吉林大学学报(工学版) ›› 2024, Vol. 54 ›› Issue (6): 1730-1737.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb.20221067
• 交通运输工程·土木工程 • 上一篇
高强格栅桩-网地基荷载传递桩-土应力特性
- 1.中南大学 土木工程学院,长沙 410075
2.中交机电工程局有限公司,北京 100088
3.黄淮学院 建筑工程学院,驻马店 463000
4.高速铁路建造技术国家工程实验室,长沙 410075
Stress features of piles-soils in load transfer of high-strength grid pile-net foundation
Gen-she YU1,2( ),Yong-hui SHANG3(
),Yong-hui SHANG3( ),Lin-rong XU1,4
),Lin-rong XU1,4
- 1.School of Civil Engineering,Central South University,Changsha 410075,China
2.CCCC Mechanical and Electrical Engineering Bureau Co. ,Ltd. ,Beijing 100088 China
3.Institute of Architecture and Engineering,Huanghuai University,Zhumadian 463000,China
4.National Engineering Laboratory for High Speed Railway Construction,Changsha 410075,China
摘要:
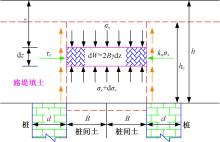
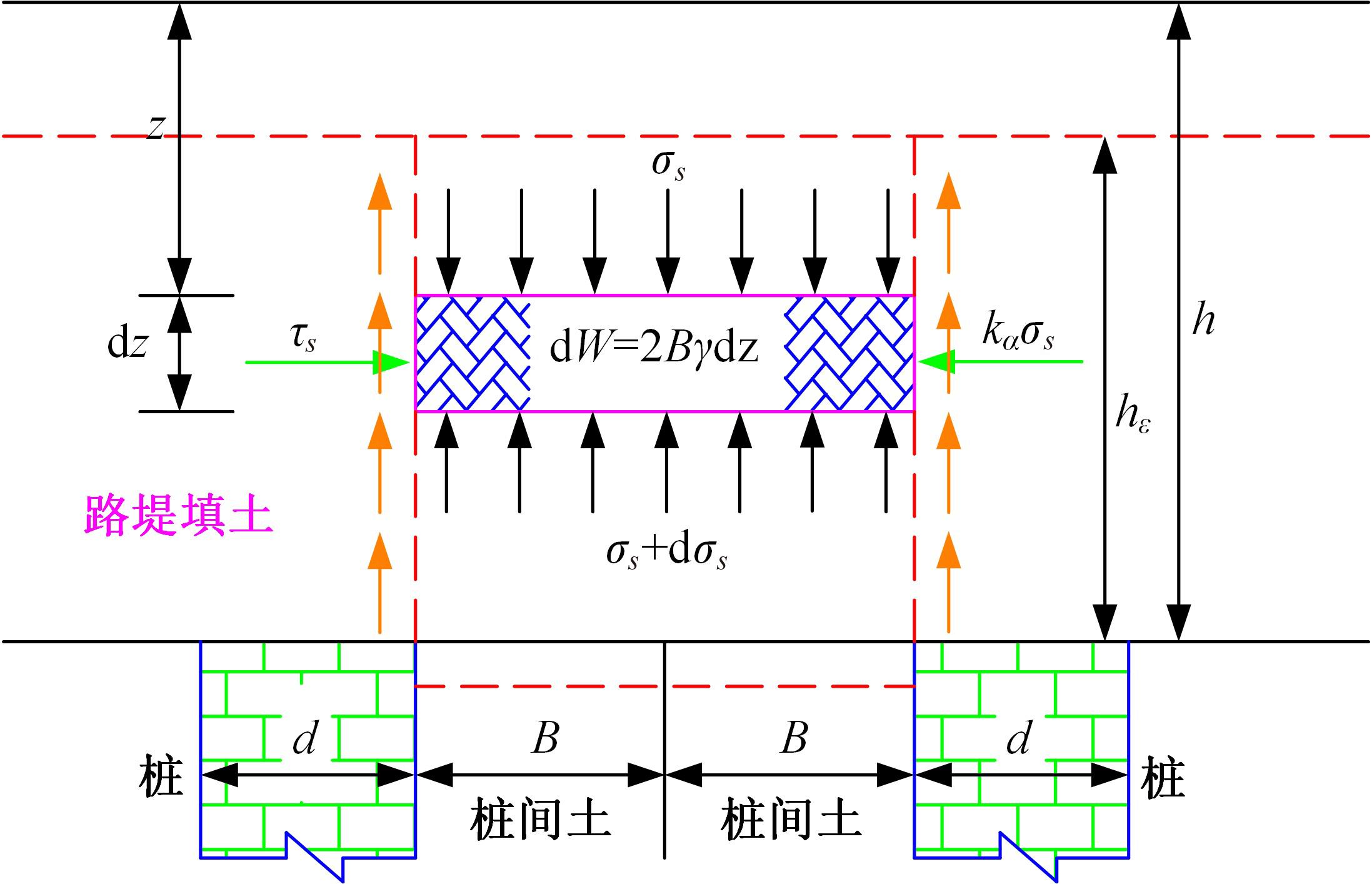
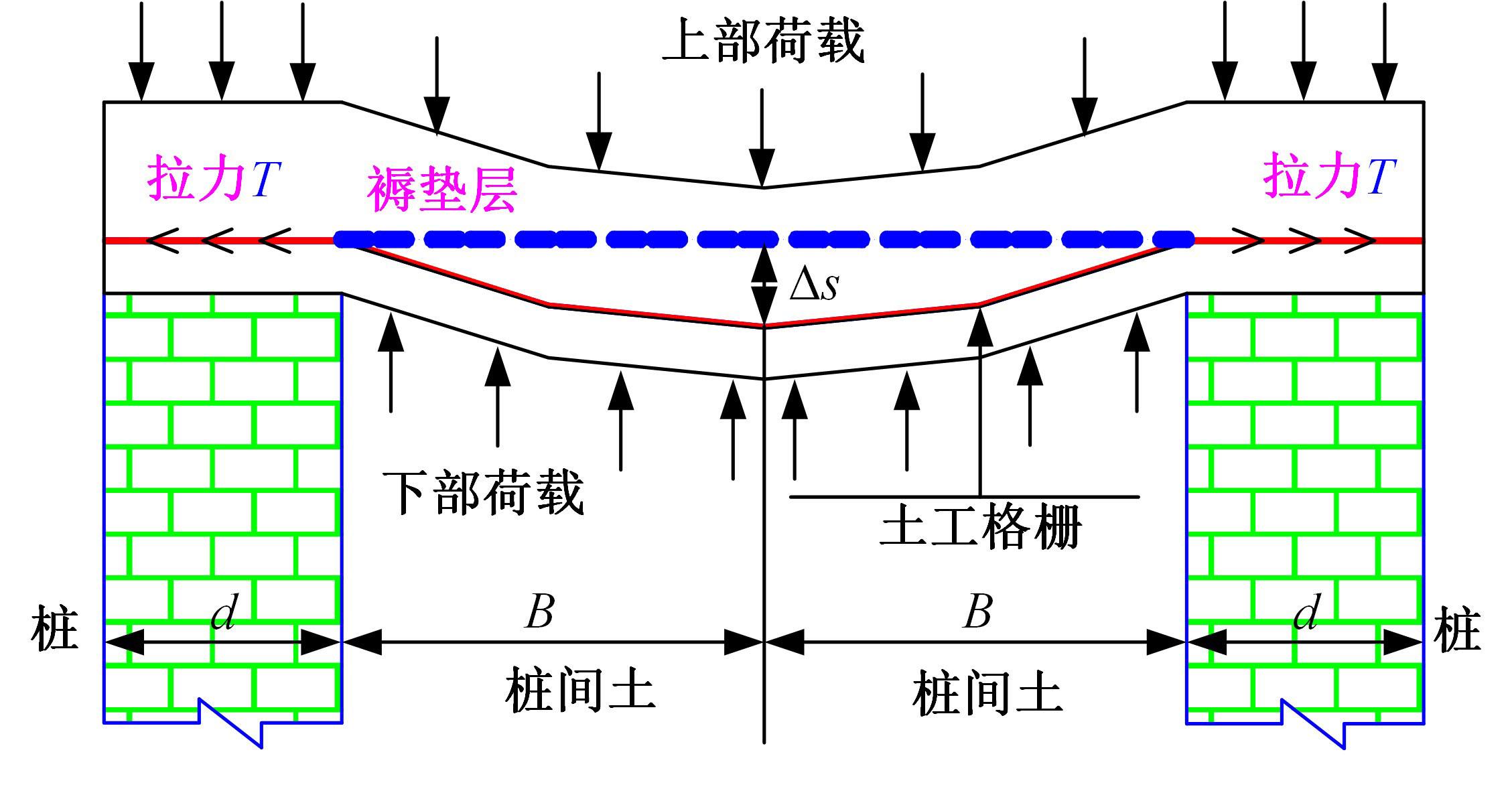
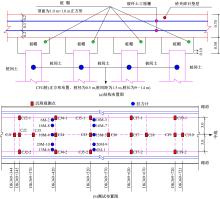
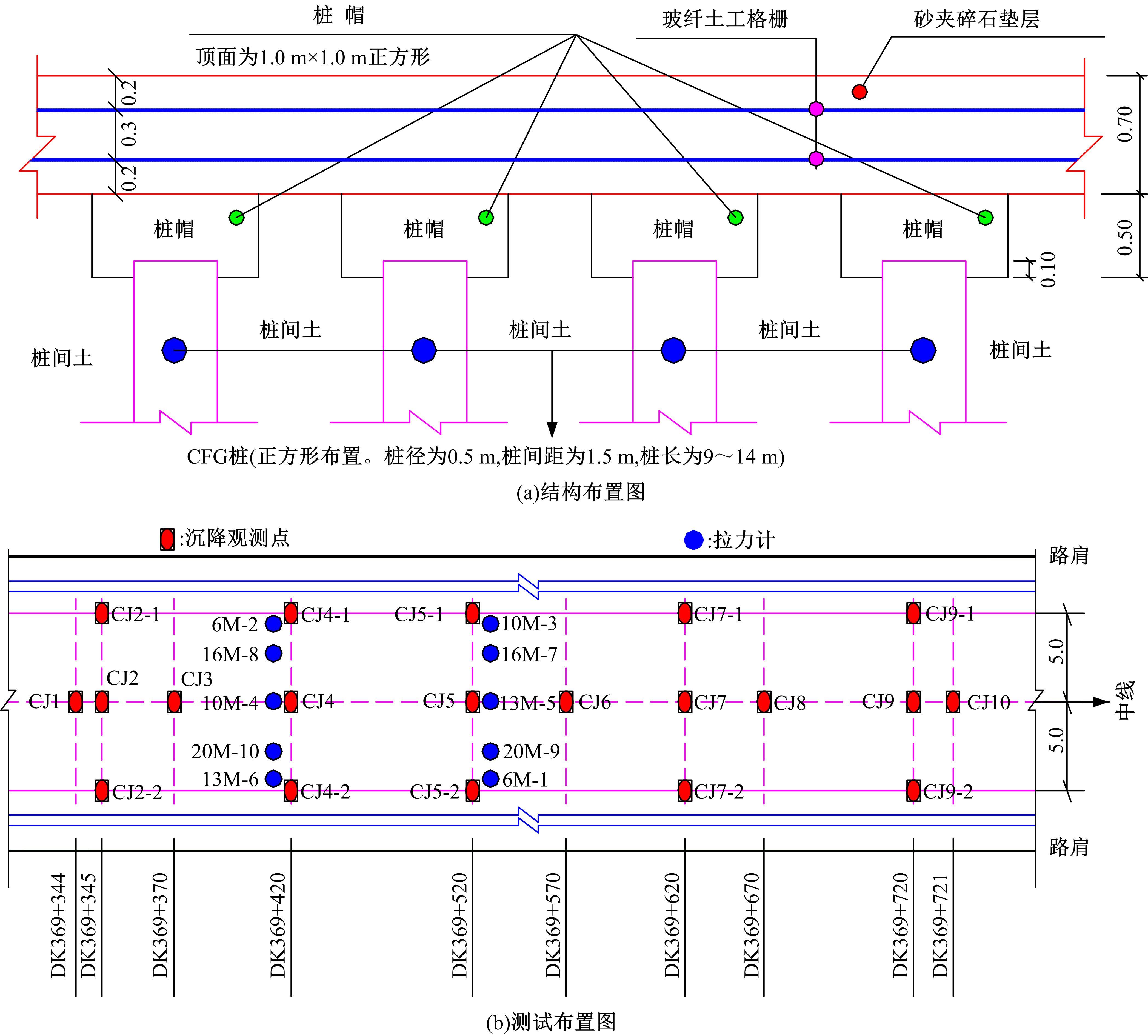
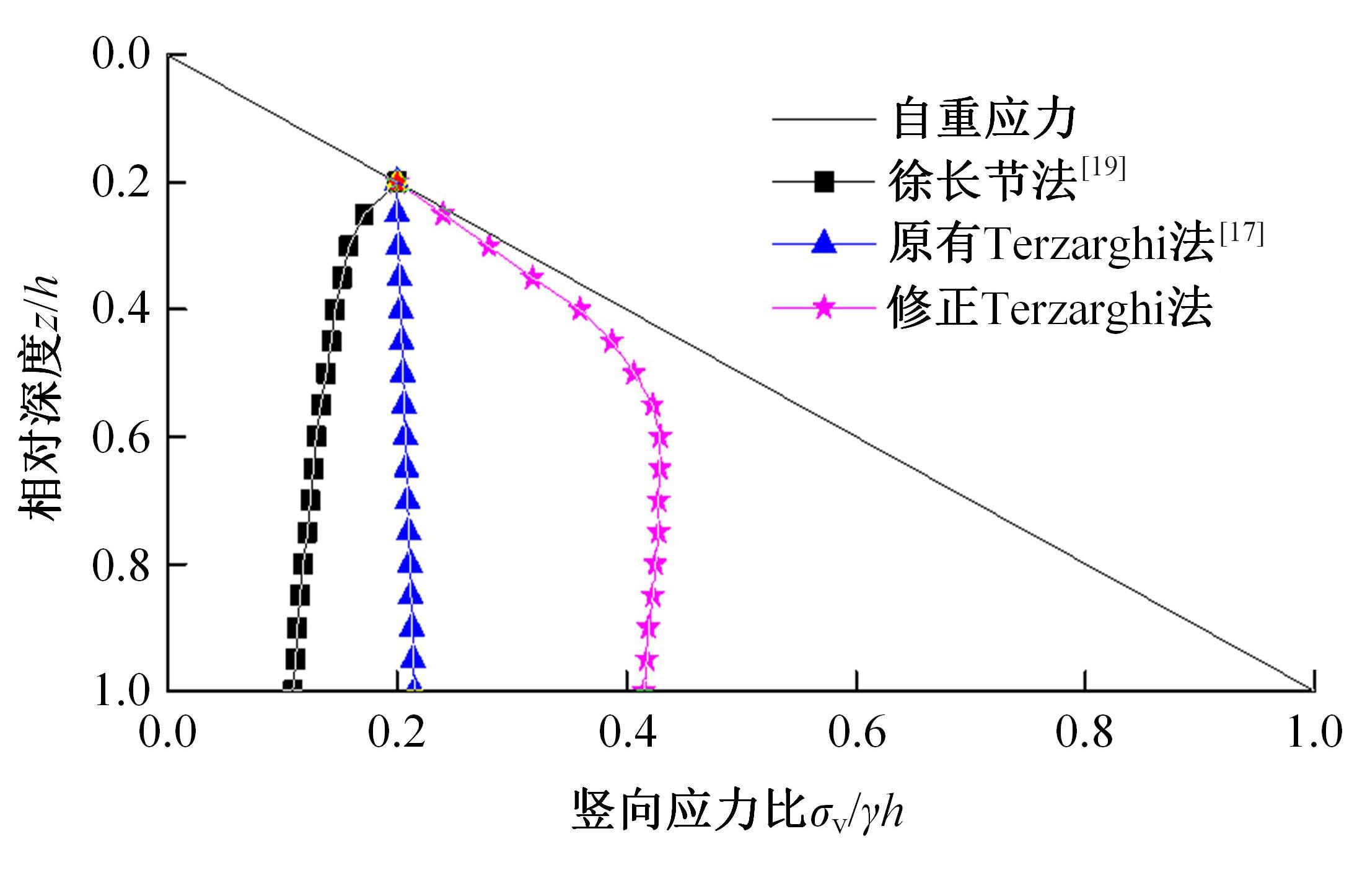
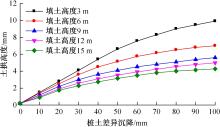
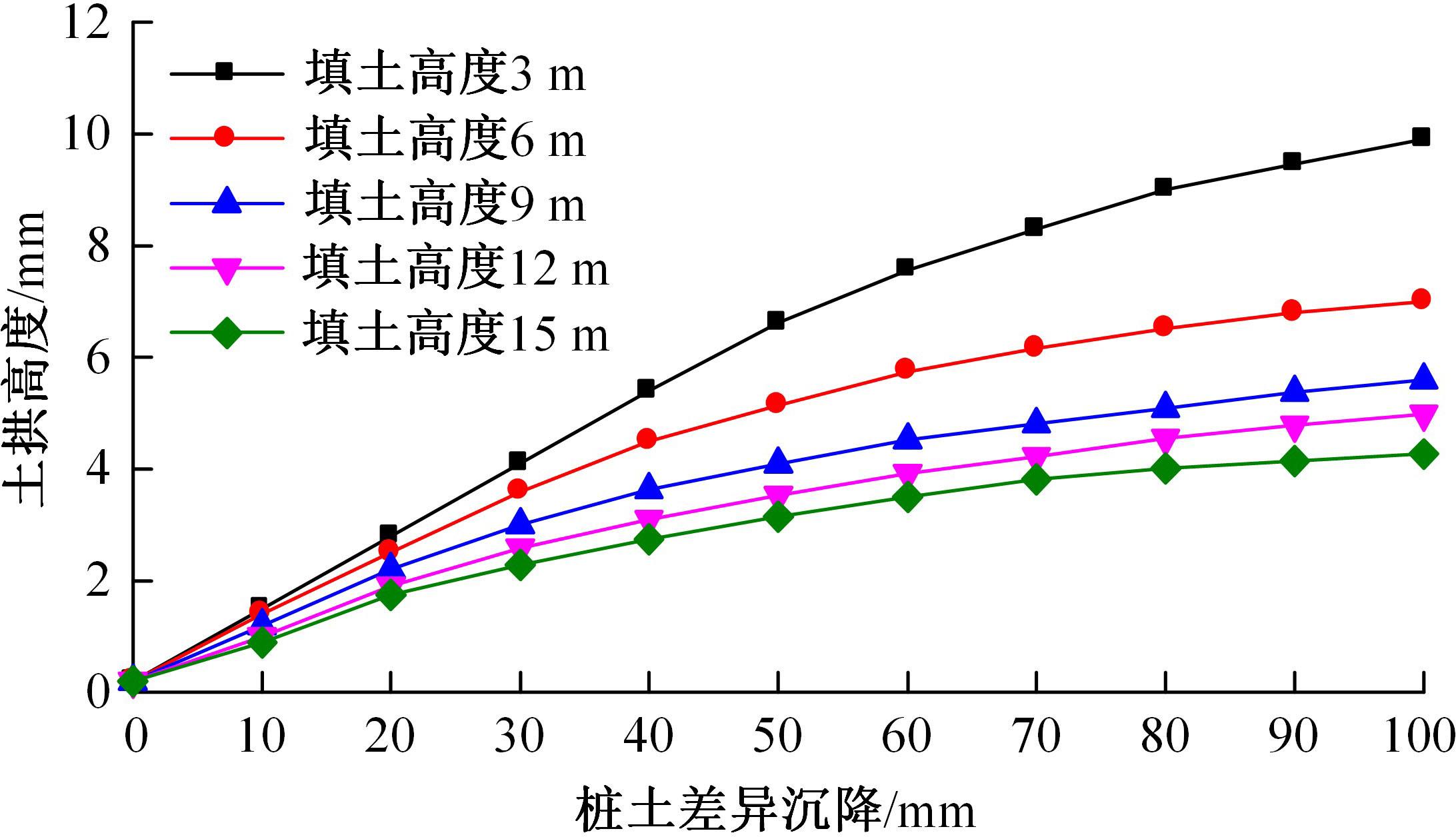
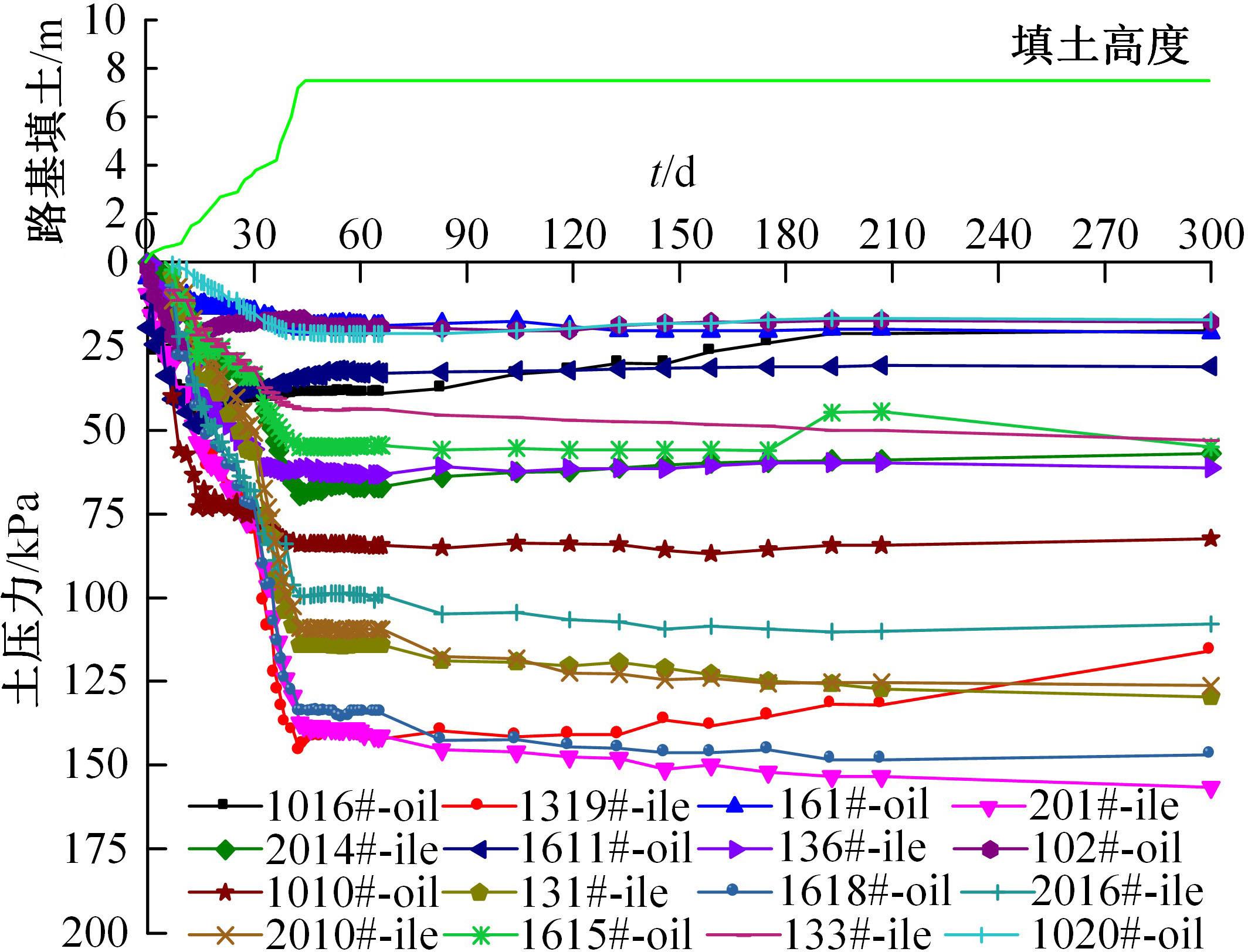
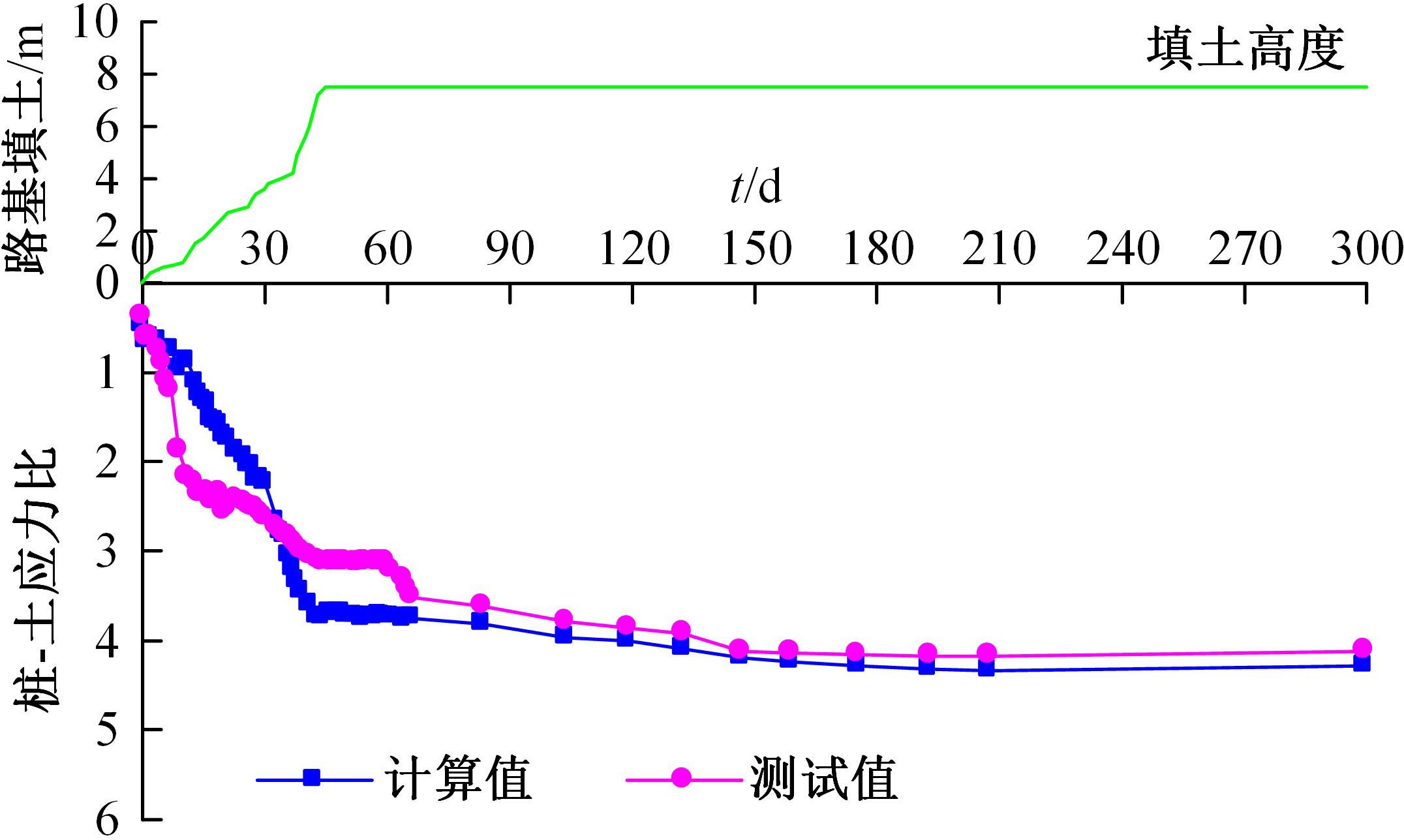
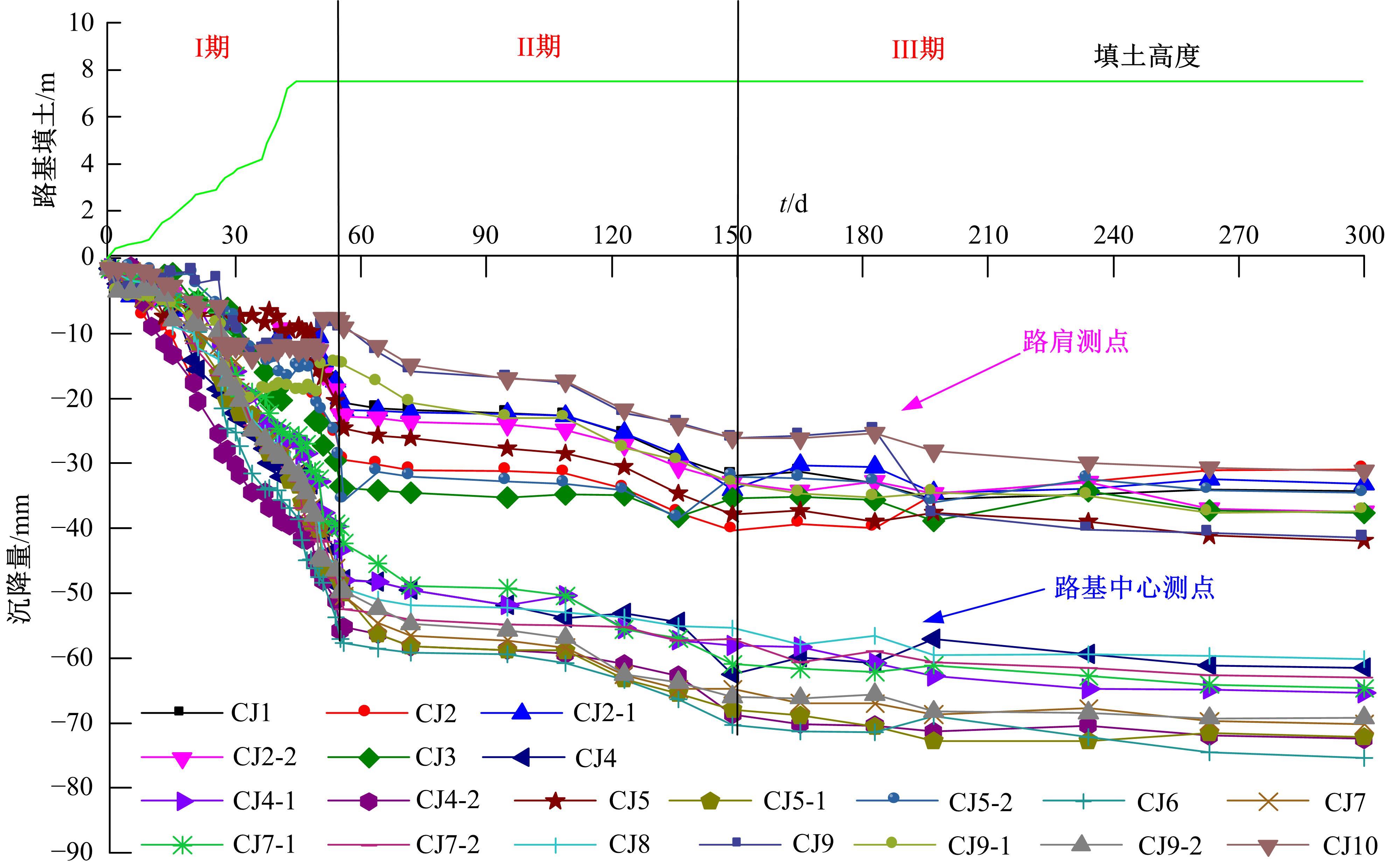
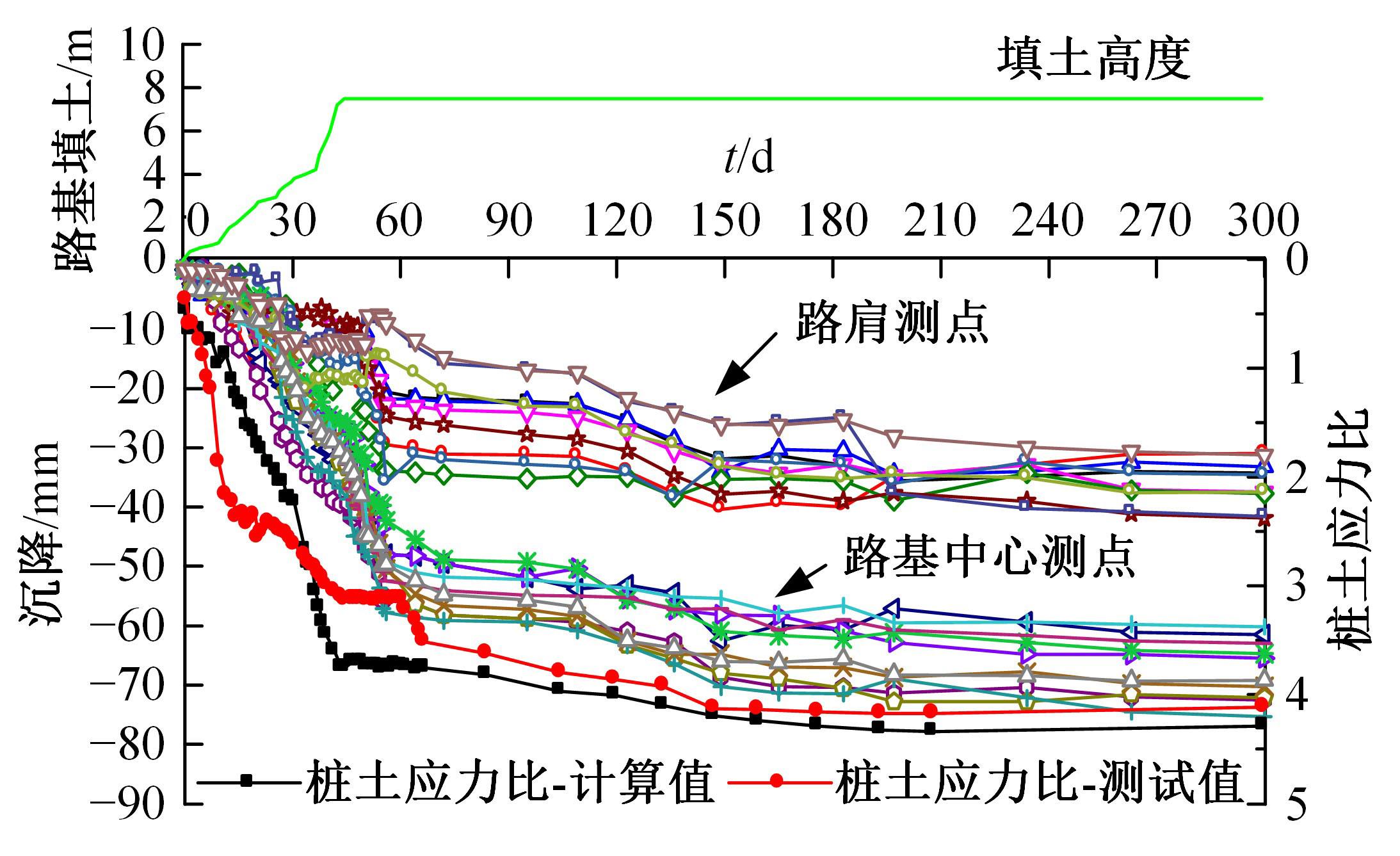
为揭示高强格栅桩-网复合地基上部路堤荷载传递过程中桩-土应力的传递特性,依托某高铁高强格栅桩-网复合地基工程背景,建立了适合较小桩-土差异沉降桩-网复合地基荷载传递特性分析的修正土拱模型,并将理论计算桩-土应力比与现场测试结果进行对比,验证模型的合理性。结果表明:本文修正模型计算的桩-土应力比与现场测试结果吻合度高,验证了模型的可靠性;相同条件下,土拱效应影响范围随填土高度的增加呈变小趋势,拉膜特征值随桩-土差异沉降的增加呈指数增大;高强格栅因具有“拉膜架驭”效应,桩-土协同发挥承载功效在填筑期基本完成,最终稳定时桩-土应力比为3.8~4.0。同时,对比桩-土应力比与沉降随填筑荷载变化规律可知,前者对填筑荷载的敏感性略大于沉降,说明利用桩-土应力比可达到高铁路基控沉效果评估的目的。研究成果可为高速铁路桩-网复合地基精细化建造提供理论依据。
中图分类号:
- TU470
| 1 | 郑俊杰, 付海平, 曹文昭, 等. 桩承式加筋路堤荷载传递效率计算方法研究[J]. 华中科技大学学报: 自然科学版, 2017, 45(8): 64-68, 80. |
| Zheng Jun-jie, Fu Hai-ping, Cao Wen-zhao, et al. Investigation of the calculation method efficacy for geogrid-reinforced pile-supported embankments[J]. Journal of Huazhong University of Science and Technology(Natural Science Edition), 2017, 45(8): 64- 68, 80. | |
| 2 | 张树明, 蒋关鲁, 廖祎来, 等.加固范围及边坡坡率对CFG桩-网复合地基受力变形特性影响分析[J].岩石力学与工程学报, 2019, 38(1): 192-202. |
| Zhang Shu-ming, Jiang Guan-lu, Liao Yi-lai, et al. Effect of the strengthening area and the slope rate on bearing and deforming behaviors of CFG pile-geogrid composite foundations[J]. Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2019, 38(1): 192-202. | |
| 3 | 牛婷婷, 刘汉龙, 丁选明, 等.高铁列车荷载作用下桩网复合地基振动特性模型试验[J]. 岩土力学, 2018, 39(3): 872-880. |
| Niu Ting-ting, Liu Han-long, Ding Xuan-ming, et al. Piled embankment model test on vibration characteristics under high-speed train loads[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2018, 39(3): 872-880. | |
| 4 | 赵明华, 刘猛, 马缤辉, 等.基于弹性地基板理论的桩网复合地基桩土应力比及沉降计算[J]. 中南大学学报: 自然科学版, 2016, 47(6): 2007-2014. |
| Zhao Ming-hua, Liu Meng, Ma Bin-hui, et al. Calculation of pile-soil stress ratio and settlement of pile-net composite foundation based on elastic foundation plate[J]. Journal of Central South University, 2016, 47(6): 2007-2014. | |
| 5 | 吕伟华, 缪林昌, 刘成, 等. 基于系统分析的桩网复合地基荷载效应定量评价模型研究[J]. 岩土工程学报, 2014, 36(12): 2291-2299. |
| Lv Wei-hua, Miao Lin-chang, Liu Cheng, et al. Quantitative evaluation of load effects of pile-net composite foundation based on systems analysis[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 2014, 36(12): 2291-2299. | |
| 6 | 郑俊杰, 罗先国, 付海平, 等. 基于H&R土拱模型的桩承式加筋路堤分析[J]. 华中科技大学学报: 自然科学版, 2019, 47(1): 50-54. |
| Zheng Jun-jie, Luo Xian-guo, Fu Hai-ping, et al. Analysis of geosynthetic-reinforced pile-supported embankment based on H&R soil arching model[J].Journal of Huazhong University of Science and Technology (Natural Science Edition), 2019, 47(1): 50-54. | |
| 7 | Terzaghi K. Theoretical Soil Mechanics[M]. New York: John Wiley & Sons Inc, 1943. |
| 8 | Handy R L. The arch in soil arching[J]. Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 1985, 111(3): 302-318. |
| 9 | Shukla S K, Gaurav S, Sivakugan N. A simplified extension of the conventional theory of arching in soils[J]. International Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 2009, 3(3): 353-359. |
| 10 | Hewlett W J, Randolph M F. Analysis of piled embankments[J].Ground Engineering, 1988, 21: 12-18. |
| 11 | 刘吉福. 路堤下复合地基“三等沉区模型”[J]. 岩土力学, 2007, 28(): 796-802. |
| Liu Ji-fu. Three-equal-settlement-zone model for composite ground under embankment[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2007, 28(Sup.1):796-802. | |
| 12 | 陈昌富, 米汪, 赵湘龙. 考虑高路堤土拱效应层状地基中带帽刚性桩复合地基的承载特性[J]. 中国公路学报, 2016, 29(7): 1-9. |
| Chen Chang-fu, Mi Wang, Zhao Xiang-long. Bearing characteristic of composite foundation reinforced by rigid pile with cap in layered ground considering soil arching effect of high embankment[J]. China Journal of Highway and Transport, 2016, 29(7): 1-9. | |
| 13 | 龚晓南, 邵佳函, 解才, 等. 桩端扩大头尺寸对承载性能影响模型试验[J]. 湖南大学学报: 自然科学版, 2018, 45(11): 102-109. |
| Gong Xiao-nan, Shao Jia-han, Xie Cai, et al. Model test on influence of enlarged head size on bearing capacity of pile end[J]. Journal of Hunan University (Natural Sciences), 2018, 45(11): 102-109. | |
| 14 | 赵明华, 牛浩懿, 刘猛, 等. 柔性基础下碎石桩复合地基桩土应力比及沉降计算[J]. 岩土工程学报, 2017, 39(9): 1549-1556. |
| Zhao Ming-hua, Niu Hao-yi, Liu Meng, et al.Pile-soil stress ratio and settlement of composite ground with gravel piles in flexible foundation[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 2017, 39(9): 1549-1556. | |
| 15 | 周龙翔, 王梦恕, 张顶立, 等. 复合地基土拱效应与桩土应力比研究[J]. 土木工程学报, 2011, 44(1): 93-99. |
| Zhou Long-xiang, Wang Meng-shu, Zhang Ding-li, et al. Study of the soil arching effect and the pile-soil stress ratio of composite ground[J]. China Civil Engineering Journal, 2011, 44(1): 93-99. | |
| 16 | Zhang L, Zhao M, Hu Y, et al. Semi-analytical solutions for geosynthetic-reinforced and pile-supported embank-ment[J]. Computers and Geotechnics, 2012,44(6): 167-175. |
| 17 | Goit C S, Saitoh M, Mylonakis G,et al. Model tests on horizontal pile-to-pile interaction incorporating local non-linearity and resonance effects[J].Soil Dynamics and Earthquake Engineering, 2013, 48(5): 175-192. |
| 18 | Lai Jin-xing, Liu Hou-quan, Fan Hao-bo, et al. Stress analysis of CFG pile composite foundation in consolidating saturated mine tailings dam[J].Advances in Materials Science and Engineering, 2016, 12:1-12. |
| 19 | 徐长节, 梁禄钜, 陈其志,等.考虑松动区内应力分布形式的松动土压力研究[J]. 岩土力学, 2018, 39(6): 1927-1934. |
| Xu Chang-jie, Liang Lu-ju, Chen Qi-zhi, et al. Research on loosening earth pressure considering the patterns of stress distribution in loosening zone[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2018, 39(6): 1927-1934. |
| [1] | 韩笑,凌贤长,田爽,丛晟亦. 高铁有砟轨道路基注浆过程冒浆分析和控制[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(2): 506-515. |
| [2] | 商拥辉,徐林荣,陈钊锋. 高铁刚性桩⁃筏地基的固结特性及影响因素[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(7): 1588-1597. |
| [3] | 苏迎社,杨媛媛. 疏排桩支护结构中土拱荷载传递比分析[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2015, 45(2): 400-405. |
| [4] | 王京, 王殿海, 曲昭伟. 适应长春-吉林高速铁路建设的公路诱增客流量预测方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2010, 40(06): 1518-1522. |
|
||