吉林大学学报(工学版) ›› 2023, Vol. 53 ›› Issue (10): 2839-2846.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb.20220134
基于贝叶斯网的空铁联程乘客出行满意度模型
杨敏1,2( ),张聪伟1,2,李大韦1,2(
),张聪伟1,2,李大韦1,2( ),马晨翔1,2
),马晨翔1,2
- 1.东南大学 城市智能交通江苏省重点实验室,南京 211189
2.东南大学 交通学院,南京 211189
Travel satisfaction model for air-rail integration passengers based on Bayesian network
Min YANG1,2( ),Cong-wei ZHANG1,2,Da-wei LI1,2(
),Cong-wei ZHANG1,2,Da-wei LI1,2( ),Chen-xiang MA1,2
),Chen-xiang MA1,2
- 1.Jiangsu Key Laboratory of Urban ITS,Southeast University,Nanjing 211189,China
2.School of Transportation,Southeast University,Nanjing 211189,China
摘要:
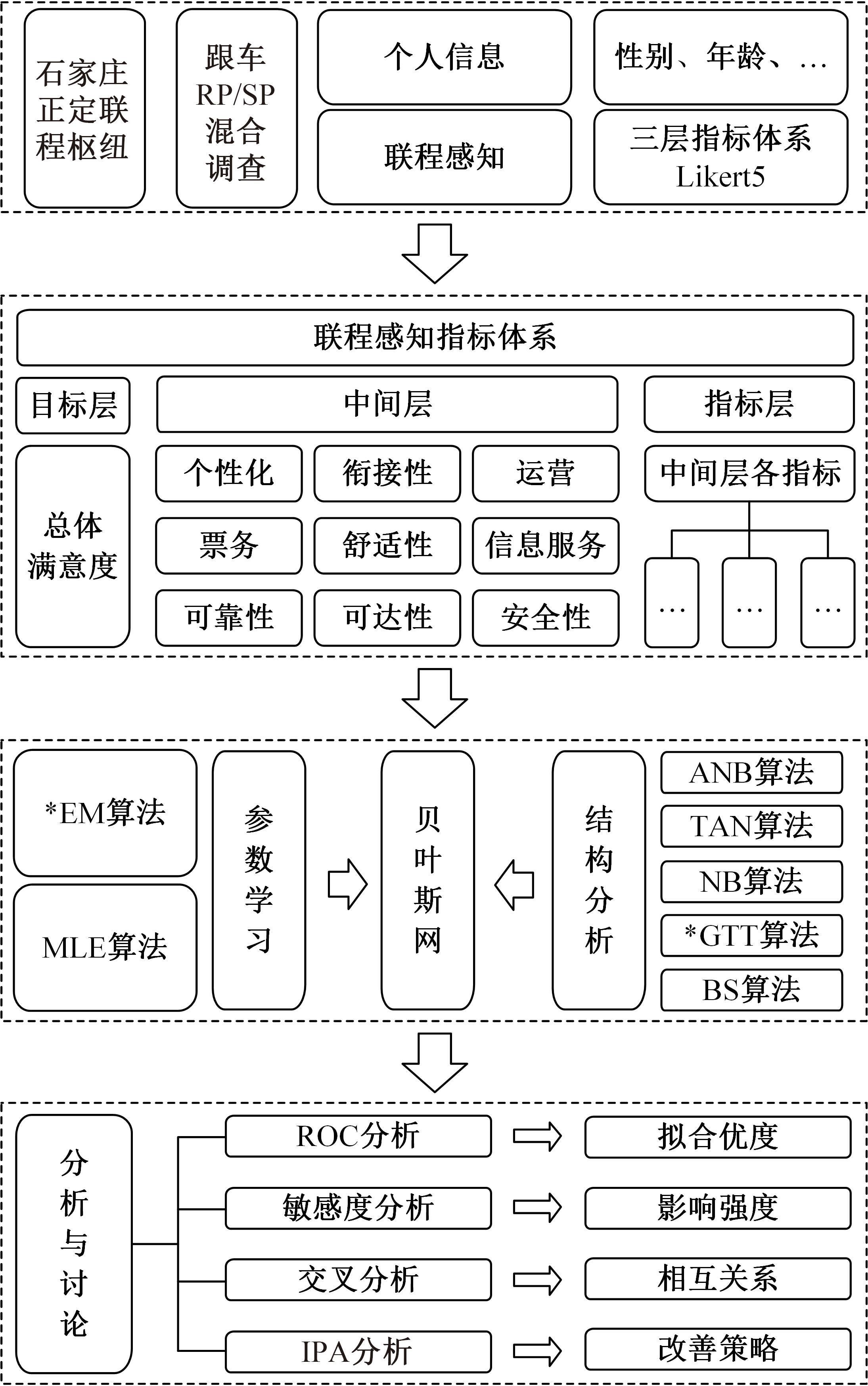
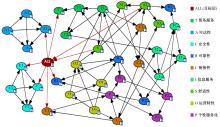
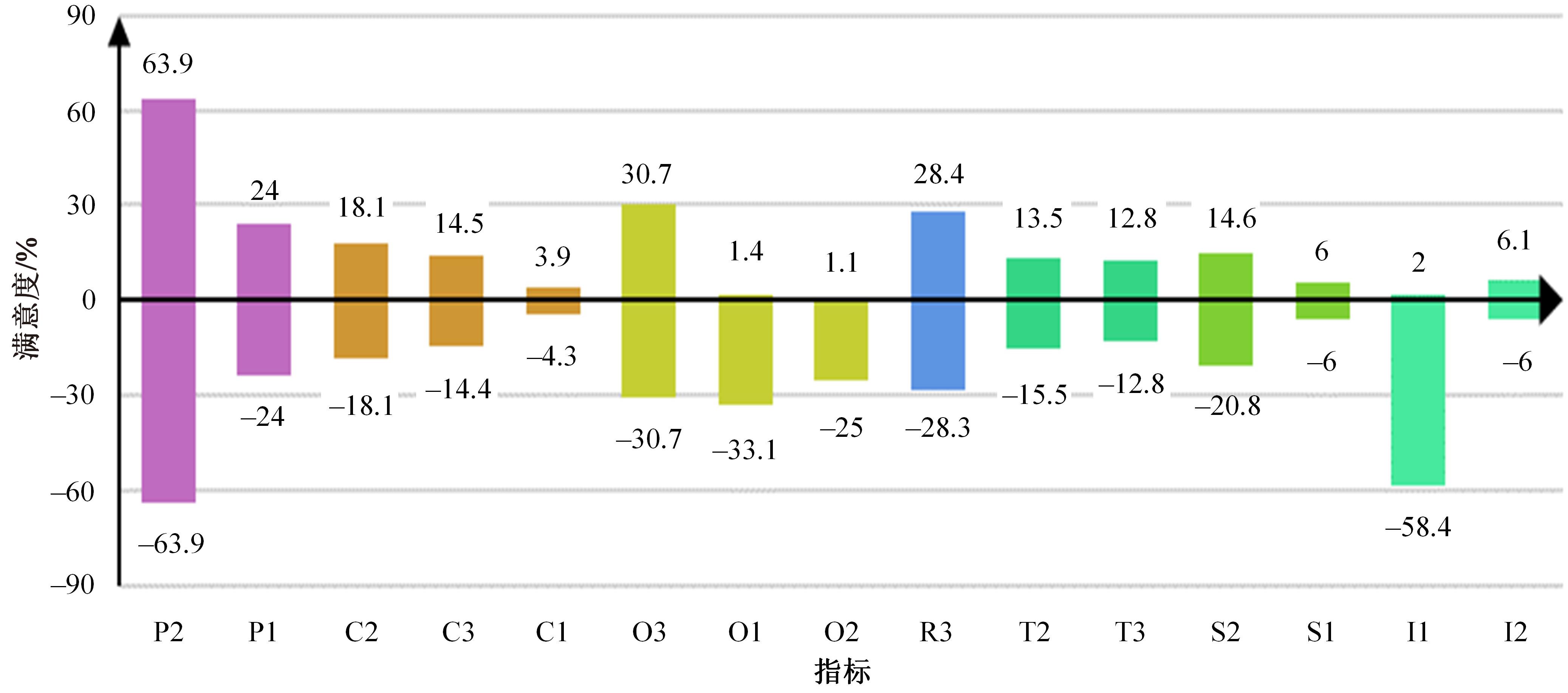
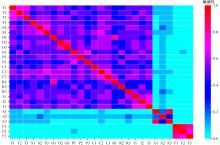
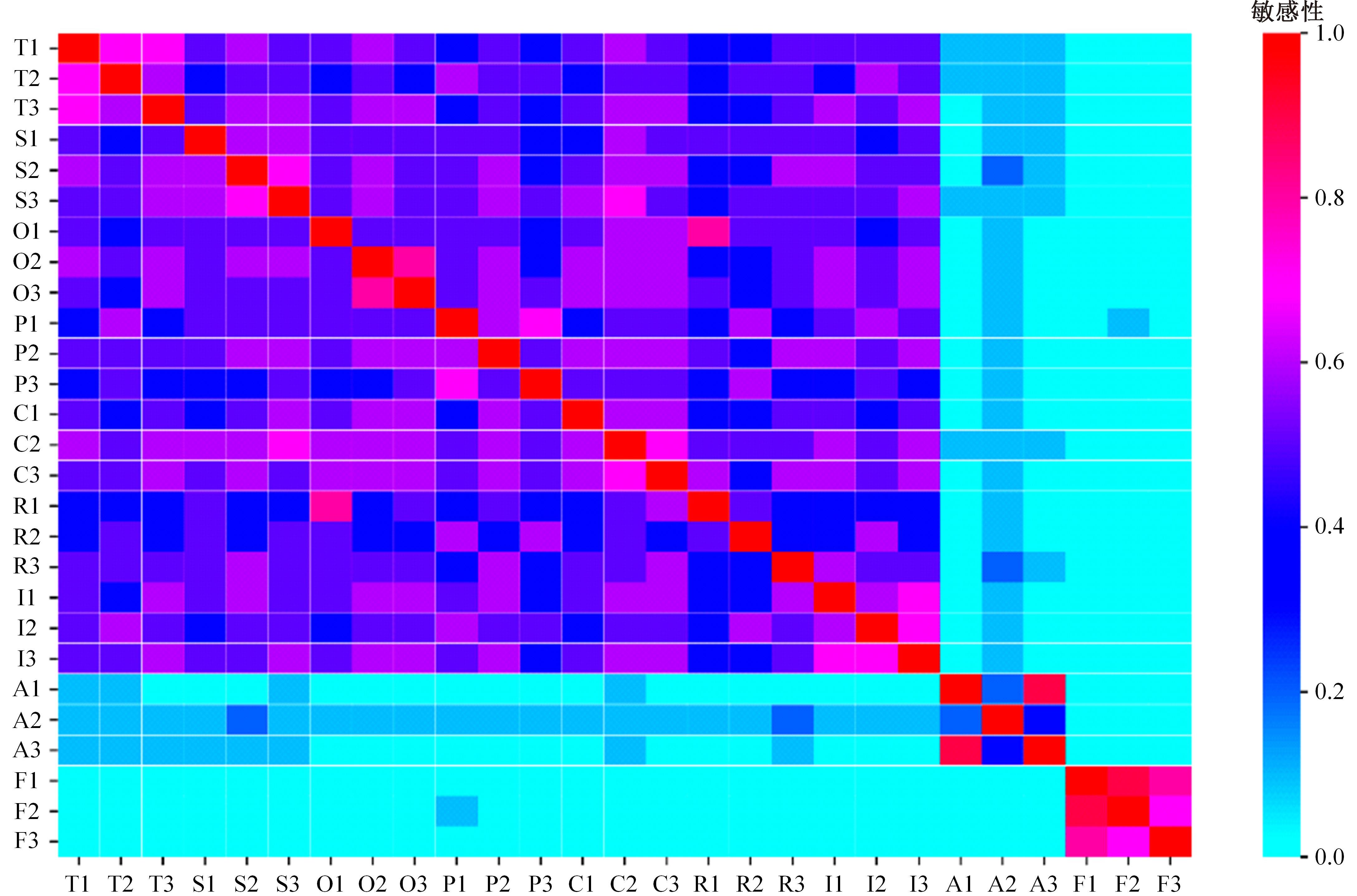
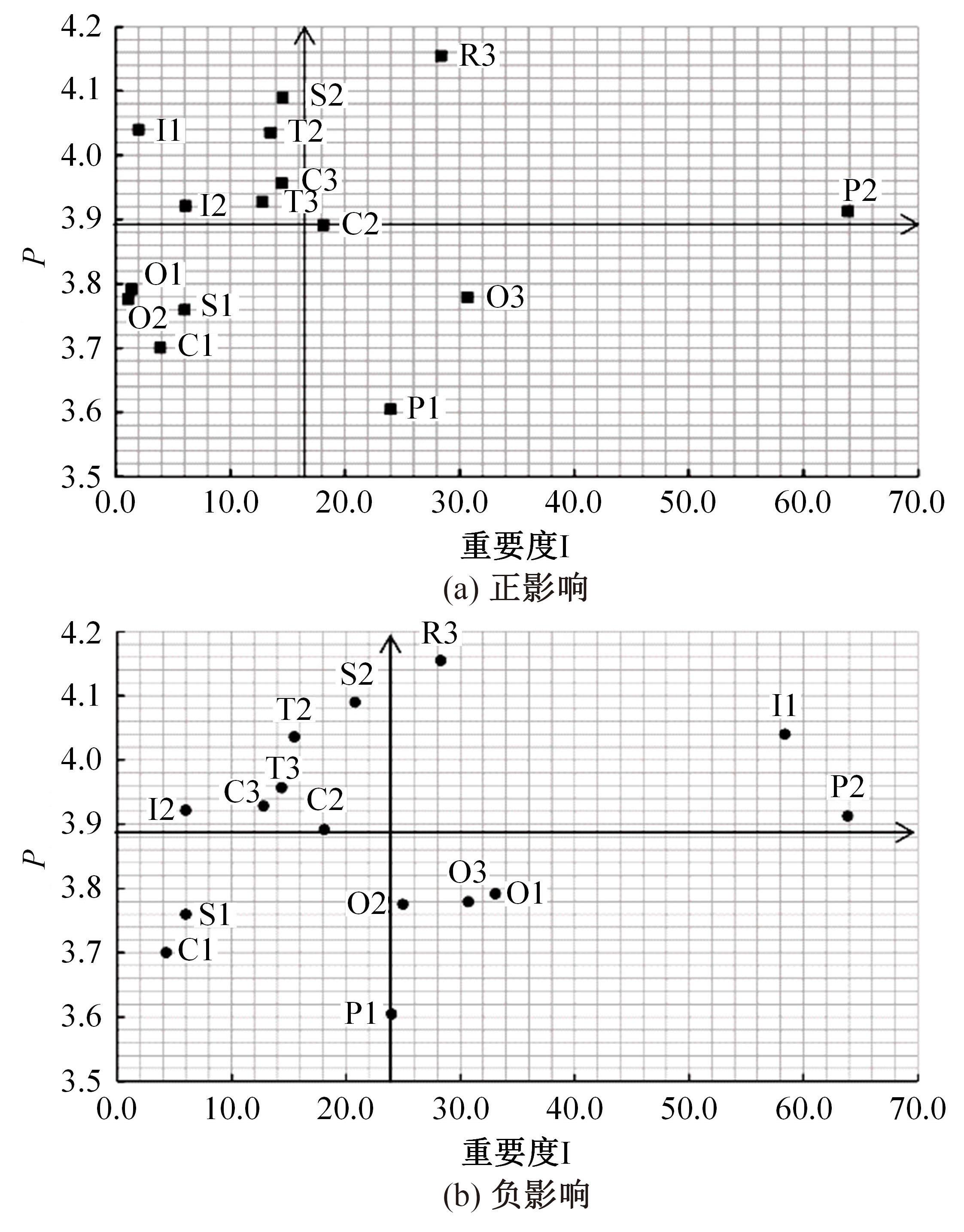
为揭示空铁联程乘客感知对乘客总体满意度影响情况,建立了包含目标层、中间层以及指标层的三层指标体系,结合GTT(Greedy thick thinning)与EM(Expectation maximization)算法构建了贝叶斯网,分析了9个分类满意度对乘客总体满意度的影响。结果显示,各分类满意度对总体满意度影响从强到弱依次为个性化、衔接性、运营、可靠性、票务、舒适性以及信息服务,可达性与安全性对总体满意度影响甚微。交叉分析结果定量反映了乘客满意度指标间的复杂相互关系。采用重要性-绩效分析法(IPA)定量分析了后续改善策略,得出目前运营班次、行李托运、开通线路、运营时段需要进行重点改善,换乘指示、座椅舒适、取票便捷、票价、换乘质量、信息规划存在过度改善问题。
中图分类号:
- U15
| 1 | 杨敏, 李宏伟, 任怡凤, 等. 基于旅客异质性画像的公铁联程出行方案推荐方法[J]. 清华大学学报: 自然科学版, 2022,62(7): 1-8. |
| Yang Min, Li Hong-Wei, Ren Yi-feng, et al. A method for recommending public-rail travel plans based on passenger heterogeneity portraits[J]. Journal of Tsinghua University(Natural Science Edition), 2022,62(7): 1-8. | |
| 2 | Gundelfinger-Casar J, Coto-Millán P. Intermodal competition between high-speed rail and air transport in Spain[J]. Utilities Policy, 2017, 47: 12-17. |
| 3 | Köse S. Investigation of the effect of rail passenger transport on air passenger transport in intermodal transport: Samsun and Trabzon example[J]. Journal of Transportation and Logistics, 2021, 6(2): 149-162. |
| 4 | Chen Z. Impacts of high-speed rail on domestic air transportation in China[J]. Journal of Transport Geography, 2017, 62: 184-196. |
| 5 | Sato K, Chen Y. Analysis of high-speed rail and airline transport cooperation in presence of non-purchase option[J]. Journal of Modern Transportation, 2018, 26(4): 231-254. |
| 6 | Li X, Jiang C, Wang K, et al. Determinants of partnership levels in air-rail cooperation[J]. Journal of Air Transport Management, 2018, 71: 88-96. |
| 7 | Jiang C, D'Alfonso T, Wan Y. Air-rail cooperation: Partnership level, market structure and welfare implications[J]. Transportation Research Part B: Methodological, 2017, 104: 461-482. |
| 8 | Li Z, Sheng D. Forecasting passenger travel demand for air and high-speed rail integration service: A case study of Beijing-Guangzhou corridor, China[J]. Transportation Research Part A: Policy and Practice, 2016, 94: 397-410. |
| 9 | Jiang Y, Yu S, Guan W, et al. Ground access behaviour of air-rail passengers: a case study of Dalian ARIS[J]. Travel Behaviour and Society, 2021, 24: 152-163. |
| 10 | 杨敏,任怡凤,盛强,等. 基于随机森林算法的旅客空铁联运中转城市选择模型[J]. 东南大学学报:自然科学版, 2022, 52(1): 162-171. |
| Yang Min, Ren Yi-feng, Sheng Qiang, et al. A random forest algorithm-based passenger air-rail transit city selection model[J]. Journal of Southeast University (Natural Science Edition), 2022, 52(1): 162-171. | |
| 11 | Román C, Martín J C. Integration of HSR and air transport: Understanding passengers' preferences[J]. Transportation Research Part E: Logistics and Transportation Review, 2014, 71: 129-141. |
| 12 | Chen X, Lin L. The Integration of Air and Rail Technologies: Shanghai's Hongqiao integrated transport hub[J]. The Journal of Urban Technology, 2016, 23(2): 23-46. |
| 13 | Jiang Y, Timmermans H J P, Chen C, et al. Determinants of air-rail integration service of Shijiazhuang airport, China: analysis of historical data and stated preferences[J]. Transportmetrica B: Transport Dynamics, 2019, 7(1): 1572-1587. |
| 14 | Yuan Y, Yang M, Feng T, et al. Heterogeneity in passenger satisfaction with air-rail integration services: Results of a finite mixture partial least squares model[J]. Transportation Research Part A: Policy and Practice, 2021, 147: 133-158. |
| 15 | Yuan Y, Yang M, Feng T, et al. Analyzing heterogeneity in passenger satisfaction, loyalty, and complaints with air-rail integrated services[J]. Transportation Research Part D: Transport and Environment, 2021, 97: No.102950. |
| 16 | Fu X, Fu X, Juan Z, et al. Understanding public transit use behavior: integration of the theory of planned behavior and the customer satisfaction theory[J]. Transportation(Dordrecht), 2017, 44(5): 1021-1042. |
| 27 | Luis Machado-Leon J, de Ona R, de Ona J. The role of involvement in regards to public transit riders' perceptions of the service[J]. Transport Policy, 2016, 48: 34-44. |
| 18 | de Oña R, Machado J L, de Oña J. Perceived service quality, customer satisfaction, and behavioral intentions[J]. Transportation Research Record: Journal of the Transportation Research Board, 2019, 2538(1): 76-85. |
| 19 | Li D, Miwa T, Morikawa T. Modeling time-of-day car use behavior: a Bayesian network approach[J]. Transportation Research Part D: Transport and Environment, 2016, 47: 54-66. |
| [1] | 郑长江,胡欢,杜牧青. 考虑枢纽失效的多式联运快递网络结构设计[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(8): 2304-2311. |
| [2] | 王殿海,胡佑薇,蔡正义,曾佳棋,姚文彬. 基于BPR函数的城市道路间断流动态路阻模型[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(7): 1951-1961. |
| [3] | 李艳波,柳柏松,姚博彬,陈俊硕,渠开发,武奇生,曹洁宁. 考虑路网随机特性的高速公路换电站选址[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(5): 1364-1371. |
| [4] | 胡莹,邵春福,王书灵,蒋熙,孙海瑞. 基于共享单车骑行轨迹的骑行质量识别方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(4): 1040-1046. |
| [5] | 王占中,蒋婷,张景海. 基于模糊双边界网络模型的道路运输效率评价[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(2): 385-395. |
| [6] | 秦严严,杨晓庆,王昊. 智能网联混合交通流CO2排放影响及改善方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(1): 150-158. |
| [7] | 王立平,朱斌,吴军,陶子寒. 基于贝叶斯网络的盘式刀库故障分析[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(2): 280-287. |
| [8] | 闫云娟,查伟雄,石俊刚,李剑. 具有随机充电需求的混合动态网络平衡模型[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(1): 136-143. |
| [9] | 李浩,陈浩. 考虑充电排队时间的电动汽车混合交通路网均衡[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(5): 1684-1691. |
| [10] | 户佐安,夏一鸣,蔡佳,薛锋. 延误条件下综合多种策略的城轨列车运行调整优化[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(5): 1664-1672. |
| [11] | 朱才华,孙晓黎,李岩. 站点分类下的城市公共自行车交通需求预测[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(2): 531-540. |
| [12] | 罗清玉,田万利,贾洪飞. 考虑通勤需求的电动汽车充电站选址与定容模型[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2019, 49(5): 1471-1477. |
| [13] | 王利民,刘洋,孙铭会,李美慧. 基于Markov blanket的无约束型K阶贝叶斯集成分类模型[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2018, 48(6): 1851-1858. |
| [14] | 曹骞, 李君, 刘宇, 曲大为. 基于马尔科夫链的长春市乘用车行驶工况构建[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2018, 48(5): 1366-1373. |
| [15] | 孙晓颖, 扈泽正, 杨锦鹏. 基于分层贝叶斯网络的车辆发动机系统电磁脉冲敏感度评估[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2018, 48(4): 1254-1264. |
|
||