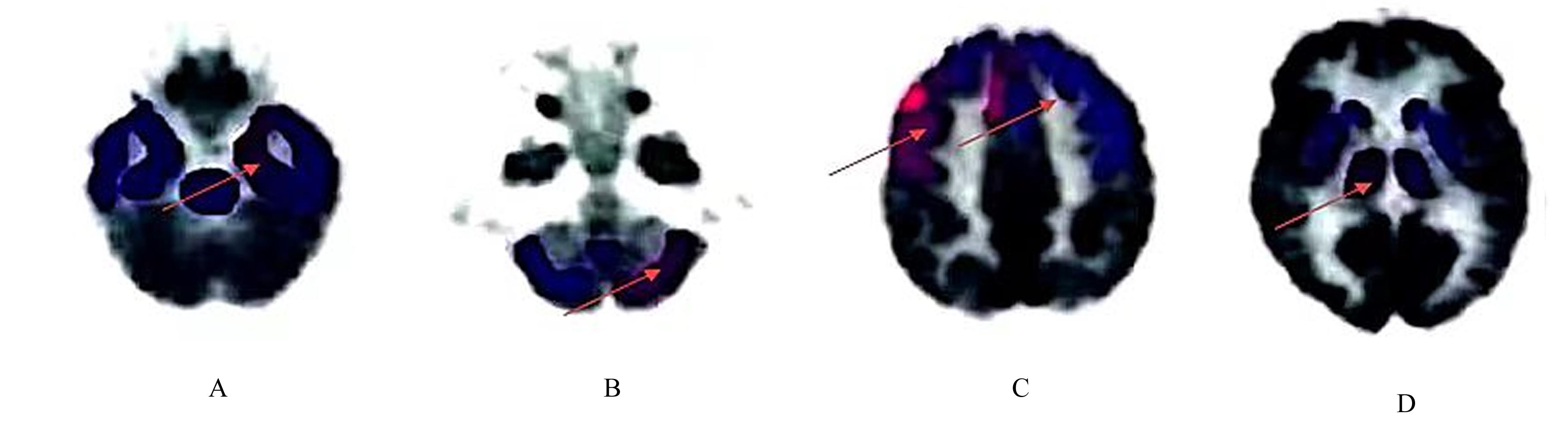
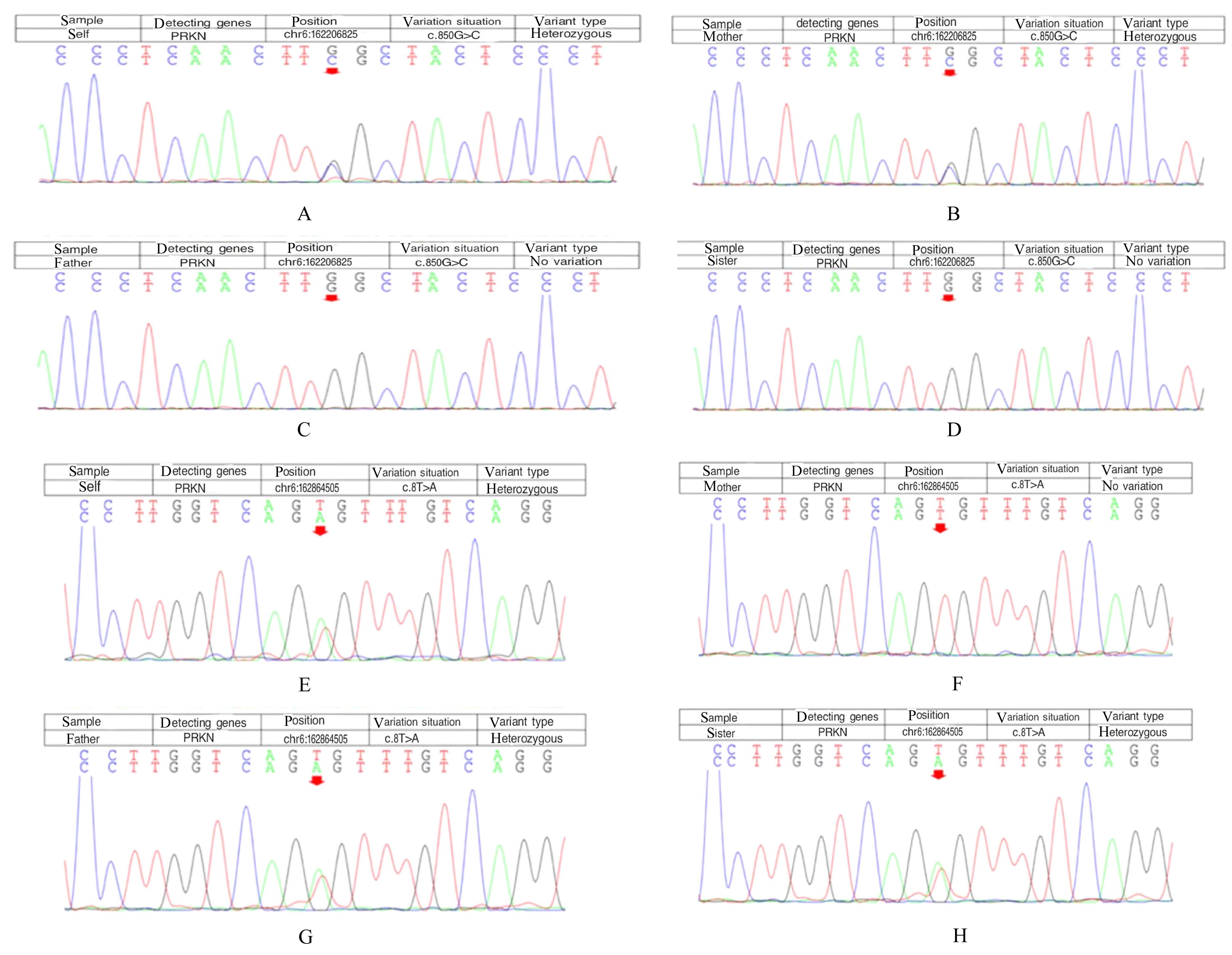
| [1] |
Xiaodong WEN,Chunling WANG,Yuanjing JIANG,Xinmei ZHOU,Yi ZHANG,Yuan WU.
Effect of fructus mume total flavone on injury of SH-SY5Y cells induced by MPP+ through regulating miR-145-3p expression and its mechanism
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2023, 49(6): 1415-1423.
|
| [2] |
Chuan LIU,Huan LI,Dawei WANG.
Effects of Dendrobium huoshanense polysaccharide on oxidative stress and inflammation in brain tissue of mice with Parkinson’s disease
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2023, 49(1): 110-115.
|
| [3] |
Lingling FAN,Shuping DING,Guomin SHEN,Zhihong HU,Aihong REN,Bo DENG.
Effect of mediodorsal thalamic nucleus lesions on electrical activity in medial prefrontal cortex of rats with Parkinson’s disease
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2022, 48(6): 1382-1388.
|
| [4] |
Qi PAN,Zizhen WANG,Fuyue YE,Wei XING,Jiahan LIN,Jianyue LU,Kun YANG.
Effect of proteasome inhibitor lactacystin on oxidative damage of dopaminergic neurons in substantia nigra of rats
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2022, 48(3): 728-733.
|
| [5] |
Xiaochen HUANG,Hao LI,Baohua WANG,Kai LI.
Protective effect of lidocaine on PC12 cells in Parkinson’s disease model and its mechanism
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2022, 48(3): 638-647.
|
| [6] |
Lingna HAN,Chunlei WANG,Yongli CHANG,Li YUAN,Xiaojing LIU.
Effect of electrical lesions of lateral habenular nucleus on spatial learning and memory functions in rats with Parkinson’s disease and its mechanism
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2021, 47(5): 1108-1115.
|
| [7] |
Xiaofeng LUO,Yao LI,Jiang HU,Chenhao ZHANG.
Regulatory effect of gardenoside on sleep disorder in rats with Parkinson’s disease and its mechanism
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2020, 46(6): 1177-1181.
|
| [8] |
ZHAO Min, JIN Xin, DI Xin, TIAN Chang, LIU Jiaying, CONG Shan, WANG Ke.
Invasive mucinous adenocarcinoma of lung: A case report and literature review
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2020, 46(03): 634-638.
|
| [9] |
WANG Chunlei, CHANG Yongli, HAN Lingna.
Improvement effects of repeated transcranial direct current stimulation on depression behaviors in rat models of Parkinson's disease and their mechanisms
[J]. Journal of Jilin University Medicine Edition, 2018, 44(04): 693-697.
|
| [10] |
YANG Dongyang, LAI Xiaorong, LI Ying, MA Liyu, LUO Gang, LI Zijun, XU Fei, MA Dong.
Influence of primary resection and KRAS gene mutation in prognosis of mild symptomatic patients with stage Ⅳ colorectal cancer
[J]. Journal of Jilin University Medicine Edition, 2017, 43(04): 805-811.
|
| [11] |
LIN Xue-jun,YAN Kang-kang,ZHAO Long-yu,BAO Hong-hong,LI Shuang,LIU Xiao-dong,LIU Xin.
Meta-analysis on association between smoking and p53
gene mutation in patients with lung cancer
[J]. Journal of Jilin University Medicine Edition, 2014, 40(05): 1046-1050.
|
| [12] |
HU Rui-ping1,CUI Jiu-wei1,LI Wei1,ZHANG Fu-ming,HAN Wei,DU Zhong-hua,HAN Xiu-li,LIU Xiao-ling,LI Hong-bing,XU Wei.
Detection of CEBPA gene mutation in patients with newly diagnosed acute myeloid leukemia and its clinical significance
[J]. Journal of Jilin University Medicine Edition, 2014, 40(02): 389-394.
|
| [13] |
LIU Li, ZHANG Zhi-Min, WANG Li-Ying, ZHENG Peng, LI Hui.
Detection of mutation of acid-resistant gene gluA in |fluoride-resistant strain of streptococcus mutans
[J]. J4, 2011, 37(1): 80-83.
|
| [14] |
Liu-Jing-Jing, LIU Yuan-Yuan, LIU Yong-Hua, WANG Feng, JIANG Yan-Fang.
Changes of HBV P gene RT region mutation model and |drug-resistant rate in patients with chronic hepatitis B treated with telbivudime for different time
[J]. J4, 2010, 36(4): 695-697.
|
| [15] |
JIA Xiao-jing, ZHANG Zhi-liang, QU Ya-qin, ZHAI Cheng-wei, YANG Tai-quan, WOLF-DIETER Rausch, GONG Shou-liang.
Establishment of cell models of dopaminergic neurons for Parkinson’s disease
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2008, 34(5): 778-781.
|
 )
)