吉林大学学报(工学版) ›› 2024, Vol. 54 ›› Issue (8): 2214-2222.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb.20221386
TrafficPro:一种针对城市信控路网的路段速度预测框架
温晓岳1( ),钱国敏2,3,孔桦桦2,缪月洁2,王殿海1(
),钱国敏2,3,孔桦桦2,缪月洁2,王殿海1( )
)
- 1.浙江大学 智能交通研究所,杭州 310058
2.银江技术股份有限公司,杭州 310023
3.浙江工业大学 信息工程学院,杭州 310023
TrafficPro: a framework to predict link speeds on signalized urban traffic network
Xiao-yue WEN1( ),Guo-min QIAN2,3,Hua-hua KONG2,Yue-jie MIU2,Dian-hai WANG1(
),Guo-min QIAN2,3,Hua-hua KONG2,Yue-jie MIU2,Dian-hai WANG1( )
)
- 1.Intelligent Transportation Research Institute,Zhejiang University,Hangzhou 310058,China
2.Enjoyor Technology Co. ,Ltd. ,Hangzhou 310023,China
3.College of Information Engineering,Zhejiang University of Technology,Hangzhou 310023,China
摘要:
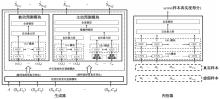
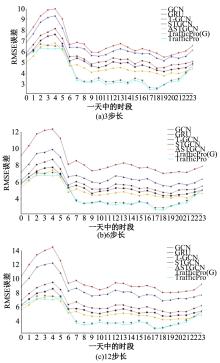
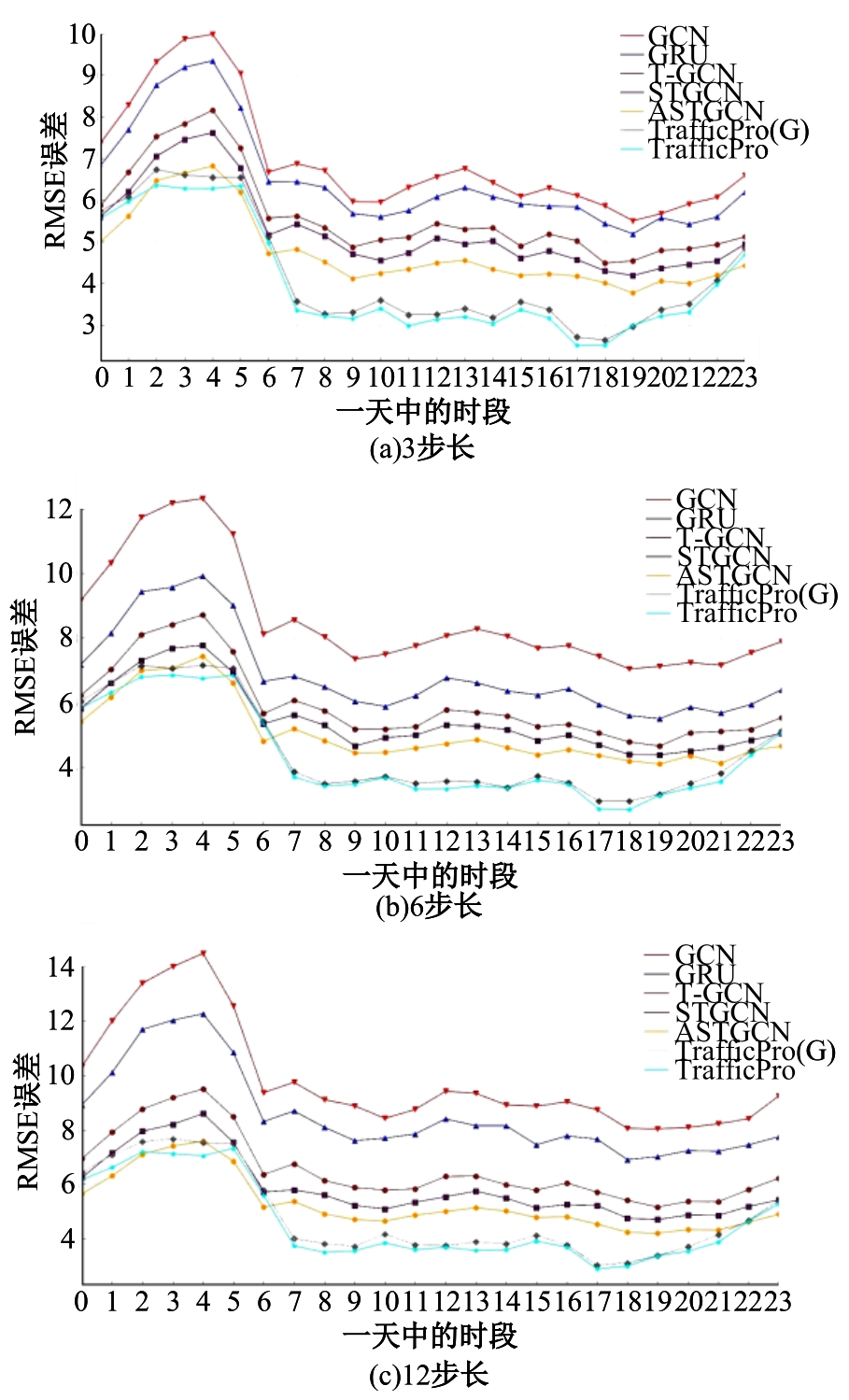
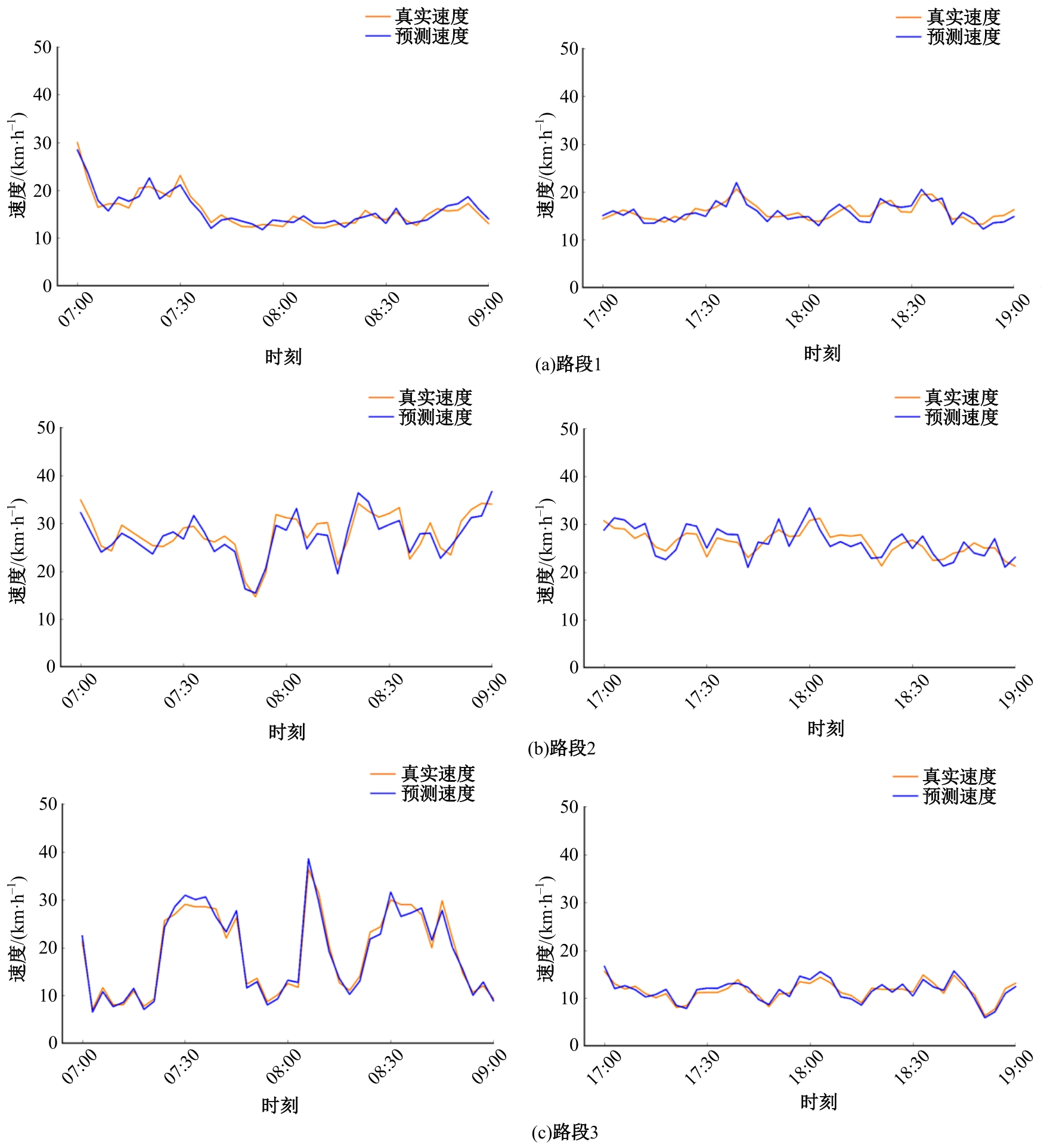
针对传统深度学习模型在城市路网速度预测时没有考虑交通流的主动时变特性(信号管控信息),而存在预测精度低的问题,提出了一种基于生成对抗网络与图神经网络的速度预测框架。在该框架中,生成器网络通过主动与被动预测模块同时编码路网交通流与信控信息,生成预测结果,随后使用判别器网络提高预测结果的泛化性。该框架可以获得比传统时间序列模型及深度学习模型更高的预测精度,在真实路网速度预测场景中,可使预测误差相比于最好的基准模型下降3%~5%。
中图分类号:
- U491
| 1 | Jin J, Rong D, Pang Y, et al. PRECOM: a parallel recommendation engine for control, operations, and management on congested urban traffic networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems, 2022, 23(7): 7332-7342. |
| 2 | 巫威眺, 曾坤, 周伟, 等. 基于多源数据和响应面优化的公交客流预测深度学习方法[J]. 吉林大学学报: 工学版, 2023, 53(7): 2001-2015. |
| Wu Wei-tiao, Zeng Kun, Zhou Wei, et al. Deep learning method for bus passenger flow prediction based on multi-source data and surrogate-based optimization[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Engineering and Technology Edition), 2023, 53(7): 2001-2015. | |
| 3 | 高海龙, 徐一博, 侯德藻, 等. 基于深度异步残差网络的路网短时交通流预测算法[J]. 吉林大学学报: 工学版, 2023, 53(12): 3458-3464. |
| Gao Hai-long, Xu Yi-bo, Hou De-zao, et al. Short-term traffic flow prediction algorithm for road network based on deep asynchronous residual network[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Engineering and Technology Edition), 2023, 53(12): 3458-3464. | |
| 4 | Guo S, Lin Y, Feng N, et al. Attention based spatial-temporal graph convolutional networks for traffic flow forecasting[C]∥Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Palo Alto, Spain, 2019: 922-929. |
| 5 | Liu J, Guan W. A summary of traffic flow forecasting methods[J]. Journal of Highway Transportation Research Development, 2004, 21(3): 82-85. |
| 6 | Welling M, Kipf T N. Semi-supervised classification with graph convolutional networks[C]∥Proceedings of International Conference on Learning Representations, Toulon, France, 2017: 1-14. |
| 7 | Veličković P, Cucurull G, Casanova A, et al. Graph attention networks[C]∥Proceedings of International Conference on Learning Representations, Vancouver, Canada, 2018: 1-12. |
| 8 | Yu B, Yin H, Zhu Z. Spatio-temporal graph convolutional networks: a deep learning framework for traffic forecasting[C]∥Proceedings of the International Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Stockholm, Sweden, 2018: 3634-3640. |
| 9 | Mahler G, Vahidi A. An optimal velocity-planning scheme for vehicle energy efficiency through probabilistic prediction of traffic-signal timing[J]. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems, 2018, 15(6): 2516-2523. |
| 10 | Shin J, Sunwoo M. Vehicle speed prediction using a markov chain with speed constraints[J]. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems, 2018, 20(9): 3201-3211. |
| 11 | Xu D, Wei C, Peng P, et al. GE-GAN: a novel deep learning framework for road traffic state estimation[J]. Transportation Research Part C: Emerging Technologies, 2020, 117: 102-135. |
| 12 | Zhang L, Wu J, Shen J, et al. SATP-GAN: self-attention based generative adversarial network for traffic flow prediction[J]. Transportmetrica B: Transport Dynamics, 2021, 9(1): 552-568. |
| 13 | Wang J, Wang W, Liu X, et al. Traffic prediction based on auto spatiotemporal multi-graph adversarial neural network[J]. Physica A: Statistical Mechanics and its Applications, 2022, 590: 126-136. |
| 14 | Du C, Chen Z, Feng F, et al. Explicit interaction model towards text classification[C]∥Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Palo Alto, Spain, 2020: 6359-6366. |
| 15 | Wang S, Cao J, Chen H, et al. SeqST-GAN: Seq2Seq generative adversarial nets for multi-step urban crowd flow prediction[J]. ACM Transactions on Spatial Algorithms and Systems, 2020, 6(4): 1-24. |
| 16 | Arjovsky M, Chintala S, Bottou L. Wasserstein generative adversarial networks[C]∥Proceedings of International Conference on Machine Learning, Sydney, Australia, 2017: 214-223. |
| 17 | Zhang Y, Wang S, Chen B, et al. GCGAN: generative adversarial nets with graph CNN for network-scale traffic prediction[C]∥Proceedings of International Joint Conference on Neural Networks, Budapest, Hungary, 2019: 1-8. |
| 18 | Cho K, Merrienboer B V, Bahdanau D, et al. On the properties of neural machine translation: encoder-decoder approaches[C]// Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing, Doha, Qatar, 2014: 103-111. |
| 19 | Zhao L, Song Y, Zhang C, et al. T-GCN: a temporal graph convolutional network for traffic prediction[J]. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems, 2019, 21(9): 3848-3858. |
| 20 | Sims A G, Dobinson K W. The Sydney coordinated adaptive traffic (SCAT) system philosophy and benefits[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 1980, 29(2): 130-137. |
| [1] | 闫云娟,查伟雄,石俊刚,严丽平. 基于随机充电需求的充电桩优化双层模型[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(8): 2238-2244. |
| [2] | 曲大义,刘浩敏,杨子奕,戴守晨. 基于车路协同的交通瓶颈路段车流动态分配机制及模型[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(8): 2187-2196. |
| [3] | 赖丹晖,罗伟峰,袁旭东,邱子良. 复杂环境下多模态手势关键点特征提取算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(8): 2288-2294. |
| [4] | 郭昕刚,何颖晨,程超. 抗噪声的分步式图像超分辨率重构算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(7): 2063-2071. |
| [5] | 陈桂珍,程慧婷,朱才华,李昱燃,李岩. 考虑驾驶员生理信息的城市交叉口风险评估方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(5): 1277-1284. |
| [6] | 赵晓华,刘畅,亓航,欧居尚,姚莹,郭淼,杨海益. 高速公路交通事故影响因素及异质性分析[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(4): 987-995. |
| [7] | 杨秀建,贾晓寒,张生斌. 考虑汽车队列动态特性的混合交通流特性[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(4): 947-958. |
| [8] | 范博松,邵春福. 城市轨道交通突发事件风险等级判别方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(2): 427-435. |
| [9] | 郑长江,胡欢,杜牧青. 考虑枢纽失效的多式联运快递网络结构设计[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(8): 2304-2311. |
| [10] | 王殿海,胡佑薇,蔡正义,曾佳棋,姚文彬. 基于BPR函数的城市道路间断流动态路阻模型[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(7): 1951-1961. |
| [11] | 李艳波,柳柏松,姚博彬,陈俊硕,渠开发,武奇生,曹洁宁. 考虑路网随机特性的高速公路换电站选址[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(5): 1364-1371. |
| [12] | 吕卫,韩镓泽,褚晶辉,井佩光. 基于多模态自注意力网络的视频记忆度预测[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(4): 1211-1219. |
| [13] | 胡莹,邵春福,王书灵,蒋熙,孙海瑞. 基于共享单车骑行轨迹的骑行质量识别方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(4): 1040-1046. |
| [14] | 王占中,蒋婷,张景海. 基于模糊双边界网络模型的道路运输效率评价[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(2): 385-395. |
| [15] | 杨敏,张聪伟,李大韦,马晨翔. 基于贝叶斯网的空铁联程乘客出行满意度模型[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(10): 2839-2846. |
|