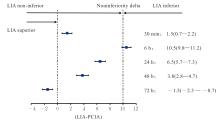
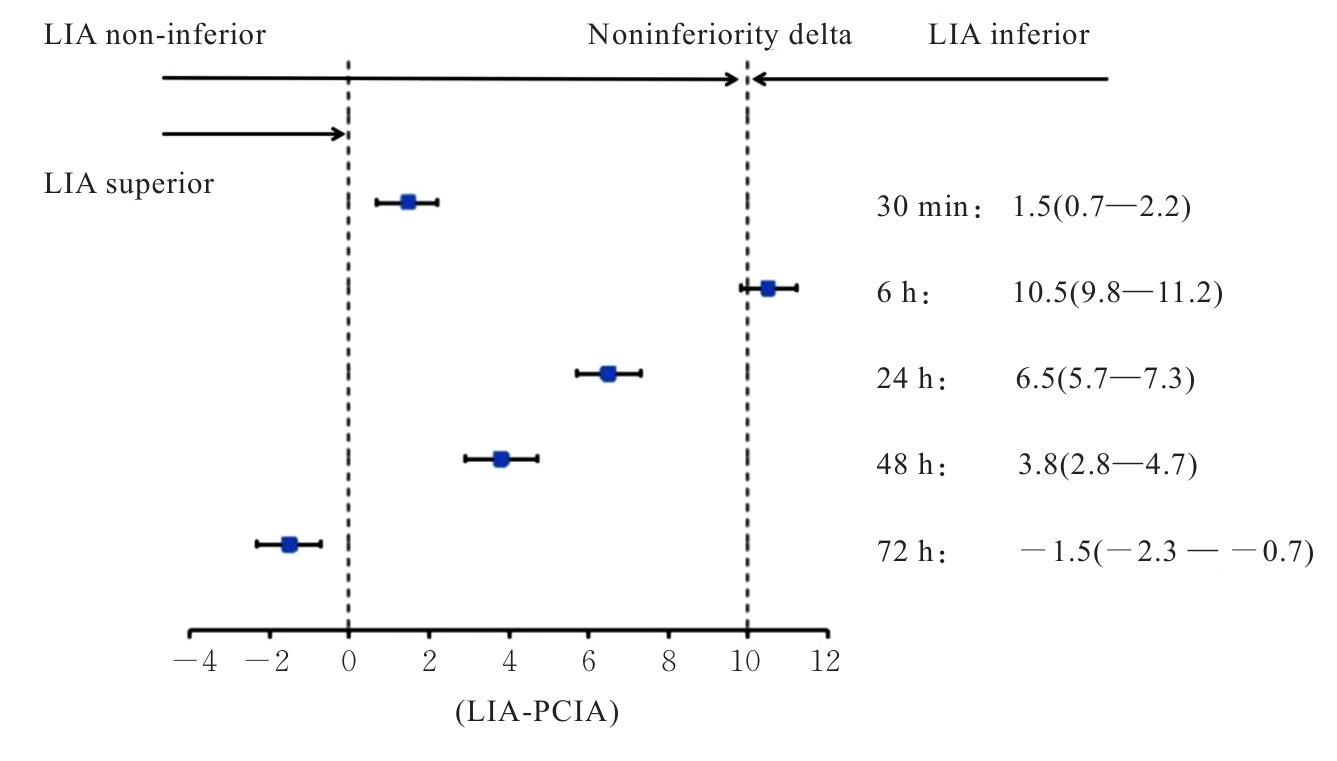
| [1] |
OHBA T, EBATA S, HARO H. Comparison of serum markers for muscle damage, surgical blood loss, postoperative recovery, and surgical site pain after extreme lateral interbody fusion with percutaneous pedicle screws or traditional open posterior lumbar interbody fusion[J]. BMC Musculoskelet Disord, 2017, 18(1): 415.
|
| [2] |
CHAHAR P, CUMMINGS K C 3rd. Liposomal bupivacaine: a review of a new bupivacaine formulation[J]. J Pain Res, 2012, 5: 257-264.
|
| [3] |
KIM J, BURKE S M, KRYZANSKI J T, et al. The role of liposomal bupivacaine in reduction of postoperative pain after transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion: a clinical study[J]. World Neurosurg, 2016, 91: 460-467.
|
| [4] |
ROH M S, KUCHER O A, SHICK K M, et al. Intramuscular liposomal bupivacaine decreases length of stay and opioid usage following lumbar spinal fusion[J]. Clin Spine Surg, 2020, 33(8): E359-E363.
|
| [5] |
MYLES P S, MYLES D B, GALAGHER W, et al. Measuring acute postoperative pain using the visual analog scale: the minimal clinically important difference and patient acceptable symptom state[J]. Br J Anaesth, 2017, 118(3): 424-429.
|
| [6] |
DEVIN C J, MCGIRT M J. Best evidence in multimodal pain management in spine surgery and means of assessing postoperative pain and functional outcomes[J]. J Clin Neurosci, 2015, 22(6): 930-938.
|
| [7] |
CHEN R, SUN S J, LI Y F, et al. Efficacy and safety evaluation of dexmedetomidine for postoperative patient controlled intravenous analgesia: a systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. Front Pharmacol, 2022, 13: 1028704.
|
| [8] |
TSAOUSI G G, POURZITAKI C, ALOISIO S, et al. Dexmedetomidine as a sedative and analgesic adjuvant in spine surgery: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials[J]. Eur J Clin Pharmacol, 2018, 74(11): 1377-1389.
|
| [9] |
付梦雨, 任周奎, 王建刚, 等. 脊柱后路手术术后镇痛的研究进展[J]. 医学综述, 2022, 28(6): 1156-1162.
|
| [10] |
NGUYEN T H, ITURRIAGA C, VERMA R. Efficacy of liposomal bupivacaine in spine surgery: a systematic review[J]. Spine J, 2021, 21(9): 1450-1459.
|
| [11] |
YU M Z, YUAN W M, XIA Z Y, et al. Characterization of exparel bupivacaine multivesicular liposomes[J]. Int J Pharm, 2023, 639: 122952.
|
| [12] |
GOLF M, DANIELS S E, ONEL E. A phase 3, randomized, placebo-controlled trial of DepoFoam® bupivacaine (extended-release bupivacaine local analgesic) in bunionectomy[J]. Adv Ther, 2011, 28(9): 776-788.
|
| [13] |
HU D, ONEL E, SINGLA N, et al. Pharmacokinetic profile of liposome bupivacaine injection following a single administration at the surgical site[J]. Clin Drug Investig, 2013, 33(2): 109-115.
|
| [14] |
GADSDEN J, LONG W J. Time to analgesia onset and pharmacokinetics after separate and combined administration of liposome bupivacaine and bupivacaine HCl: considerations for clinicians[J]. Open Orthop J, 2016, 10: 94-104.
|
| [15] |
BECKER D E, REED K L. Local anesthetics: review of pharmacological considerations[J]. Anesth Prog, 2012, 59(2): 90-101;quiz102-3.
|
| [16] |
郝定均, 孙宏慧, 张永远. 脊柱内固定术后手术部位感染预防中国专家共识[J]. 实用骨科杂志, 2024, 30(2): 97-103.
|
| [17] |
ON'GELE M O, WEINTRAUB S, QI V, et al. Local anesthetics, local anesthetic systemic toxicity (LAST), and liposomal bupivacaine[J]. Clin Sports Med, 2022, 41(2): 303-315.
|
| [18] |
HAMILTON T W, ATHANASSOGLOU V, MELLON S, et al. Liposomal bupivacaine infiltration at the surgical site for the management of postoperative pain[J]. Cochrane Database Syst Rev, 2017, 2(2): CD011419.
|
| [19] |
CHEUNG B M, NG P Y, LIU Y, et al. Pharmacokinetics and safety of liposomal bupivacaine after local infiltration in healthy Chinese adults: a phase 1 study[J]. BMC Anesthesiol, 2021, 21(1): 197.
|
| [20] |
RICE D, HEIL J W, BIERNAT L. Pharmacokinetic profile and tolerability of liposomal bupivacaine following a repeated dose via local subcutaneous infiltration in healthy volunteers[J]. Clin Drug Investig, 2017, 37(3): 249-257.
|
 )
)