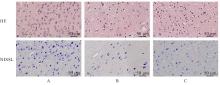
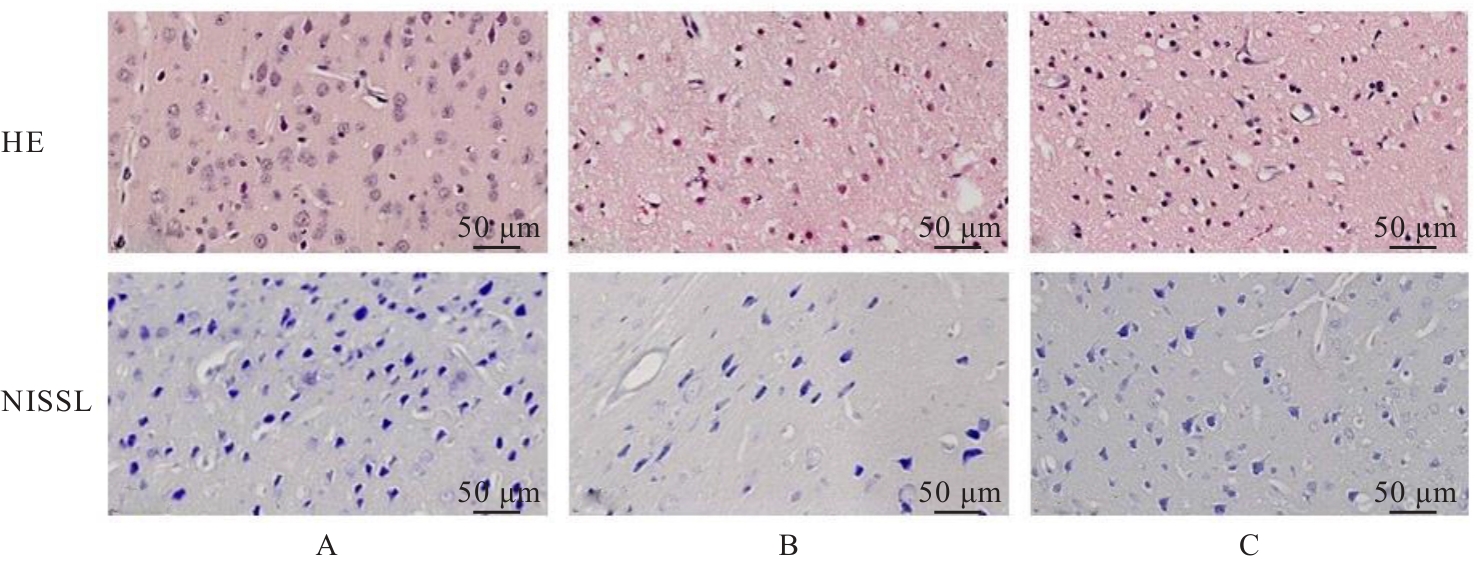
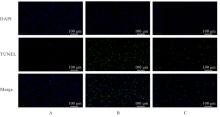
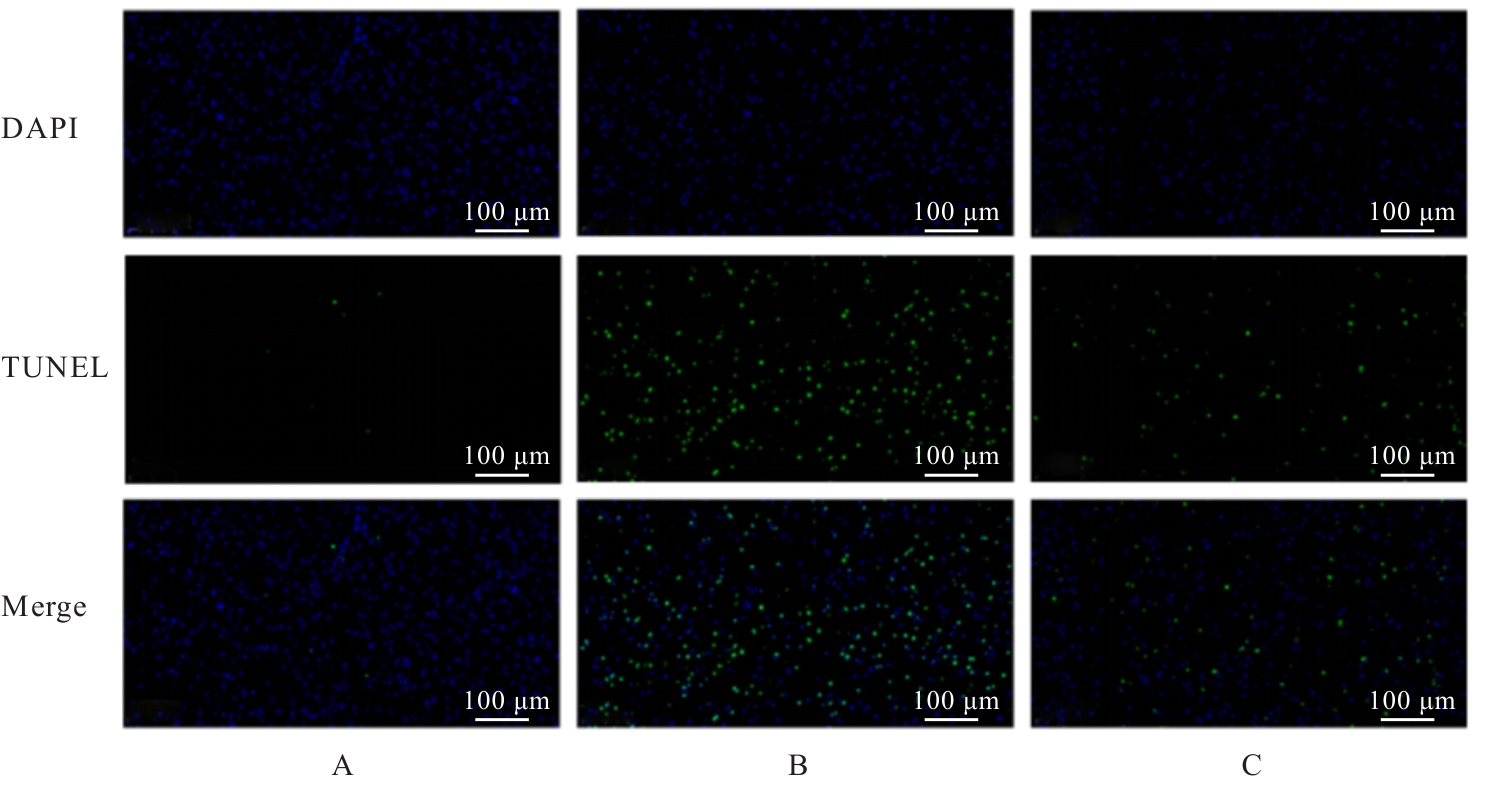
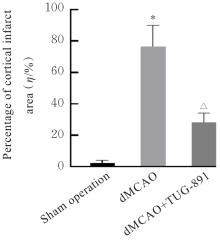
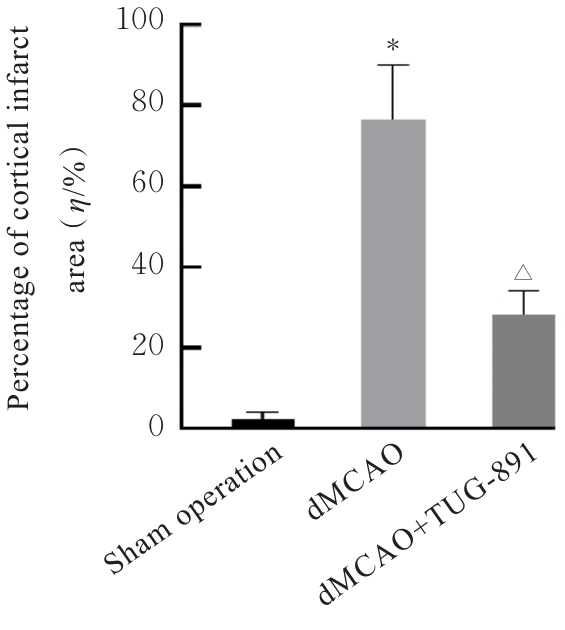
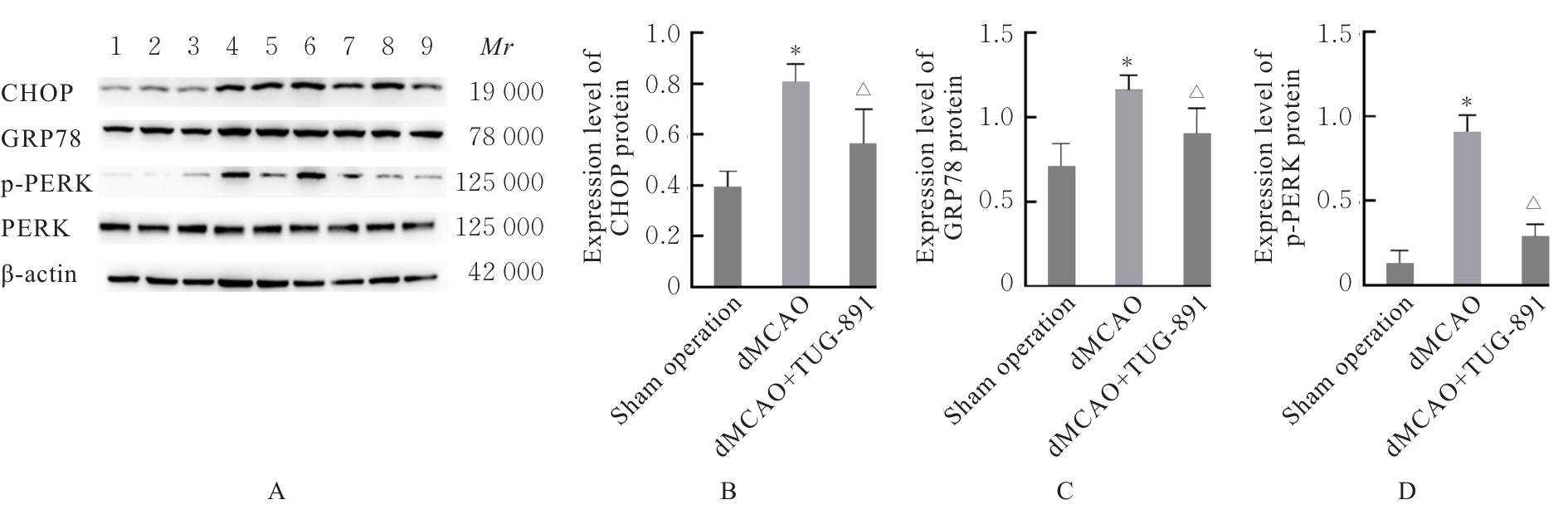
| [1] |
DATTA A, SARMAH D, MOUNICA L, et al. Cell death pathways in ischemic stroke and targeted pharmacotherapy[J]. Transl Stroke Res, 2020, 11(6): 1185-1202.
|
| [2] |
ZHANG Y, LI M, LI X M, et al. Catalytically inactive RIP1 and RIP3 deficiency protect against acute ischemic stroke by inhibiting necroptosis and neuroinflammation[J]. Cell Death Dis, 2020, 11(7): 565.
|
| [3] |
HAFEZ S, HODA M N, GUO X Y, et al. Comparative analysis of different methods of ischemia/reperfusion in hyperglycemic stroke outcomes: interaction with tPA[J]. Transl Stroke Res, 2015, 6(3): 171-180.
|
| [4] |
NAKAJIMA S, DEMERS G, MACHUCA-PARRA A I, et al. Central activation of the fatty acid sensor GPR120 suppresses microglia reactivity and alleviates sickness- and anxiety-like behaviors[J]. J Neuroinflammation, 2023, 20(1): 302.
|
| [5] |
ZHAO Y F, WANG L, QIU J H, et al. Linoleic acid stimulates [Ca2+] i increase in rat pancreatic beta-cells through both membrane receptor- and intracellular metabolite-mediated pathways[J]. PLoS One, 2013, 8(4): e60255.
|
| [6] |
ZHAO Y F, PEI J M, CHEN C. Activation of ATP-sensitive potassium channels in rat pancreatic beta-cells by linoleic acid through both intracellular metabolites and membrane receptor signalling pathway[J]. J Endocrinol, 2008, 198(3): 533-540.
|
| [7] |
KITAJIMA S, SAKAMOTO K, KURODA M. Effects of TUG-891, a potent GPR120 agonist, on the physical and oral lipid- coating properties, and secretion of saliva[J]. Physiol Behav, 2023, 265: 114160.
|
| [8] |
MILLIGAN G, ALVAREZ-CURTO E, HUDSON B D, et al. FFA4/GPR120: pharmacology and therapeutic opportunities[J]. Trends Pharmacol Sci, 2017, 38(9): 809-821.
|
| [9] |
ZHAO Y F, LI X C, LIANG X Y, et al. GPR120 regulates pancreatic polypeptide secretion from male mouse islets via PLC-mediated calcium mobilization[J]. Endocrinology, 2020, 161(10): bqaa157.
|
| [10] |
MONIRI N H. Free-fatty acid receptor-4 (GPR120): cellular and molecular function and its role in metabolic disorders[J]. Biochem Pharmacol, 2016, 110/111: 1-15.
|
| [11] |
WANG H X, LIU C, LI Y Y, et al. TUG-891 inhibits neuronal endoplasmic reticulum stress and pyroptosis activation and protects neurons in a mouse model of intraventricular hemorrhage[J]. Neural Regen Res, 2023, 18(10): 2278-2284.
|
| [12] |
HUANG Z, GUO F, XIA Z J, et al. Activation of GPR120 by TUG891 ameliorated cisplatin-induced acute kidney injury via repressing ER stress and apoptosis[J]. Biomed Pharmacother, 2020, 126: 110056.
|
| [13] |
PRESCOTT K, COTHREN T O, HOLSTEN J T, et al. Increased sensitivity in detection of deficits following two commonly used animal models of stroke[J]. Behav Brain Res, 2024, 467: 114991.
|
| [14] |
YANG P X, FAN X X, LIU M X, et al. Longxuetongluo Capsule alleviate ischemia/reperfusion induced cardiomyocyte apoptosis through modulating oxidative stress and mitochondrial dysfunction[J]. Phytomedicine, 2024, 134: 155993.
|
| [15] |
DONG X L, LI C P, YAO Y Y, et al. Xingnaojing injection alleviates cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury through regulating endoplasmic reticulum stress in Vivo and in Vitro [J]. Heliyon, 2024, 10(3): e25267.
|
| [16] |
ZHAO H, HAN Z, JI X, et al. Epigenetic regulation of oxidative stress in ischemic stroke[J]. Aging Dis, 2016, 7(3): 295-306.
|
| [17] |
YUAN Y J, GUO Q L, YE Z, et al. Ischemic postconditioning protects brain from ischemia/reperfusion injury by attenuating endoplasmic reticulum stress-induced apoptosis through PI3K-Akt pathway[J]. Brain Res, 2011, 1367: 85-93.
|
| [18] |
HAUPT M, ZECHMEISTER B, BOSCHE B, et al. Lithium enhances post-stroke blood-brain barrier integrity, activates the MAPK/ERK1/2 pathway and alters immune cell migration in mice[J]. Neuropharmacology, 2020, 181: 108357.
|
| [19] |
WANG Y, JASPER H, TOAN S, et al. Mitophagy coordinates the mitochondrial unfolded protein response to attenuate inflammation-mediated myocardial injury[J]. Redox Biol, 2021, 45: 102049.
|
| [20] |
FENG D Y, WANG B, WANG L, et al. Pre-ischemia melatonin treatment alleviated acute neuronal injury after ischemic stroke by inhibiting endoplasmic reticulum stress-dependent autophagy via PERK and IRE1 signalings[J]. J Pineal Res, 2017, 62(3). DOI: 10.1111/jpi.12395 .
doi: 10.1111/jpi.12395
|
| [21] |
LIU D S, GU Y T, WANG W T, et al. Astragalin alleviates ischemia/reperfusion-induced brain injury via suppression of endoplasmic reticulum stress[J]. Mol Med Rep, 2020, 22(5): 4070-4078.
|
| [22] |
LI Y Y, ZHANG Y J, FU H D, et al. Hes1 knockdown exacerbates ischemic stroke following tMCAO by increasing ER stress-dependent apoptosis via the PERK/eIF2α/ATF4/CHOP signaling pathway[J]. Neurosci Bull, 2020, 36(2): 134-142.
|
| [23] |
OIDA Y, SHIMAZAWA M, IMAIZUMI K, et al. Involvement of endoplasmic reticulum stress in the neuronal death induced by transient forebrain ischemia in gerbil[J]. Neuroscience, 2008, 151(1): 111-119.
|
 ),Lili WEI(
),Lili WEI( )
)