma patients mainly caused by TP53 mutation[J]. Front Oncol, 2020, 10: 594224.
|
| 15 |
SCLAFANI F, WILSON S H, CUNNINGHAM D, et al. Analysis of KRAS, NRAS, BRAF, PIK3CA and TP53 mutations in a large prospective series of locally advanced rectal cancer patients[J]. Int J Cancer, 2020, 146(1): 94-102.
|
| 16 |
张 弛, 李炳宗. TP53基因异常多发性骨髓瘤治疗进展[J]. 中国实用内科杂志, 2024, 44(1): 80-85.
|
| 17 |
BOECKLER F M, JOERGER A C, JAGGI G, et al. Targeted rescue of a destabilized mutant of p53 by an in silico screened drug[J]. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A, 2008, 105(30): 10360-10365.
|
| 18 |
罗海荣, 郝向芳, 李锦军. TC21/R-Ras 2在肿瘤中的研究进展[J]. 肿瘤, 2008, 28(8): 723-725.
|
| 19 |
ESCOBAR-HOYOS L F, PENSON A, KANNAN R, et al. Altered RNA splicing by mutant p53 activates oncogenic RAS signaling in pancreatic cancer[J]. Cancer Cell, 2020, 38(2): 198-211.e8.
|
| 20 |
DONG L Q, LU D Y, CHEN R, et al. Proteogenomic characterization identifies clinically relevant subgroups of intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma[J]. Cancer Cell, 2022, 40(1): 70-87.e15.
|
| 21 |
MARABELLE A, FAKIH M, LOPEZ J, et al. Association of tumour mutational burden with outcomes in patients with advanced solid tumours treated with pembrolizumab: prospective biomarker analysis of the multicohort, open-label, phase 2 KEYNOTE-158 study[J]. Lancet Oncol, 2020, 21(10): 1353-1365.
|
| 22 |
向林果, 谭憬一, 姚 远, 等. 结直肠癌组织中MMR蛋白表达、MSI、RAS和BRAF基因突变与临床病理特征的关系[J]. 检验医学与临床, 2024, 21(1): 1-7.
|
 )
)