吉林大学学报(工学版) ›› 2022, Vol. 52 ›› Issue (8): 1934-1942.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb20210149
• 通信与控制工程 • 上一篇
偶极直流电渗场效应晶体管及其在微流控中的应用
- 长安大学 电子与控制工程学院,西安 710064
Bipolar DC flow field⁃effect⁃transistor and its application in microfluidics
Yan-bo LI( ),Yu ZHANG,Wei-yu LIU(
),Yu ZHANG,Wei-yu LIU( ),Qi-sheng WU,Biao WANG,Bo-bin YAO
),Qi-sheng WU,Biao WANG,Bo-bin YAO
- School of Electronics and Control Engineering,Chang'an University,Xi'an 710064,China
摘要:
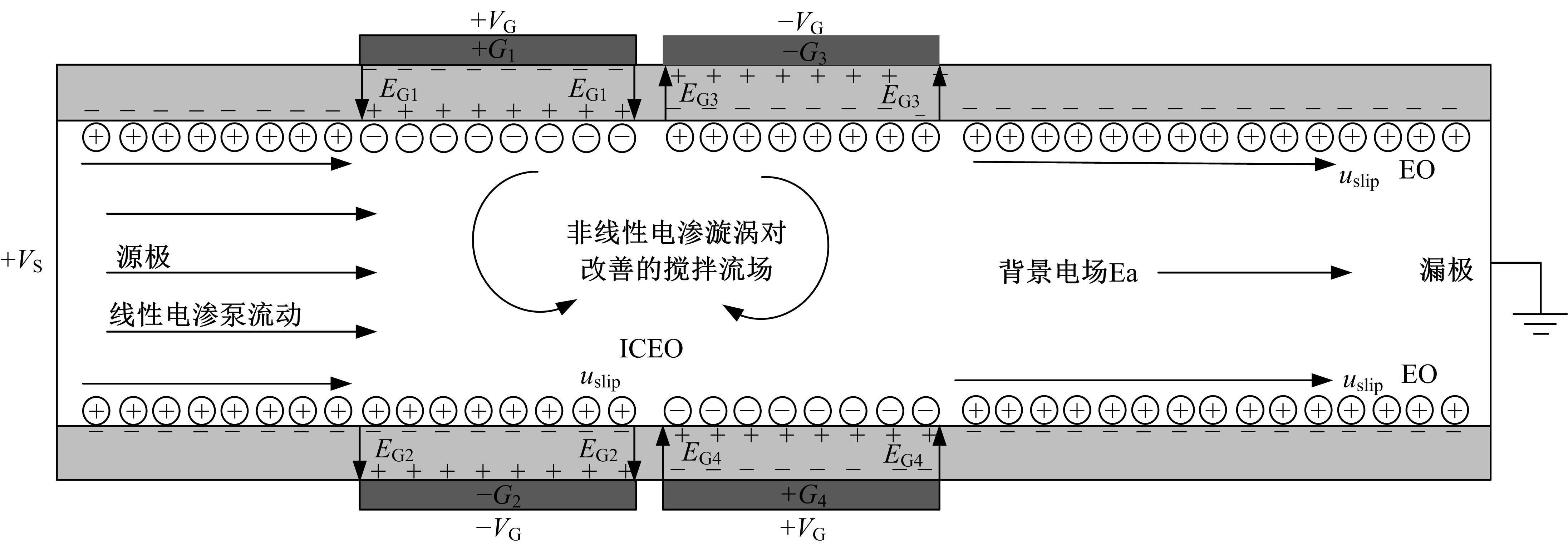
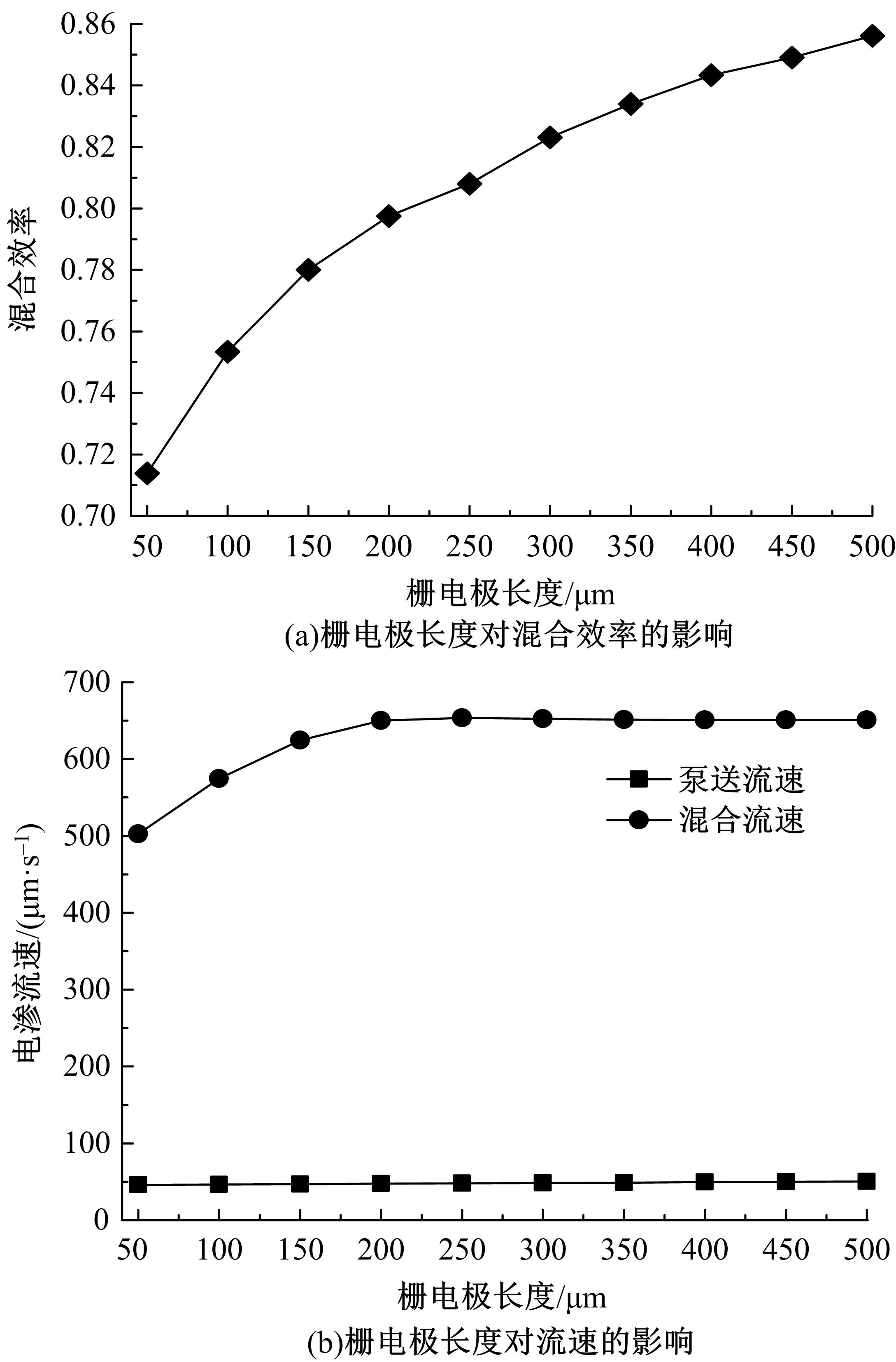
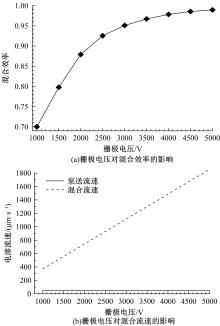
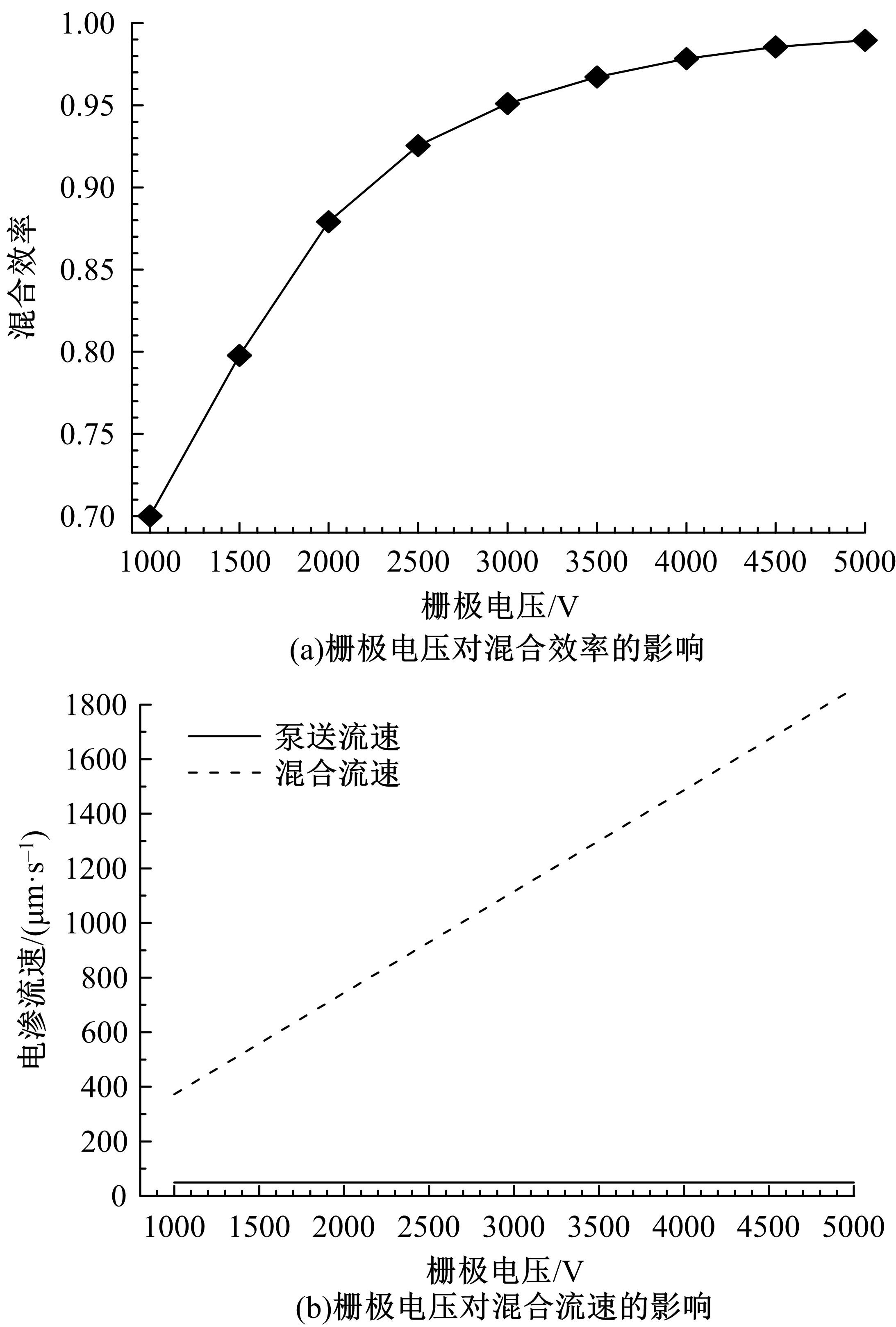
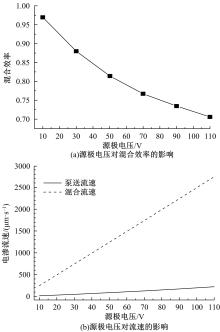
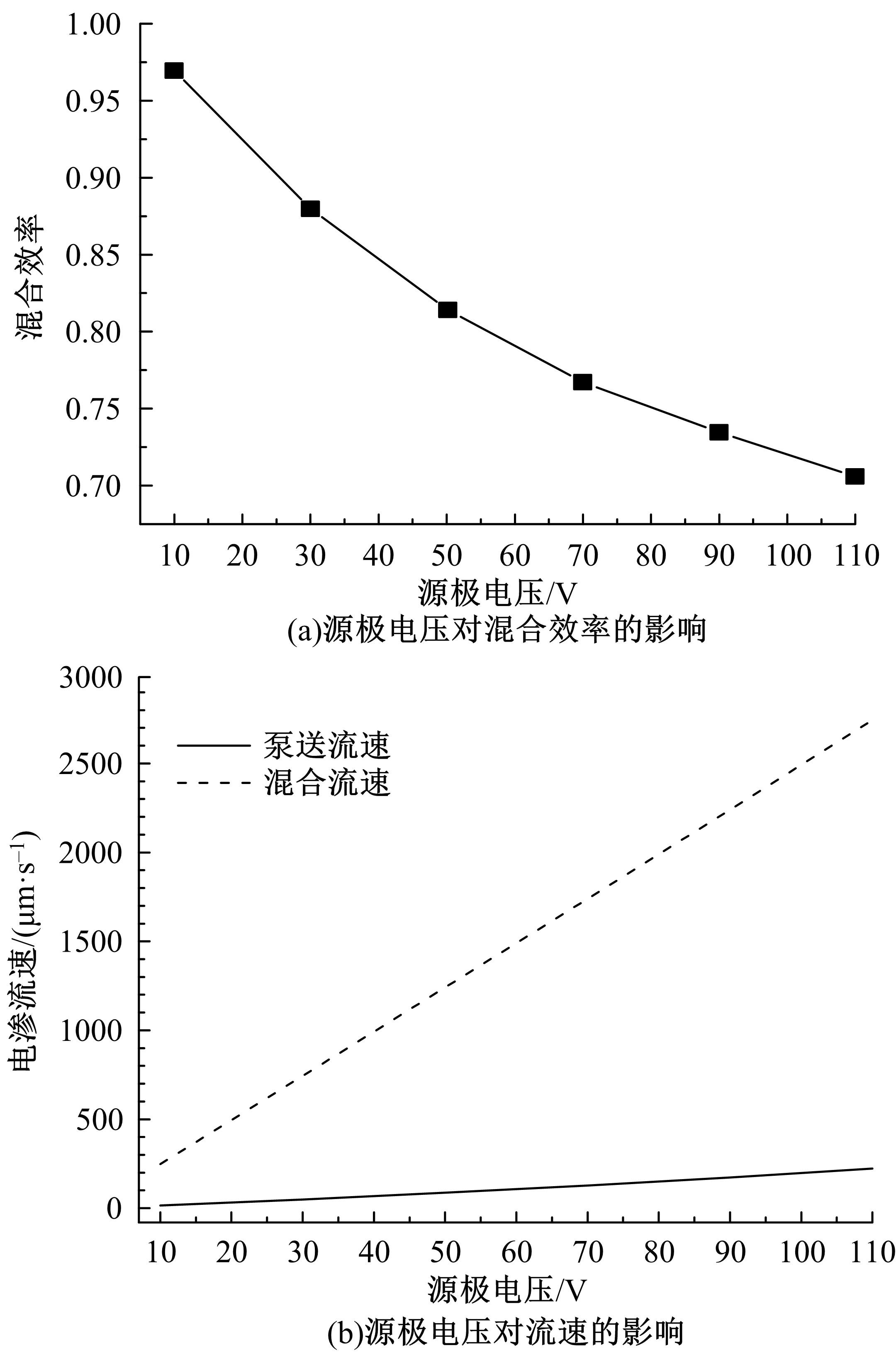
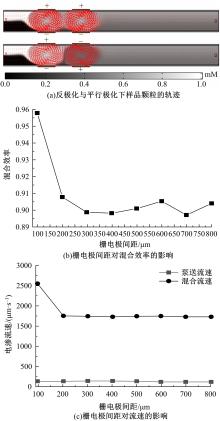
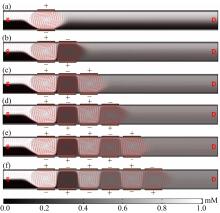
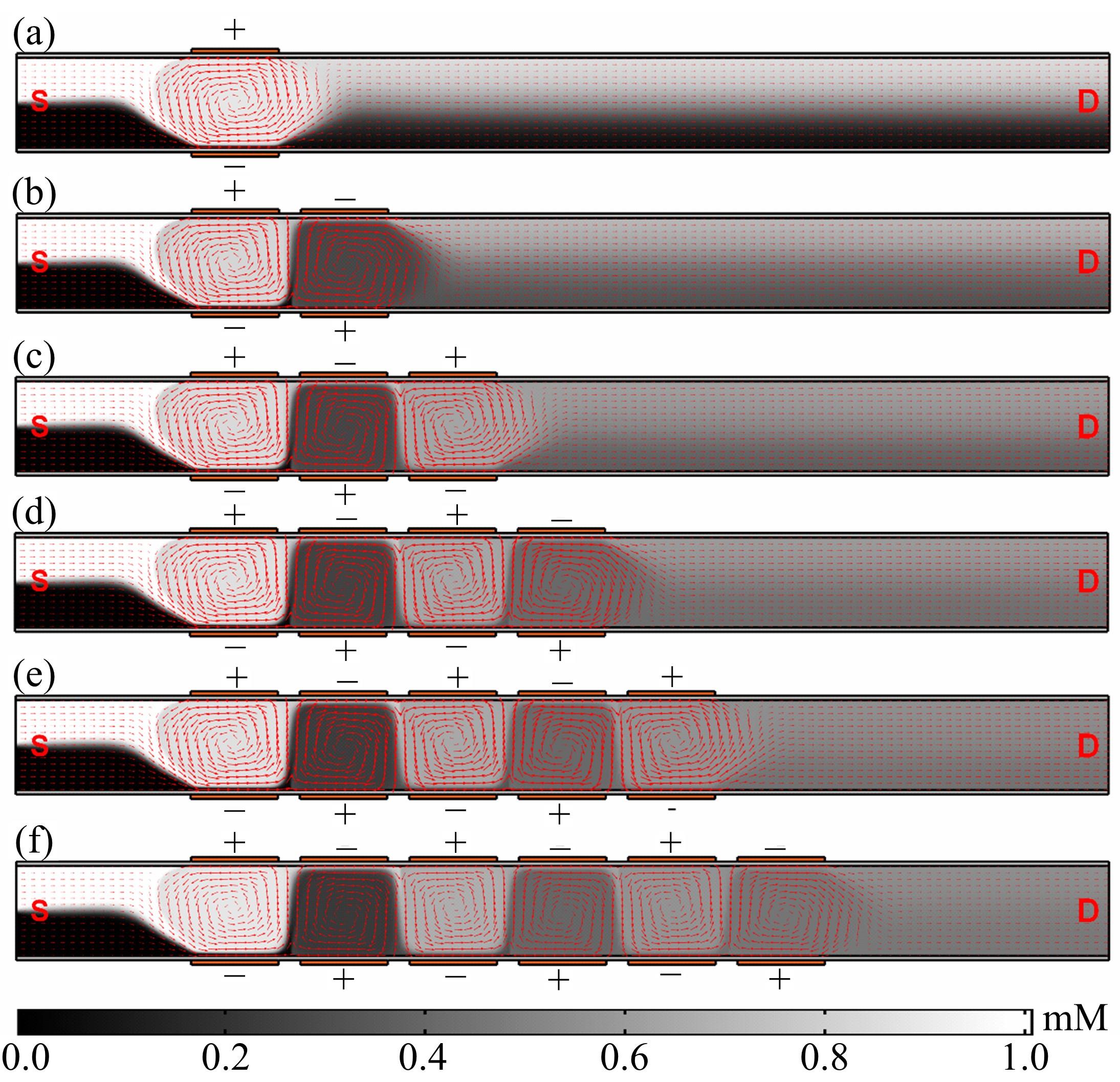
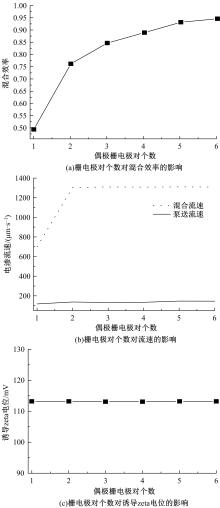
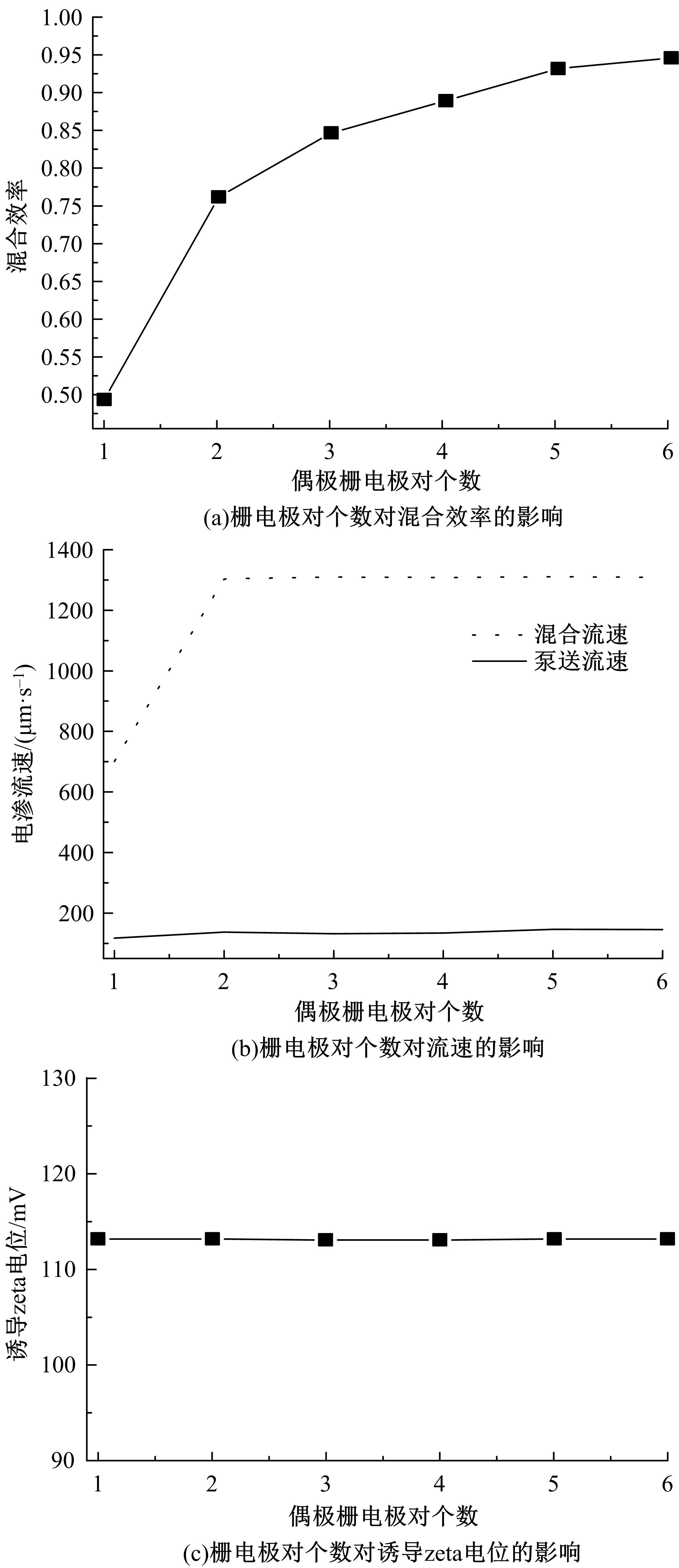
从电动力学的角度提出了一种新的偶极直流电渗场效应控制方法。在薄层近似和低压极限下建立数学模型,验证偶极直流流动场效应晶体管结构在微米尺度进行流体电动操纵的可行性。采用两组并排反极性栅电极对的集成器件设计,建立了一种用于全电动驱动分析物处理的微器件模型,通过使用较小的栅极电压便可获得液体混合物,从而在小Dukhin数下产生较少的不利影响。该项技术在现代微流控系统中开发全自动液相执行器等方面具有应用价值。
中图分类号:
- TN42
| 1 | García-Sánchez P, Ramos A. Electrorotation of a metal sphere immersed in an electrolyte of finite Debye length[J]. Physical Review. E, Statistical, Nonlinear, and Soft Matter Physics, 2015, 92(5):052313. |
| 2 | Yalcin S Y, Sharma A, Qian S Z, et al. Manipulating particles in microfluidics by floating electrodes[J]. Electrophoresis, 2010, 31(22): 3711-3718. |
| 3 | Hu Q M, Guo J H, Cao Z L, et al. Asymmetrical induced charge electroosmotic flow on a herringbone floating electrode and its application in a micromixer[J]. Micromachines, 2018, 9(8): 391-406. |
| 4 | 唐文来,项楠,张鑫杰,等.非对称弯曲微流道中粒子惯性聚焦动态过程及流速调控机理研究[J]. 物理学报, 2015, 64(18): 391-401. |
| Tang Wen-lai, Xiang Nan, Zhang Xin-jie, et al. Dynamic process and flow-rate regulation mechanism of particle inertial focusing in an asymmetric ally curved microchannel[J]. Acta Physica Sinica, 2015, 64(18): 391-401. | |
| 5 | 闵伶俐,陈松月,盛智芝, 等. 仿生微流控的发展与应用[J]. 物理学报, 2016, 65(17): 160-175. |
| Min Ling-li, Chen Song-yue, Sheng Zhi-zhi, et al. Development and application of bio-inspired and biomimetic microfluidics[J]. Acta Physica Sinica, 2016, 65(17):160-175. | |
| 6 | 张敏,李松晶,蔡申. 基于无阀压电微泵控制的微流控液体变色眼镜[J]. 吉林大学学报: 工学版, 2017, 47(2): 498-503. |
| Zhang Min, Li Song-jing, Cai Shen. Microfluidic liquid color-changing glasses controlled by valveless piezoelectric micro-pump[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2017, 47(2): 498-503. | |
| 7 | Lian C, Gallegos A, Liu H L, et al. Non-scaling behavior of electroosmotic flow in voltage-gated nanopores[J]. Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics, 2016, 19(1): 450-457. |
| 8 | Jimenez E, Escandón J, Méndez F, et al. Combined viscoelectric and steric effects on the electroosmotic flow in nano/microchannels with heterogeneous zeta potentials[J]. Elsevier, 2019, 577: 347-359. |
| 9 | Gajar S A, Geis M W. An ionic liquid‐channel field‐effect transistor[J]. Journal of The Electrochemical Society, 2019, 139(10): 2833-2849. |
| 10 | Leclercq L, Morvan M, Koch J, et al. Modulation of the electroosmotic mobility using polyelectrolyte multilayer coatings for protein analysis by capillary electrophoresis[J]. Analytica Chimica Acta, 2019, 1057: 152-161. |
| 11 | 刘国君,张炎炎,杨旭豪, 等. 声表面波技术在金纳米粒子可控制备中的应用[J]. 吉林大学学报: 工学版, 2017, 47(4): 1102-1108. |
| Liu Guo-jun, Zhang Yan-yan, Yang Xu-hao, et al. Application of surface acoustic wave in controlled synthesis of gold nanoparticles[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2017, 47(4): 1102-1108. | |
| 12 | Guan W H, Fan R, Reed M A. Field-effect reconfigurable nanofluidic ionic diodes[J]. Nature Communications, 2011, 2(1): 506. |
| 13 | Zehavi M, Boymelgreen A, Yossifon G. Competition between induced-charge electro-osmosis and electrothermal effects at low frequencies around a weakly polarizable microchannel corner[J]. Physical Review Applied, 2016, 5(4): 044013. |
| 14 | Feng H C, Chang H L, Zhong X, et al. Recent advancement in induced-charge electrokinetic phenomena and their micro- and nano-fluidic applications[J]. Advances in Colloid and Interface Science, 2020, 280: 102159. |
| 15 | Peng C H, Lavrentovich O D. Liquid crystals-enabled AC electrokinetics[J]. Micromachines, 2019, 10(1): 45-63. |
| 16 | Zhao C, Yang C. AC field induced‐charge electroosmosis over leaky dielectric blocks embedded in a microchannel[J].Electrophoresis, 2015, 32(5): 629-637. |
| 17 | Bashirzadeh Y, Maruthamuthu V, Qian S Z. Electrokinetic phenomena in pencil lead-based microfluidics[J]. Micromachines, 2016, 7(12): 235-247. |
| 18 | Ory S, Ehud Y. Induced-charge electro-osmosis beyond weak fields[J]. Physical Review. E, Statistical, Nonlinear, and Soft Matter Physics,2012,86(6Pt1): 061506. |
| 19 | 郭硕鸿. 电动力学[M].北京: 高等教育出版社, 2008. |
| 20 | Chen Z S, Rhee S H. Effect of traveling wave on the vortex-induced vibration of a long flexible pipe[J]. Applied Ocean Research, 2019, 84(1): 122-132. |
| 21 | Rida A, Gijs M A M. Manipulation of self-assembled structures of magnetic beads for microfluidic mixing and assaying[J]. Analytical Chemistry, 2004, 76(21): 6239-6246. |
| 22 | Cahill B P, Heyderman L J, Gobrecht J, et al. Electro-osmotic streaming on application of traveling-wave electric fields[J]. Physical Review. E, Statistical, Nonlinear, and Soft Matter Physics, 2004, 70(3Pt2): 6305. |
| 23 | Chi Xin-li, Wang Cun-xu, Gao Qing-zhong, et al.Application of fuzzy predictive control in adding medicament of water treatment[C]∥International Conference on Electronics and Optoelectronics, Proceedings, 2011: 1108-1110. |
| 24 | Chi Xin-li, Lin Sheng, Han Xi-chang, et al. Application studies of fuzzy control on adding medicament in circulating water treatment[J]. Advanced Materials Research, 2012, 466/467: 328-331. |
| 25 | Chi Xin-li, Zhang Yu-yan, Lin Sheng, et al. Research of coordinated control for thermal power unit based on fractional order controller[J]. International Journal of Control and Automation, 2016, 9(11): 103-112. |
| 26 | Chi Xin-li, Yu Hong-xia, Gao Qing-zhong. Dissipative control for an epidemic system with exponential incidence rate[C]∥Proceedings of the 36th Chinese Control Conference, 2017: 439-444. |
| No related articles found! |
|
||