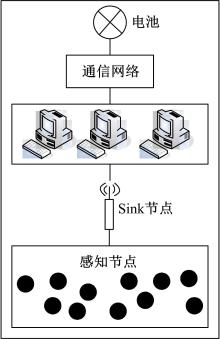
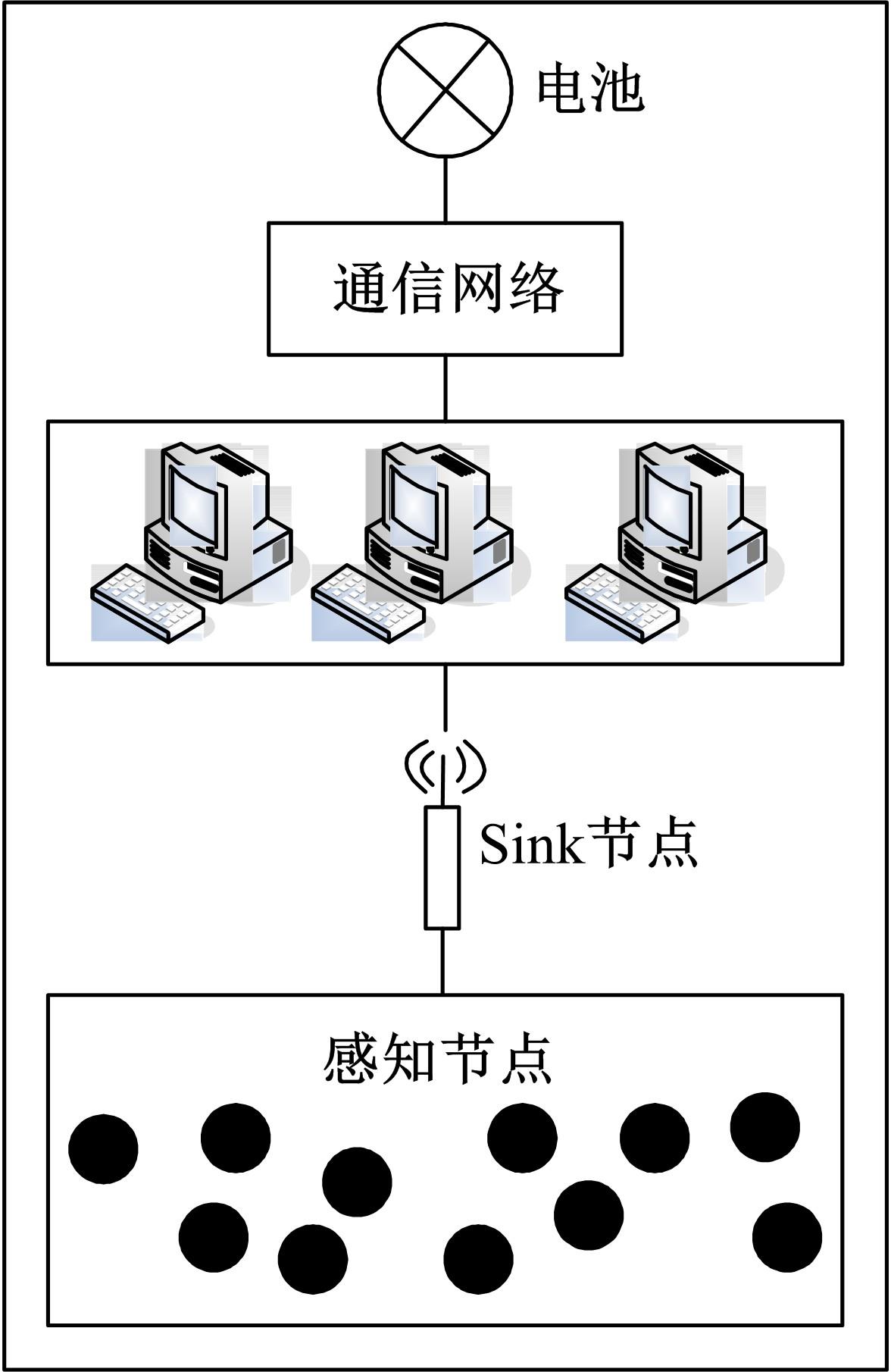
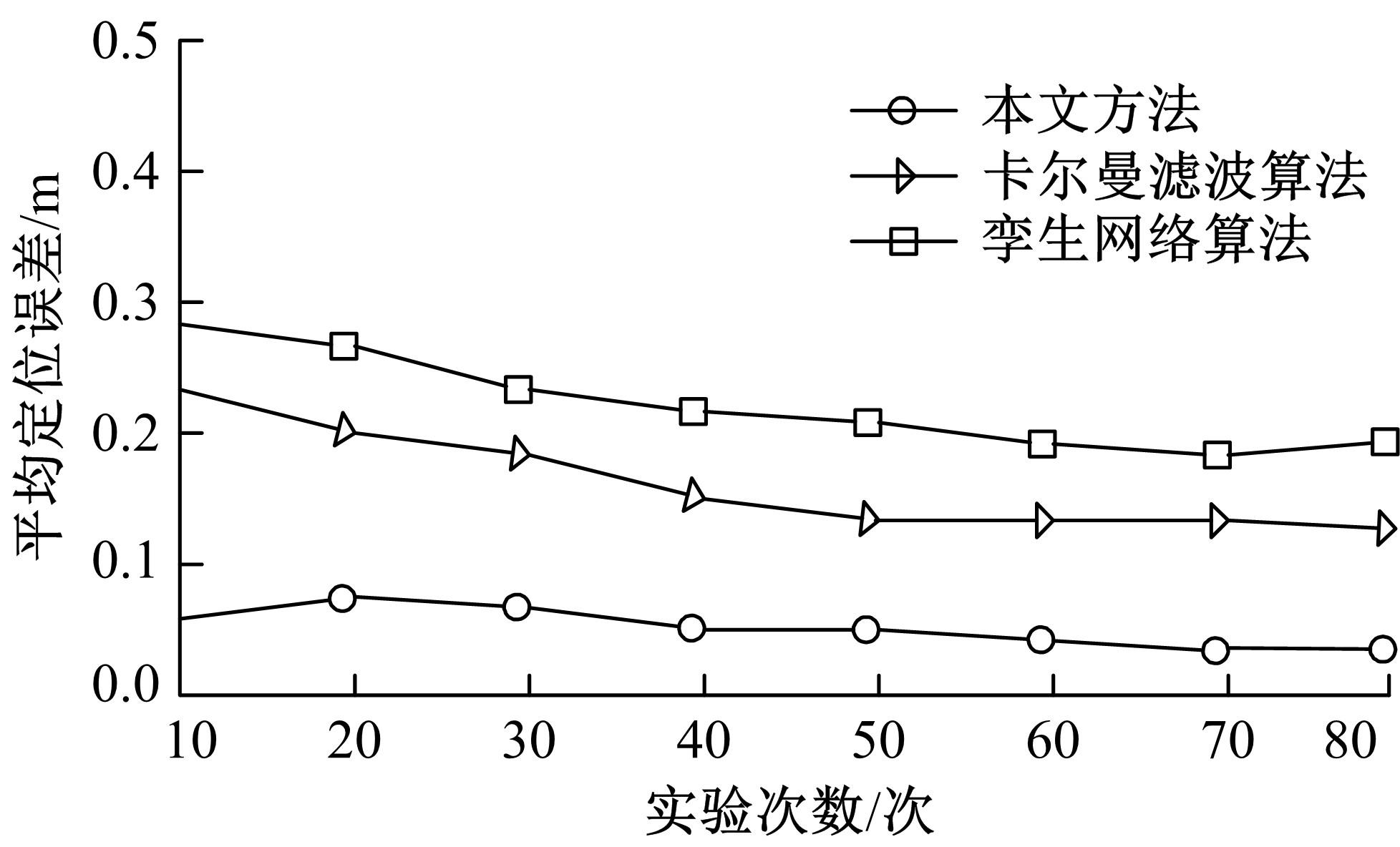
Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition) ›› 2023, Vol. 53 ›› Issue (5): 1458-1464.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb.20220137
Real⁃time tracking method of underground moving target based on weighted centroid positioning
Nan ZHANG1( ),Jian-hua SHI1,Ji YI2,Ping WANG1
),Jian-hua SHI1,Ji YI2,Ping WANG1
- 1.College of Mechanical and Electrical Engineering,Shanxi Datong University,Datong 037003,China
2.College of Coal Engineering,Shanxi Datong University,Datong 037003,China
CLC Number:
- TP242
| 1 | 赵文杰, 汤新民, 黄忠涛, 等. 基于改进IMM算法的机场移动目标轨迹跟踪与预测[J]. 武汉理工大学学报: 交通科学与工程版, 2020, 44(3): 468-473, 479. |
| Zhao Wen-jie, Tang Xin-min, Huang Zhong-tao, et al. Track tracking and prediction of airport moving target based on improved IMM algorithm[J]. Journal of Wuhan University of Technology(Traffic Science and Engineering Edition), 2020, 44(3): 468-473, 479. | |
| 2 | 徐义晗. 基于无迹卡尔曼滤波的移动目标跟踪算法[J]. 火力与指挥控制, 2020, 45(12): 149-152. |
| Xu Yi-han. Unscented KF-based mobile target tracking algorithm[J]. Fire Control & Command Control, 2020, 45(12): 149-152. | |
| 3 | 刘子龙, 王晨. 基于双模态输入的孪生网络目标跟踪算法[J]. 计算机应用研究, 2021, 38(12): 3796-3800. |
| Liu Zi-long, Wang Chen. Target tracking algorithm in Siamese network based on bimodal input[J]. Application Research of Computers, 2021, 38(12): 3796-3800. | |
| 4 | 国强, 崔玉强, 王勇. 无线传感器网络中基于动态簇的节点调度算法[J]. 吉林大学学报: 工学版, 2022, 52(6): 1466-1476. |
| Guo Qiang, Cui Yu-qiang, Wang Yong. Dynamic cluster-based node scheduling algorithm in wireless sensor networks[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2022, 52(6): 1466-1476. | |
| 5 | Lu M, Yi J, Wan X, et al. Target tracking in time-division-multifrequency-based passive radar[J]. IEEE Sensors Journal, 2020, 6(9): 4382-4394. |
| 6 | 陈丹, 姚伯羽. 运动模型引导的自适应核相关目标跟踪方法[J]. 电子学报, 2021, 49(3): 550-558. |
| Chen Dan, Yao Bo-yu. Adaptive response kernel correlation target tracking method guided by motion model[J]. Acta Electronica Sinica, 2021, 49(3): 550-558. | |
| 7 | Taguchi S, Kidono K. Exclusive association sampling to improve bayesian multi-target tracking[J]. IEEE Access, 2020, 8(25): 193116-193127. |
| 8 | 余汉蓉, 林彬, 俞增林. 结合SAMF和视觉显著性的目标跟踪算法[J]. 电光与控制, 2021, 28(1): 15-18, 32. |
| Yu Han-rong, Lin Bin, Yu Zeng-lin. An object tracking algorithm combining SAMF with visual saliency[J]. Electronics Optics & Control, 2021, 28(1): 15-18, 32. | |
| 9 | 尹莉莙, 蒋峥, 刘斌. 一种检测区域动态更新的目标跟踪算法[J]. 计算机仿真, 2021, 38(8): 333-338, 429. |
| Yin Li-jun, Jiang Zheng, Liu Bin. A target tracking algorithm for dynamic update of detecting regions[J]. Computer Simulation, 2021, 38(8): 333-338, 429. | |
| 10 | Luo J, Wang Z, Chen Y, et al. An improved unscented particle filter approach for multi-sensor fusion target tracking[J]. Sensors, 2020, 20(23): 20236842. |
| 11 | 张楠, 霍羽. 煤矿环境下人员移动无线传感器节点协同定位算法[J]. 吉林大学学报: 工学版, 2022, 52(5): 1168-1173. |
| Zhang Nan, Huo Yu. Cooperative location algorithm of wireless sensor nodes for personnel movement in coal mine environment[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2022, 52(5): 1168-1173. | |
| 12 | 张红颖, 贺鹏艺, 王汇三. 基于改进SiamFC的实时目标跟踪算法[J]. 激光与光电子学进展, 2021, 58(6): 308-316. |
| Zhang Hong-ying, He Peng-yi, Wang Hui-san. A real-time target-tracking algorithm based on improved siamFC[J]. Laser & Optoelectronics Progress, 2021, 58(6): 308-316. | |
| 13 | Li S, Feng X, Deng Z, et al. Minimum error entropy based multiple model estimation for multisensor hybrid uncertain target tracking systems[J]. IET Signal Processing, 2020, 14(3): 1049-1053. |
| 14 | 刘云, 钱美伊, 李辉, 等. 特征融合与训练加速的高效目标跟踪[J]. 计算机工程与应用, 2021, 57(10): 101-109. |
| Liu Yun, Qian Mei-yi, Li Hui, et al. Efficient object tracking with feature fusion and training acceleration[J]. Computer Engineering and Applications, 2021, 57(10): 101-109. | |
| 15 | 符磊, 顾文彬, 艾勇保, 等. 基于双孪生网络的可见光热红外目标实时鲁棒跟踪[J]. 吉林大学学报: 工学版, 2022, 52(12): 2906-2915. |
| Fu Lei, Gu Wen-bin, Ai Yong-bao, et al. Real-time robust tracking of visible light thermal infrared targets based on twin networks[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2022, 52(12): 2906-2915. | |
| 16 | Sxa B, Xg A, Qlh A, et al. Distributed guaranteed two-target tracking over heterogeneous sensor networks under bounded noises and adversarial attacks[J]. Information Sciences, 2020, 535(23): 187-203. |
| 17 | 慕巍, 张宝宜, 王新明, 等. 适用于光电跟踪仪的高速目标跟踪控制算法[J]. 激光与红外, 2020, 50(4): 468-474. |
| Mu Wei, Zhang Bao-yi, Wang Xin-ming, et al. High speed target tracking control algorithm for electro-optical tracker[J]. Laser & Infrared, 2020, 50(4): 468-474. | |
| 18 | Anvaripour M, Saif M, Ahmadi M. A novel approach to reliable sensor selection and target tracking in sensor networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics, 2020, 16(1): 171-182. |
| 19 | 罗元, 肖航, 欧俊雄. 基于深度学习的目标跟踪技术的研究综述[J]. 半导体光电, 2020, 41(6): 757-767. |
| Luo Yuan, Xiao Hang, Jun-xiong Ou. Research on target tracking technology based on deep learning[J]. Semiconductor Optoelectronics, 2020, 41(6): 757-767. | |
| 20 | 陈富健, 谢维信. 引入抗遮挡机制的SiamVGG网络目标跟踪算法[J]. 信号处理, 2020, 36(4): 562-571. |
| Chen Fu-jian, Xie Wei-xin. SiamVGG network target tracking algorithm with anti-occlusion mechanism [J]. Journal of Signal Processing, 2020, 36(4): 562-571. | |
| 21 | Li Z, Liao C, Yang Y, et al. High sensitivity gas pressure sensor based on multimode interferometer using hollow-core tube lattice fiber[J]. Optics Letters, 2020, 45(16): 4571-4574. |
| 22 | 李松, 程咏梅, 王会宾, 等. 时间偏差校准分布式多传感器多目标跟踪算法[J].西北工业大学学报,2020, 38(4): 797-805. |
| Li Song, Cheng Yong-mei, Wang Hui-bin, et al. Distributed multisensor multitarget tracking algorithm with time-offset registration[J]. Journal of Northwestern Polytechnical University, 2020, 38(4): 797-805. |
| [1] | Jun WANG,Yan-hui XU,Li LI. Data fusion privacy protection method with low energy consumption and integrity verification [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2022, 52(7): 1657-1665. |
| [2] | Qiang GUO,Yu-qiang CUI,Yong WANG. Nodes scheduling algorithm based on dynamic cluster in wireless sensor network [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2022, 52(6): 1466-1476. |
| [3] | Bin-bin YU,Liang HU,Ling CHI. Digital signature scheme against internal and external attack for wireless sensor networks [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2019, 49(5): 1676-1681. |
| [4] | LIU Zhou-zhou, PENG Han. Topology control algorithm based on node reliability in WSN [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2018, 48(2): 571-577. |
| [5] | TANG Kun, SHI Rong-hua. Detection of wireless sensor network failure area based on butterfly effect signal [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2017, 47(6): 1939-1948. |
| [6] | YU Bin-bin, WU Xin-yu, CHU Jian-feng, HU Liang. Signature protocol for wireless sensor network based on group key agreement [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2017, 47(3): 924-929. |
| [7] | DONG Ying, ZHOU Zhan-ying, SU Zhen-zhen, XU Yang, QIAN Zhi-hong. Cross-layer MAC protocol based on routing information for WSN [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2017, 47(2): 647-654. |
| [8] | ZHU Hai-yang, ZHANG He, MA Shao-jie. Parameter optimization of enhanced ultrasonic circumferential scanning node in WSN [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2017, 47(1): 262-267. |
| [9] | LIU Zhou-zhou, WANG Fu-bao. Improvement of discrete shuffled frog-leaping algorithm and application in compressed sensing reconstruction [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2016, 46(4): 1261-1268. |
| [10] | ZHANG Jing, LIU Yan-heng, ZHANG Jin-dong, SUN Geng. Cluster size adaptive adjustable strategy for wireless sensor networks [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2016, 46(3): 876-883. |
| [11] | TENG Zhi-jun, ZHANG Fan, SONG Ming-hui. Wireless sensor network energy balance ant colony routing algorithm [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2016, 46(1): 327-332. |
| [12] | WANG Li-ding, YUE Guo-dong, XU Zheng, LIU Chong, CHEN Yi, ZHAO Yue-xuan, WANG Tian-rao. Architecture and performance test of wireless sensor network system for distributed stress monitoring in high-speed railway track [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2015, 45(6): 1974-1979. |
| [13] | SONG Xiao-ying, WEN Tao, GUO Quan, ZHANG Dong-qing, SHENG Gang. Unequal cluster data gathering protocol with optimal cluster size in sensor networks [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2015, 45(6): 1961-1973. |
| [14] | LIU Kui, LIU San-yang. Mobile data collecting algorithm based on mixed sink strategy in WSNs [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2015, 45(5): 1680-1687. |
| [15] | KUANG Zhe-jun, SHI Wei-jia, HU Liang, ZHOU Hang. Delay-tolerant mobile-sink strategy on energy saving for wireless sensor networks [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2015, 45(5): 1586-1591. |
|
||