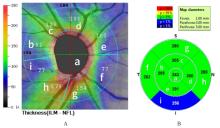
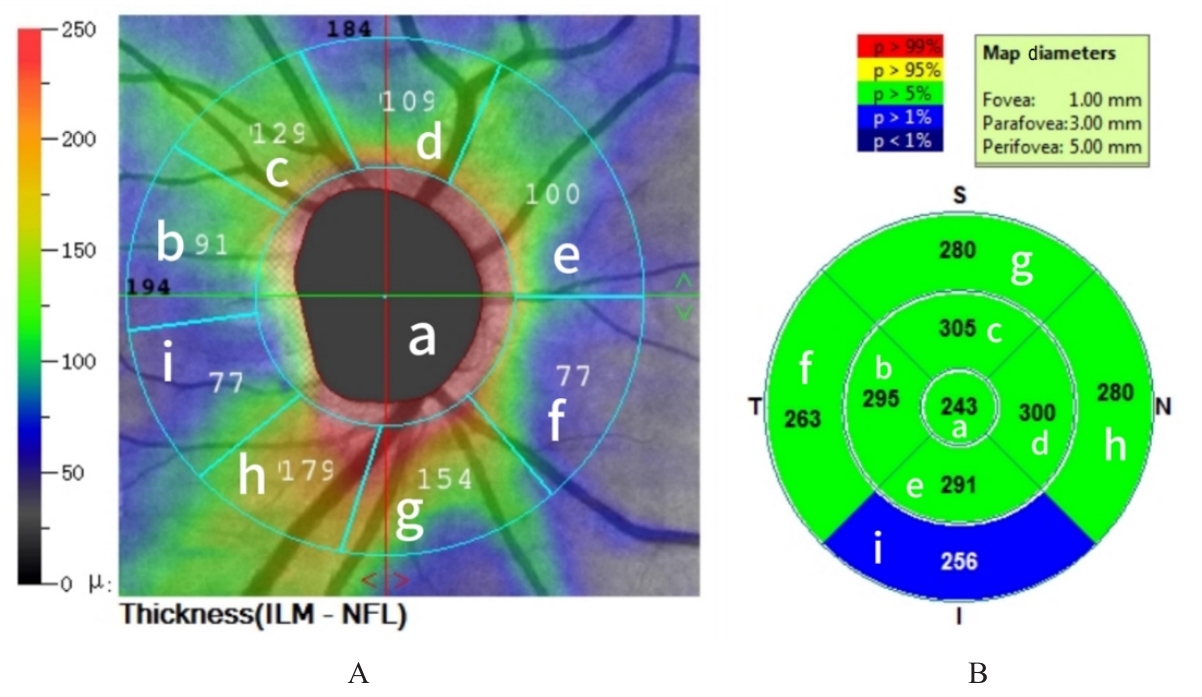
| [1] |
杨冬梅, 梁 刚, 李 俊, 等. 高度近视巩膜病理改变特征及相关调控分子[J]. 眼科新进展, 2025, 45(1): 55-59.
|
| [2] |
曾俊鸿. 高度近视合并青光眼的诊断研究进展[J]. 中文科技期刊数据库(全文版)医药卫生, 2024(6): 16-19.
|
| [3] |
时雪静, 郑天烁, 王 强. 高度近视并发症眼底病变的研究进展[J]. 眼科新进展, 2024, 44(5): 415-420.
|
| [4] |
龙丹宁, 莫 亚, 何 希, 等. 高度近视与脉络膜微循环相关研究进展[J]. 中国中医眼科杂志, 2023, 33(4): 374-378.
|
| [5] |
TSENG G L, CHEN C Y. Evaluation of high myopia complications prevention program in university freshmen[J]. Medicine, 2016, 95(40): e5093.
|
| [6] |
LI J, DAN Y S, CHUA S Q, et al. Pathologic myopia in highly myopic patients with high axial anisomyopia[J]. Br J Ophthalmol, 2024, 108(3): 411-416.
|
| [7] |
XU Q Z, ZHANG W W, ZHU H J, et al. FOVEAL AVASCULAR ZONE VOLUME: a new index based on optical coherence tomography angiography images[J]. Retina, 2021, 41(3): 595-601.
|
| [8] |
SUNG M S, LEE T H, HEO H, et al. Association between optic nerve head deformation and retinal microvasculature in high myopia[J]. Am J Ophthalmol, 2018, 188: 81-90.
|
| [9] |
HE J N, CHEN Q Y, YIN Y, et al. Association between retinal microvasculature and optic disc alterations in high myopia[J]. Eye, 2019, 33(9): 1494-1503.
|
| [10] |
PIAO H L, GUO Y, ZHANG H W, et al. Acircularity and circularity indexes of the foveal avascular zone in high myopia[J]. Sci Rep, 2021, 11(1): 16808.
|
| [11] |
CHENG D, CHEN Q, WU Y F, et al. Deep perifoveal vessel density as an indicator of capillary loss in high myopia[J]. Eye, 2019, 33(12): 1961-1968.
|
| [12] |
YU J, JIANG C H, WANG X L, et al. Macular perfusion in healthy Chinese: an optical coherence tomography angiogram study[J]. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci, 2015, 56(5): 3212-3217.
|
| [13] |
TAN C S, LIM L W, CHOW V S, et al. Optical coherence tomography angiography evaluation of the parafoveal vasculature and its relationship with ocular factors[J]. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci, 2016, 57(9): OCT224-OCT234.
|
| [14] |
郭春玲, 王丽曌, 郑 丹, 等. 非病理性高度近视青少年患者患眼黄斑区浅层视网膜血流密度特征研究[J]. 临床军医杂志, 2024, 52(12): 1262-1264, 1268.
|
| [15] |
张逸非, 都婉红, 赵梅生, 等. OCTA检测高度近视患者视网膜脉络膜厚度及血流变化的研究进展[J]. 国际眼科杂志, 2023, 23(4): 597-601.
|
| [16] |
FAN H, CHEN H Y, MA H J, et al. Reduced macular vascular density in myopic eyes[J]. Chin Med J, 2017, 130(4): 445-451.
|
| [17] |
AL-SHEIKH M, PHASUKKIJWATANA N, DOLZ-MARCO R, et al. Quantitative OCT angiography of the retinal microvasculature and the choriocapillaris in myopic eyes[J]. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci, 2017, 58(4): 2063-2069.
|
| [18] |
朱紫怡, 杨叶蓁, 张 凤, 等. 视网膜静脉阻塞合并黄斑灌注状态不良与视力的相关性[J]. 中南大学学报(医学版), 2024, 49(6): 943-950.
|
| [19] |
邵伊润, 毛剑波, 沈丽君, 等. 高度近视继发脉络膜新生血管和单纯高度近视患眼以及正常眼黄斑区血流参数对比观察[J]. 中华眼底病杂志, 2019, 35(5): 446-450.
|
| [20] |
冯立淼, 杨 叶, 胡 亮, 等. 应用光学相干断层扫描血管成像技术分析近视眼黄斑区微血管变化[J]. 温州医科大学学报, 2017, 47(6): 391-396.
|
| [21] |
LI M, YANG Y, JIANG H, et al. Retinal microvascular network and microcirculation assessments in high myopia[J]. Am J Ophthalmol, 2017, 174: 56-67.
|
| [22] |
ZHAO Z N, ZHOU X T, JIANG C H, et al. Effects of myopia on different areas and layers of the macula: a Fourier-domain optical coherence tomography study of a Chinese cohort[J]. BMC Ophthalmol, 2015, 15: 90.
|
| [23] |
JONAS R A, YAN Y N, ZHANG Q, et al. Elongation of the disc-fovea distance and retinal vessel straightening in high myopia in a 10-year follow-up of the Beijing eye study[J]. Sci Rep, 2021, 11(1): 9006.
|
| [24] |
ŽIVKOVIĆ M L J, LAZIĆ L, ZLATANOVIC M, et al. The influence of myopia on the foveal avascular zone and density of blood vessels of the macula: an OCTA study[J]. Medicina, 2023, 59(3): 452.
|
| [25] |
SUI J Y, LI H R, BAI Y, et al. Morphological characteristics of the foveal avascular zone in pathological myopia and its relationship with macular structure and microcirculation[J]. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol, 2024, 262(7): 2121-2133.
|
| [26] |
LIU Y L, WANG L J, XU Y Y, et al. The influence of the choroid on the onset and development of myopia: from perspectives of choroidal thickness and blood flow[J]. Acta Ophthalmol, 2021, 99(7): 730-738.
|
| [27] |
QI J, LI H, DU Y, et al. Circulating autoantibody profiling identifies LIMS1 as a potential target for pathogenic autoimmunity in pathologic myopia[J]. Mol Cell Proteomics, 2024, 23(6): 100783.
|
| [28] |
刘晓静, 吴峥峥, 邓铂林. 高度近视患者眼底改变的研究进展: 基于OCTA观察[J]. 眼科新进展, 2022, 42(2): 164-168.
|
 ),Weiwei ZHANG(
),Weiwei ZHANG( )
)