吉林大学学报(工学版) ›› 2020, Vol. 50 ›› Issue (5): 1832-1843.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb20190042
• 计算机科学与技术 • 上一篇
大规模流数据处理中代价有效的弹性资源分配策略
李丽娜1,2( ),魏晓辉1,3,郝琳琳1,王兴旺1(
),魏晓辉1,3,郝琳琳1,王兴旺1( ),王储1
),王储1
- 1.吉林大学 计算机科学与技术学院,长春 130012
2.长春大学 计算机科学技术学院,长春 130022
3.吉林大学 符号计算与知识工程教育部重点实验室,长春 130012
Cost⁃effective elastic resource allocation strategy in large⁃scale streaming data processing
Li-na LI1,2( ),Xiao-hui WEI1,3,Lin-lin HAO1,Xing-wang WANG1(
),Xiao-hui WEI1,3,Lin-lin HAO1,Xing-wang WANG1( ),Chu WANG1
),Chu WANG1
- 1.College of Computer Science and Technology,Jilin University,Changchun 130012,China
2.College of Computer Science and Technology,Changchun University,Changchun 130022,China
3.Key Laboratory of Symbolic Computation and Knowledge Engineering of Ministry of Education,Jilin University,Changchun 130012,China
摘要:
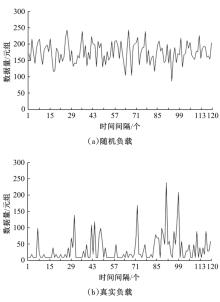
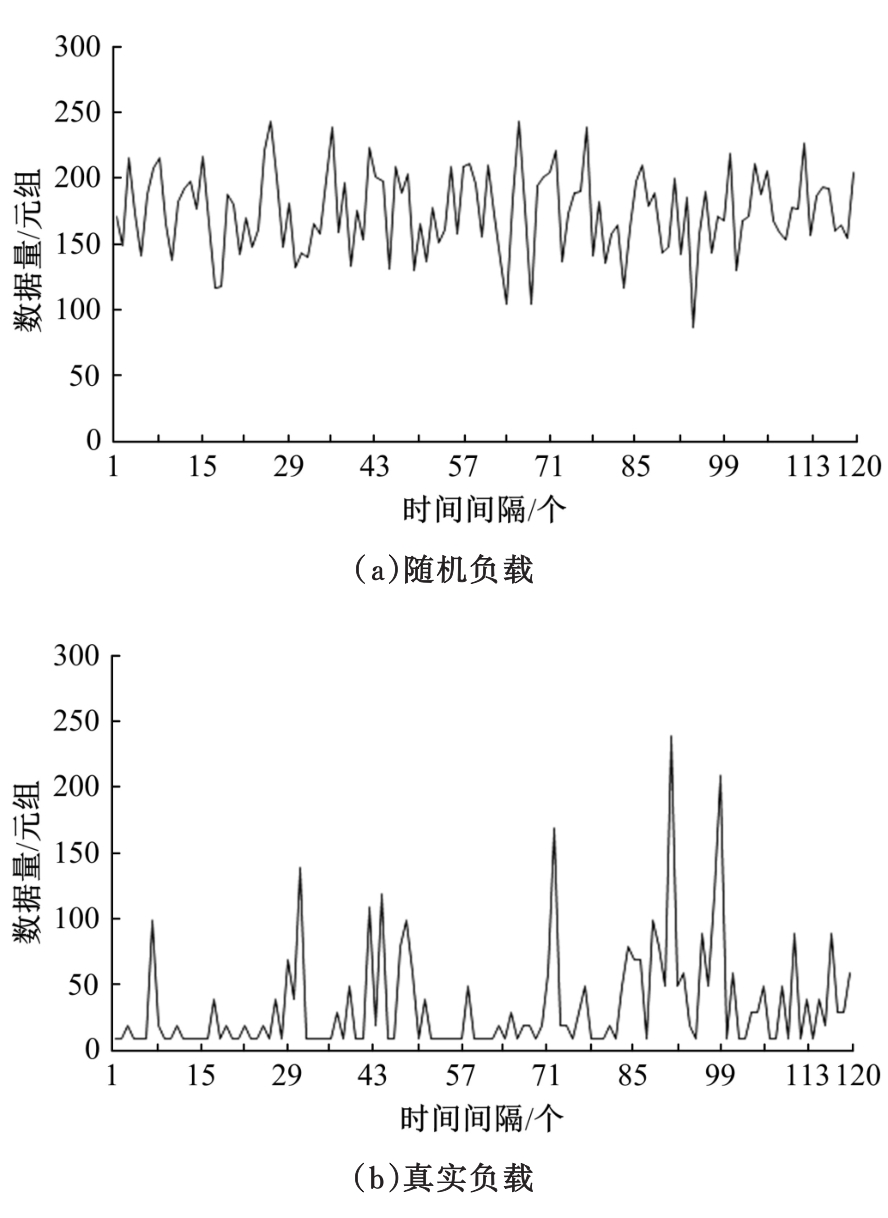
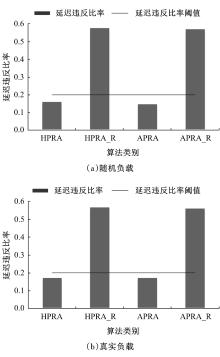
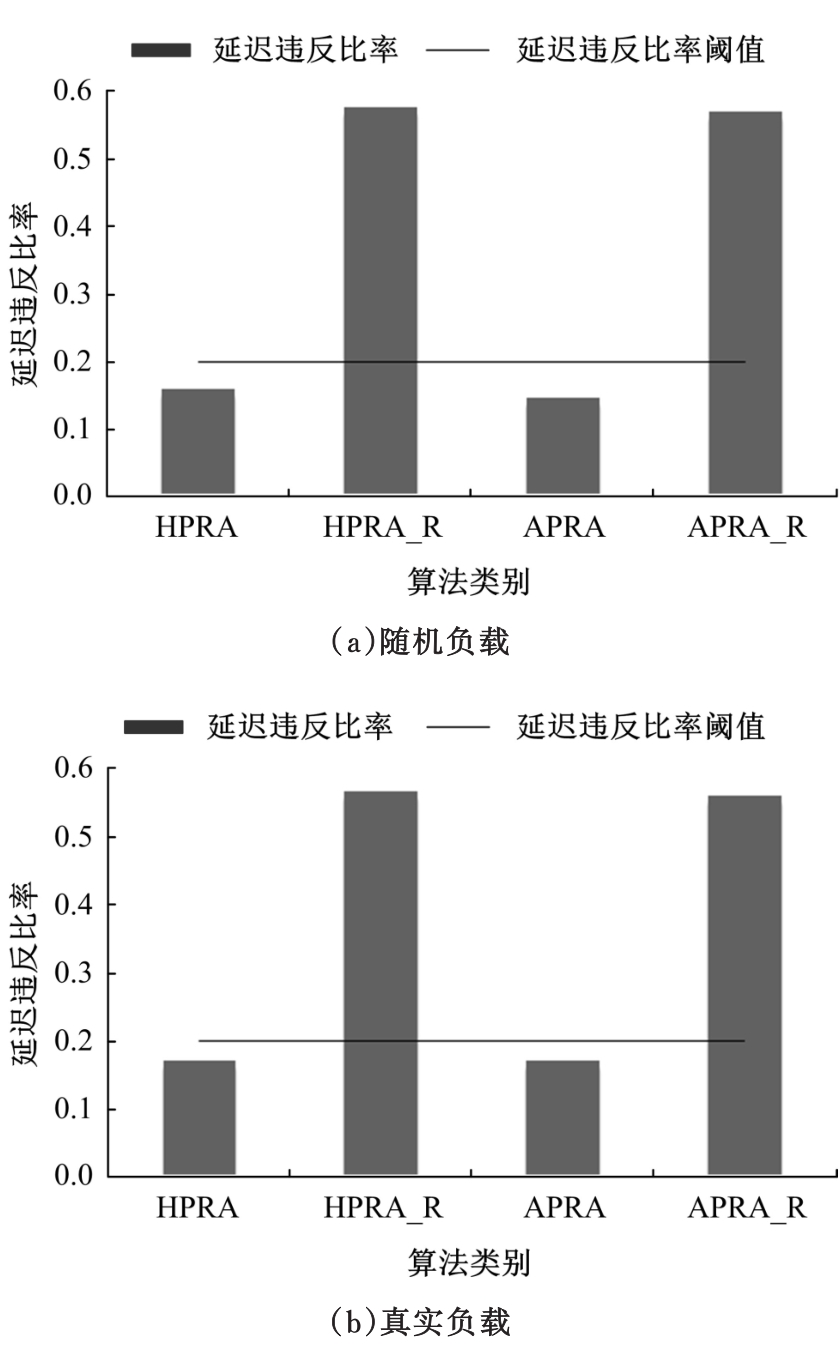
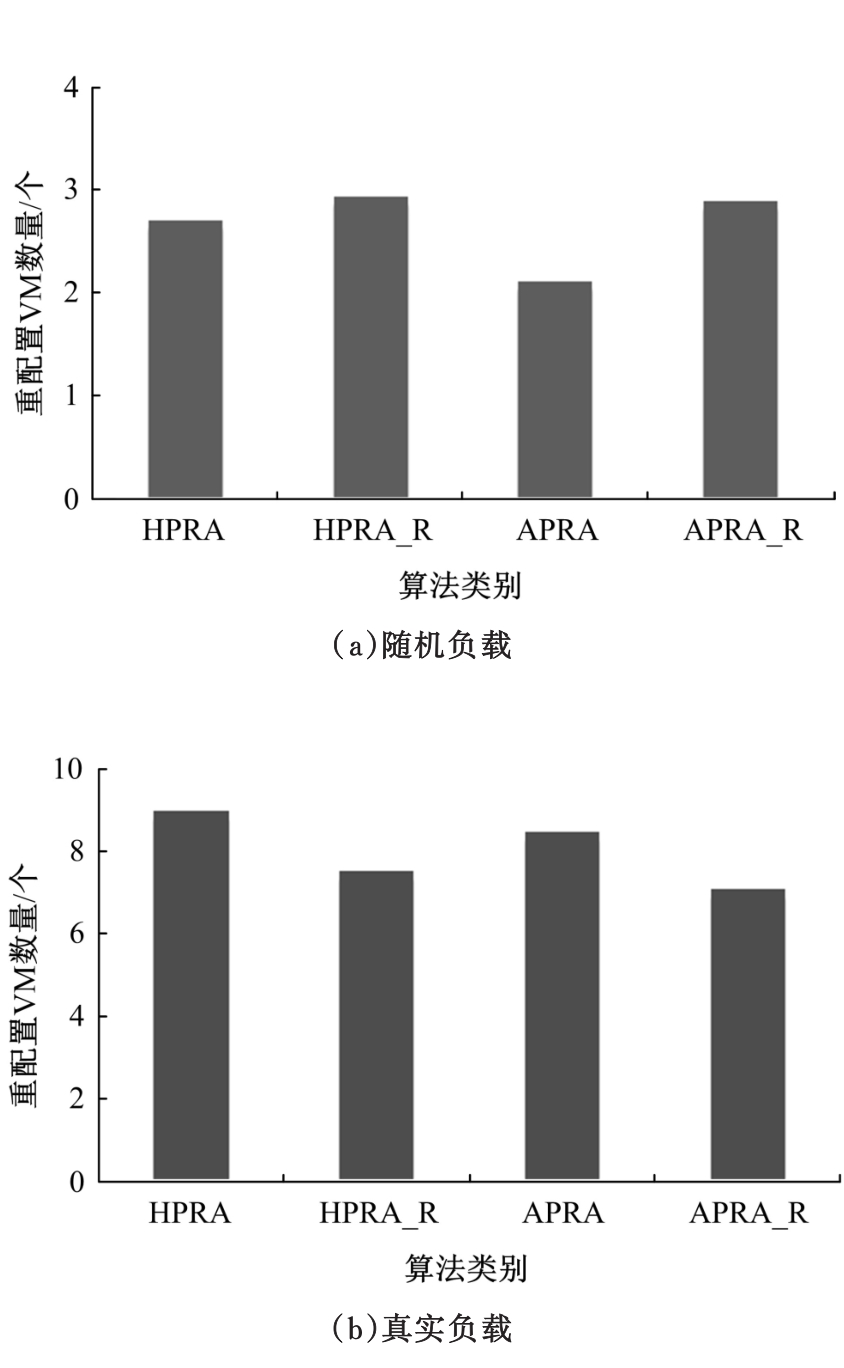
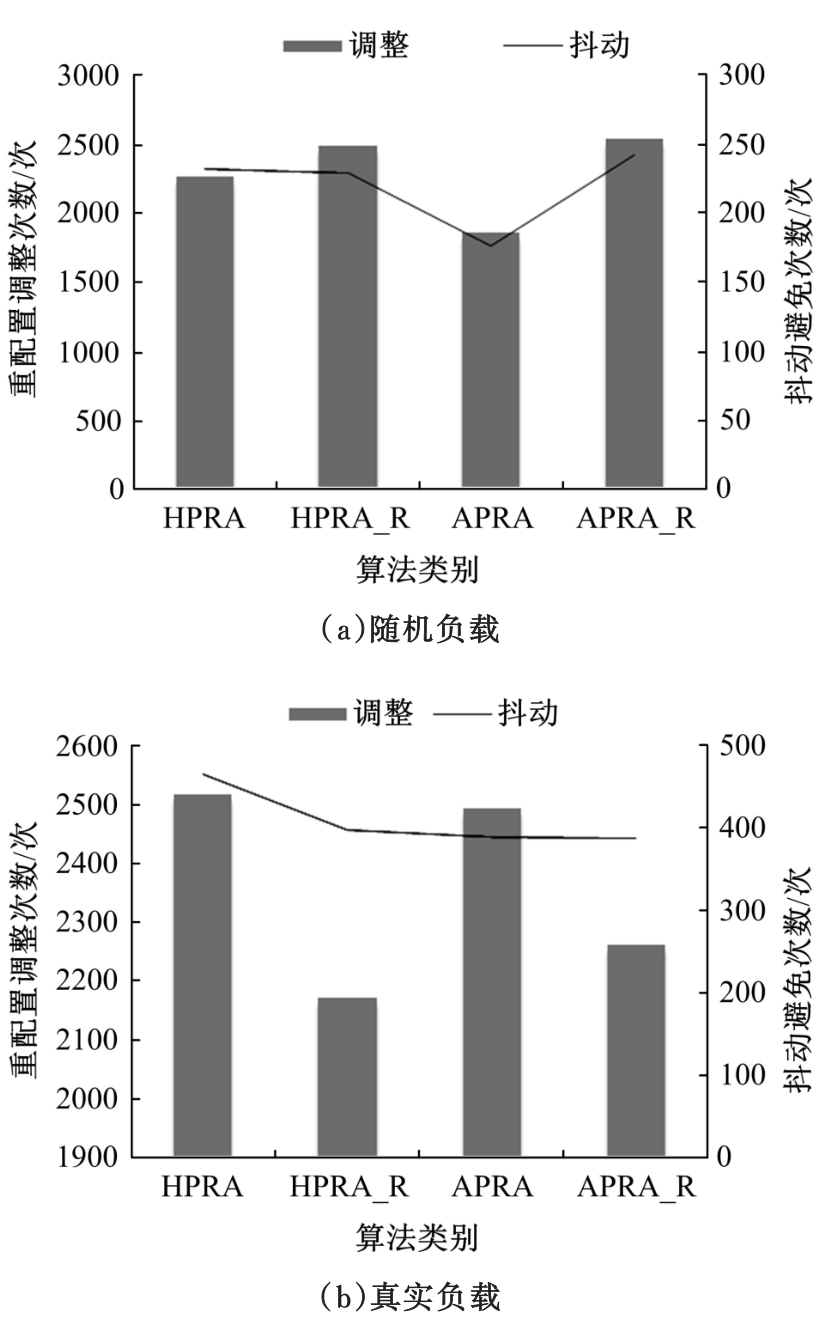
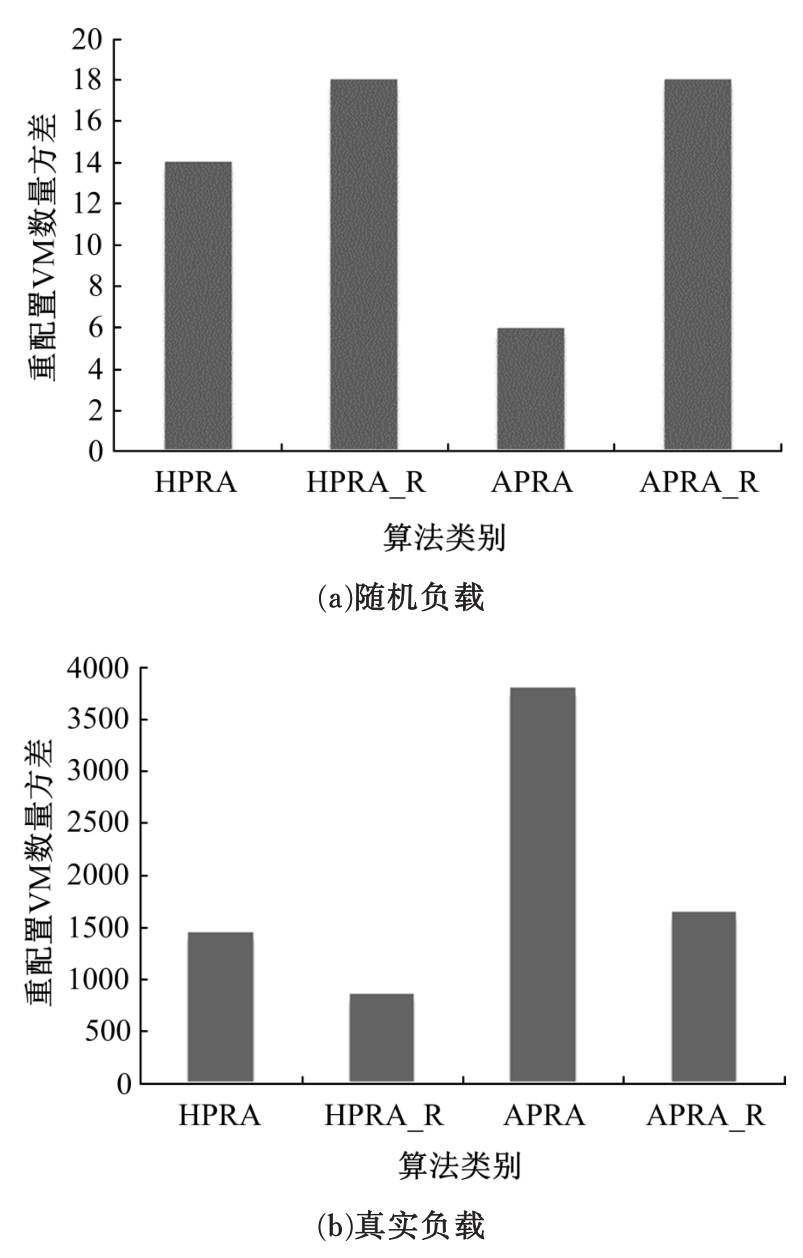
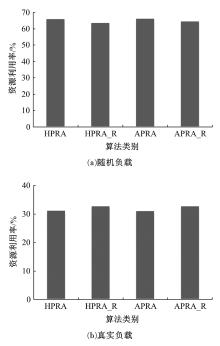
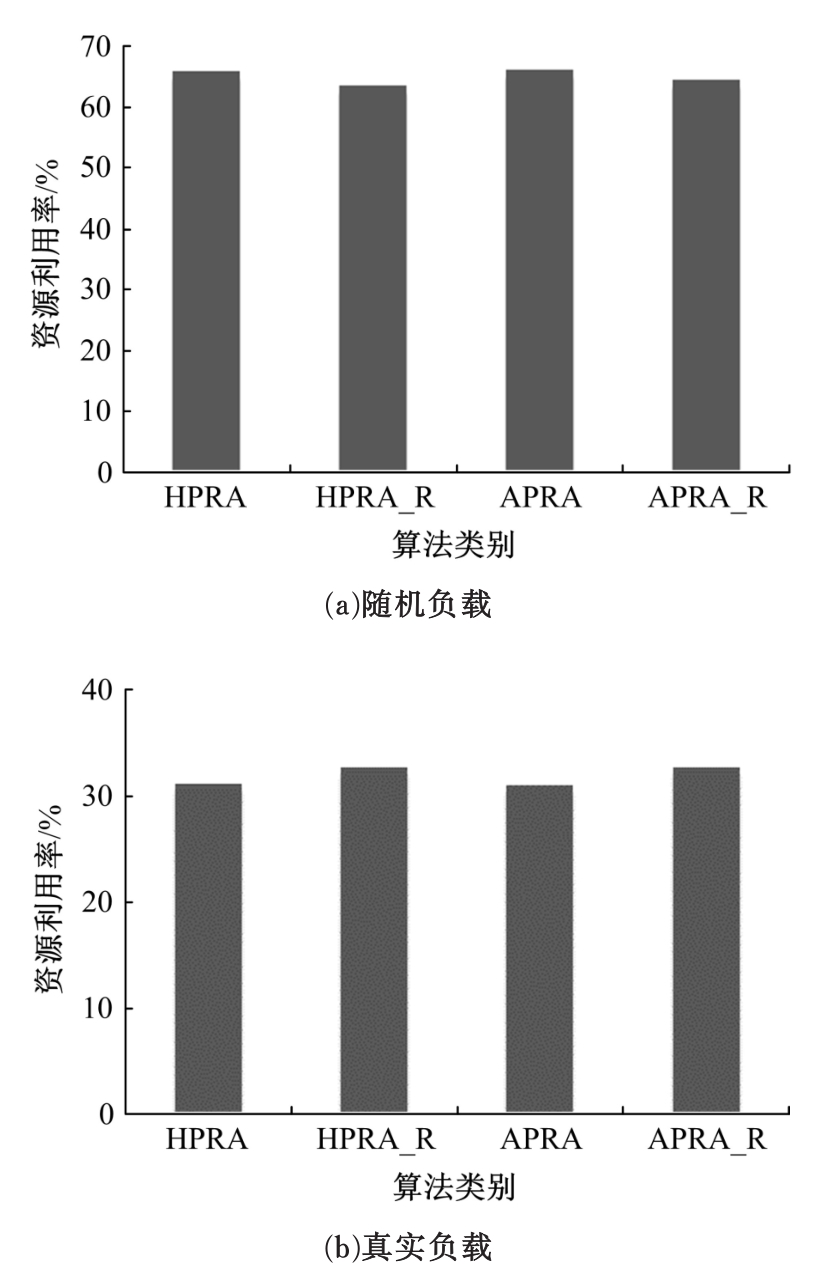
基于资源预留的思想并结合负载预测模型,以最小化应用的重配置代价和最大化资源利用率为目标,分别从启发式和智能化的角度设计主动式的弹性资源分配策略。两种策略均在流水线式处理模式下计算应用的延迟,且概率性地保证应用延迟性能的约束。其中,启发式策略采用本地阈值方法进行资源分配;智能化策略基于强化学习技术自适应地分配资源。实验结果表明:与反应式策略相比,本文提出的主动资源分配策略具有较低的重配置代价和较高的资源利用率,且智能化策略的性能更优,尤其在突发负载变化相对稳定的情况下表现更好。
中图分类号:
- TP391
| 1 | Pitman A, Zanker M. Insights from applying sequential pattern mining to E-commerce click stream data[C]∥IEEE International Conference on Data Mining Workshops, Sydney, NSW, 2010: 967-975. |
| 2 | Schnitzler F, Artikis A, Weidlich M, et al. Heterogeneous stream processing and crowdsourcing for traffic monitoring: highlights[C]∥Joint European Conference on Machine Learning and Knowledge Discovery in Databases, Nancy, France, 2014: 520-523. |
| 3 | Verma A, Kumar G, Koller R. The cost of reconfiguration in a cloud[C]∥International Middleware Conference Industrial Track, New York, NY, USA, 2010: 11-16. |
| 4 | Luo Z, Qian Z. Burstiness-aware server consolidation via queuing theory approach in a computing cloud[C]∥IEEE International Symposium on Parallel & Distributed Processing, Boston, MA, USA, 2013: 332-341. |
| 5 | Sutton R S, Barto A G. Reinforcement Learning: An Introduction[M]. MIT Press, 1998. |
| 6 | Kumbhare A G, Simmhan Y, Frincu M, et al. Reactive resource provisioning heuristics for dynamic dataflows on cloud infrastructure[J]. IEEE Transactions on Cloud Computing, 2015, 3(2): 105-118. |
| 7 | De Matteis T, Mencagli G. Keep calm and react with foresight: strategies for low-latency and energy-efficient elastic data stream processing[C]∥Principles and Practice of Parallel Programming, Barcelona, Spain, 2016: 1-12. |
| 8 | 李丽娜, 魏晓辉, 李翔, 等. 流数据处理中负载突发感知的弹性资源分配[J]. 计算机学报, 2018, 41(10): 2193-2208. |
| Li Li-na, Wei Xiao-hui, Li Xiang, et al. Burstiness-aware elastic resource allocation in stream data processing[J]. Chinese Journal of Computers, 2018, 41(10): 2193-2208. | |
| 9 | Das R, Tesauro G J, Walsh W E. Model-based and model-free approaches to autonomic resource allocation[J/OL]. [2005-11-16]. |
| gate.net/publication/246843416_Model-Based_and_Model-Free_Approaches_to_Autonomic_Resource_Allocation | |
| 10 | Tesauro G. Online resource allocation using decompositional reinforcement learning[C]∥Proc of AAAI, Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania, 2005: 886-891. |
| 11 | Tesauro G, Jong N K, Das R, et al. A hybrid reinforcement learning approach to autonomic resource allocation[C]∥IEEE International Conference on Autonomic Computing, Dublin, Ireland, 2006: 65-73. |
| 12 | Dutreilh X, Rivierre N, Moreau A, et al. From data center resource allocation to control theory and back[C]∥IEEE International Conference on Cloud Computing, Miami, USA, 2010: 410-417. |
| 13 | Dutreilh X, Kirgizov S, Melekhova O, et al. Using reinforcement learning for autonomic resource allocation in clouds: towards a fully automated workflow[C]∥International Conference on Autonomic and Autonomous Systems, Venice, Italy, 2011: 67-74. |
| 14 | Heinze T, Pappalardo V, Jerzak Z, et al. Auto-scaling techniques for elastic data stream processing[C]∥Proceedings of the 30th IEEE International Conference on Data Engineering Workshops. Chicago, Illinois, USA, 2014: 318-321. |
| 15 | Heinze T, Ji Y, Pan Y, et al. Elastic complex event processing under varying query load[C]∥International Workshop on Big Dynamic Distributed Data, Trento, Italy, 2013: 25-30. |
| 16 | Cardellini V, Presti F L, Nardelli M, et al. Auto-scaling in data stream processing applications: a model-based reinforcement learning approach[C]∥Workshop on New Frontiers in Quantitative Methods in Informatics, Venice, Italy, 2017: 97-110. |
| 17 | Wei X, Li L, Li X, et al. Pec: proactive elastic collaborative resource scheduling in data stream processing[J]. IEEE Transactions on Parallel and Distributed Systems, 2019, 30(7): 1628-1642. |
| 18 | Bitran G R, Morabito R. State-of-the-art survey: open queueing networks: optimization and performance evaluation models for discrete manufacturing systems[J]. Production and Operations Management, 1996, 5(2): 163-193. |
| 19 | Leskovec J, Backstrom L, Kleinberg J. Meme-tracking and the dynamics of the news cycle[C]∥International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining, Paris, France, 2009: 497-506. |
| [1] | 吴昊天,郭锐锋,彭阿珍,王品. 一种考虑可靠性的常带宽服务器低功耗调度算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2020, 50(5): 1802-1808. |
| [2] | 刘毅,肖玲玲,王改静,张武军. 基于联合优化的D2D资源分配算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2020, 50(1): 306-314. |
| [3] | 于斌斌,胡亮,迟令. 可抵抗内外部攻击的无线传感器网络数字签名方案[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2019, 49(5): 1676-1681. |
| [4] | 杨顺,蒋渊德,吴坚,刘海贞. 基于多类型传感数据的自动驾驶深度强化学习方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2019, 49(4): 1026-1033. |
| [5] | 肖堃. 基于Hoare逻辑的密码软件安全性形式化验证方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2019, 49(4): 1301-1306. |
| [6] | 余宜诚, 胡亮, 迟令, 初剑峰. 一种改进的适用于多服务器架构的匿名认证协议[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2018, 48(5): 1586-1592. |
| [7] | 董坚峰, 张玉峰, 戴志强. 改进的基于狄利克雷混合模型的推荐算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2018, 48(2): 596-604. |
| [8] | 赵博, 秦贵和, 赵永哲, 杨文迪. 基于半陷门单向函数的公钥密码[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2018, 48(1): 259-267. |
| [9] | 姜来为, 沙学军, 吴宣利, 张乃通. LTE-A异构网络中新的用户选择接入和资源分配联合方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2017, 47(6): 1926-1932. |
| [10] | 董立岩, 王越群, 贺嘉楠, 孙铭会, 李永丽. 基于时间衰减的协同过滤推荐算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2017, 47(4): 1268-1272. |
| [11] | 刘磊, 刘利娟, 吴新维, 张鹏. 基于ECPMR的编译器测试方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2017, 47(4): 1262-1267. |
| [12] | 于斌斌, 武欣雨, 初剑峰, 胡亮. 基于群密钥协商的无线传感器网络签名协议[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2017, 47(3): 924-929. |
| [13] | 邓昌义, 郭锐锋, 张忆文, 王鸿亮. 基于平衡因子的动态偶发任务低功耗调度算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2017, 47(2): 591-600. |
| [14] | 郝娉婷, 胡亮, 姜婧妍, 车喜龙. 基于多管理节点的乐观锁协议[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2017, 47(1): 227-234. |
| [15] | 魏晓辉, 刘智亮, 庄园, 李洪亮, 李翔. 支持大规模流数据在线处理的自适应检查点机制[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2017, 47(1): 199-207. |
|
||