吉林大学学报(工学版) ›› 2025, Vol. 55 ›› Issue (1): 256-268.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb.20240622
• 交通运输工程·土木工程 • 上一篇
水热耦合变化下衬砌渠道冻胀响应
- 1.宁夏大学 土木与水利工程学院,银川 750021
2.旱区现代农业水资源高效利用教育部工程研究中心,银川 750021
3.宁夏节水灌溉与水资源调控工程技术研究中心,银川 750021
Freezing and expansion response of lined channels under changes in hydrothermal coupling
Yu-dai WANG1( ),Bin WANG1,2,3,Fu-sheng MIAO1(
),Bin WANG1,2,3,Fu-sheng MIAO1( ),Nan MA1
),Nan MA1
- 1.School of Civil and Hydraulic Engineering,Ningxia University,Ningxia 750021,China
2.The Engineering Research Center of the Ministry of Education for Efficient Utilization of Modern Agricultural Water Resources in Arid Areas,Yinchuan 750021,China
3.Ningxia Water?saving irrigation and Water Resource Regulation Engineering Technology Research Center,Yinchuan 750021,China
摘要:
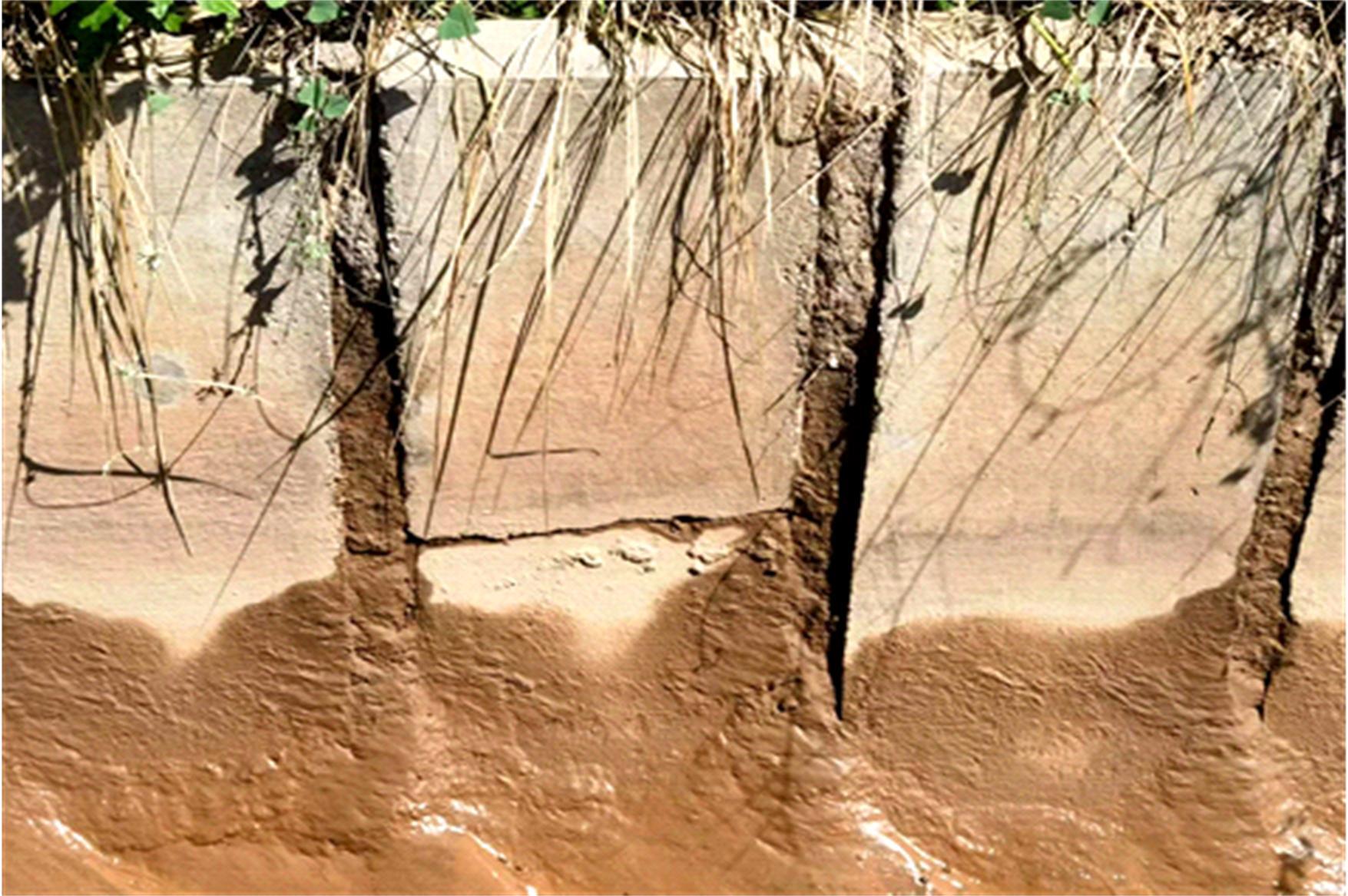
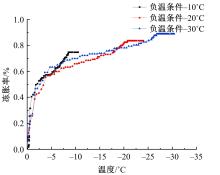
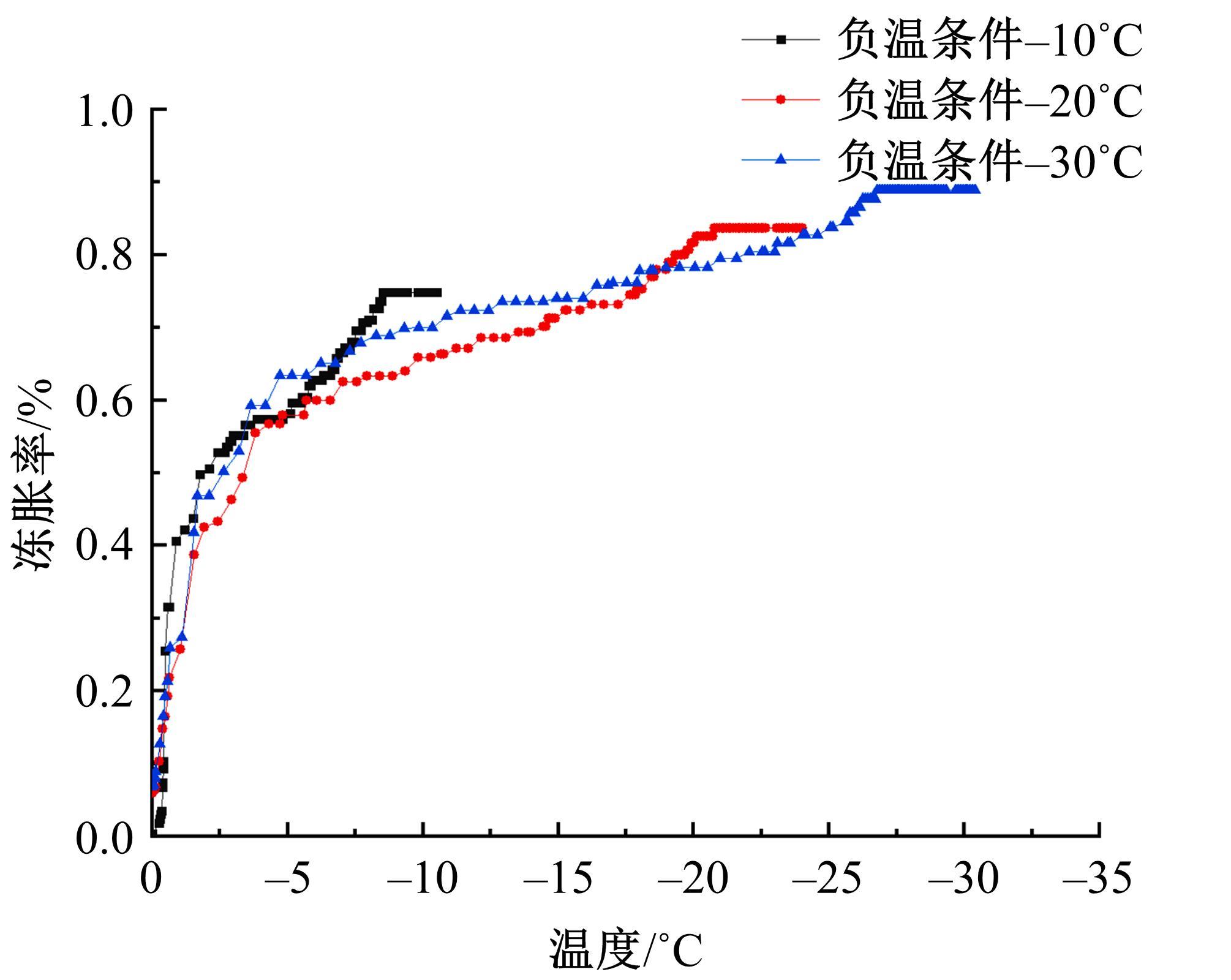
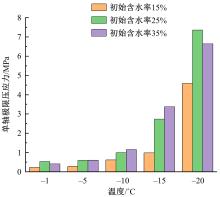
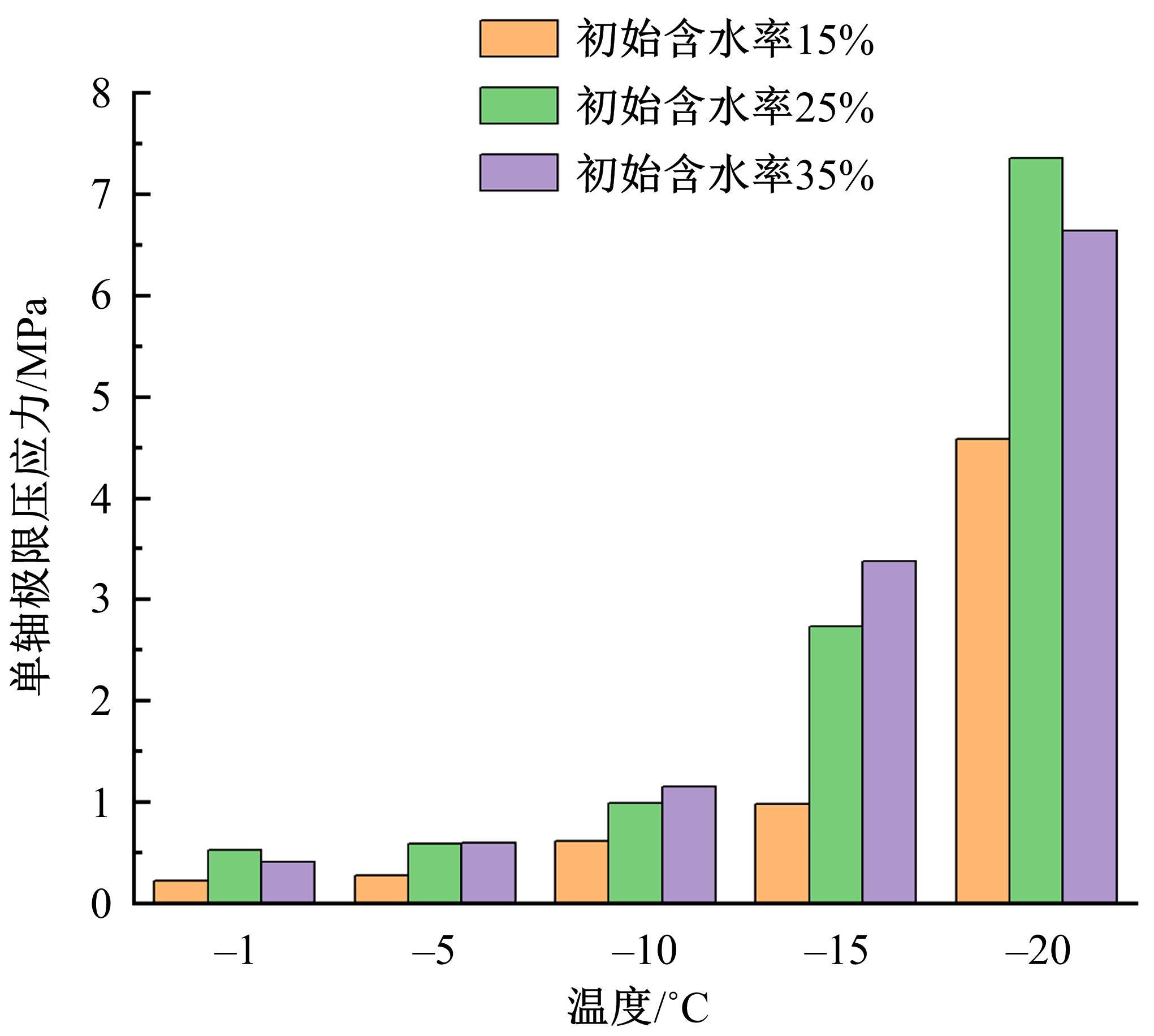
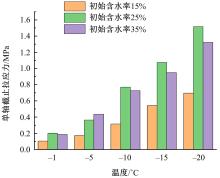
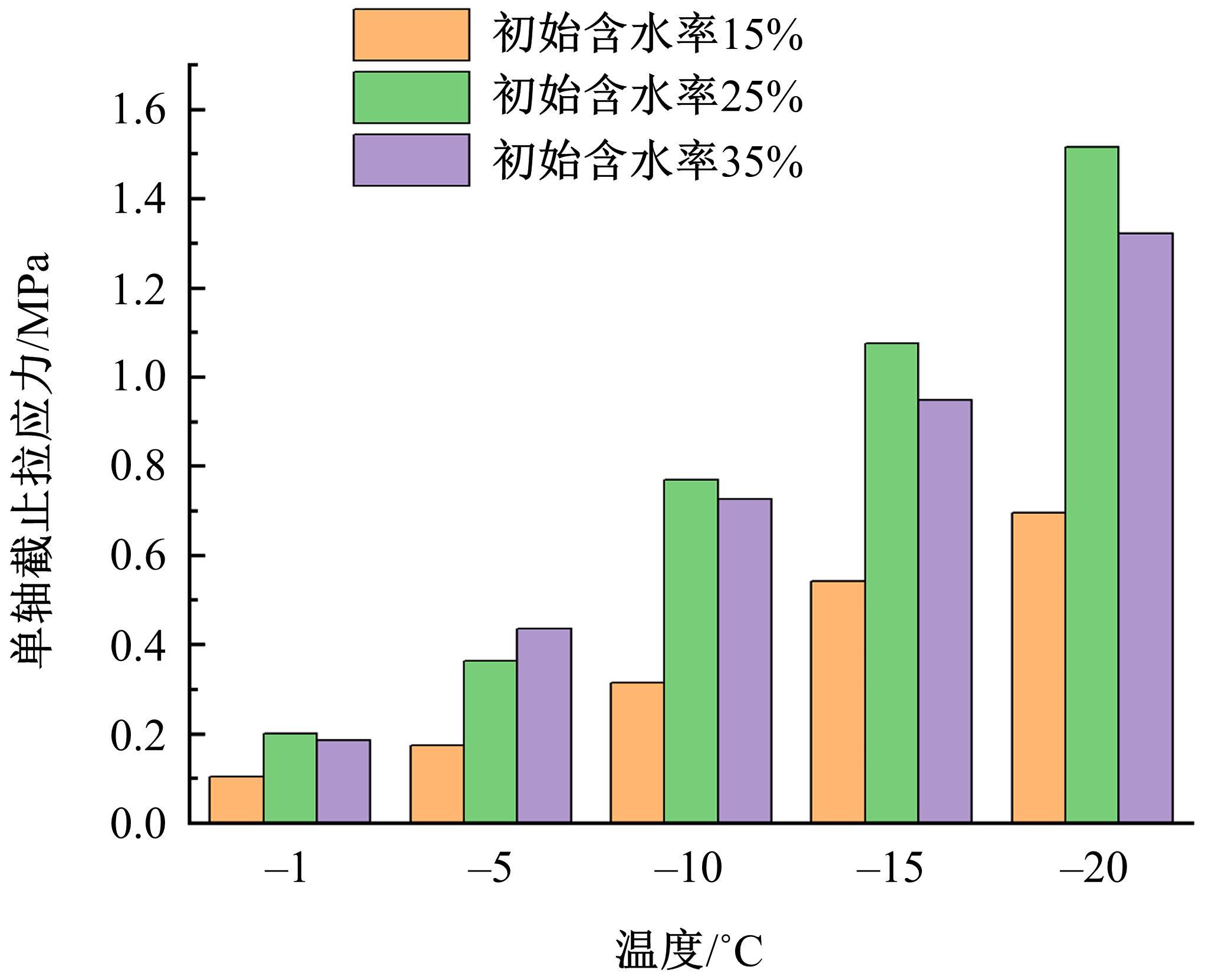
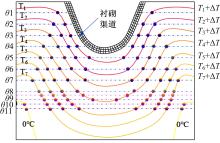
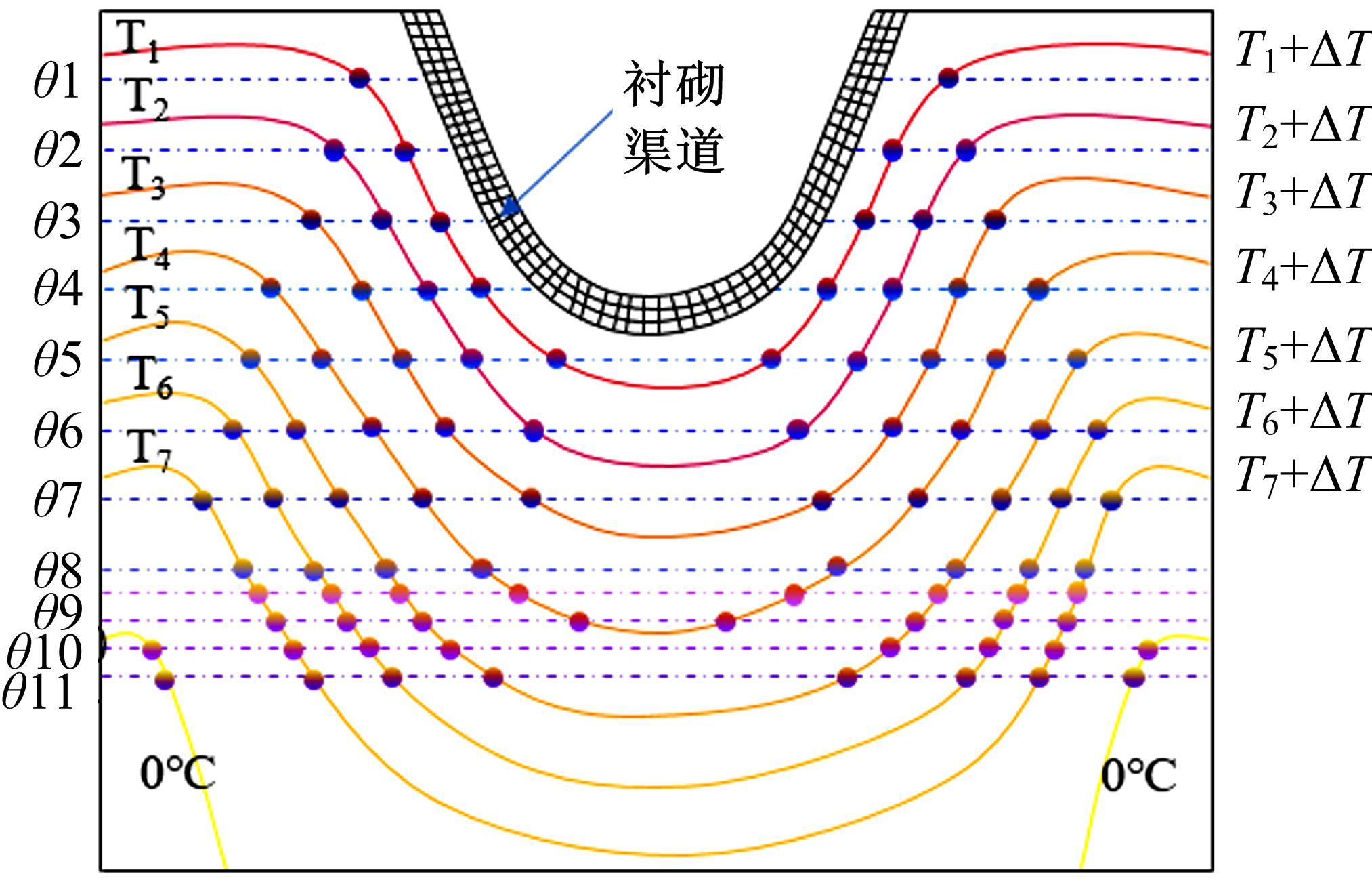
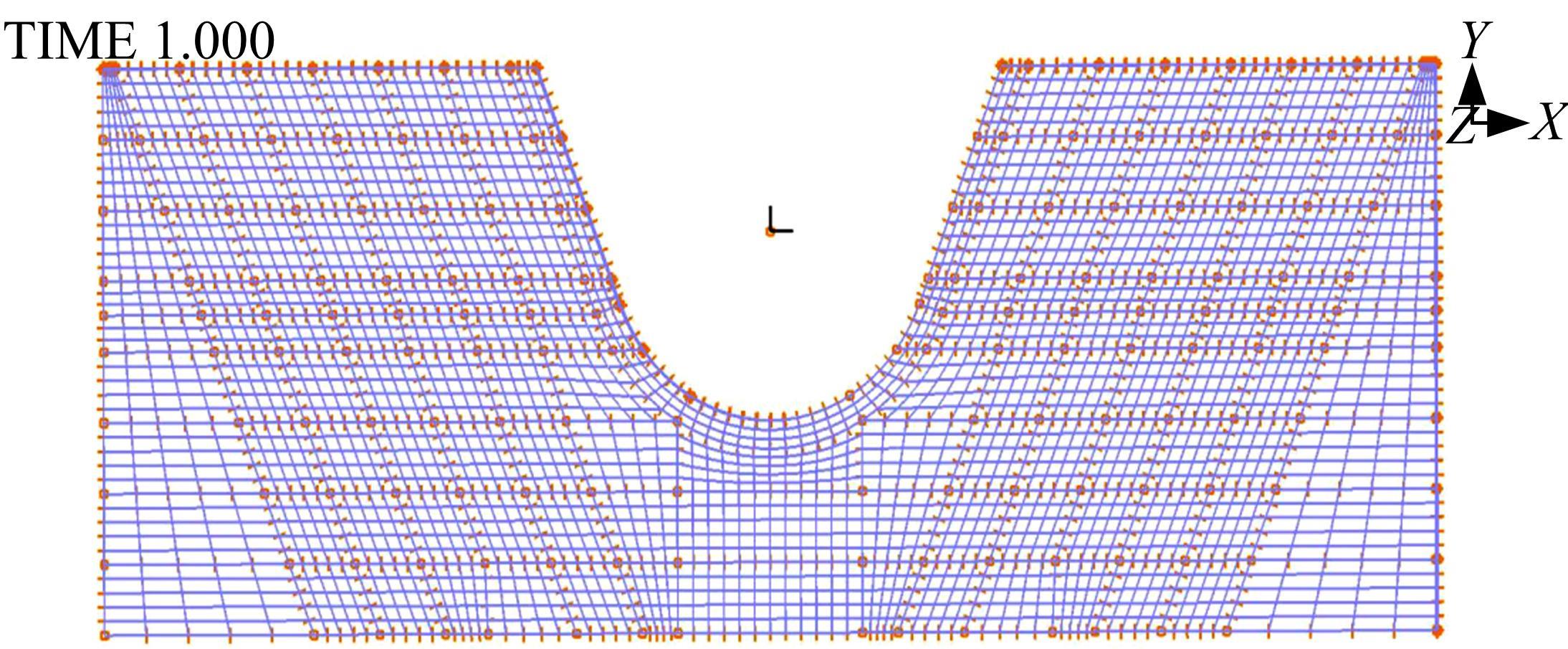
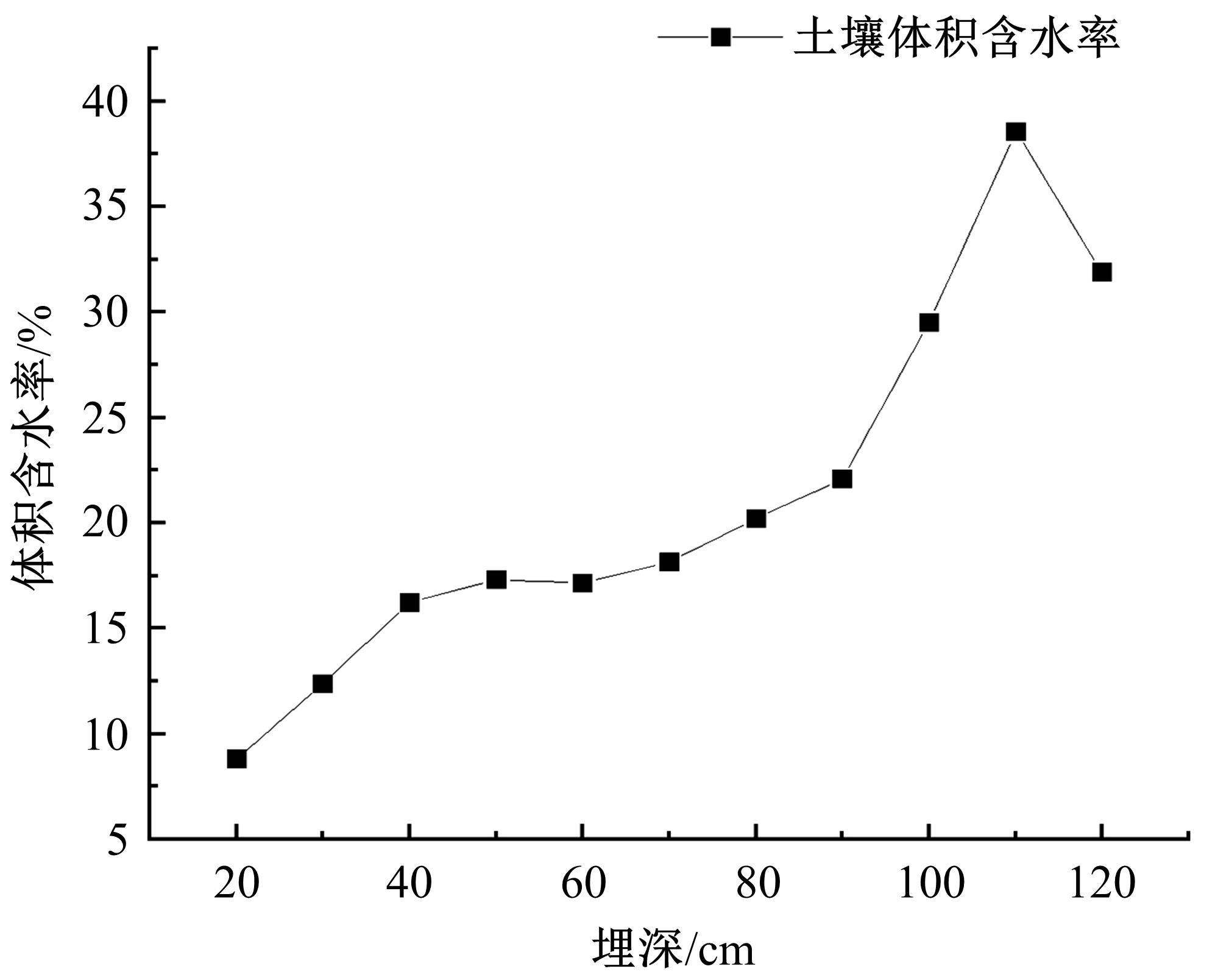
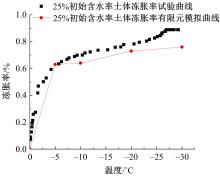
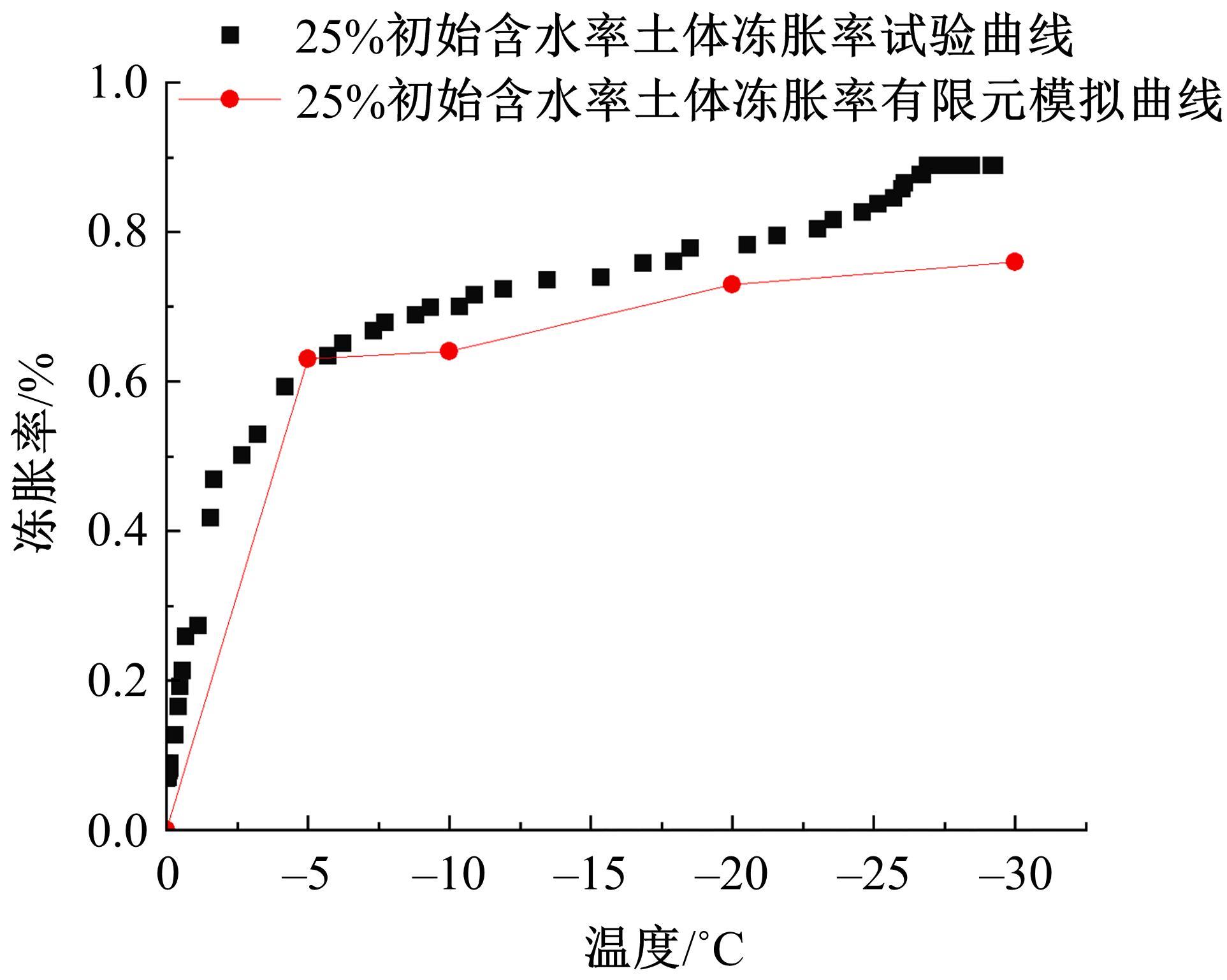
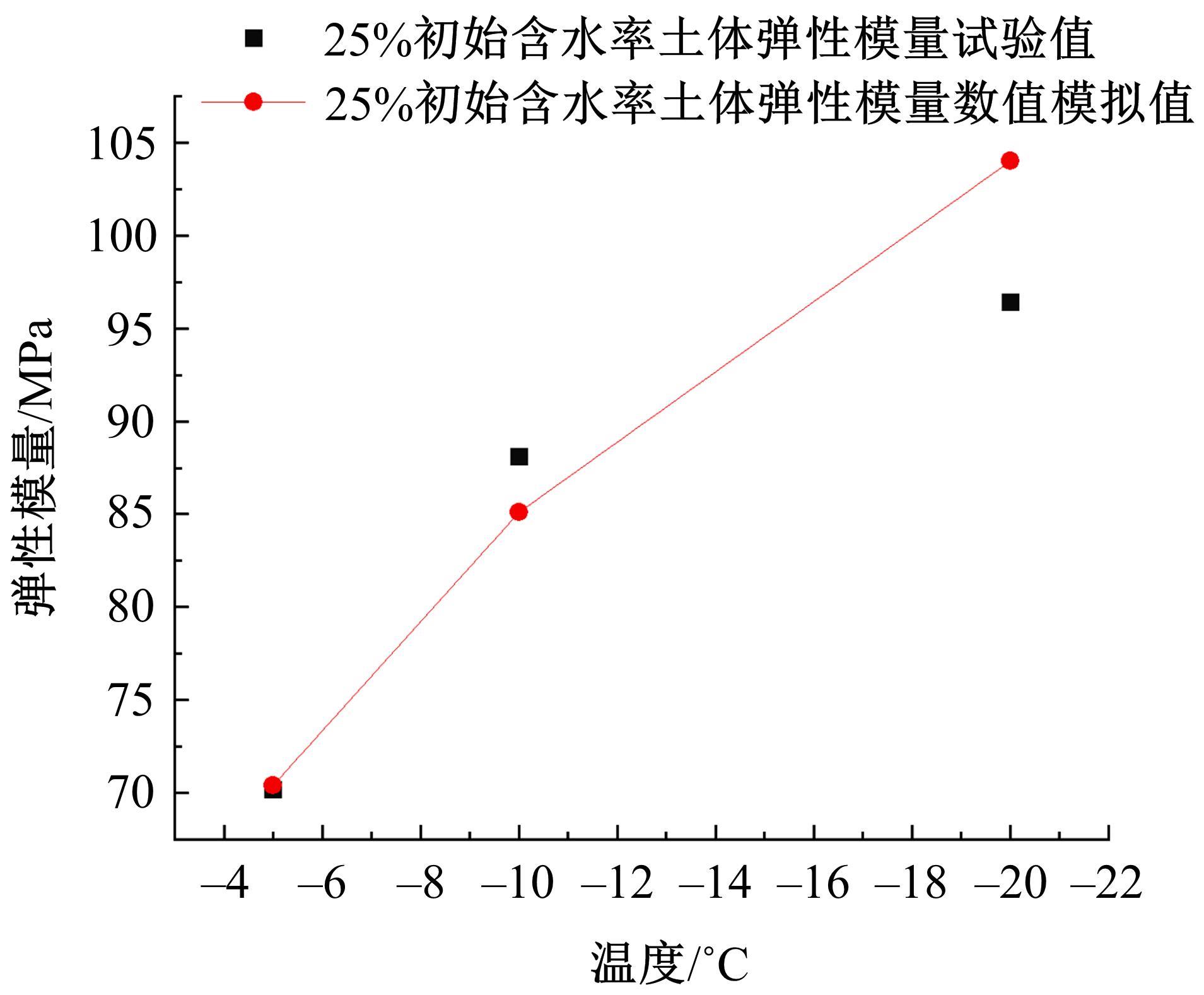
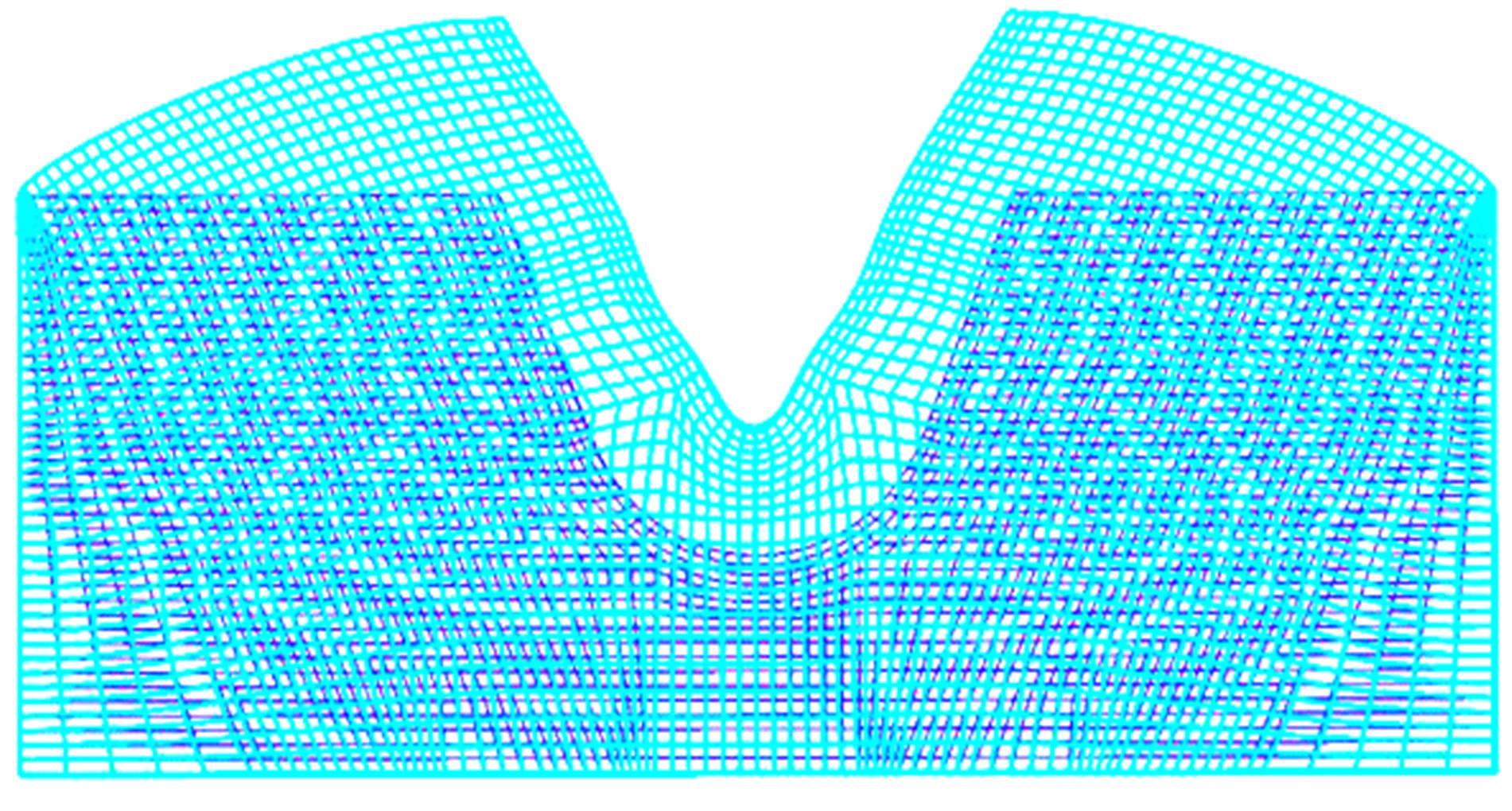
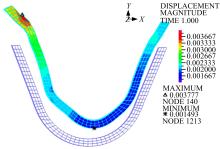
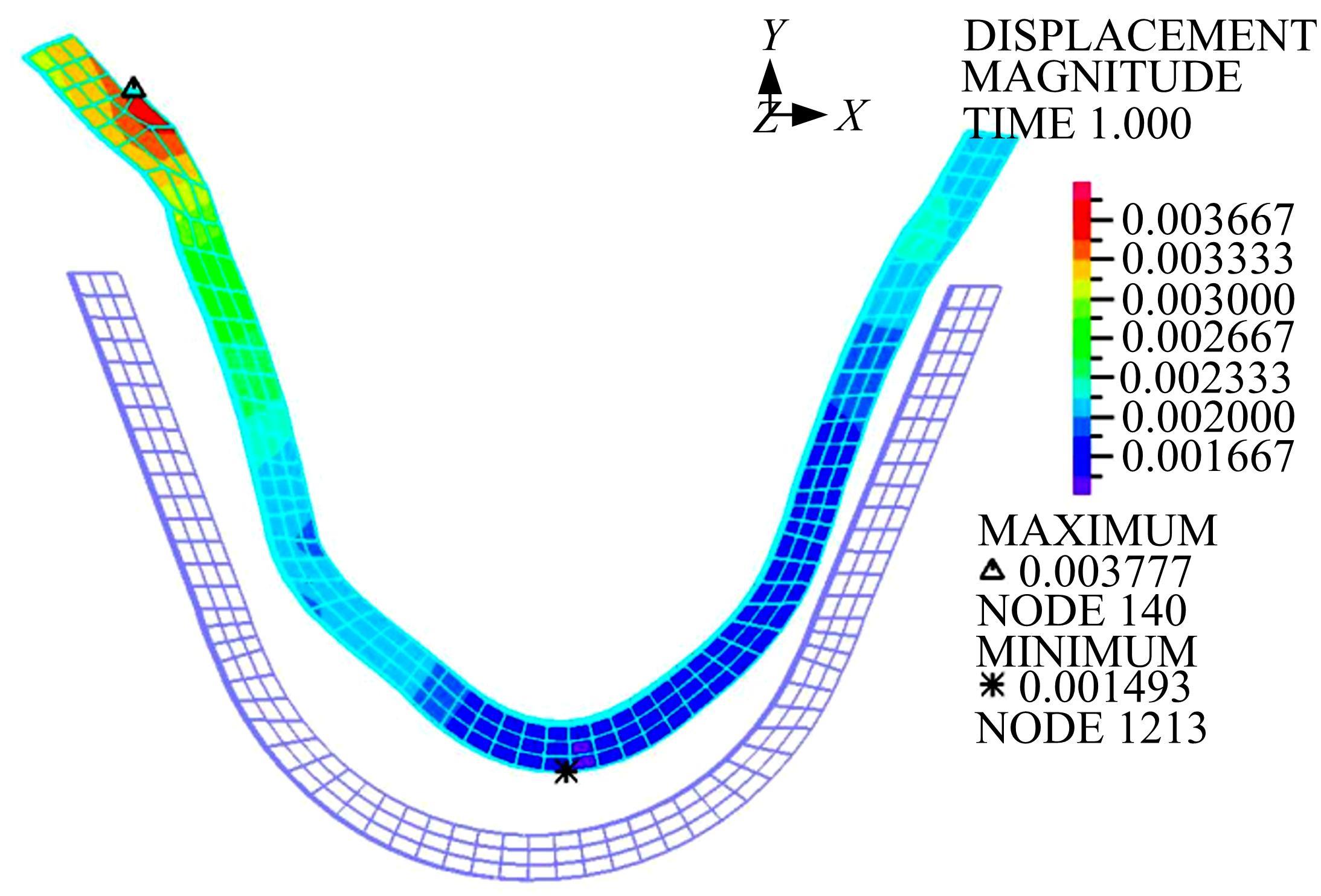
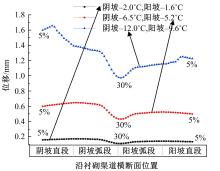
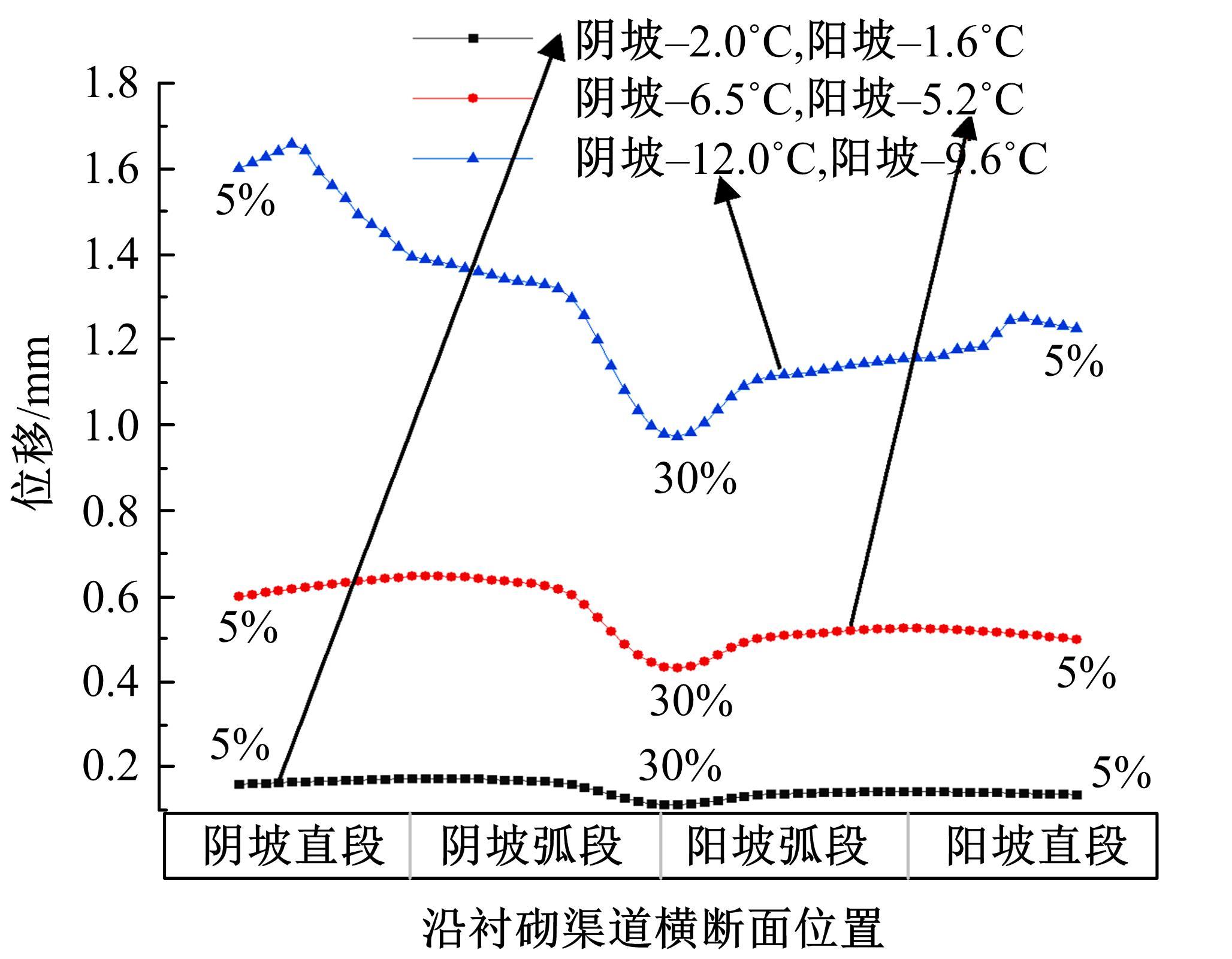
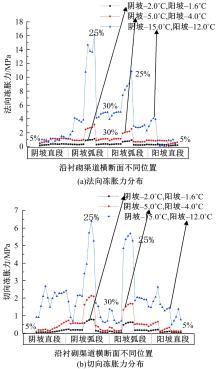
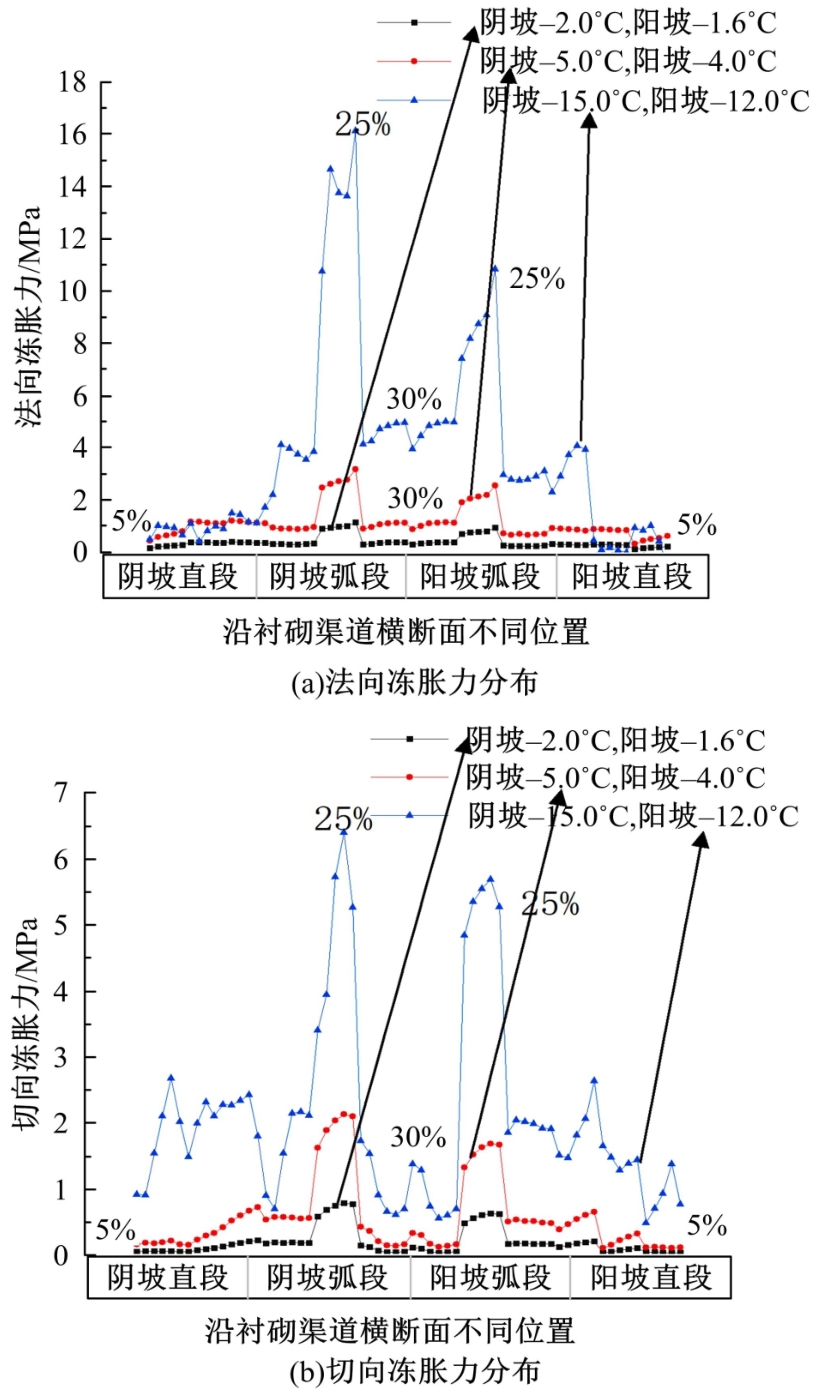
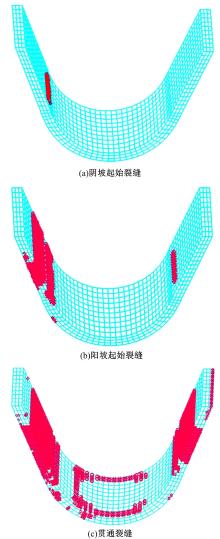
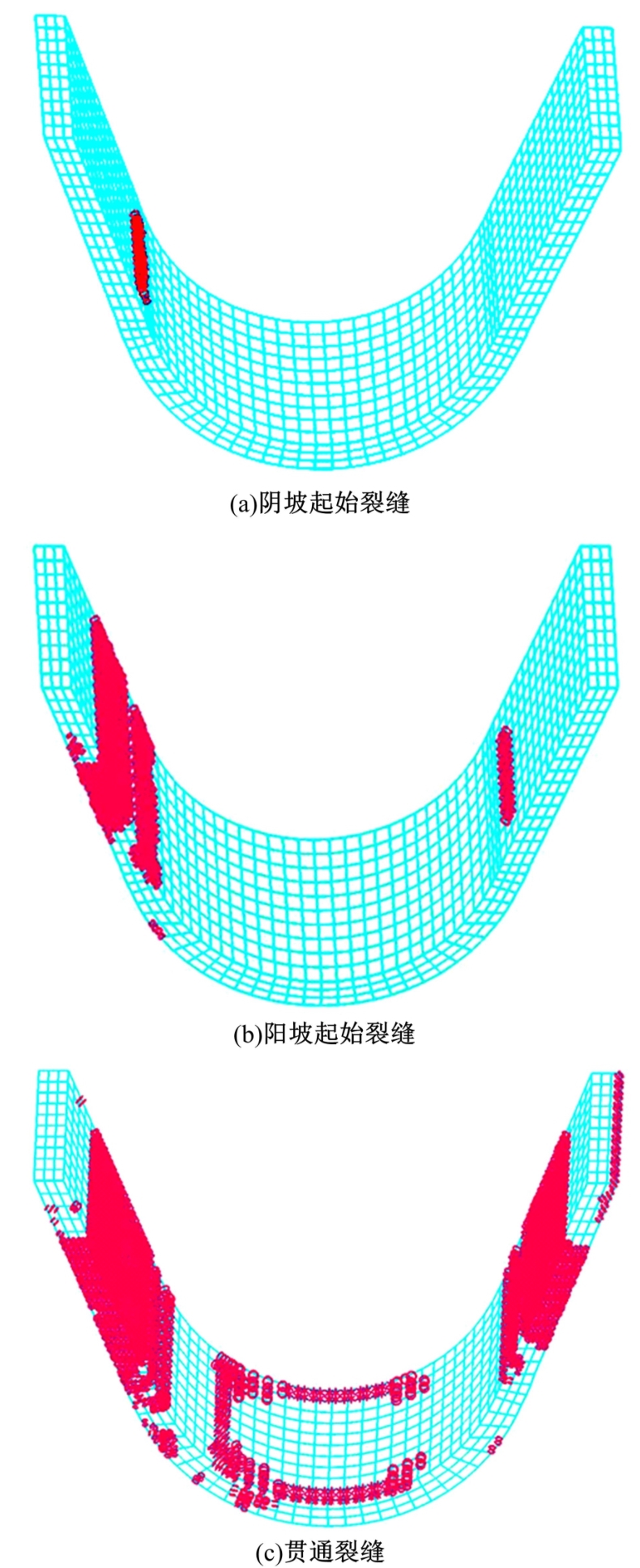
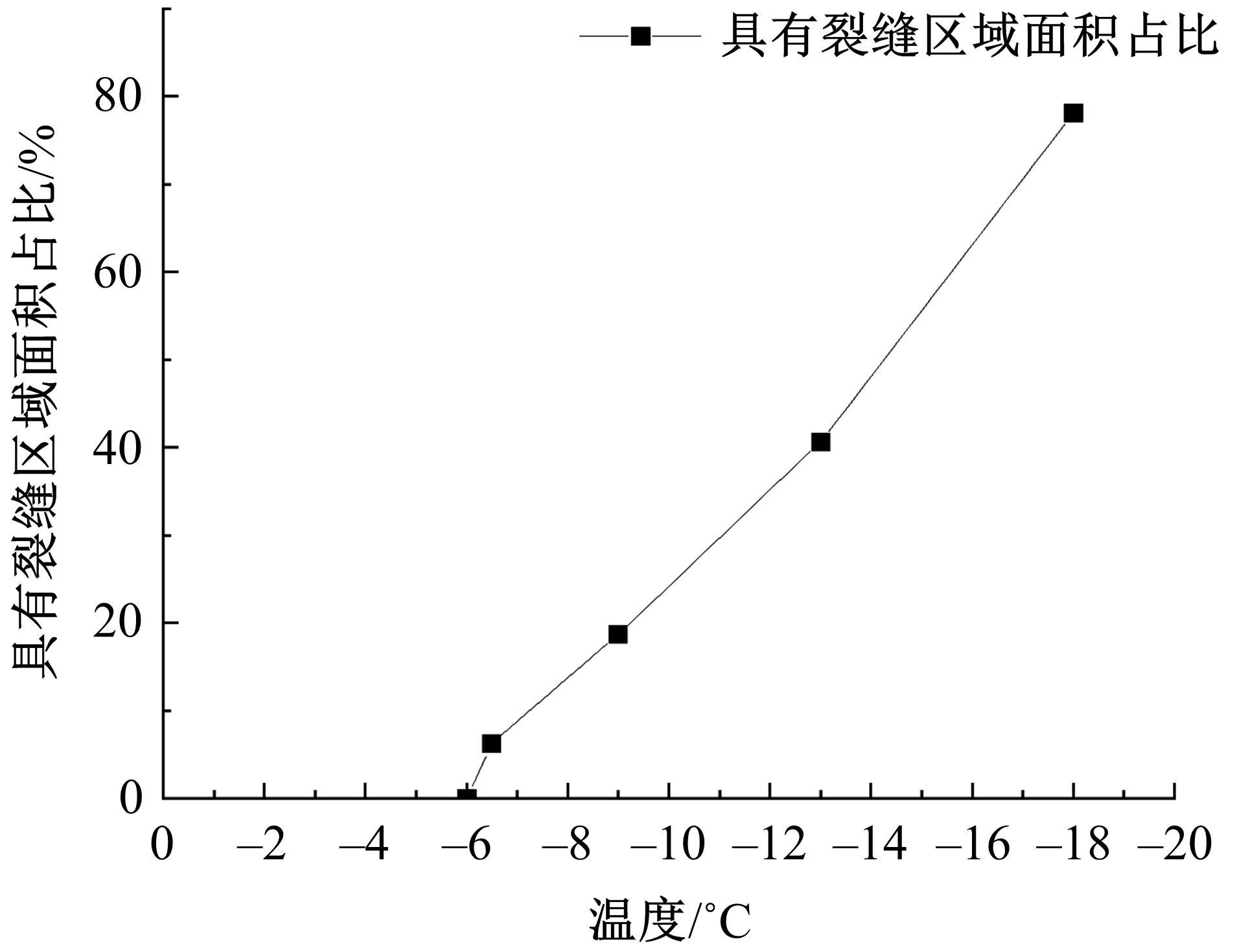
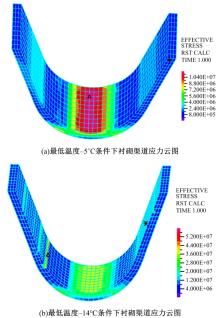
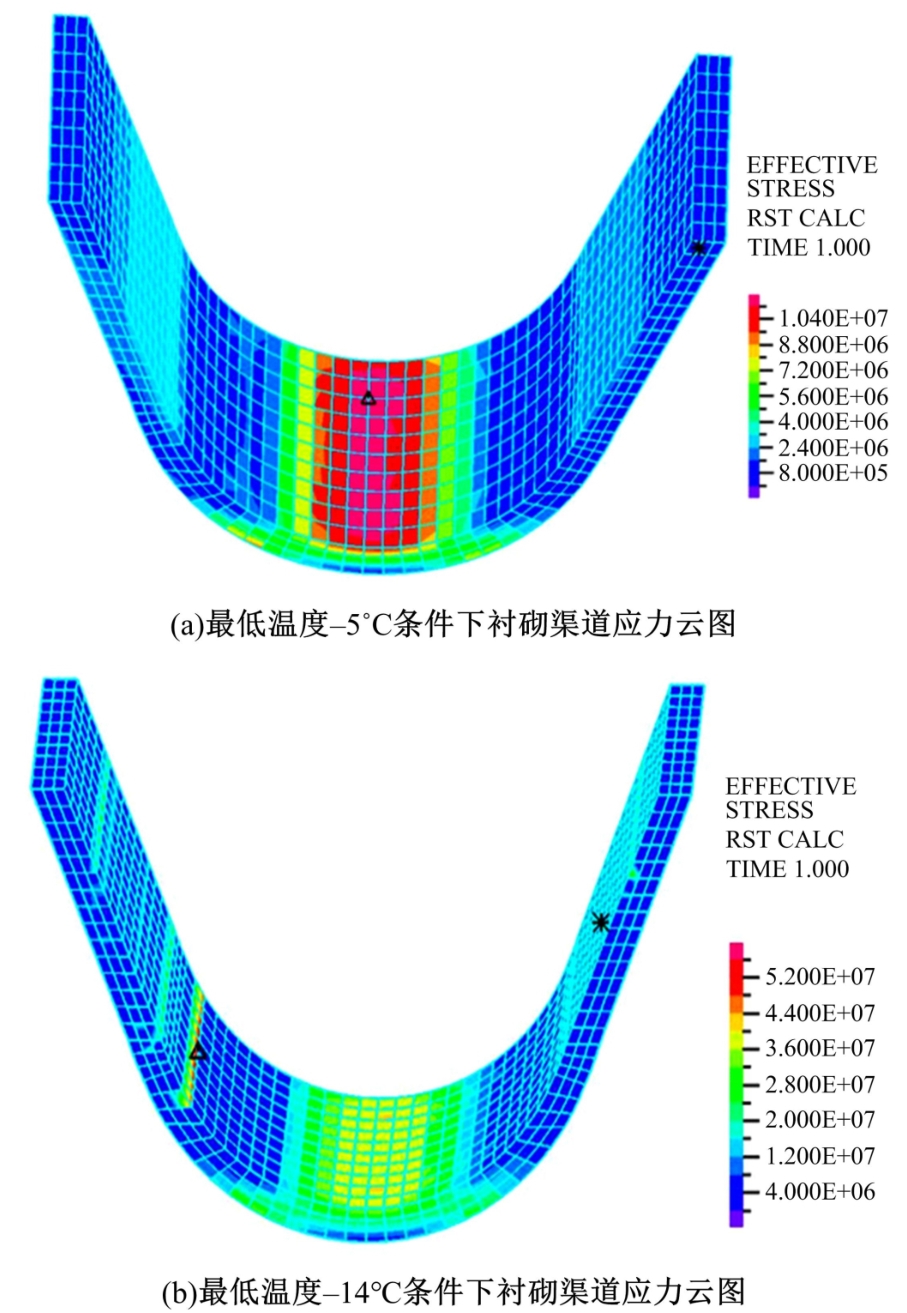
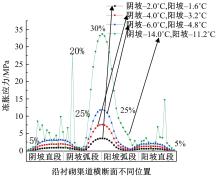
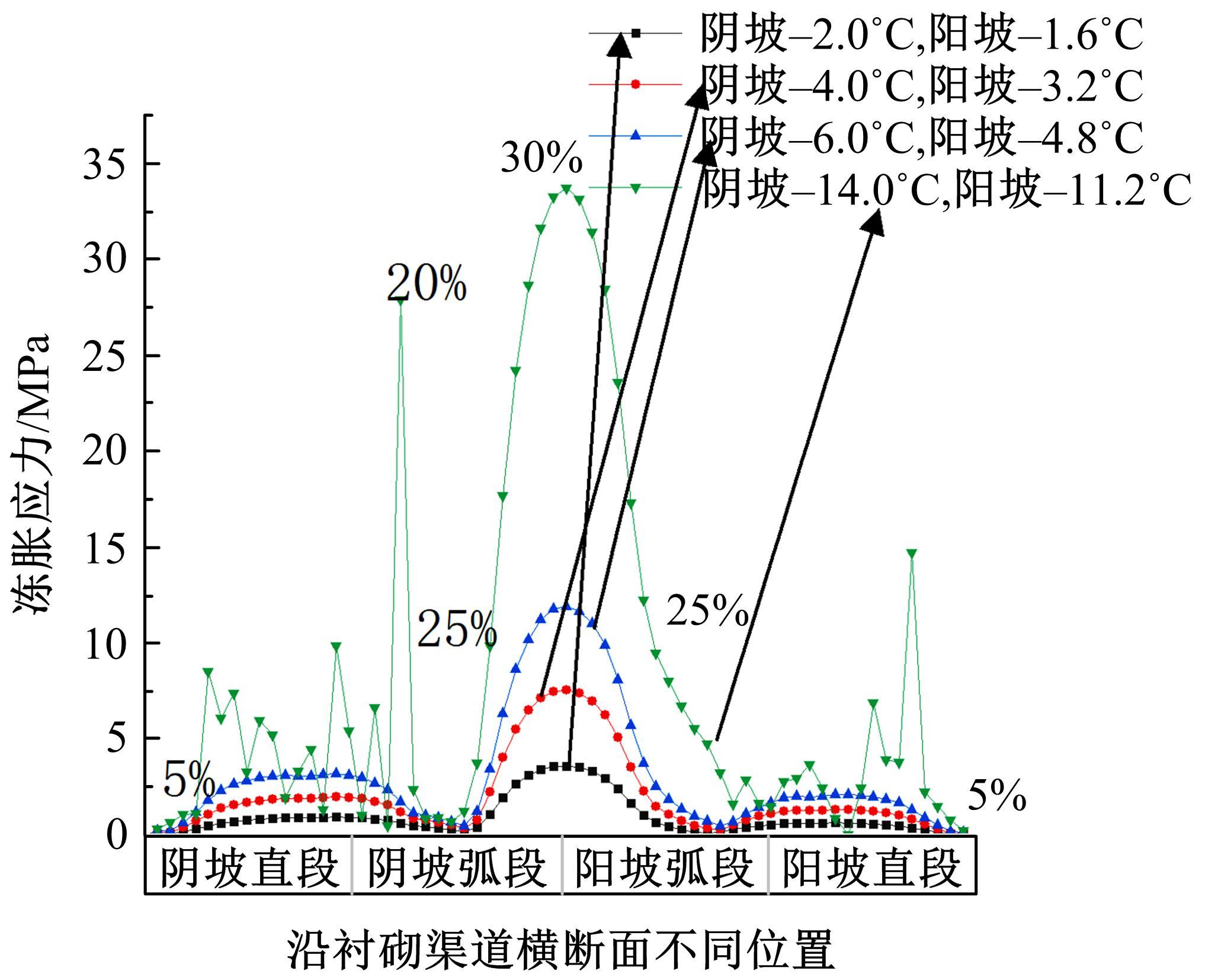
为研究渠基土在水分与温度变化下的力学特性与冻胀特性变化特征及在水分与温度变化下衬砌渠道的冻胀响应,本文通过对渠基土进行力学特性与冻胀特性试验,研究了不同水分、不同温度条件下渠基土力学特性和冻胀特性的变化规律。并以此为依据,采用有限元数值模拟,基于水热耦合变化,对渠基土冻胀下衬砌渠道冻胀响应进行了研究。结果表明:渠基土力学特性与冻胀特性在水热耦合下呈现出复杂性。温度差异小时,水分差异对衬砌渠道冻胀变形影响小。温度差异大时,水热耦合对衬砌渠道冻胀变形影响显著。-2℃、-12℃下,衬砌渠道最大冻胀变形相较渠道底部变形大54%、70%。温度差异越大,不同温度条件下法、切向冻胀力差距越大。-5℃下最大法向、切向冻胀力相较-2℃大175%、173%,-15℃下最大法向、切向冻胀力相较-5℃大408%、200%。水分差异相较温度差异对冻胀作用影响小。在水热耦合下,渠基土冻胀作用分布具有非均匀性特征且衬砌渠道裂缝发展与分布特征具有一定规律性。温度差异越大,不同水热条件下衬砌渠道冻胀应力差距越大。-6℃下最大冻胀应力相较-4℃大57%。-14℃下最大冻胀应力相较-6℃大183%。温度越低,水分越多,对衬砌渠道冻胀应力影响越显著。本研究可为衬砌渠道在水热耦合变化下防冻胀设计与结构优化提供参考。
中图分类号:
- S277
| 1 | 冯瑞萍, 张学艺, 舒志亮, 等. 宁夏季节性最大冻土深度的分布和变化特征[J]. 宁夏大学学报:自然科学版, 2012, 33(03):314-318. |
| Feng Rui-ping, Zhang Xue-yi, Shu Zhi-liang, et al. Distribution and variation characteristics of the seasonal maximum permafrost depth in Ningxia[J]. Journal of Ningxia University(Natural Science Edition), 2012, 33(03): 314-318. | |
| 2 | 王羿, 刘瑾程, 刘铨鸿, 等. 温-水-土-结构耦合作用下寒区梯形衬砌渠道结构形体优化[J]. 清华大学学报:自然科学版, 2019, 59(08): 645-654. |
| Wang Yi, Liu Jin-cheng, Liu Quan-hong, et al. Shape optimization of a trapezoidal canal structure for coupled temperature-water-soil conditions in cold regions[J]. Journal of Tsinghua University(Science and Technology), 2019, 59(08): 645-654. | |
| 3 | Duan A. Numerical simulation of the freezing process of concrete[J]. Mater Civ Eng, 2013, 25: 1317–1325. |
| 4 | 薛珂, 温智, 张明礼, 等. 土体冻结过程中基质势与水分迁移及冻胀的关系[J]. 农业工程学报, 2017, 33(10): 176-183. |
| Xue Ke, Wen Zhi, Zhang Ming-li, et al. Relationship between matric potential, moisture migration and frost heave in freezing process of soil[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering, 2017, 33(10): 176-183. | |
| 5 | 李学军, 费良军, 任之忠. 大型U型渠道渠基季节性冻融水分运移特性研究[J]. 水利学报, 2007(11): 1383-1387. |
| Li Xue-jun, Fei Liang-jun, Ren Zhi-zhong, et al. Soil moisture transfer in the base of U-shape canal with concrete lining in the process of seasonal freezing and thawing[J]. Journal of Hydraulic Engineering, 2007(11): 1383-1387. | |
| 6 | 明锋, 李东庆. 非饱和正冻土一维水热耦合模型与试验[J]. 中南大学学报:自然科学版, 2014, 45(03): 889-894. |
| Ming Feng, Li Dong-qing. Modeling and experimental investigation of one dimension coupled moisture and heat in unsaturated freezing soil[J]. Journal of Central South University (Science and Technology), 2014, 45(03): 889-894. | |
| 7 | 邓青松, 曾超, 何先志, 等. 季冻区公路路基水热场阴阳坡差异与防冻胀模拟[J]. 中南大学学报:自然科学版, 2022, 53(08): 3113-3128. |
| Deng Qing-song, Zeng Chao, He Xian-zhi, et al. Simulation of hydrothermal field difference and anti rost heaving of highway subgrade with sunny-shady slopes in seasonally frozen regions[J]. Journal of Central South University (Science and Technology), 2022, 53(08): 3113-3128. | |
| 8 | 毛卫南, 刘建坤. 冻土区路基与埋地管道水热变化模拟分析[J]. 土木工程学报, 2015, 48(S2): 380-385. |
| Mao Wei-nan, Liu Jian-kun, et al. Water and heat distribution analysis of subgrade and pipeline in permafrost regions[J]. China Civil Engineering Journal, 2015, 48(S2): 380-385. | |
| 9 | 何鹏飞, 候光亮, 董建华, 等. 梯形渠道衬砌冻胀破坏弹性地基板模型[J]. 农业工程学报, 2022, 38(23): 91-100. |
| He Peng-fei, Hou Guang-liang, Dong Jian-hua, et al. Elastic foundation plate model for the frost heave damage of trapezoidal canal lining[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering, 2022, 38(23): 91-100. | |
| 10 | 肖旻, 王正中, 刘铨鸿, 等. 考虑冻土与结构相互作用的梯形渠道冻胀破坏弹性地基梁模型[J]. 水利学报, 2017, 48(10): 1229-1239. |
| Xiao Min, Wang Zheng-zhong, Liu Quan-hong, et al. Elastic foundation beam model of frost heave damage of trapezoidal canal considering interaction between frozen soil and lining stucture[J]. Journal of Hydraulic Engineering, 2017, 48(10): 1229-1239. | |
| 11 | 唐少容, 王红雨. 三板拼接式小型U形混凝土衬砌渠道冻胀破坏力学模型[J]. 农业工程学报, 2016, 32(11): 159-166. |
| Tang Shao-rong, Wang Hong-yu. Mechanical model of small U-shaped concrete lining canal with three arc-plates under frost heaving[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2016, 32(11): 159-166. | |
| 12 | 李爽, 王正中, 高兰兰, 等. 考虑混凝土衬砌板与冻土接触非线性的渠道冻胀数值模拟[J]. 水利学报, 2014, 45(04): 497-503. |
| Li Shuang, Wang Zheng-zhong, Gao Lan-lan, et al. Numerical simulation of canal frost heaving considering nonlinear contact between concrete lining board and soil[J]. Journal of Hydraulic Engineering, 2014, 45(04): 497-503. | |
| 13 | 李卓, 范光亚, 刘斯宏, 等. 土工袋防渠道冻胀水-热-力耦合数值模拟[J]. 河海大学学报:自然科学版, 2018, 46(05): 408-417. |
| Li Zhuo, Fan Guang-ya, Liu Si-hong, et al. Moisture-heat-stress coupled numerical simulation of soilbags preventing the frost heaving of channel[J]. Journal of Hohai University, 2018, 46(05): 408-417. | |
| 14 | 白青波, 李旭, 田亚护, 等. 冻土水热耦合方程及数值模拟研究[J]. 岩土工程学报, 2015, 37(S2): 131-136. |
| Bai Qing-bo, Li Xu, Tian Ya-hu, et al. Equations and numerical simulation for coupled water and heat transfer in frozen soil[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 2015, 37(S2): 131-136. | |
| 15 | 陈肖柏, 刘建坤, 刘鸿绪. 土的冻结作用与地基[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2006. |
| 16 | 王玉宝, 吴浩兴, 刘荣, 等. 整体式U型混凝土渠道衬砌-冻土接触模型[J]. 农业工程学报, 2023, 39(9): 142-151. |
| Wang Yu-bao, Wu Hao-xing, Liu Rong, et al. Lining-frozen soil contact model in an integral U-shaped concrete canal[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering, 2023, 39(9): 142-151. | |
| 17 | 李顺群, 高凌霞, 柴寿喜. 冻土力学性质影响因素的显著性和交互作用研究[J]. 岩土力学, 2012, 33(04): 1173-1177. |
| Li Shun-qun, Gao Ling-xia, Chai Shou-xi, et al. Significance and interaction of factors on mechanical properties of frozen soil[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2012, 33(04): 1173-1177. | |
| 18 | Li Shuang-yang, Zhang Ming-yi, Tian Yi-bin, et al. Experimental and numerical investigations on frost damage mechanism of a canal in cold regions[J]. Cold Regions Science and Technology, 116(2015). 1-11. |
| 19 | 郭富强, 李钢铁, 霍轶珍, 等. 基于ADINA的河套灌区预制混凝土渠道保温防冻胀效果数值模拟[J]. 干旱区资源与环境, 2023, 37(10): 84-92. |
| Guo Fu-qiang, Li Gang-tie, Huo Yi-zhen, et al. Numerical simulation of thermal insulation and frost heave effect of precast concrete channel in Hetao Irrigation District based on ADINA[J]. Journal of Arid Land Resources and Environment, 2023, 37(10): 84-92. | |
| 20 | 张茹, 王正中, 牟声远, 等. 基于横观各向同性冻土的U形渠道冻胀数值模拟[J]. 应用基础与工程科学学报, 2010, 18(05): 773-783. |
| Zhang Ru, Wang Zheng-zhong, Mou Sheng-yuan, et al. Numerical Simulation of Frost Heaving for U Canal Based on Transverse Isotropy[J]. Journal of Basic Science and Engineering, 2010, 18(05): 773-783. | |
| 21 | 张海东, 朱志武, 宁建国, 等. 冻土单轴动态加载下的力学性能[J]. 固体力学学报, 2014, 35(01): 39-48. |
| Zhang Hai-dong, Zhu Zhi-wu, Ning Jian-guoet al. Mechanical behavior of frozen soil with uniaxial dynamic loading[J]. Chinese Journal of Solid Mechanics, 2014, 35(01): 39-48. | |
| 22 | FuTian-tian, Zhu Zhi-wu, Zhang Dan, et al. Research on damage viscoelastic dynamic constitutive model of frozen soil [J]. Cold Regions Science and Technology, 160(2019). 209-221. |
| 23 | 芦琴, 王正中, 刘计良, 等. 弧脚梯形衬砌渠道抗冻胀及水力合理断面的分析[J]. 西北农林科技大学学报:自然科学版, 2010, 38(01): 231-234. |
| Lu Qin, Wang Zheng-zhong, Liu Ji-liang, et al. Analysis of anti frost heaving and reasonable hydraulic section of the channel in trapezoidal section with curved sloptoe[J]. Journal of Northwest A&F University, 2010, 38(01): 231-234. | |
| 24 | 陈立杰, 王正中, 刘旭东, 等. 高地下水位灌排渠道衬砌结构抗冻胀数值模拟[J]. 长江科学院院报, 2009, 26(09): 66-70. |
| Chen Li-jie, Wang Zheng-zhong, Liu Xu-dong, et al. Simulation Analysis of Channel Frost Heave under High Groundwater Level[J]. Journal of Yangtze River Scientific Research Institute, 2009, 26(09): 66-70. | |
| 25 | Wang B, Tian J J, Zhou J J. Effect of different concrete properties on frost heave crack in U-shaped canal lining and joint[J]. Physics and Chemistry of the Earth, 2021, 121: 102983. |
| [1] | 王俊发,马旭 . 地膜防渗灌溉渠道的机械化铺膜[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2009, 39(03): 648-0651. |
|
||