吉林大学学报(工学版) ›› 2020, Vol. 50 ›› Issue (2): 445-453.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb20190231
• 车辆工程·机械工程 • 上一篇
基于双向长短期记忆模型的起重机智能操控方法
- 吉林大学 机械与航空航天工程学院,长春 130022
Intelligent manipulation method of crane based on BiLSTM model
Tao NI( ),Hai-qiang LIU,Lin-lin WANG,Shao-yuan ZOU,Hong-yan ZHANG,Ling-tao HUANG(
),Hai-qiang LIU,Lin-lin WANG,Shao-yuan ZOU,Hong-yan ZHANG,Ling-tao HUANG( )
)
- School of Mechanical and Aerospace Engineering, Jilin University, Changchun 130022, China
摘要:
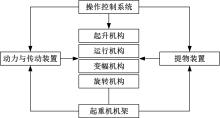
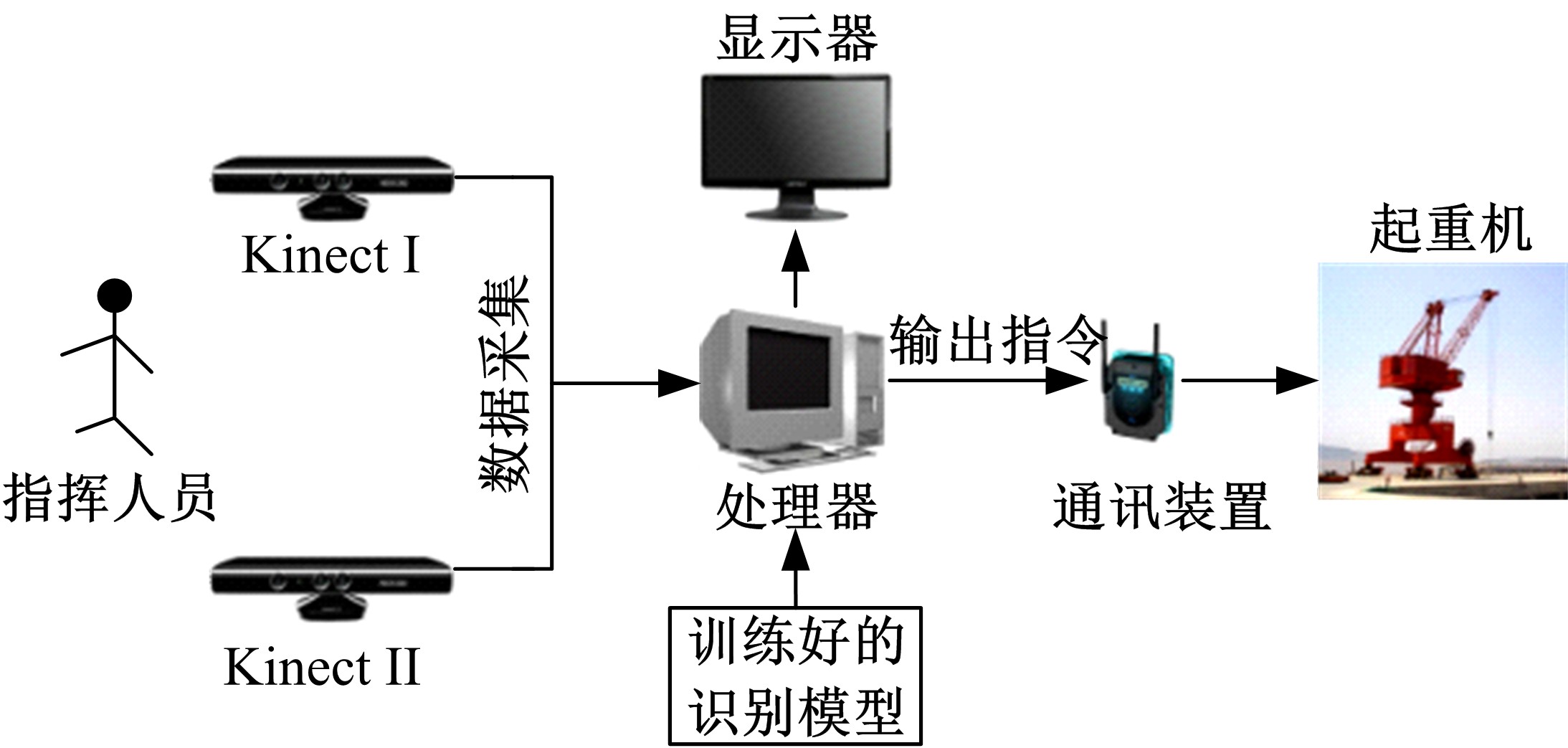
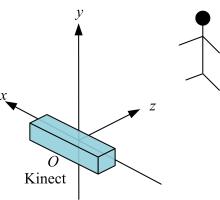
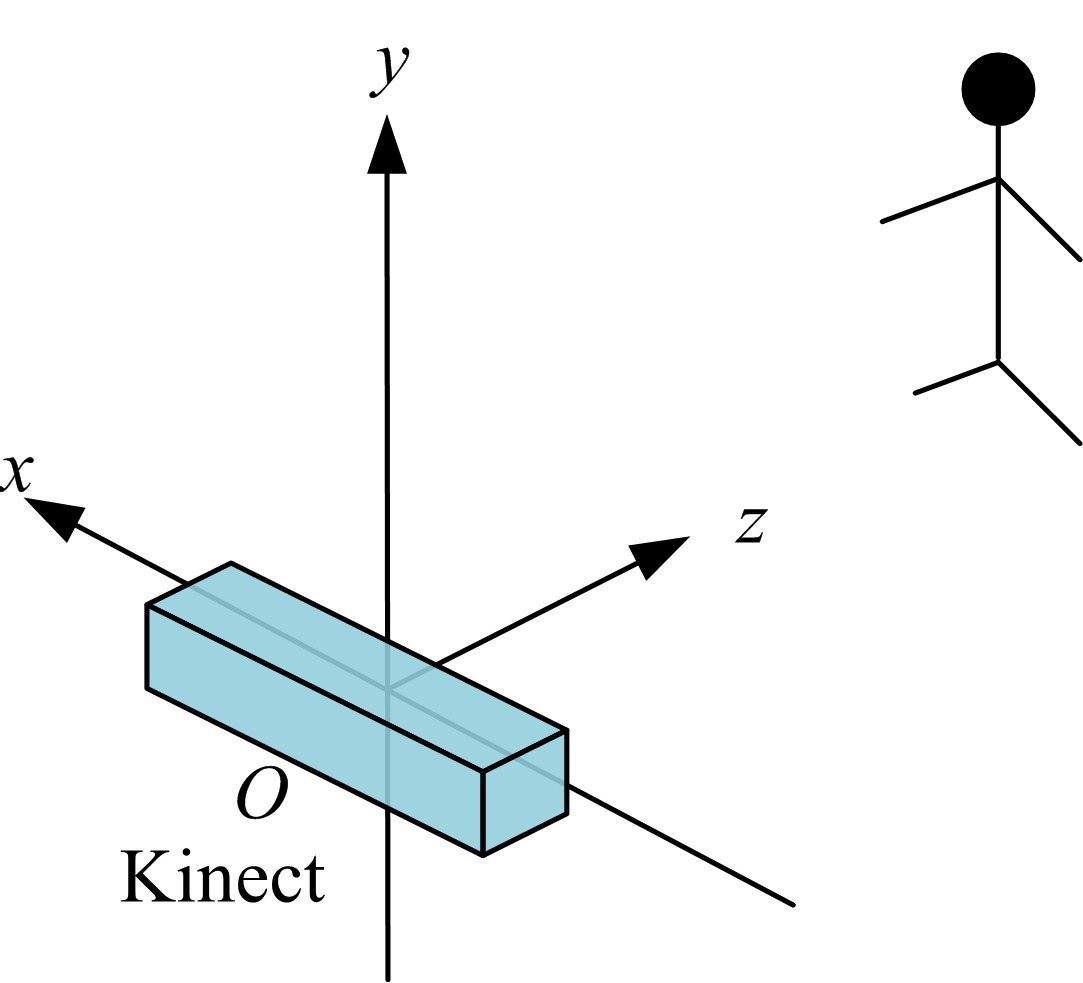
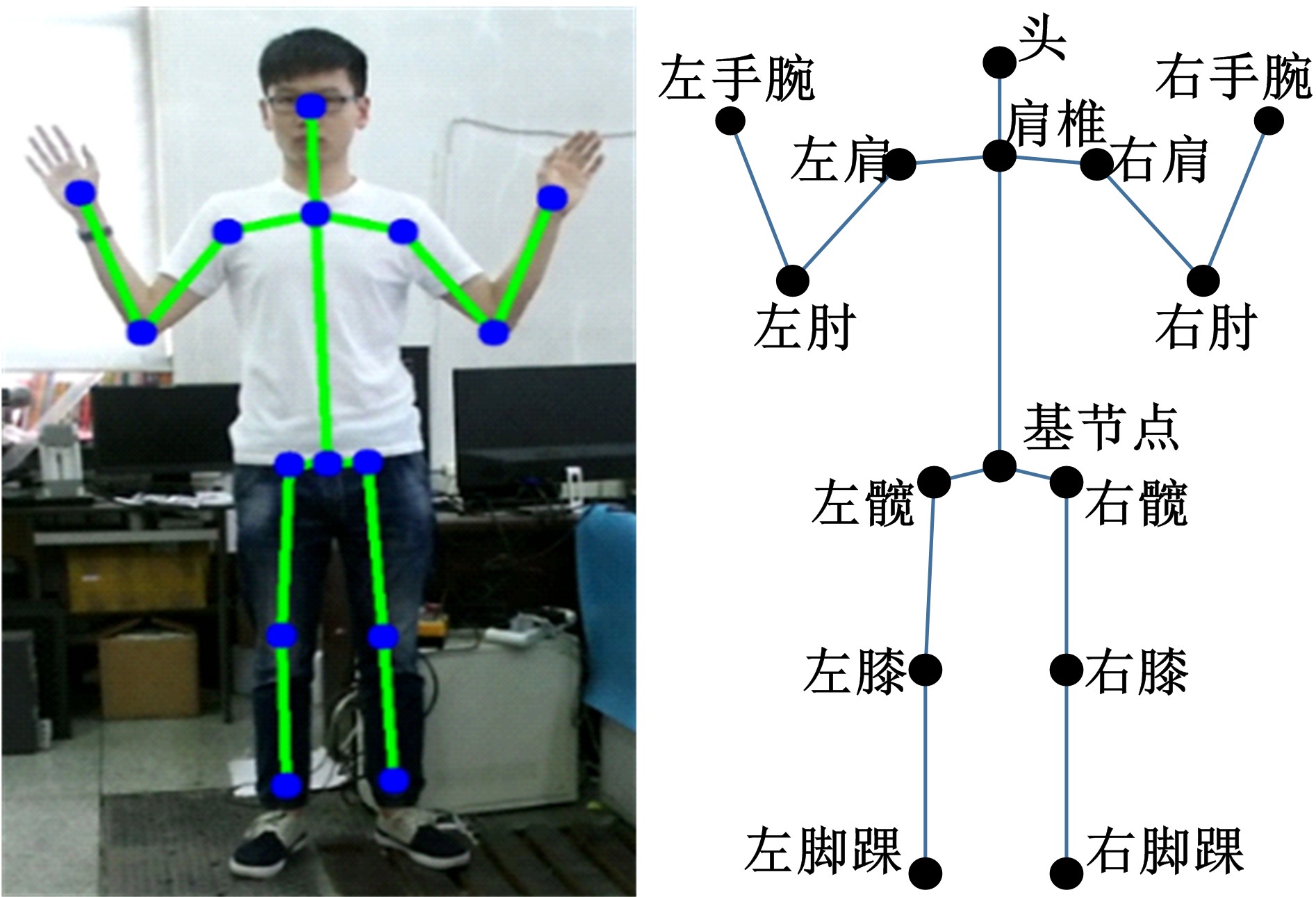
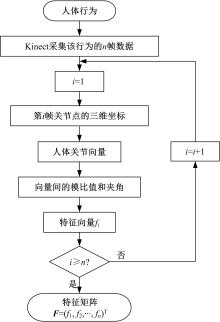
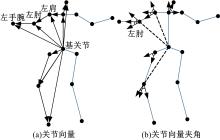
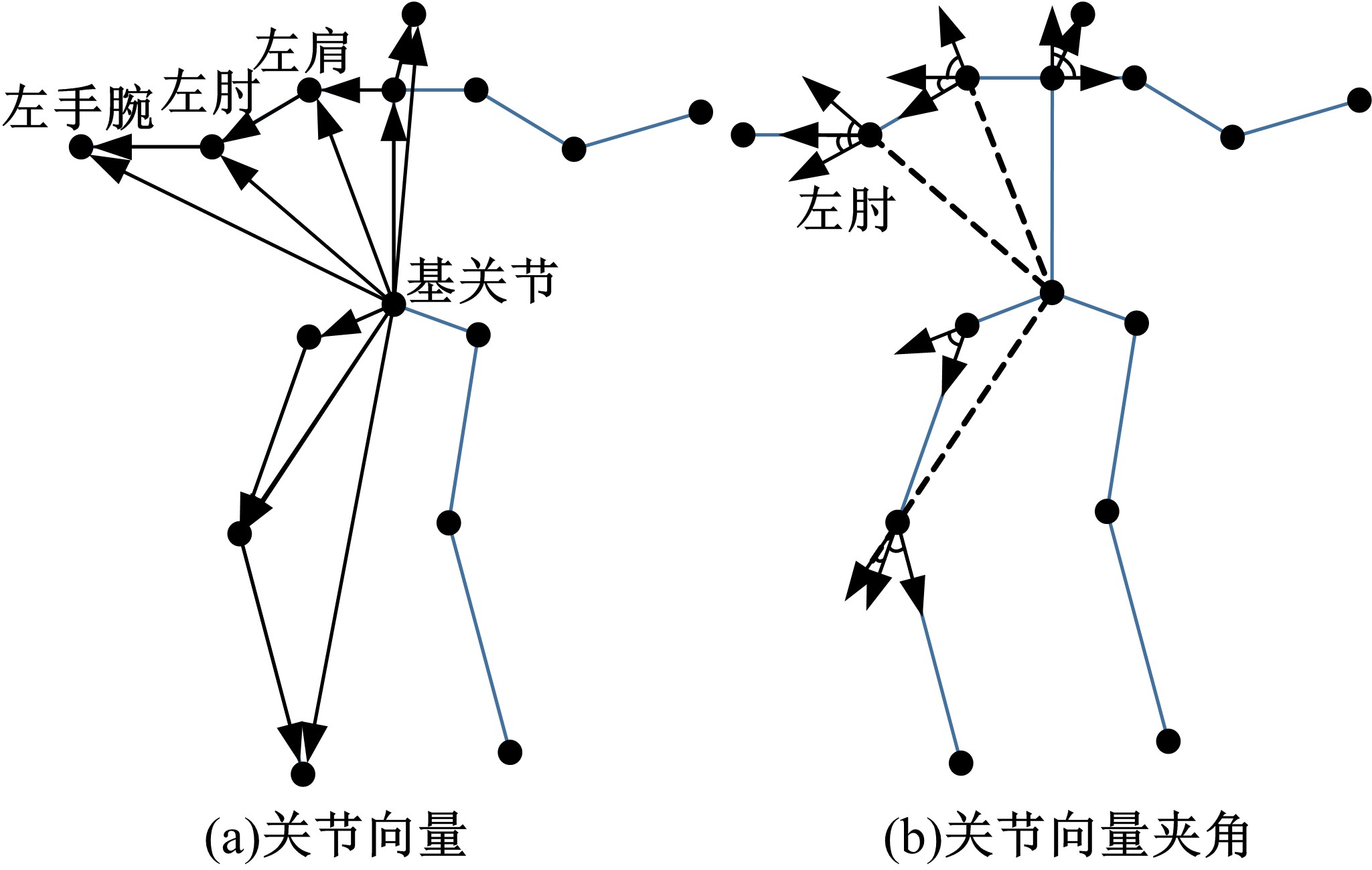
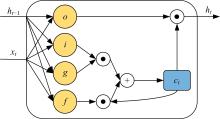
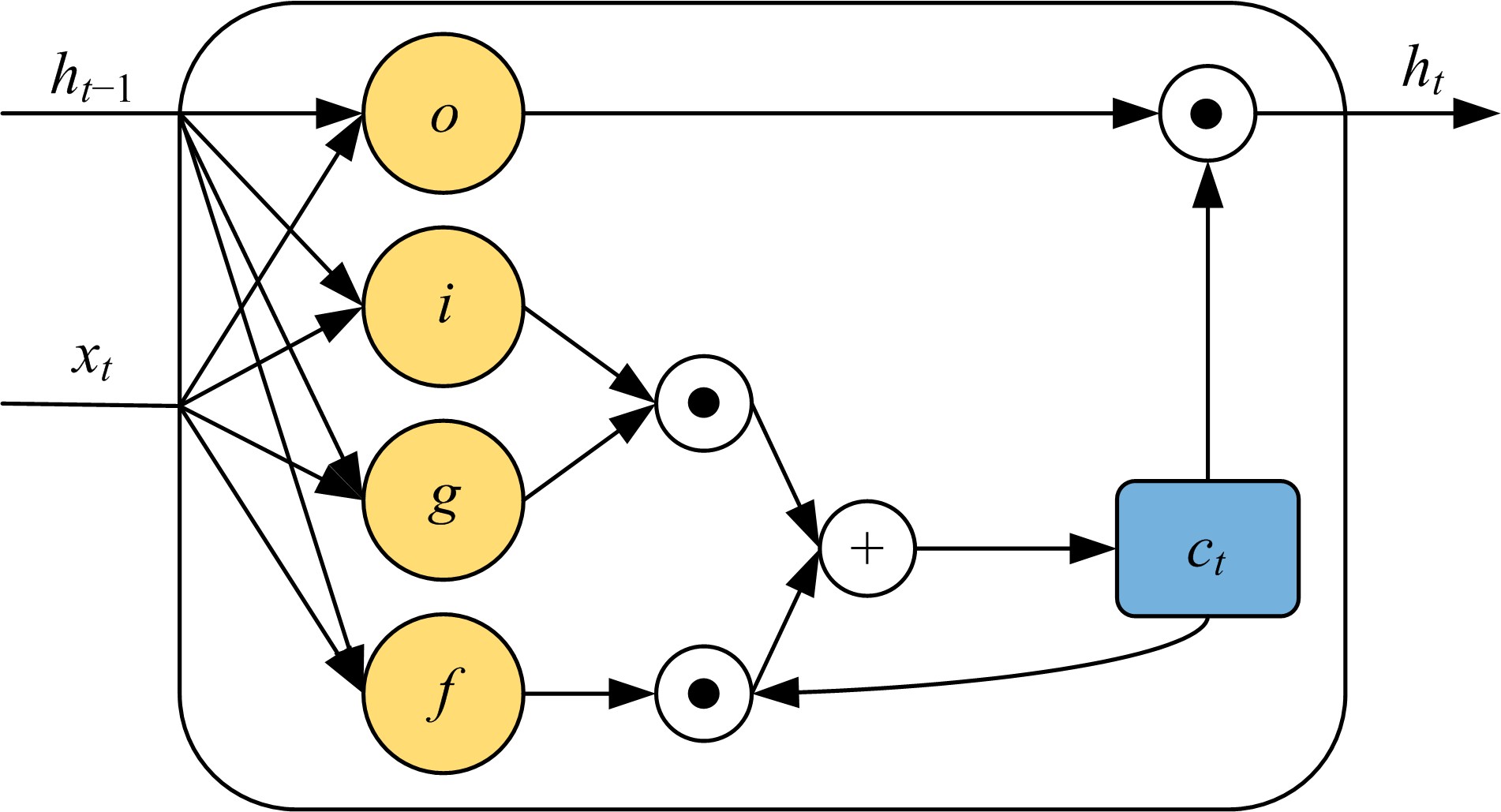
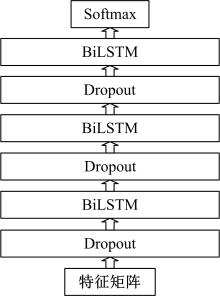
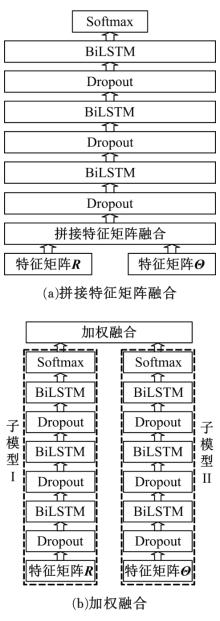
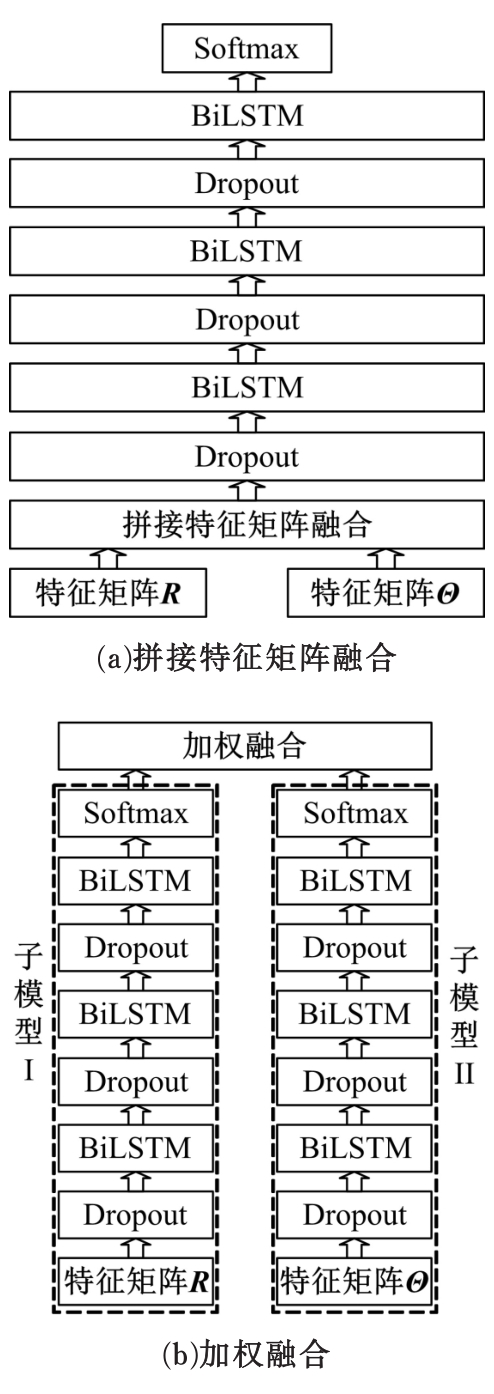
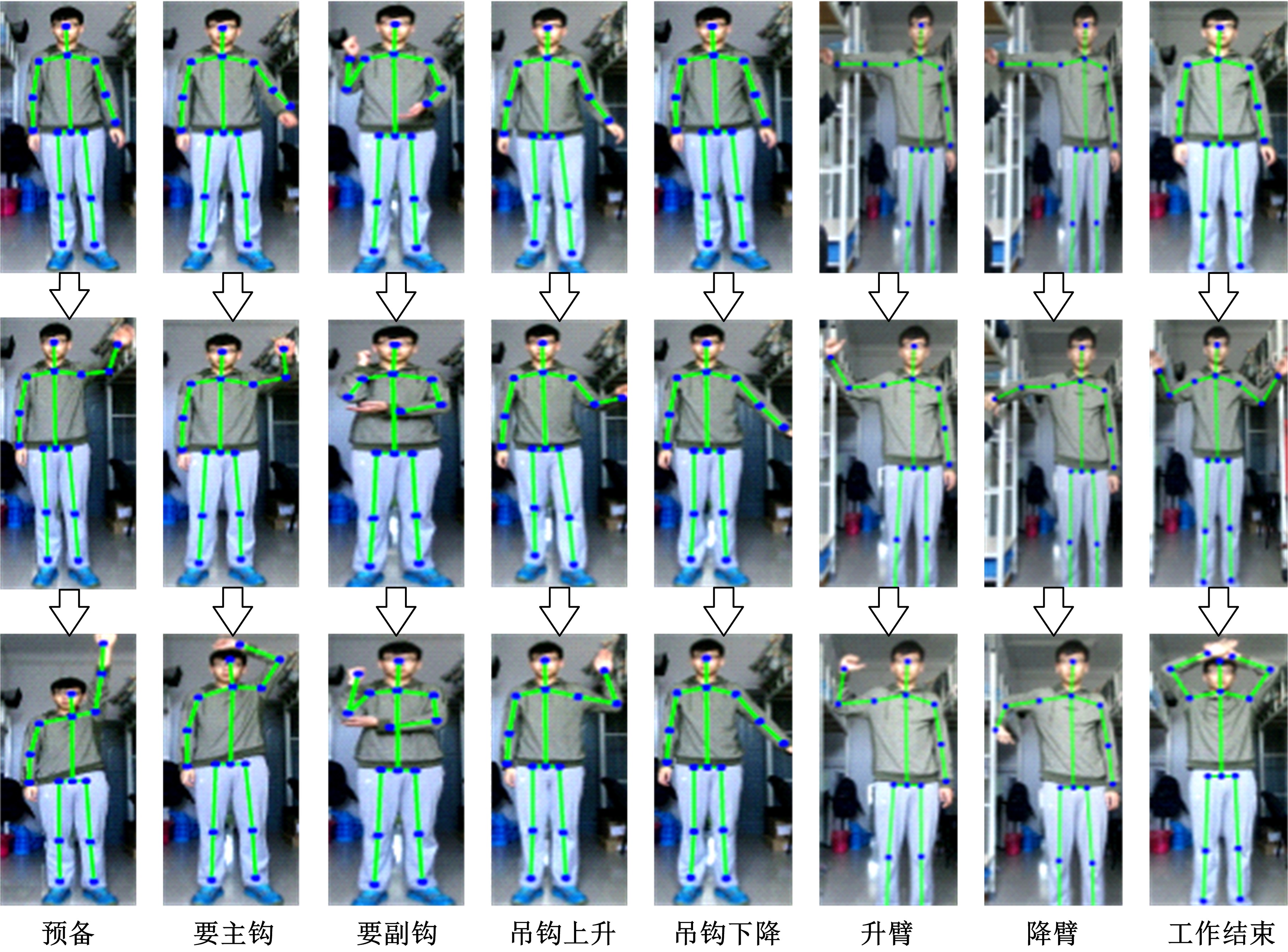
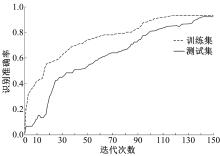
为解决地面指挥人员和司机协同操控起重机难度大的问题,提出一种基于双向长短期记忆(BiLSTM)模型的起重机智能操控方法,实现了对起重机的单人控制,降低了人力成本。首先,使用Kinect从指挥人员的一段动作指令中采集出人体关节点的坐标序列;然后,利用这些坐标构造人体关节向量,通过计算向量间的夹角和模比值构造出两种区分不同指令的特征矩阵;之后,将夹角特征矩阵输入到基于BiLSTM模型的指令识别网络,并与支持向量机(SVM)和反向传播(BP)神经网络的识别结果作比较;最后,将夹角和模比值特征矩阵进行融合识别,以进一步提升准确率。实验结果表明:本文指令识别网络具有较高的识别率;提出的融合识别方法有效地利用多种特征的信息,对训练集的识别准确率达99.13%,对测试集的识别准确率达96.75%。
中图分类号:
- TH218
| 1 | 臧大进, 戚玉强. 塔式起重机智能监控系统的研制[J]. 冶金设备, 2009(1): 50-53. |
| Zang Da-jin, Qi Yu-qiang. Development of intelligent monitoring system of tower cranes[J]. Metallurgical Equipment, 2009(1): 50-53. | |
| 2 | 潘斌, 汪小东. 塔式起重机安全管理的特点及对策[J]. 工业设计, 2011(6): 136. |
| Pan Bin, Wang Xiao-dong. Safety management characteristics and countermeasures of tower crane[J]. Design Ideas, 2011(6): 136. | |
| 3 | 腾文花. 关于塔吊使用的安全监控措施[J]. 建筑安全, 2007, 22(11): 36-36. |
| Teng Wen-hua. Safety monitoring measures for tower crane use[J]. Construction Safety, 2007, 22(11): 36-36. | |
| 4 | 李雄祥, 潘英俭, 廖拓. 起重机械的工作特点及发展趋势[J]. 中国水运: 理论版, 2007, 5(1): 171. |
| Li Xiong-xiang, Pan Ying-jian, Liao Tuo. Working characteristics and development trend of hoisting machinery[J]. China Water Transport, 2007, 5(1): 171. | |
| 5 | 张敏. 起重机检验中危险因素的识别与控制[J]. 科技风, 2015(12): 100. |
| Zhang Min. Identification and control of dangerous factors in crane inspection [J]. Technology Wind, 2015(12): 100. | |
| 6 | 尹浩. 港口门式起重机安全监控管理系统研究[D]. 武汉: 武汉纺织大学机械工程与自动化学院, 2015. |
| Yin Hao. Safety management characteristics and countermeasures of tower crane[D]. Wuhan: School of Mechanical Engineering and Automation, Wuhan Textile University, 2015. | |
| 7 | 贾秋枫. 大型履带式起重机吊装市场现状及发展趋势[J]. 石油化工建设, 2008, 30(5): 20-22. |
| Jia Qiu-feng. On the large scale crawler cranes hoisting business in China[J]. Petroleum & Chemical Construction, 2008, 30(5): 20-22. | |
| 8 | Zhang C C. Design of a crane intelligent control system[C]∥International Conference on Humanities and Social Science Research, Busan, South Korea, 2016: 861-864. |
| 9 | An J Q, Chen F, Chen X, et al. Three dimensional hoisting simulation system based on virtual reality for truck crane[C]∥2015 34th Chinese Control Conference (CCC), Hangzhou, China, 2015: 8892-8897. |
| 10 | 祁家榕, 张昌伟. 行为识别技术的研究与发展[J]. 智能计算机与应用, 2017, 7(4): 24-26, 30. |
| Qi Jia-rong, Zhang Chang-wei. Research and development of behavior recognition technology[J]. Intelligent Computer and Applications, 2017, 7(4): 24-26, 30. | |
| 11 | 倪涛, 赵泳嘉, 张红彦, 等. 基于Kinect动态手势识别的机械臂实时位姿控制系统[J]. 农业机械学报, 2017, 48(10): 417-423, 407. |
| Ni Tao, Zhao Yong-jia, Zhang Hong-yan, et al. Real-time mechanical arm position and pose control system by dynamic hand gesture recognition based on kinect device[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society for Agricultural Machinery, 2017, 48(10): 417-423, 407. | |
| 12 | Canal G, Escalera S, Angulo C. A real-time human-robot interaction system based on gestures for assistive scenarios[J]. Computer Vision and Image Understanding, 2016, 149: 65-77. |
| 13 | 张质文, 王金诺, 程文明, 等. 起重机设计手册[M]. 北京:中国铁道出版社, 2013. |
| 14 | 石忠晓. 智能化起重机安全监控系统[D]. 大连: 大连理工大学机械工程学院, 2003. |
| Shi Zhong-xiao. Intelligent crane safety monitoring system[D]. Dalian: School of Mechanical Engineering, Dalian University of Technology, 2003. | |
| 15 | 韩旭. 应用Kinect的人体行为识别方法研究与系统设计[D]. 济南: 山东大学控制科学与工程学院, 2013. |
| Han Xu. The human behavior recognition research and system design using kinect[D]. Jinan: School of Control Science and Engineering, Shandong University, 2013. | |
| 16 | Zhang S, Yang Y, Xiao J, et al. Fusing feometric features for skeleton-based action recognition using multilayer LSTM networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Multimedia, 2018, 20(9): 2330-2343. |
| 17 | Cho K, Van M B, Gulcehre C, et al. Learning phrase representations using RNN encoder-decoder for statistical machine translation[C]∥Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing (EMNLP), Doha, Qatar, 2014: 1724-1734. |
| 18 | 王鑫, 吴际, 刘超, 等. 基于LSTM循环神经网络的故障时间序列预测[J]. 北京航空航天大学学报, 2018, 44(4): 772-784. |
| Wang Xin, Wu Ji, Liu Chao, et al. Exploring LSTM based recurrent neural network for failure time series prediction[J]. Journal of Beijing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2018, 44(4): 772-784. | |
| 19 | Greff K, Srivastava R K, Koutník J, et al. LSTM: a search space odyssey[J]. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 2017, 28(10): 2222-2232. |
| 20 | GB5 082-1985起重吊运指挥信号[S]. |
| [1] | 丁宁, 王龙山, 何平. 稀土起重永磁吊的设计原理[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2001, (1): 86-90. |
|
||