吉林大学学报(工学版) ›› 2024, Vol. 54 ›› Issue (1): 251-258.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb.20220280
• 通信与控制工程 • 上一篇
基于弱监督迁移网络的3D人体关节点识别
- 1.重庆大学 光电技术教育部重点实验室,重庆 400044
2.重庆警察学院 基础教研部,重庆 401331
3D human joint point recognition based on weakly supervised migration network
Zhi-yong SUN1( ),Hong-you LI2,Jun-yong YE1(
),Hong-you LI2,Jun-yong YE1( )
)
- 1.Key Laboratory of Optoelectronic Technology of the Ministry of Education,Chongqing University,Chongqing 400044,China
2.Department of Basic Education,Chongqing Police College,Chongqing 401331,China
摘要:
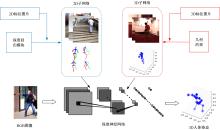
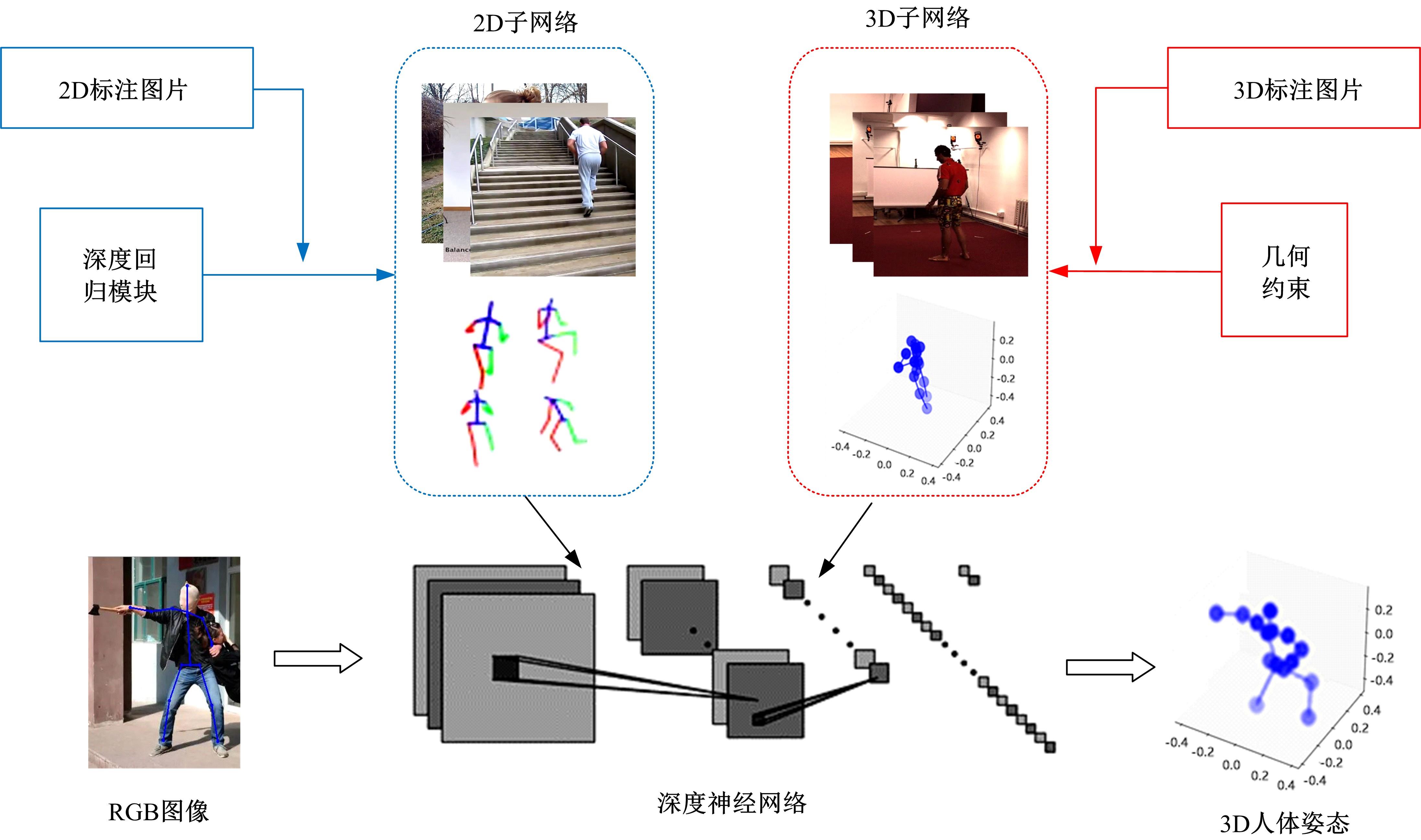
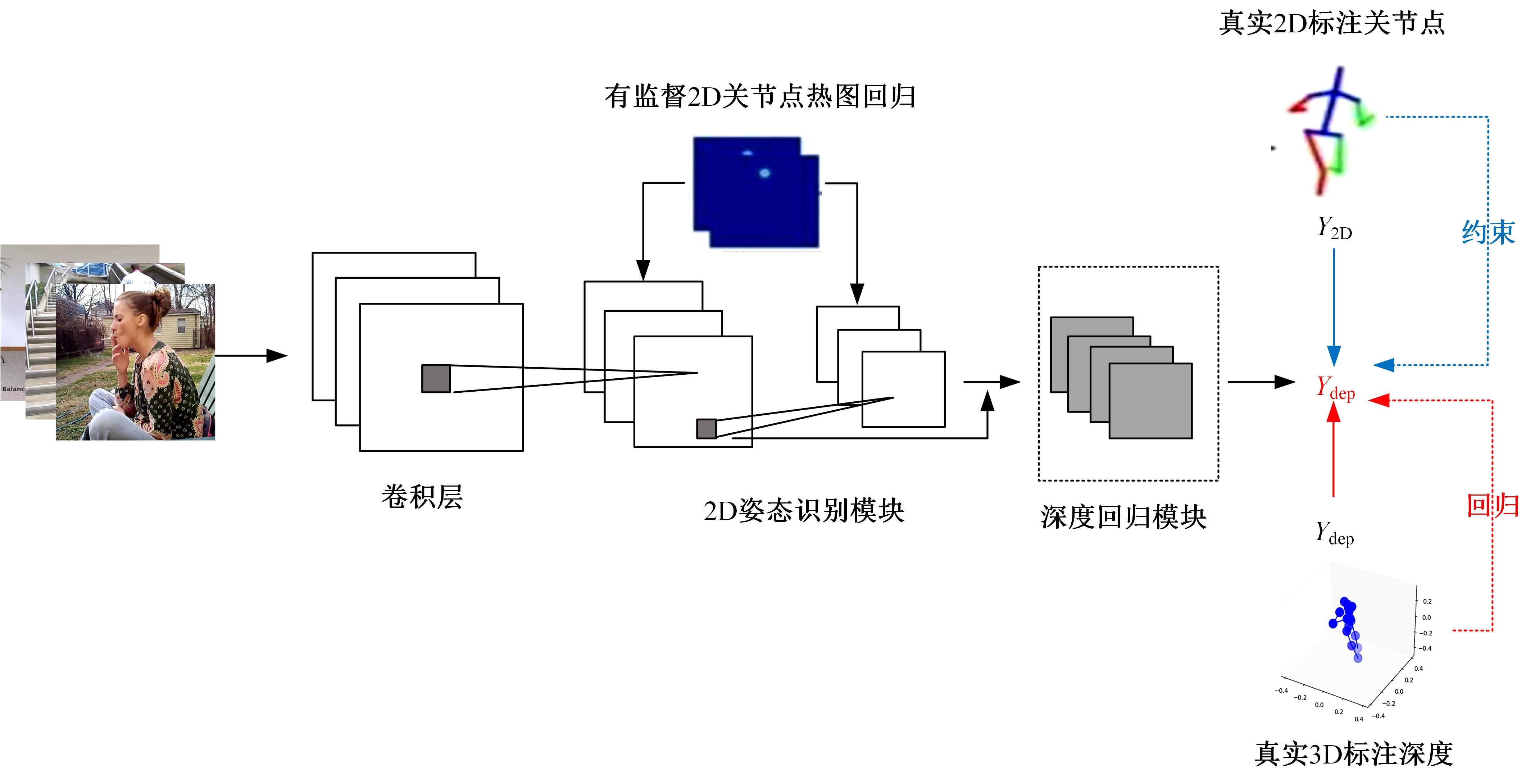
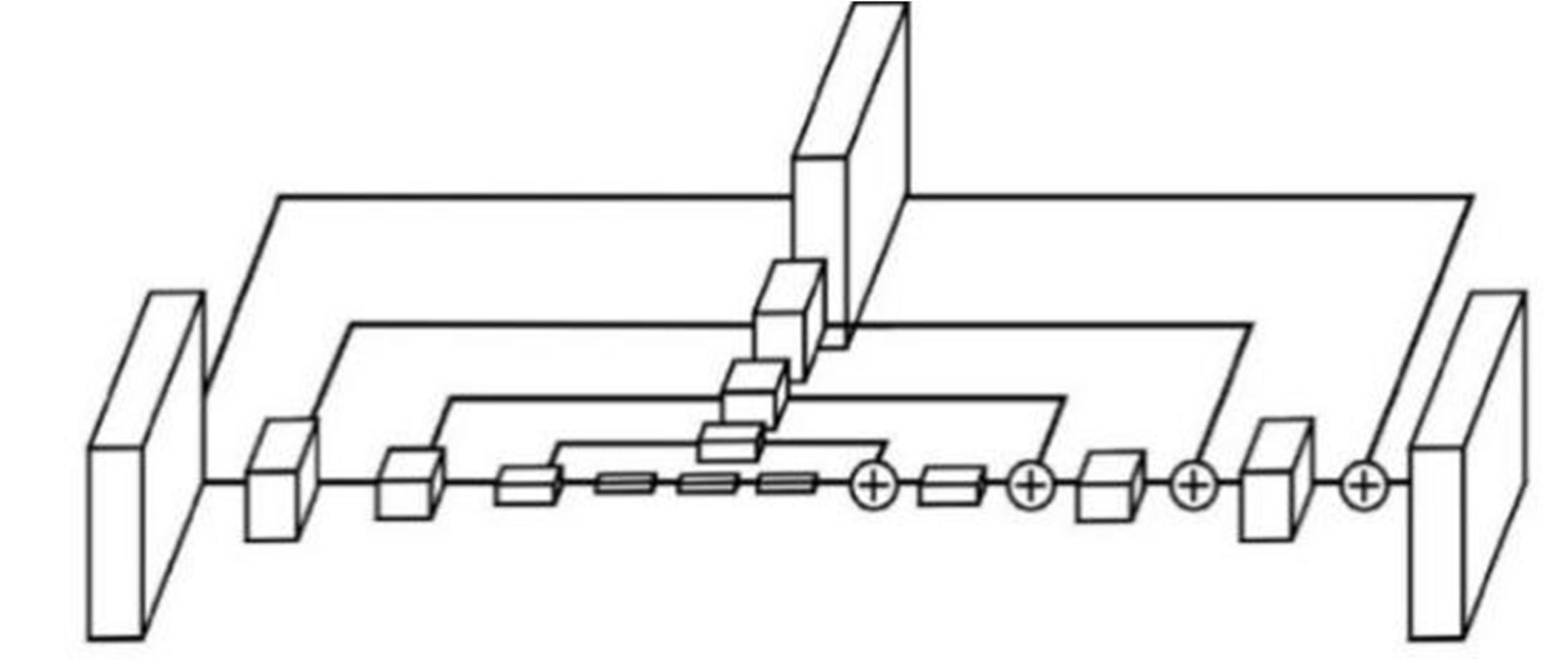
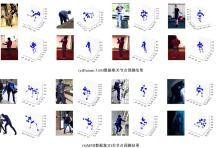
针对2D图像缺少深度信息,行为姿态空间结构信息不完备的问题,提出一种基于弱监督迁移网络的3D人体关节点识别方法。首先,提出一种用于真实图像的端到端3D人体姿态估计框架,使用2D与3D混合标签图像对深度神经网络进行训练,在2D人体姿态识别子网络中,添加深度回归模块对2D人体姿态识别子网络进行改进,解决3D人体姿态识别出现的深度歧义性问题;其次,在3D人体姿态识别子网络中,引入3D几何约束对人体姿态识别进行规范化操作,针对无真实深度标签的情况,可更好地学习深度特征,有效解决存在遮挡情况的人体姿态识别问题。在Human 3.6M和MPII数据集中关节点预测平均误差低于其他方法,具有更好的3D人体姿态识别效果。
中图分类号:
- TP391
| 1 | Insafutdinov E, Pishchulin L, Andres B, et al. DeeperCut: a deeper, stronger, and faster multi-person pose estimation model[J/OL].[2016-12-10]. |
| 2 | Bulat A, Tzimiropoulos G. Human pose estimation via convolutional part heat map regression[C]∥The 14th European Conference on Computer Vision, Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2016: 717-732. |
| 3 | Chu X, Yang W, Ouyang W, et al. Multi-context attention for human pose estimation[C]∥Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, USA, 2017: 1831-1840. |
| 4 | Newell A, Yang K, Deng J. Stacked hourglass networks for human pose estimation[C]∥The 14th European Conference Computer Vision, Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2016: 483-499. |
| 5 | Ionescu C, Papava D, Olaru V, et al. Human3.6M: large scale datasets and predictive methods for 3D human sensing in natural environments[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis & Machine Intelligence, 2014, 36(7): 1325-1339. |
| 6 | Sigal L, Balan A O, Black M J. Humaneva: synchronized video and motion capture dataset and baseline algorithm for evaluation of articulated human motion[J]. International Journal of Computer Vision, 2010, 87(1/2): 4-27. |
| 7 | Zhou X, Sun X, Zhang W, et al. Deep kinematic pose regression[C]∥The 14th European Conference Computer Vision, Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2016: 186-201. |
| 8 | Li S, Chan A B. 3D human pose estimation from monocular images with deep convolutional neural network[C]∥The 12th Asian Conference on Computer Vision, Singapore, 2014: 332-347. |
| 9 | Bogo F, Kanazawa A, Lassner C, et al. Keep it SMPL: automatic estimation of 3D human pose and shape from a single image[C]∥The 14th European Conference, Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2016: 561-578. |
| 10 | Chen C H, Ramanan D. 3D human pose estimation= 2d pose estimation+ matching[C]∥Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, USA,2017: 7035-7043. |
| 11 | Tome D, Russell C, Agapito L. Lifting from the deep: convolutional 3D pose estimation from a single image[C]∥Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, USA, 2017: 2500-2509. |
| 12 | Wu J, Xue T, Lim J J, et al. Single image 3D interpreter network[C]∥The 14th European Conference, Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2016: 365-382. |
| 13 | Yasin H, Iqbal U, Kruger B, et al. A dual-source approach for 3D pose estimation from a single image[C]∥Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, USA, 2016: 4948-4956. |
| 14 | Zhou X, Zhu M, Leonardos S, et al. Sparseness meets deepness: 3D human pose estimation from monocular video[C]∥Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, USA, 2016: 4966-4975. |
| 15 | Wei S E, Ramakrishna V, Kanade T, et al. Convolutional pose machines[C]∥Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, USA, 2016: 4724-4732. |
| 16 | Akhter I, Black M J. Pose-conditioned joint angle limits for 3D human pose reconstruction[C]∥Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Boston, USA, 2015: 1446-1455. |
| 17 | Ramakrishna V, Kanade T, Sheikh Y. Reconstructing 3D human pose from 2D image landmarks[C]∥The 12th European Conference on Computer Vision, Florence, Italy, 2012: 573-586. |
| 18 | Zhou X, Leonardos S, Hu X, et al. 3D shape estimation from 2D landmarks: a convex relaxation approach[C]∥Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Boston, USA, 2015: 4447-4455. |
| 19 | Wei S E, Ramakrishna V, Kanade T, et al. Convolutional pose machines[C]∥Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, USA, 2016: 4724-4732. |
| 20 | Tome D, Russell C, Agapito L. Lifting from the deep: Convolutional 3D pose estimation from a single image[C]∥Proceedings of the IEEE Conference On Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, USA, 2017: 2500-2509. |
| 21 | Zhou X, Zhu M, Leonardos S, et al. Sparseness meets deepness: 3d human pose estimation from monocular video[C]∥Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, USA, 2016: 4966-4975. |
| 22 | Zhang Z, Hu L, Deng X, et al. Weakly supervised adversarial learning for 3D human pose estimation from point clouds[J]. IEEE Transactions on Visualization and Computer Graphics, 2020, 26(5): 1851-1859. |
| 23 | Hoffman J, Wang D, Yu F, et al. FCNs in the wild: pixel-level adversarial and constraint-based adaptation[J/OL]. [2016-12-10]. |
| 24 | Zhou X, Zhu M, Pavlakos G, et al. Monocap: monocular human motion capture using a CNN coupled with a geometric prior[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2018, 41(4): 901-914. |
| 25 | Mehta D, Rhodin H, Casas D, et al. Monocular 3D human pose estimation using transfer learning and improved CNN supervision[J/OL]. [2016-12-10]. |
| 26 | Andriluka M, Pishchulin L, Gehler P,et al.Human pose estimation: new benchmark and state of the art analysis[C]∥Computer Vision and Pattern Recognitio,Columbus,USA,2014. |
| [1] | 朱凌,王秋成. 空间几何约束下新能源汽车驱动系统协调控制方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(7): 1509-1514. |
| [2] | 李文辉, 孙明玉, 许光星, 曹春红. 基于二部图模型的欠、过约束几何约束系统的识别和处理[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2017, 47(5): 1583-1590. |
| [3] | 李文辉, 孙明玉, 曹春红. 几何约束求解的扩展C-树分解法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2017, 47(4): 1273-1279. |
| [4] | 易荣庆,李文辉,袁华,王铎,郭武 . 几何约束多解问题[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2008, 38(04): 871-875. |
|
||