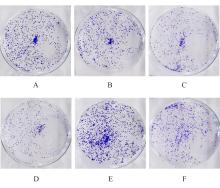
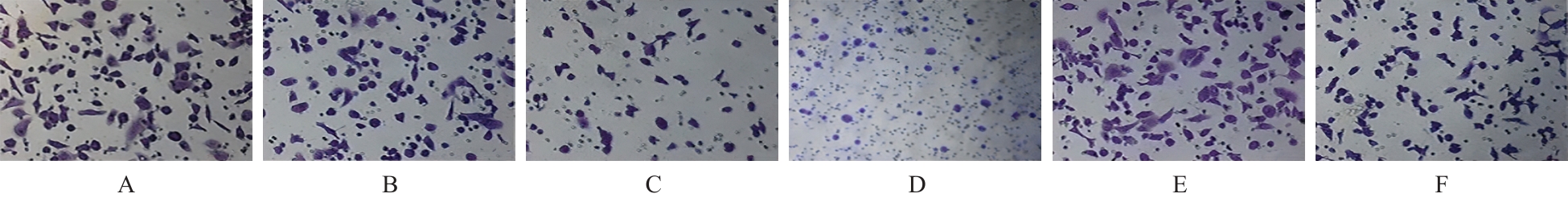
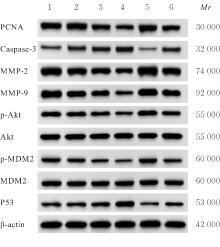
| [1] |
Siqi LI,Guangdao CHEN,Qiyi ZENG.
Improvement effect of chrysophanol on hydrogen peroxide-induced apoptosis of EA. hy926 cells and its mechanism
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2024, 50(6): 1512-1518.
|
| [2] |
Jingshun ZHANG,Yinggang ZOU,Lianwen ZHENG.
Effect of over-expression SLC7A5 on apoptosis of ovarian granulosa cells in rats and its mechanism
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2024, 50(6): 1526-1534.
|
| [3] |
Gao SUN,Jing HE,Qi ZHAO,Jianhong SHI,Zhiling LIAO,Yuanye TIAN,Guomin WU.
Therapeutic effect of resveratrol on osteoarthritis of temporomandibular joint and its mechanism
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2024, 50(6): 1547-1556.
|
| [4] |
Xuan MA,Kaixiang YANG,Hai DENG,Yucheng HUANG.
Effect of parthenolide on apoptosis of chondrocyte under mechanical stretch stress by inhibiting Piezo1 expression and its mechanism
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2024, 50(6): 1621-1631.
|
| [5] |
Bin ZHAO,Jinye YANG,Zhiyao LI,Chengwei BI,Libo YANG,Zhiyu SHI,Xin LI,Jianpeng ZHANG,Yuanlong SHI,Yong YANG,Guoying ZHANG.
Inhibitory effect of miR-30c-5p on proliferation, migration, and invasion of prostate cancer cells and its mechanism
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2024, 50(6): 1632-1643.
|
| [6] |
Yuxiao SHI,Meilan LIU,Meilin ZHU,Feng WEI.
Effects of 5-Aza-CdR on autophagy and apoptosis of papillary thyroid cancer cells in subcutaneous xenograft tumor tissue of nude mice and its mechanism
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2024, 50(5): 1330-1338.
|
| [7] |
Hua CHEN,Na SHA,Ning LIU,Yang LI,Haijun HU.
Effect of human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells on biological behavior of human liposarcoma SW872 cells through YAP
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2024, 50(4): 1000-1008.
|
| [8] |
Yongjing YANG,Tianyang KE,Shixin LIU,Xue WANG,Dequan XU,Tingting LIU,Ling ZHAO.
Synergistic sensitization of apatinib mesylate and radiotherapy on hepatocarcinoma cells invitro
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2024, 50(4): 1009-1015.
|
| [9] |
Chaojie GUO,Jiajia ZHANG,Jie ZENG,Huiyu WANG, AIERFATI·Aimaier,Jiang XU.
Expressions of PLOD1 in oral squamous cell carcinoma tissue and cells and their significances
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2024, 50(4): 1035-1043.
|
| [10] |
Guoxing YU,Xin ZHANG,Hengwei DU,Bingjie CUI,Na GAO,Cuilan LIU,Jing DU.
Effect of urolithin C on proliferation, apoptosis and autophagy of human acute myeloid leukemia HL-60 cells and its mechanism
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2024, 50(4): 908-916.
|
| [11] |
Chao LIANG,Juanjuan DAI,Ning ZHOU,Dandan WANG,Jie ZHAO,Di AN,Yan WU.
Effect of oridonin on cell proliferation, migration, and apoptosis of human nasopharynx carcinoma HONE-1 cells
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2024, 50(4): 917-924.
|
| [12] |
Shan CAO,Yijia ZHANG,Yang BAI,Fang CHEN,Sha XIE,Qianqian HAN.
Network pharmacological analysis and in vitro experimental verification based on anti-atherosclerosis mechanism of Xiaoban Tongmai Formula
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2024, 50(4): 925-938.
|
| [13] |
Xueting CHI,Fangyuan CHEN,Zifeng PI,Guangfu LYU,Yuchen WANG,Yinqing LI,Xiaowei HUANG,Zhe LIN.
Improvement effect of velvet antler polypeptide on postmenopausal osteoporosis in rats and its mechanism
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2024, 50(4): 963-969.
|
| [14] |
Tengfei WANG, Feng CHEN, Ling QI, Ting LEI, Meihui SONG.
Inhibitory effect of D-limonene on proliferation of glioblastoma cells and its mechanism
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2024, 50(3): 647-657.
|
| [15] |
Jiacai FU,Lingsha QING,Lu YANG,Meihui SONG,Xianying ZHANG,Xiaocui LIU,Fengjin LI,Ling QI.
Inhibitory effect of Schisandrin B on proliferation of pancreatic cancer Pan02 cells and its mechanism
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2024, 50(3): 638-646.
|
 )
)