吉林大学学报(工学版) ›› 2022, Vol. 52 ›› Issue (10): 2447-2455.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb20210263
• 通信与控制工程 • 上一篇
基于多阵列合成孔径的局部超声阵列聚焦方法
- 1.吉林大学 通信工程学院,长春 130022
2.吉林大学 计算机科学与技术学院,长春 130012
Local ultrasound array focusing method based on multiarray synthetic aperture
Jian CHEN1( ),Fan YU1,Lin LIN1,Ming⁃hui SUN2
),Fan YU1,Lin LIN1,Ming⁃hui SUN2
- 1.College of Communication Engineering,Jilin University,Changchun 130022,China
2.College of Computer Science and Technology,Jilin University,Changchun 130012,China
摘要:
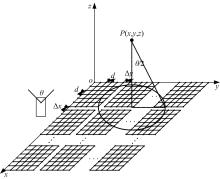
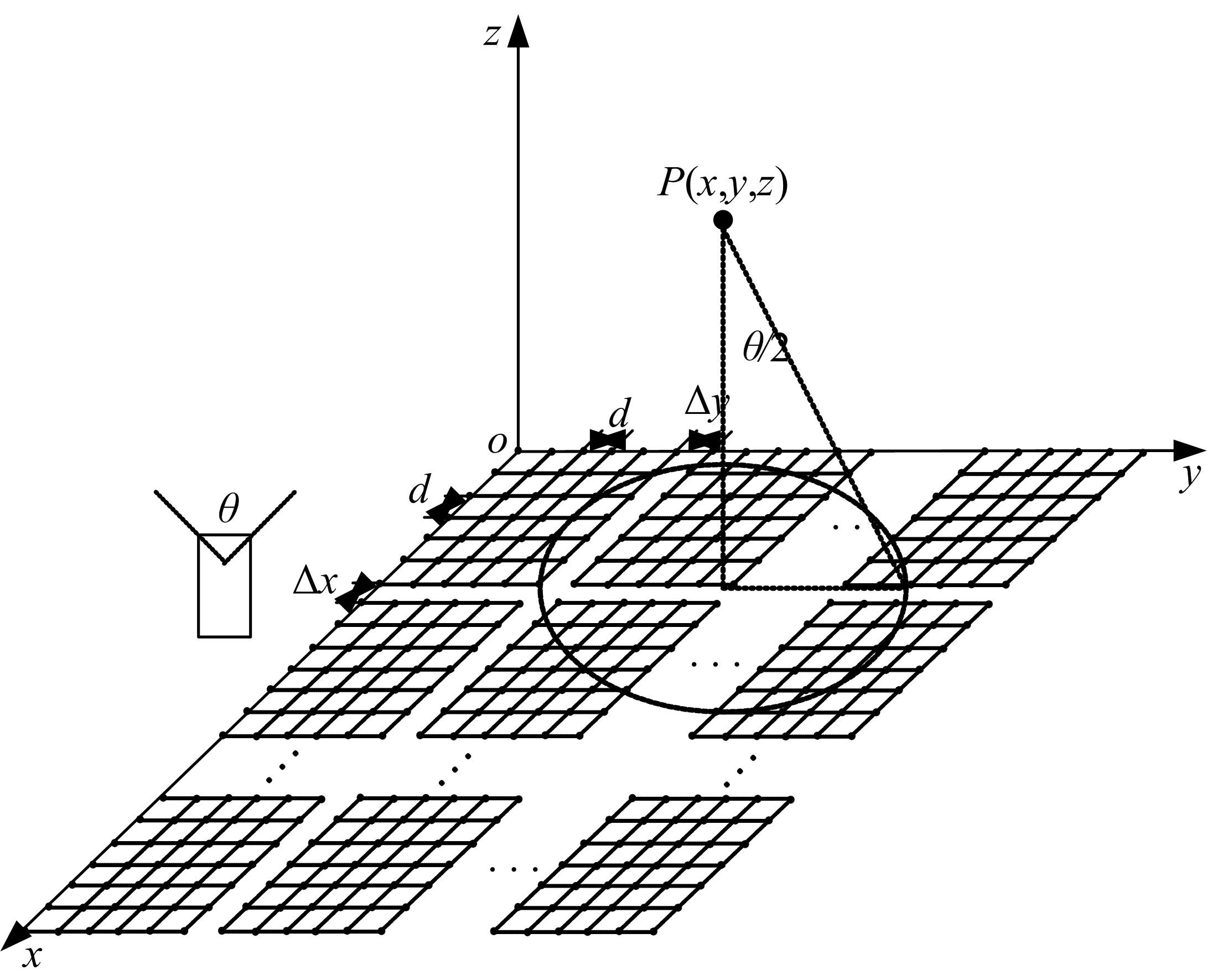
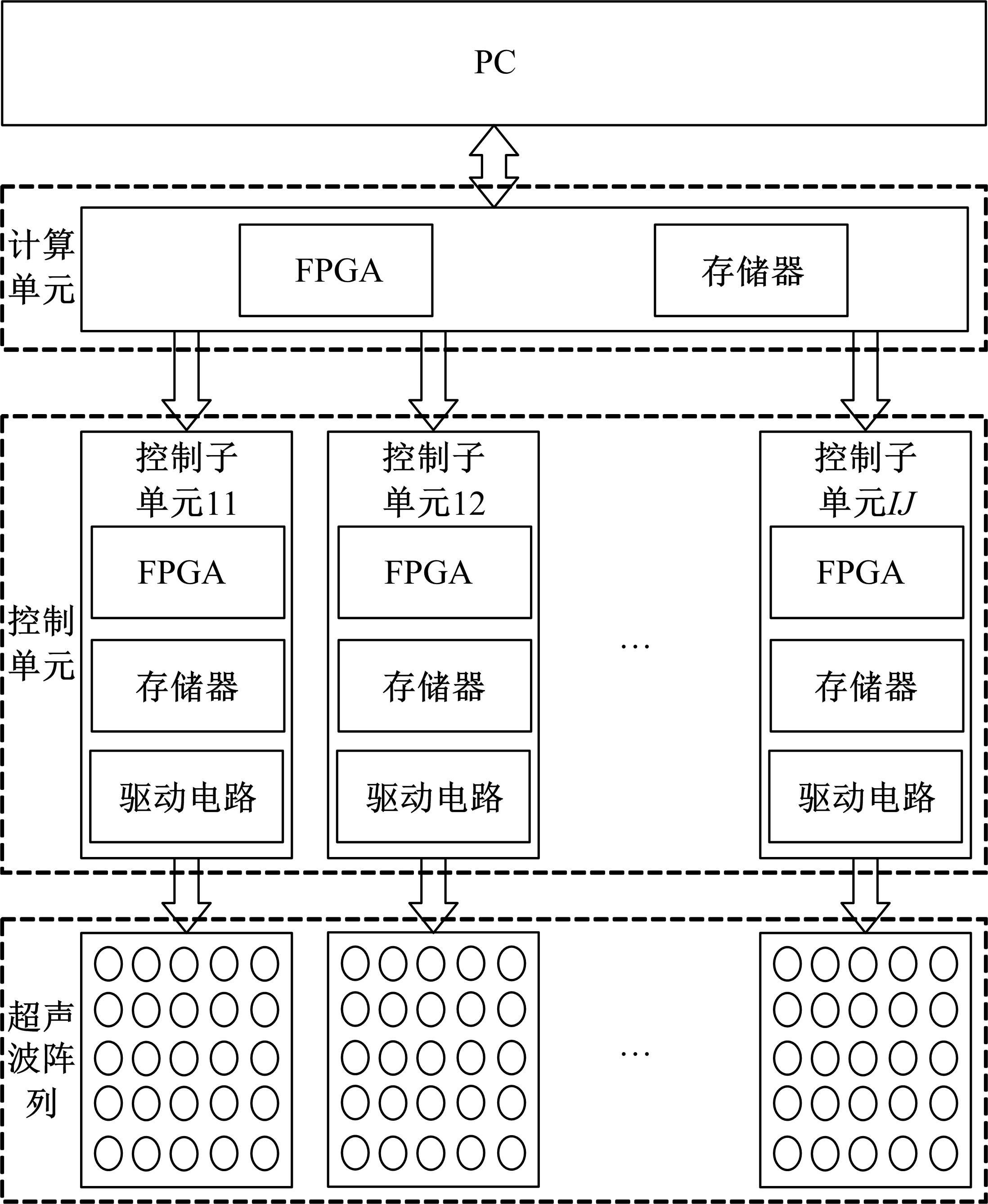
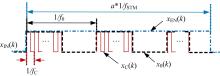
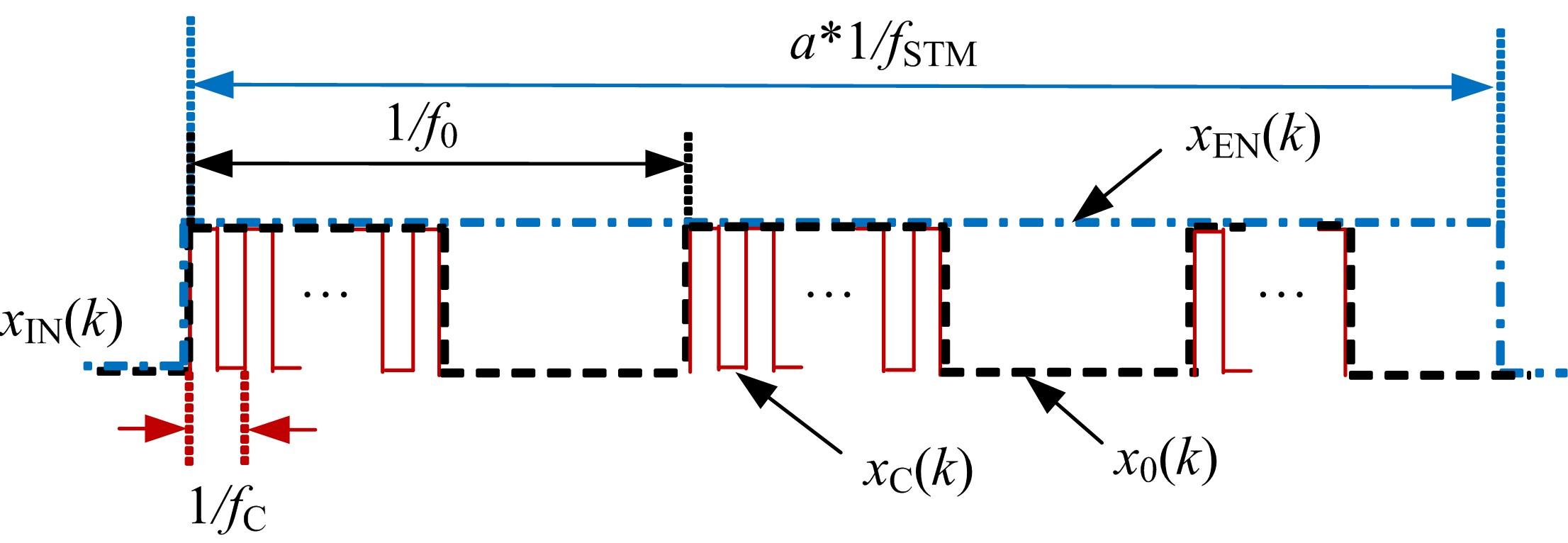
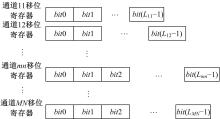
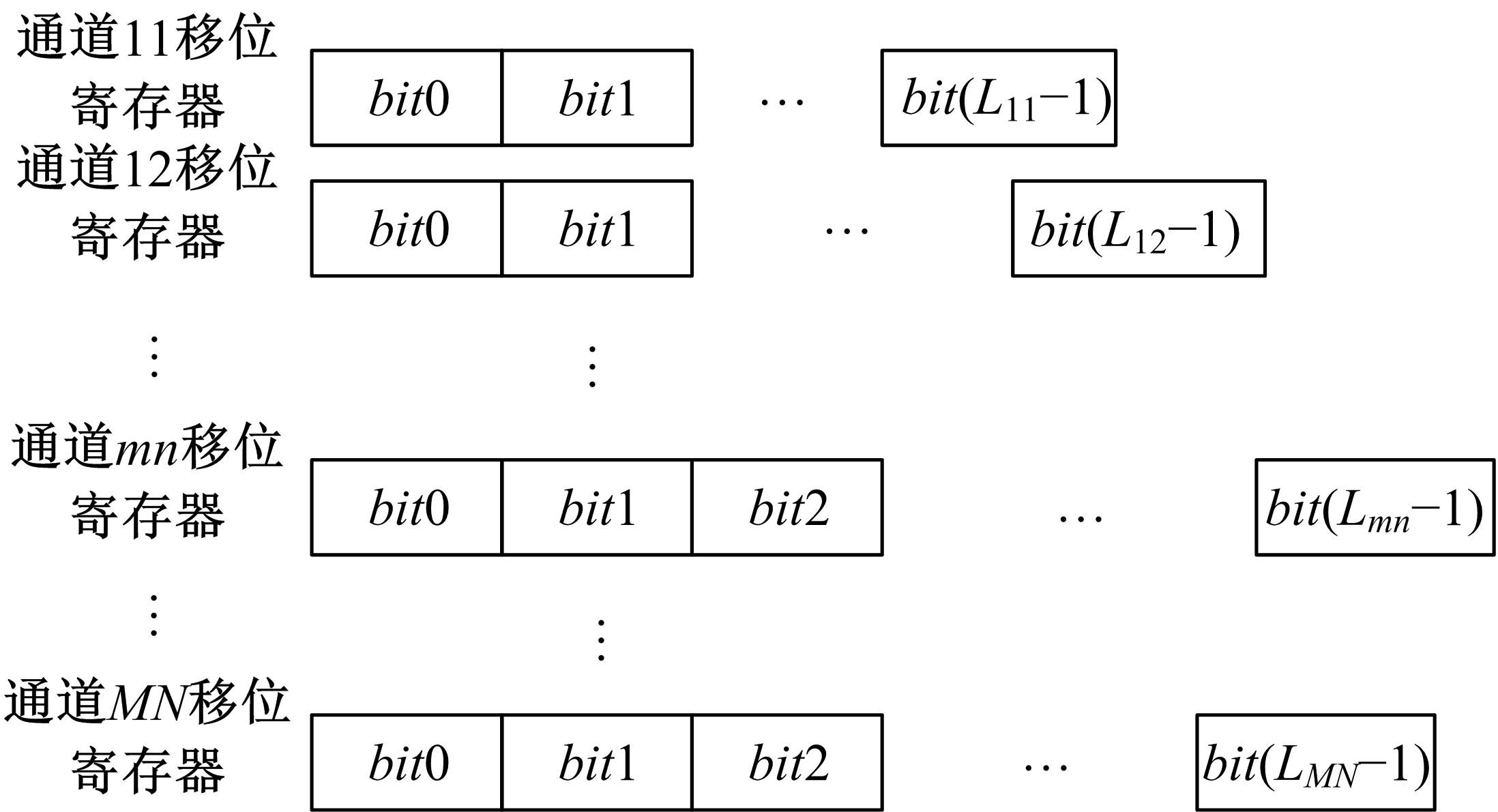
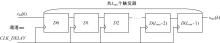
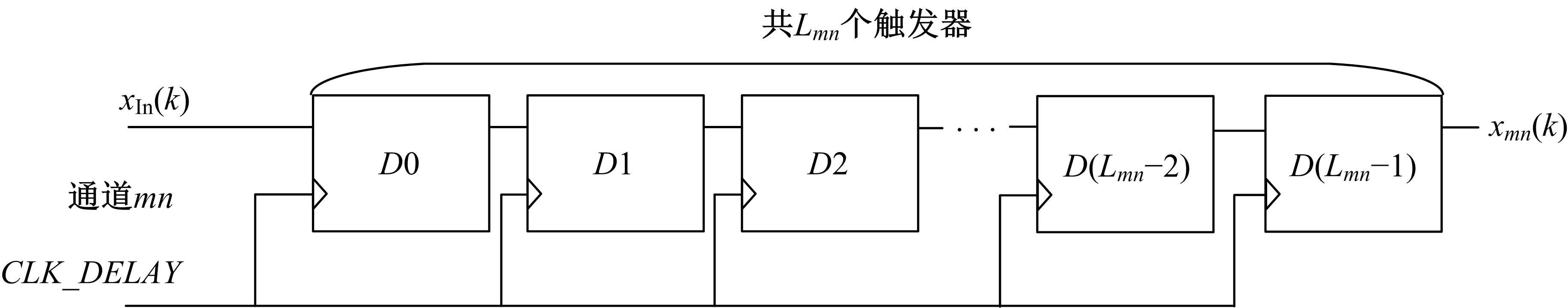
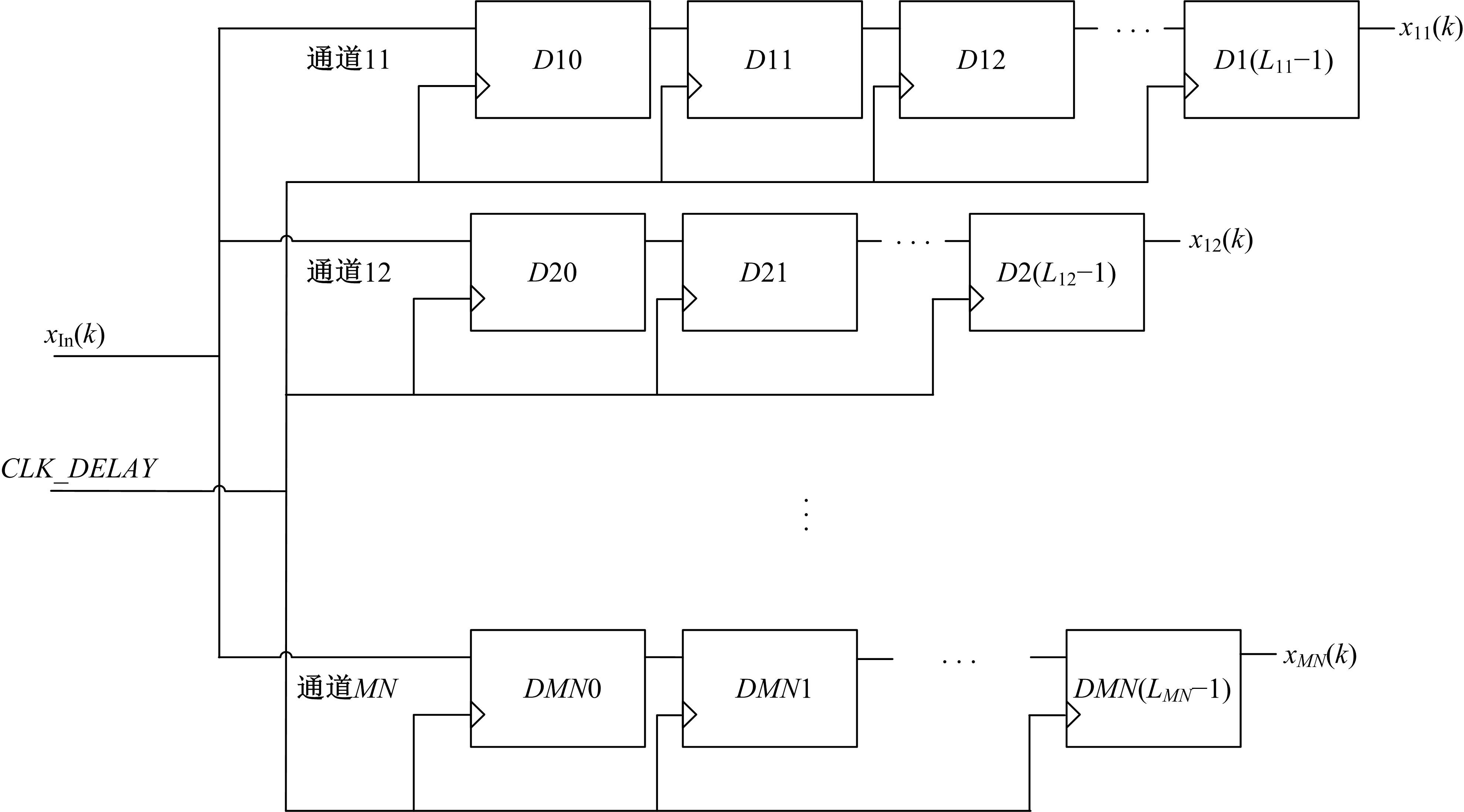
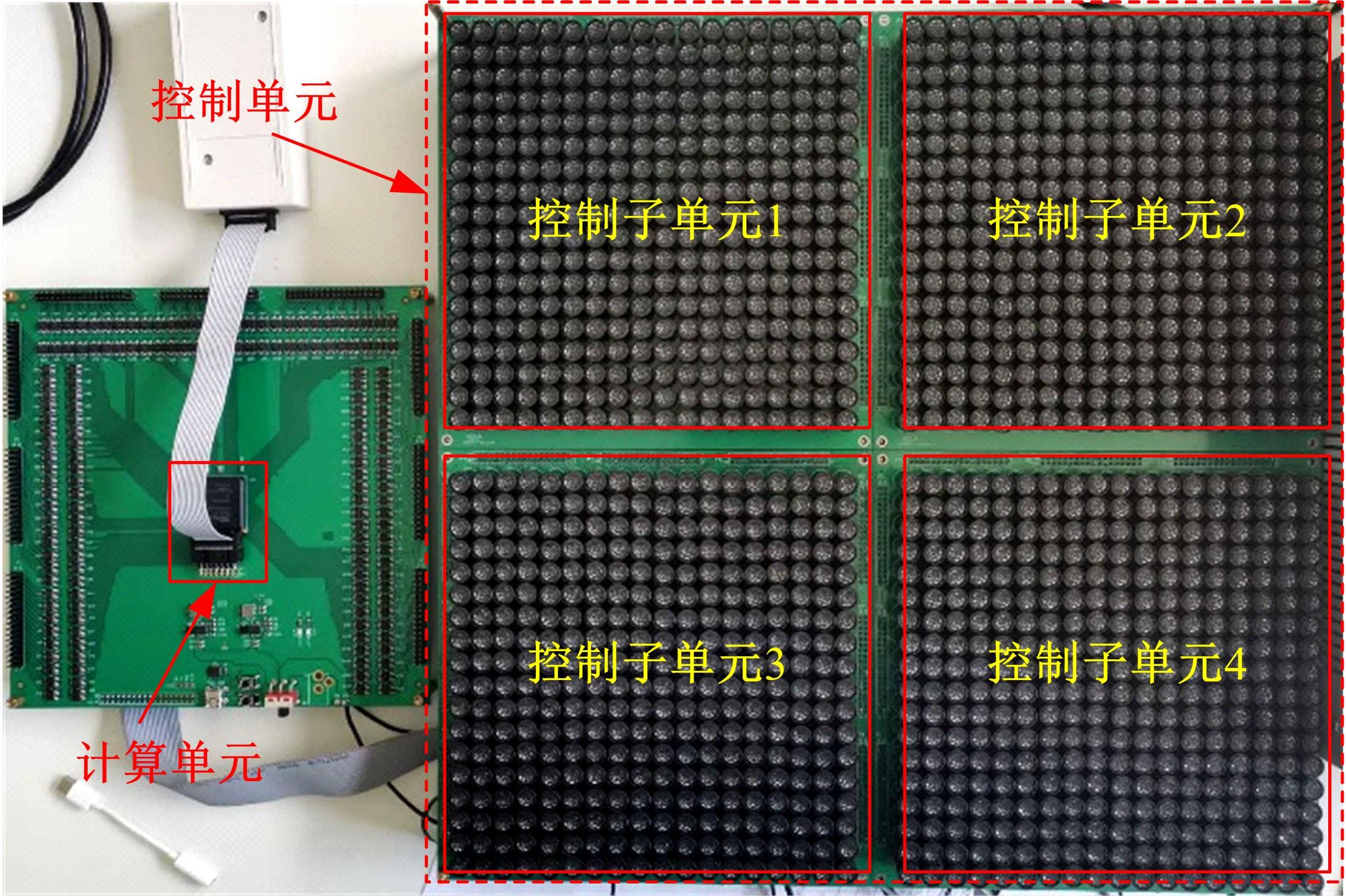
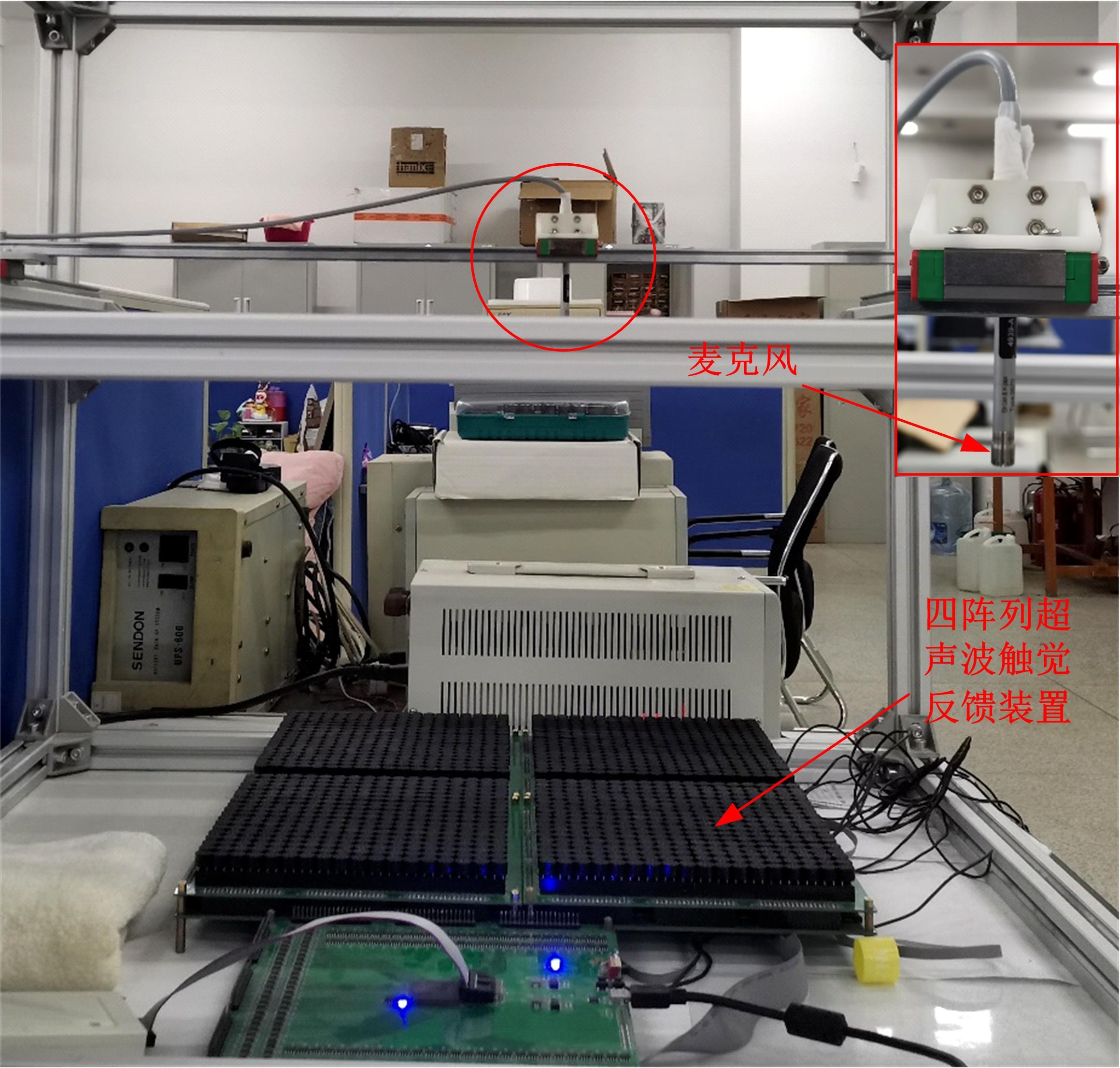
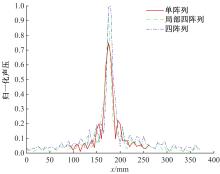
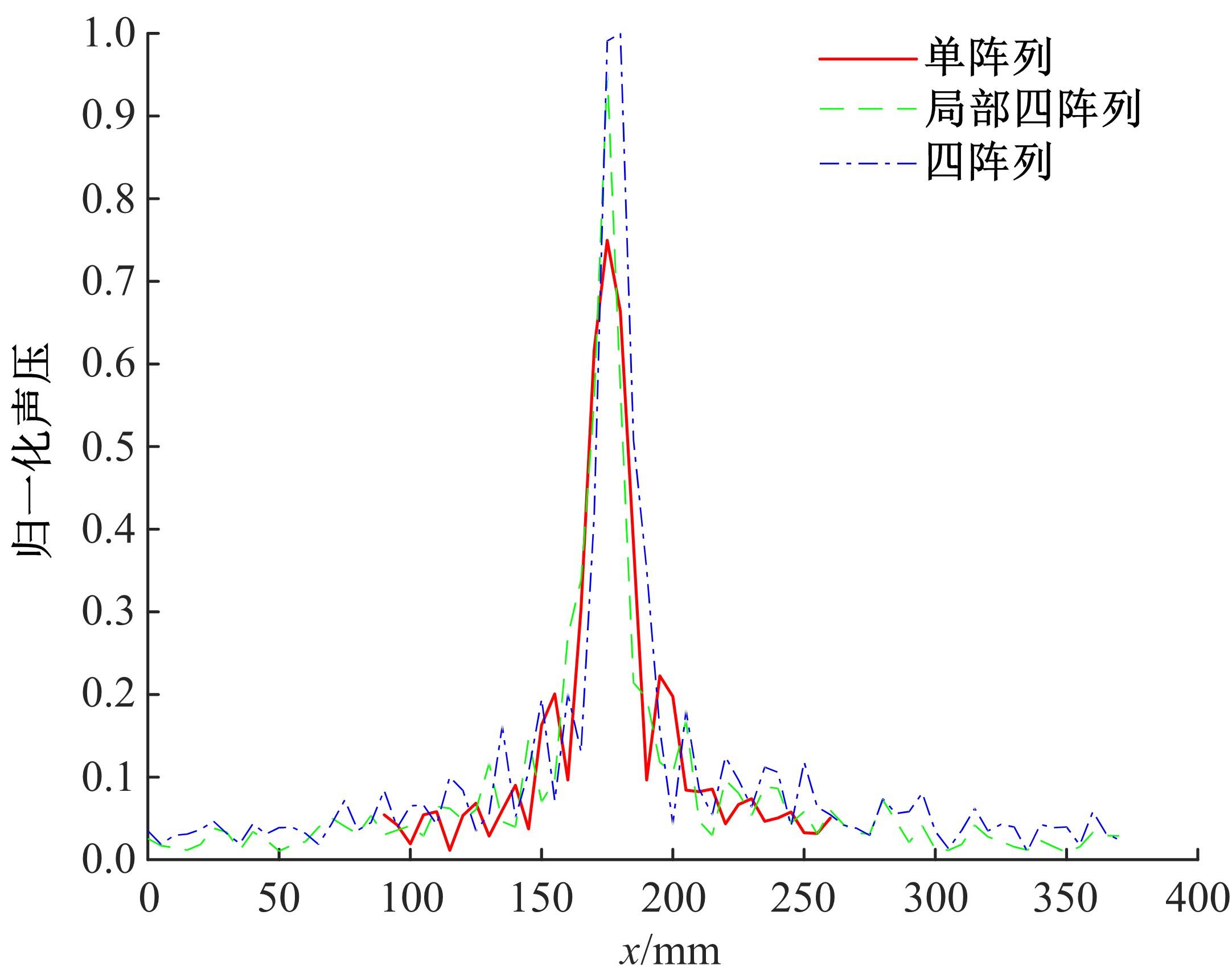
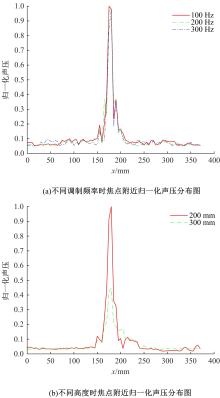
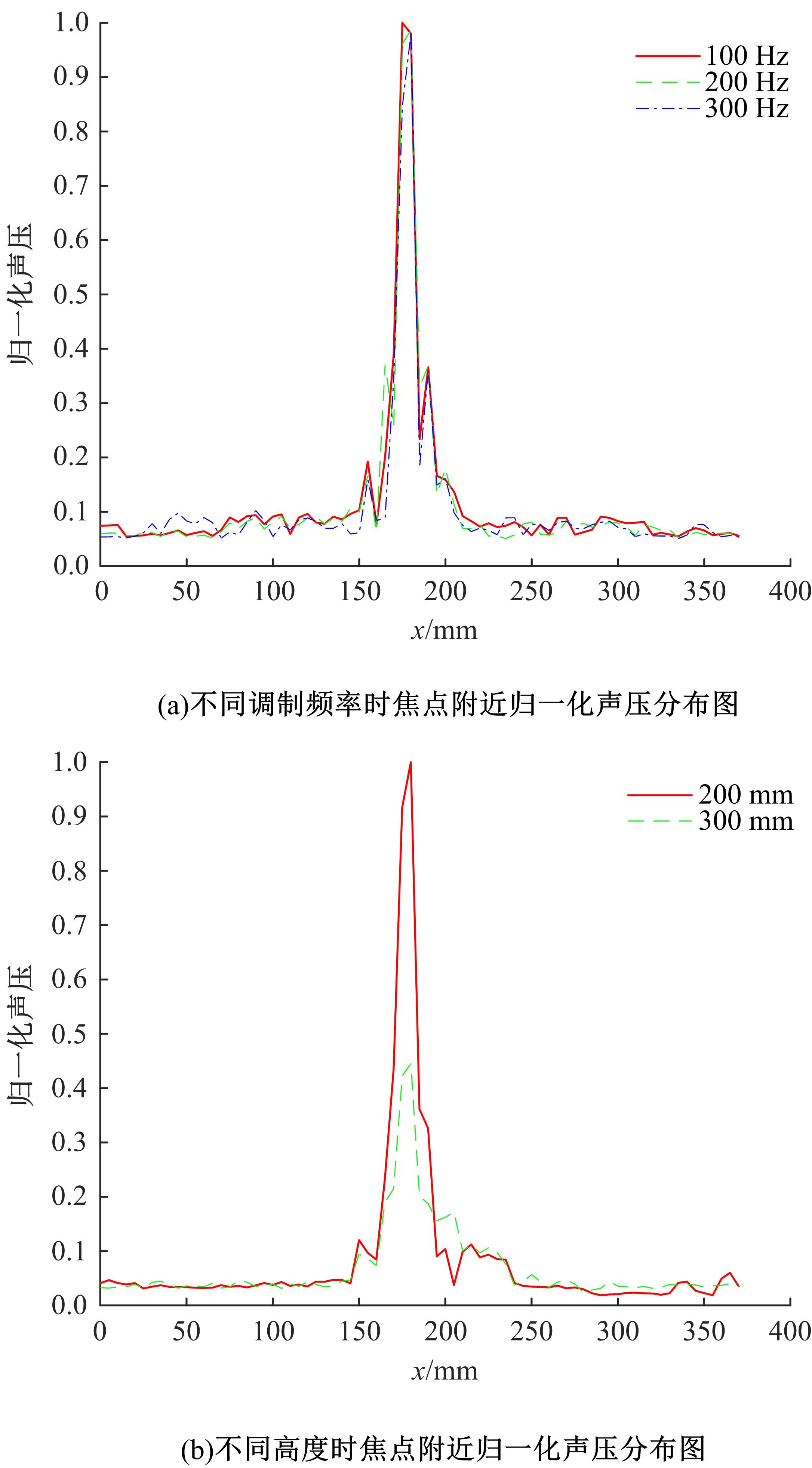
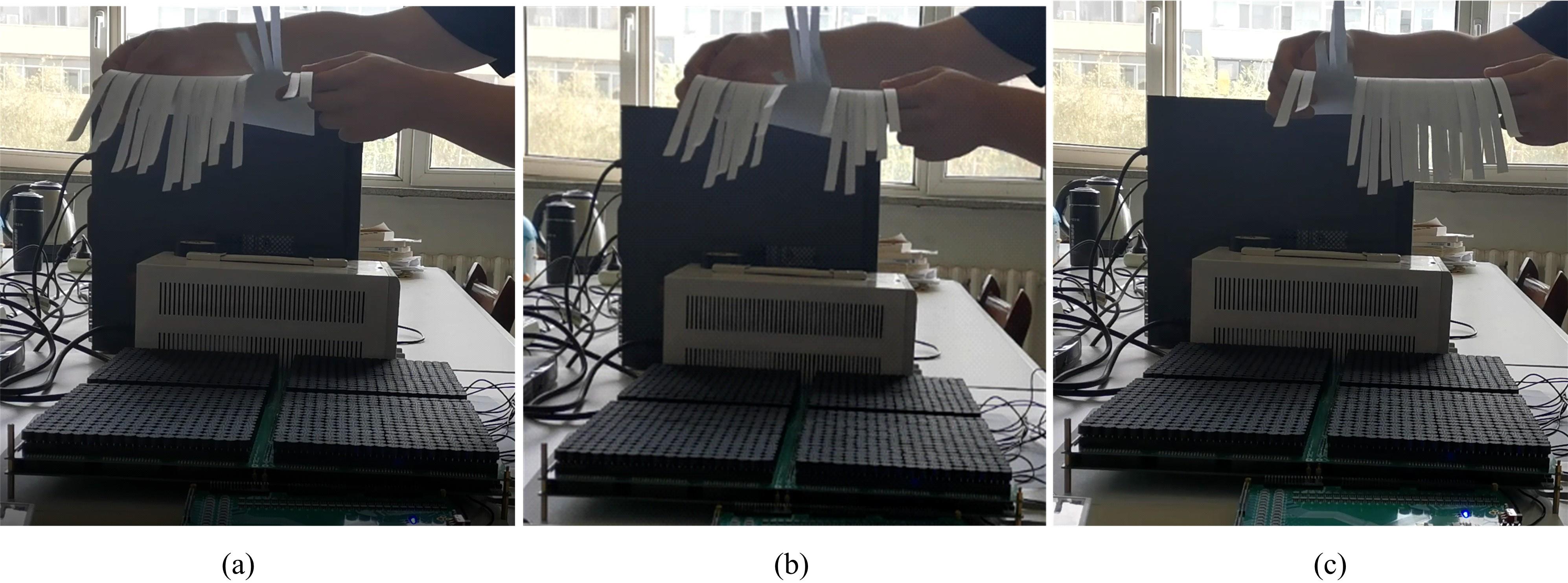
针对增大超声波阵列孔径虽然能够提高超声波聚焦的精度,但同时带来功耗和聚焦噪声的增加的问题,提出了一种基于多阵列合成孔径的局部超声阵列聚焦方法。该方法根据超声波发射器的辐射角度确定参与聚焦的发射器数目,通过减少同时工作的发射器数目降低功耗,减小噪声。对比测试了局部阵列聚焦方法和全阵列聚焦方法的聚焦精度和功耗。结果表明,相比于全阵列聚焦方法,本文所提方法的聚焦精度略有提高,聚焦强度减小了5%,但功耗降低了31%。
中图分类号:
- TN958
| 1 | Hoshi T, Abe D, Shinoda H. Adding tactile reaction to hologram[C]∥RO-MAN 2009-The 18th IEEE International Symposium on Robot and Human Interactive Communication, Toyama, Japan, 2009: 7-11. |
| 2 | Minamizawa K, Kamuro S, Fukamachi S, et al. GhostGlove: Haptic existence of the virtual world[C]//The 35th International Conference on Computer Graphics and Interactive Techniques,Los Angeles,USA,2008. |
| 3 | Kim S C, Kim C H, Yang T H, et al. SaLT: small and lightweight tactile display using ultrasonic actuators[C]∥The 17th IEEE International Symposium on Robot and Human Interactive Communication, Munich,Germany, 2008: 430-435. |
| 4 | Gurocak H, Jayaram S, Parrish B, et al. Weight sensation in virtual environments using a haptic device with air jets[J]. J Comput Inf Sci Eng, 2003, 3(2): 130-135. |
| 5 | Tsalamlal M Y, Issartel P, Ouarti N, et al. HAIR: HAptic feedback with a mobile AIR jet[C]∥IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Hong Kong, China, 2014: 2699-2706. |
| 6 | Sodhi R, Poupyrev I, Glisson M, et al. AIREAL: interactive tactile experiences in free air[J]. ACM Transactions on Graphics (TOG), 2013, 32(4): 1-10. |
| 7 | Jun J H, Park J R, Kim S P, et al. Laser-induced thermoelastic effects can evoke tactile sensations[J]. Scientific Reports, 2015, 5(1): No. 11016. |
| 8 | Lee H, Kim J S, Kim J Y, et al. Mid-air tactile stimulation using indirect laser radiation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Haptics, 2016, 9(4): 574-585. |
| 9 | Ochiai Y, Kumagai K, Hoshi T, et al. Cross-field aerial haptics: Rendering haptic feedback in air with light and acoustic fields[C]∥Proceedings of the CHI Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems, San Jose, USA, 2016: 3238-3247. |
| 10 | Hoshi T, Takahashi M, Iwamoto T, et al. Noncontact tactile display based on radiation pressure of airborne ultrasound[J]. IEEE Transactions on Haptics, 2010, 3(3): 155-165. |
| 11 | Makino Y, Furuyama Y, Inoue S, et al. HaptoClone (Haptic-Optical Clone) for mutual tele-environment by real-time 3D image transfer with midair force Feedback[C]∥Proceedings of the 2016 CHI Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems, San Jose, USA, 2016: 1980-1990. |
| 12 | Hasegawa K, Shinoda H. Aerial vibrotactile display based on multiunit ultrasound phased array[J]. IEEE Transactions on Haptics, 2018, 11(3): 367-377. |
| 13 | Qian Y, Salehian A, Han S W, et al. Design of an ultrasonic tactile sensor using electro-mechanical analogy[J]. Ultrasonics, 2020, 105: No. 106129. |
| 14 | Awatani J. Studies on acoustic radiation pressure. i. (general considerations)[J]. Journal of the Acoustical Society of America, 1955, 27(2):278-281. |
| 15 | Hasegawa T, Kido T, Iizuka T, et al. A general theory of Rayleigh and Langevin radiation pressures[J]. Acoustical Science and Technology, 2000, 21(3): 145-152. |
| 16 | Vallbo A B, Johansson R S. Properties of cutaneous mechanoreceptors in the human hand related to touch sensation[J]. Hum Neurobiol, 1984, 3(1): 3-14. |
| 17 | Chen J, Yu F, Wang Z Q, et al. Multichannel ultrasound focusing delay control method based on variable-length shift register for airborne ultrasound tactile feedback[J]. IEEE Access, 2020, 8: 24904-24913. |
| [1] | 孙洪亮,沈伟达,陈玲玲. 时延QoS约束下的混合业务带宽补偿算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(8): 1912-1917. |
| [2] | 侯春萍,赵春月,王致芃,田海瑞. 基于有效异常样本构造的视频异常检测算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(5): 1823-1829. |
| [3] | 王义君,张有旭,缪瑞新,豆佳敏. 5G中基于系统中断概率的D2D资源分配算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(1): 331-339. |
| [4] | 胡钊政,李招康,陶倩文. 基于分布式二维激光测距仪的室内行人检测与跟踪[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2020, 50(2): 719-729. |
| [5] | 赵鹏,蒋宇中,陈斌,李春腾,张杨勇. 基于局部方差域自适应Blanking的超低频信道噪声抑制方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2019, 49(5): 1696-1705. |
|
||