吉林大学学报(工学版) ›› 2019, Vol. 49 ›› Issue (5): 1696-1705.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb20180446
• • 上一篇
基于局部方差域自适应Blanking的超低频信道噪声抑制方法
- 1. 海军工程大学 电子工程学院,武汉 430033
2. 中船重工集团公司第七二二研究所,武汉 430079
SLF channel noise suppression method based on adaptive blanking in local variance domain
Peng ZHAO1( ),Yu-zhong JIANG1(
),Yu-zhong JIANG1( ),Bin CHEN1,Chun-teng LI1,Yang-yong ZHANG2
),Bin CHEN1,Chun-teng LI1,Yang-yong ZHANG2
- 1. College of Electronic Engineering,Naval University of Engineering, Wuhan 430033, China
2. No. 722 Research Institute of CSIC, Wuhan 430079, China
摘要:
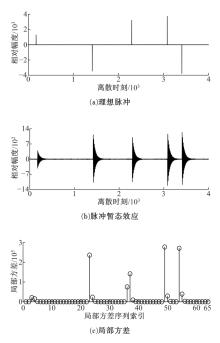
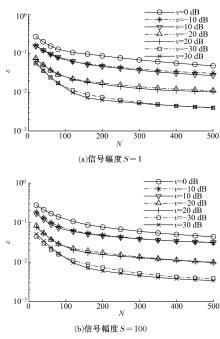
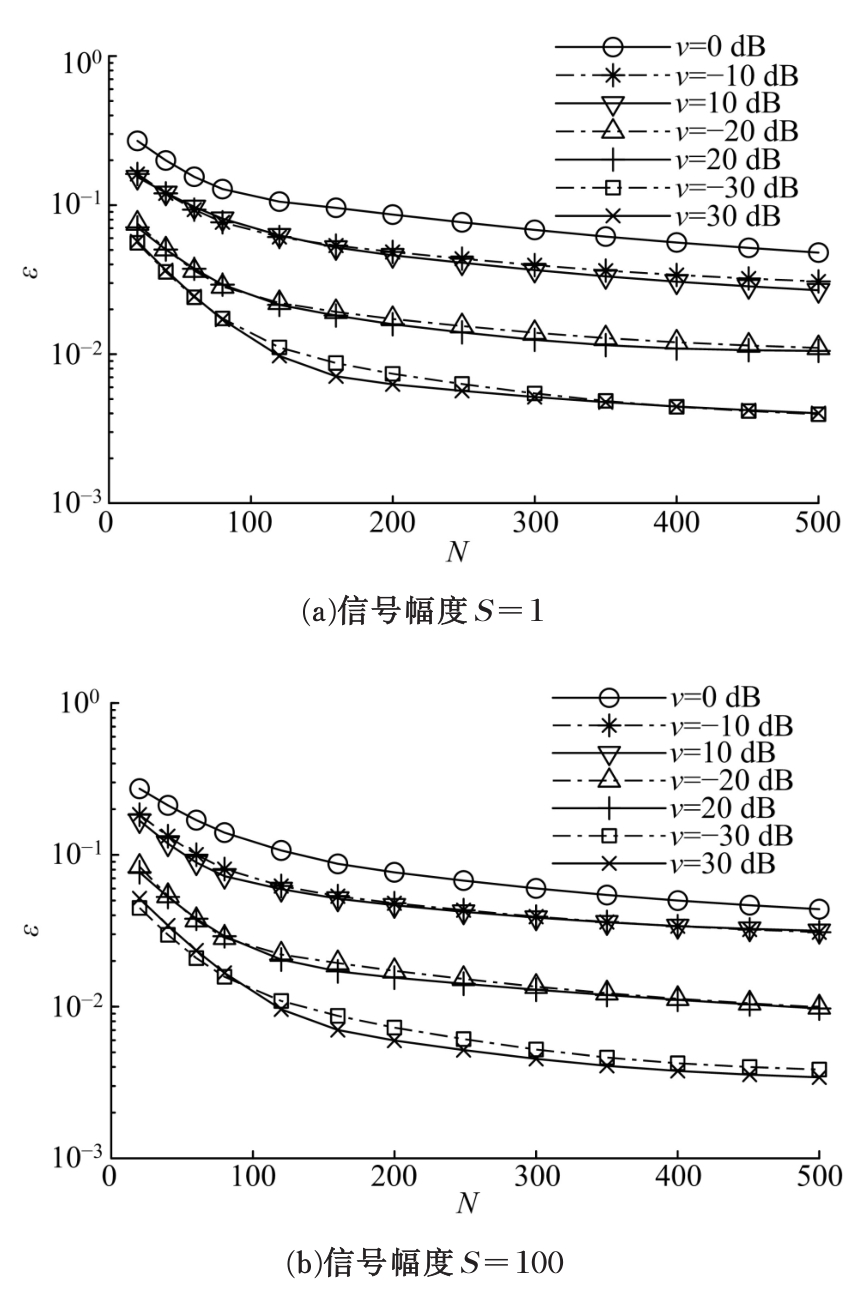
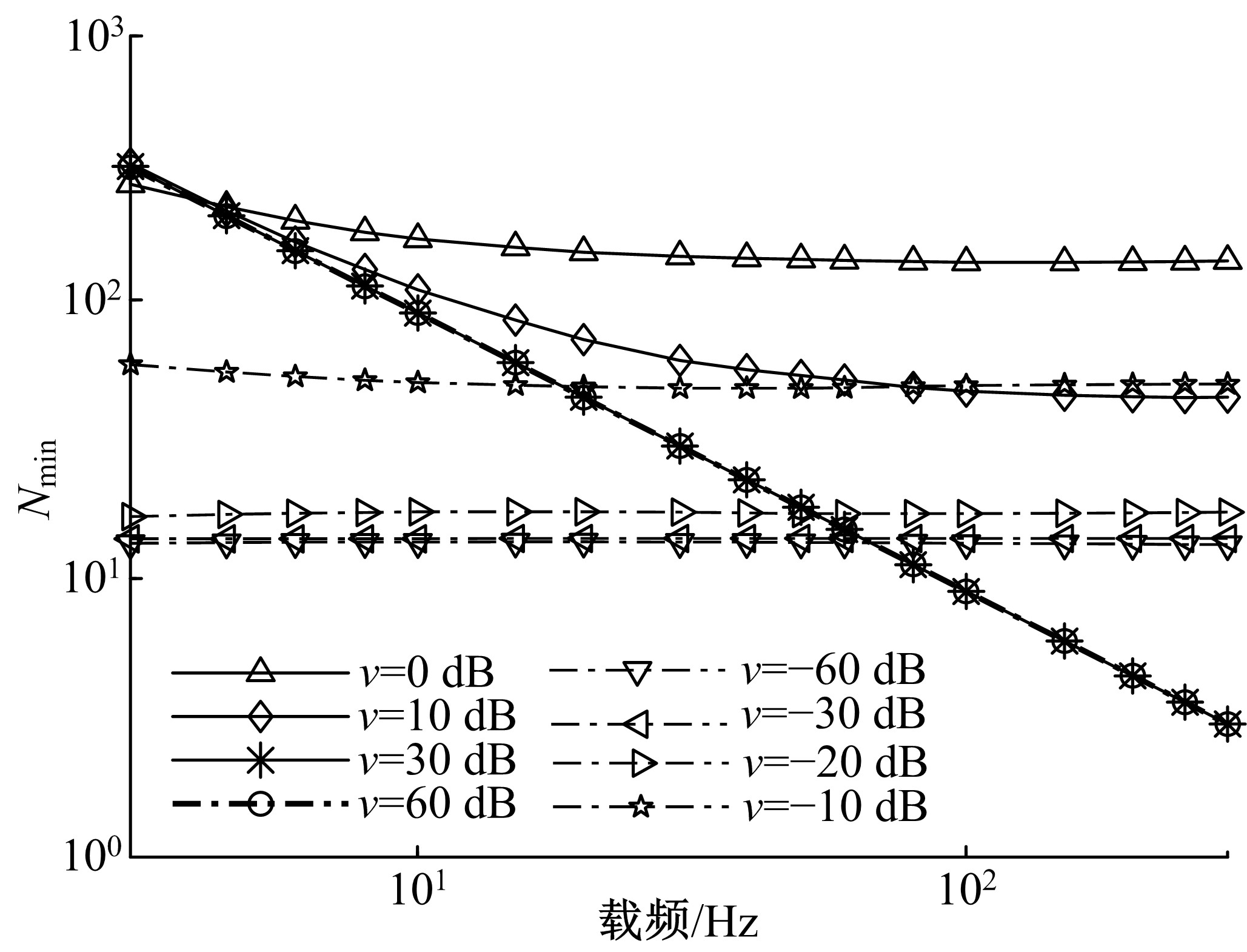
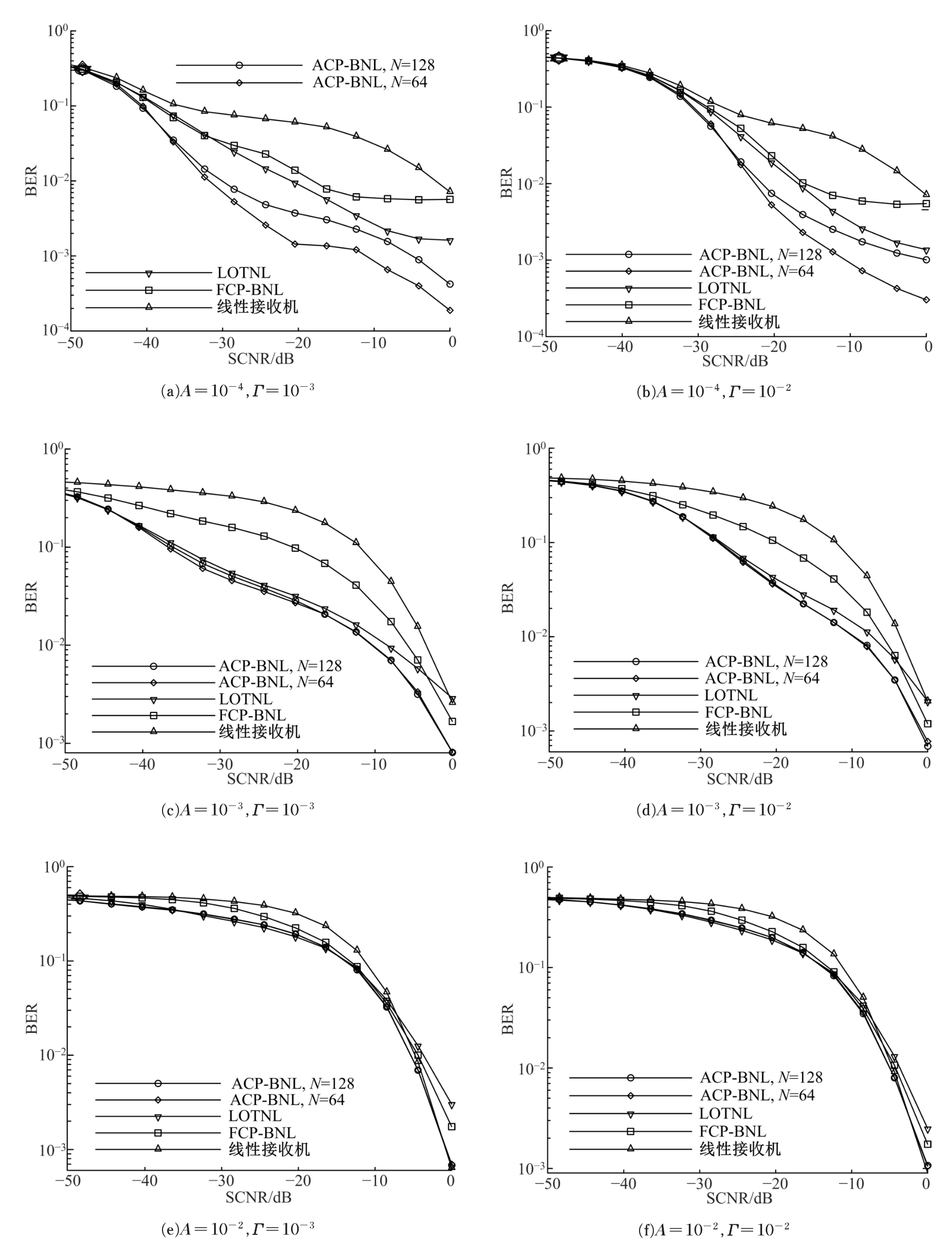
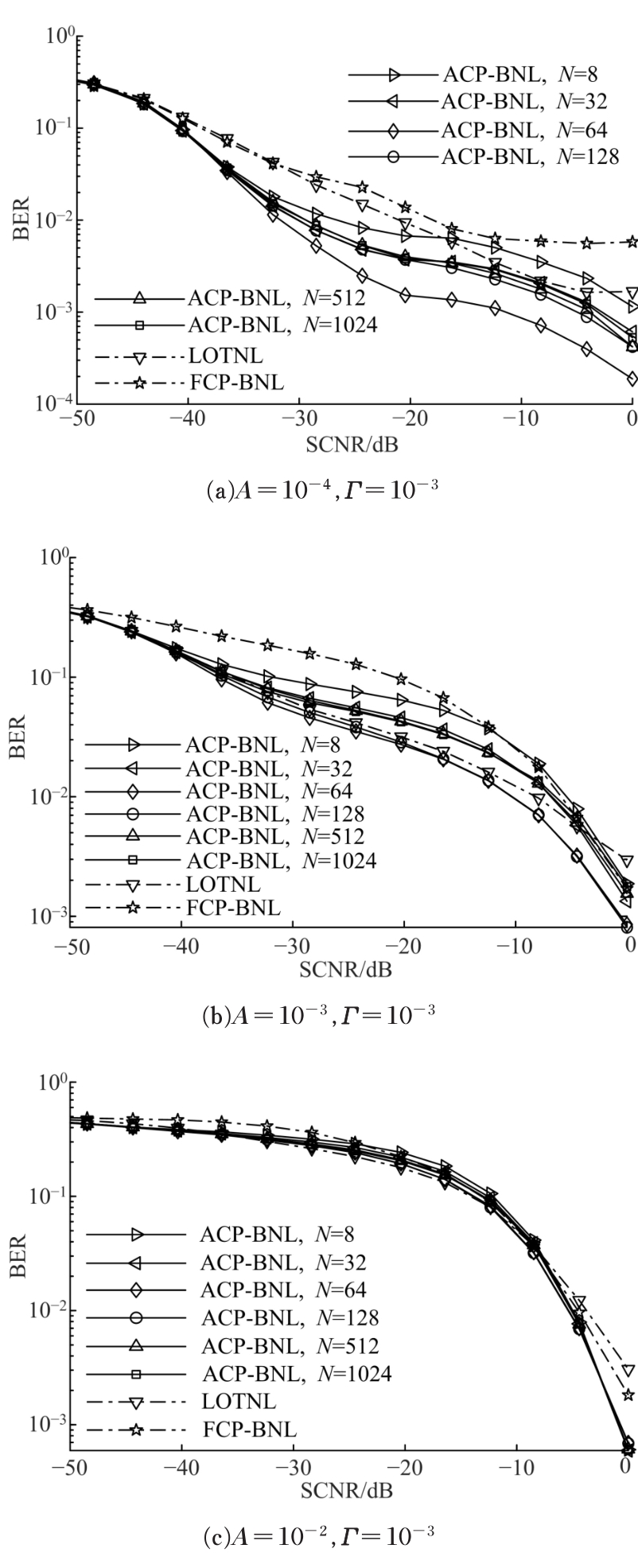
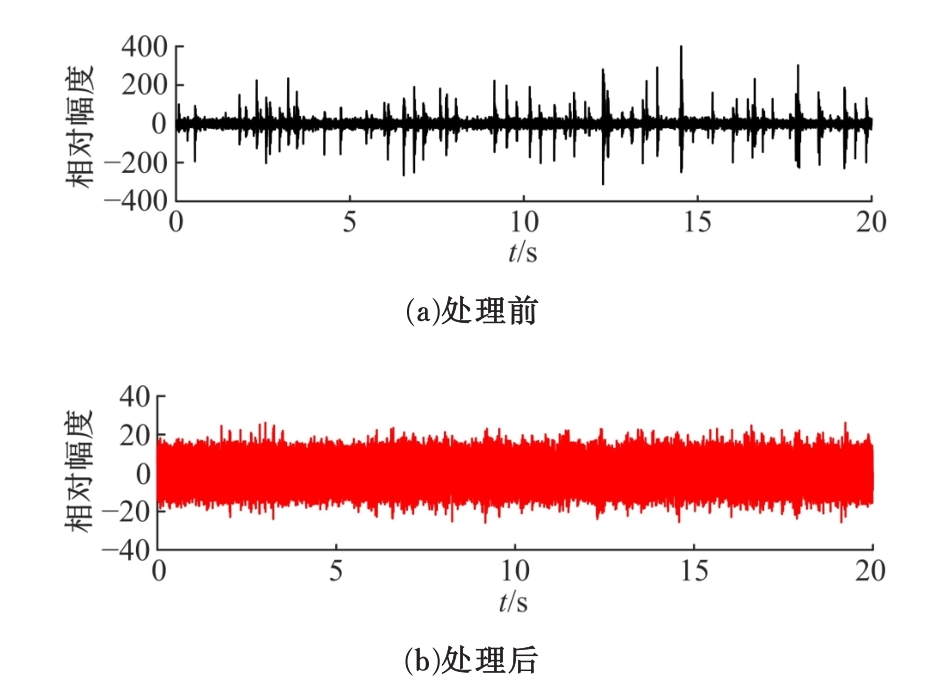
针对超低频信道噪声脉冲因接收机前端暂态效应而钝化导致常规Blanking非线性抑噪性能退化的问题,在分析脉冲暂态响应波形特点以及常规Blanking性能退化机制基础上,结合局部方差域变换(LVDT)能增强脉冲性的特性,提出了一种基于LVDT的自适应Blanking处理方法,给出了恒虚警率准则下信道噪声脉冲检测门限以及Blanking门限优化准则。仿真和实测结果表明:本文方法在超低频信道噪声抑制方面具有比常规非线性处理更好的性能,考虑到该方法无需信道噪声模型假设及其参数估计,是一种盲抑制方法,因而更具工程实用意义。
中图分类号:
- TN85
| 1 | EvansJ, GriffithsA S. Design of a sanguine noise processor based upon world-wide extremely low frequency (ELF) recordings[J]. IEEE Transactions on Communications, 1974, 22(4): 528-539. |
| 2 | IngramR. Performance of the locally optimum threshold receiver and several suboptimal nonlinear receivers for ELF noise[J]. IEEE Journal of Oceanic Engineering, 1984, 9(3): 202-208. |
| 3 | MiddletonD. Statistical-physical models of electromagnetic interference[J]. IEEE Transactions on Electromagnetic Compatibility, 1977, 19(3): 106-127. |
| 4 | 蒋宇中, 应文威, 张曙霞, 等. 超低频非高斯噪声模型及应用[M]. 北京: 国防工业出版社, 2014. |
| 5 | OhH, NamH, ParkS. Adaptive threshold blanker in an impulsive noise environment[J]. IEEE Transactions on Electromagnetic Compatibility, 2014, 56(5): 1045-1052. |
| 6 | OhH, NamH. Design and performance analysis of nonlinearity preprocessors in an impulsive noise environment[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2017, 66(1): 364-376. |
| 7 | 应文威, 欧勇恒, 蒋宇中, 等. 新型自适应非高斯接收机设计[J]. 吉林大学学报: 工学版, 2013, 43(6): 1685-1689. |
| YingWen-wei, Yong-hengOu, JiangYu-zhong, et al. New adaptive receiver for channels with non-gaussian noise[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Engineering and Technology Edition), 2013, 43(6): 1685-1689. | |
| 8 | SaaifanK A, HenkelW. Decision boundary evaluation of optimum and suboptimum detectors in class-a interference[J]. IEEE Transactions on Communications, 2013, 61(1): 197-205. |
| 9 | AlsusaE, RabieK M. Dynamic peak-based threshold estimation method for mitigating impulsive noise in power-line communication systems[J]. IEEE Transactions on Power Delivery, 2013, 28(4): 2201-2208. |
| 10 | EppleU, SchnellM. Advanced blanking nonlinearity for mitigating impulsive interference in OFDM systems[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2017, 66(1): 146-158. |
| 11 | BernsteinS L, BurrowsM L, EvansJ E, et al. Long-range communications at extremely low frequencies[J]. Proceedings of the IEEE, 1974, 62(3): 292-312. |
| 12 | VartiainenJ, LehtomakiJ, SaarnisaariH, et al. Interference suppression in several transform domains[C]∥IEEE Military Communications Conference, Atlantic City, NJ, USA, 2005: 2294-2300. |
| 13 | AromaaS, HenttuP, JunttiM. Transform-selective interference suppression algorithm for spread-spectrum communications[J]. IEEE Signal Processing Letters, 2005, 12(1): 49-51. |
| 14 | WangS, AnJ P, WangA H, et al. A minimum value based threshold setting strategy for frequency domain interference excision[J]. IEEE Signal Processing Letters, 2010, 17(5): 501-504. |
| 15 | JiaQ, LiB, MaS, et al. Local variance detection for multi-antenna spectrum sensing[J]. IEEE Communications Letters, 2015, 19(12): 2142-2145. |
| 16 | SaarnisaariH, HenttuP, JunttiM. Iterative multidimensional impulse detectors for communications based on the classical diagnostic methods[J]. IEEE Transactions on Communications, 2005, 53(3): 395-398. |
| 17 | ChenY. Improved energy detector for random signals in gaussian noise[J]. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2010, 9(2): 558-563. |
| 18 | AndrásS, BariczA, SunY. The generalized Marcum Q-Function: an orthogonal polynomial approach[J]. Acta Universitatis Sapientiae Mathematica, 2011, 3(1): 60-76. |
| 19 | RuderS. An overview of gradient descent optimization algorithms[J/OL]. [2016-05-12]. https:∥ |
| No related articles found! |
|
||