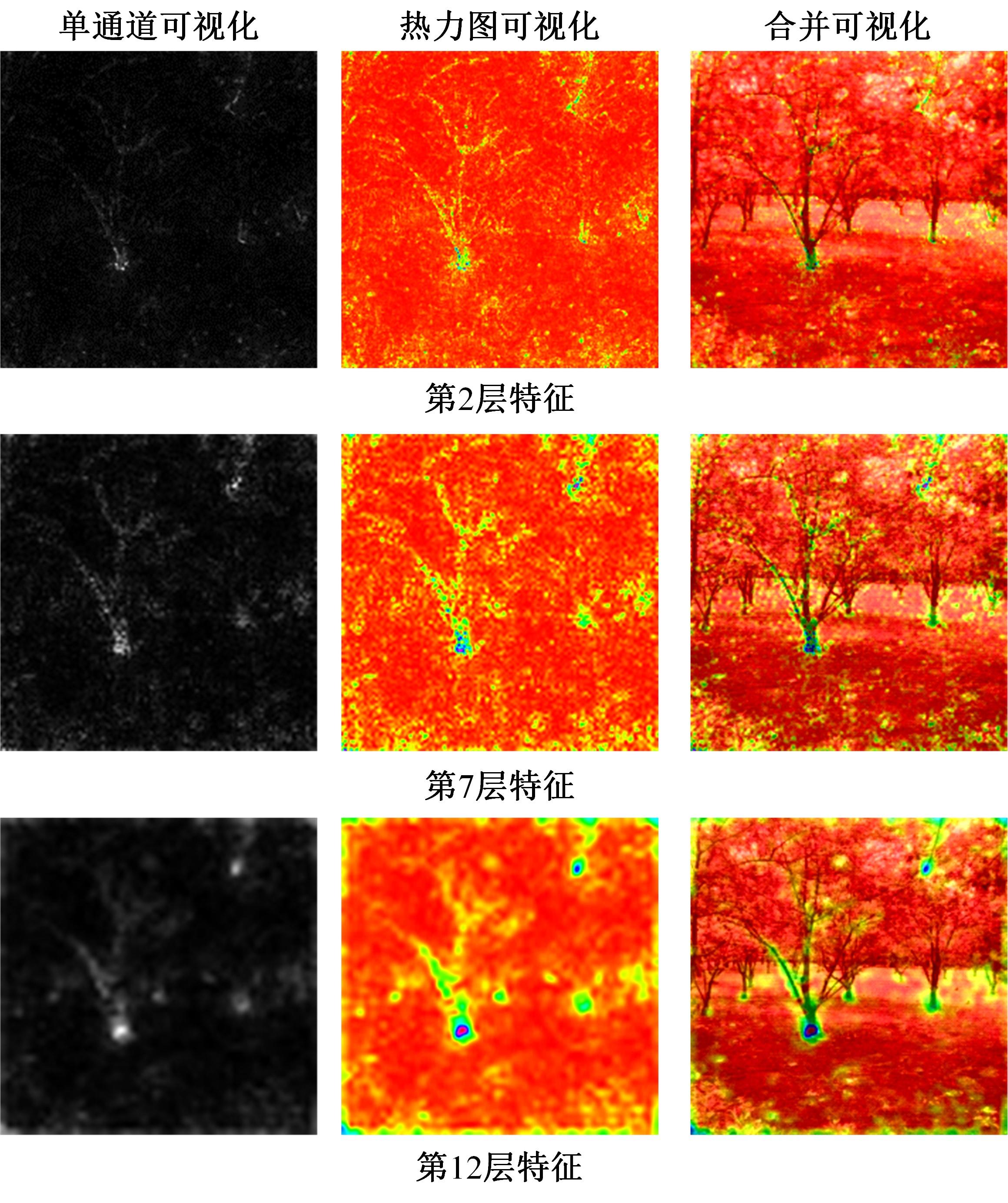
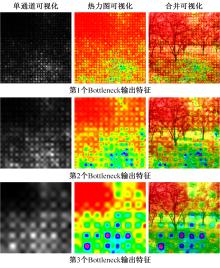
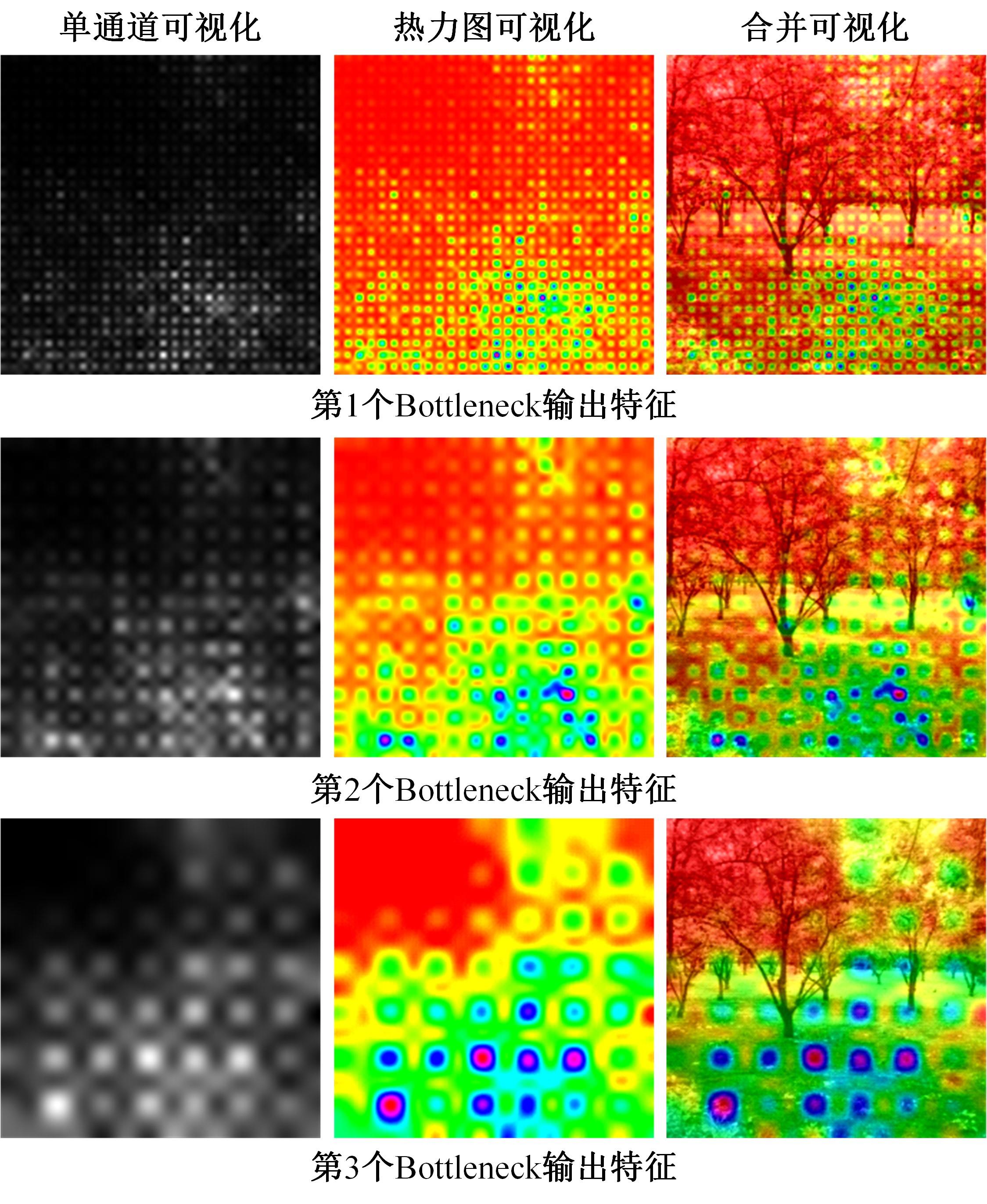
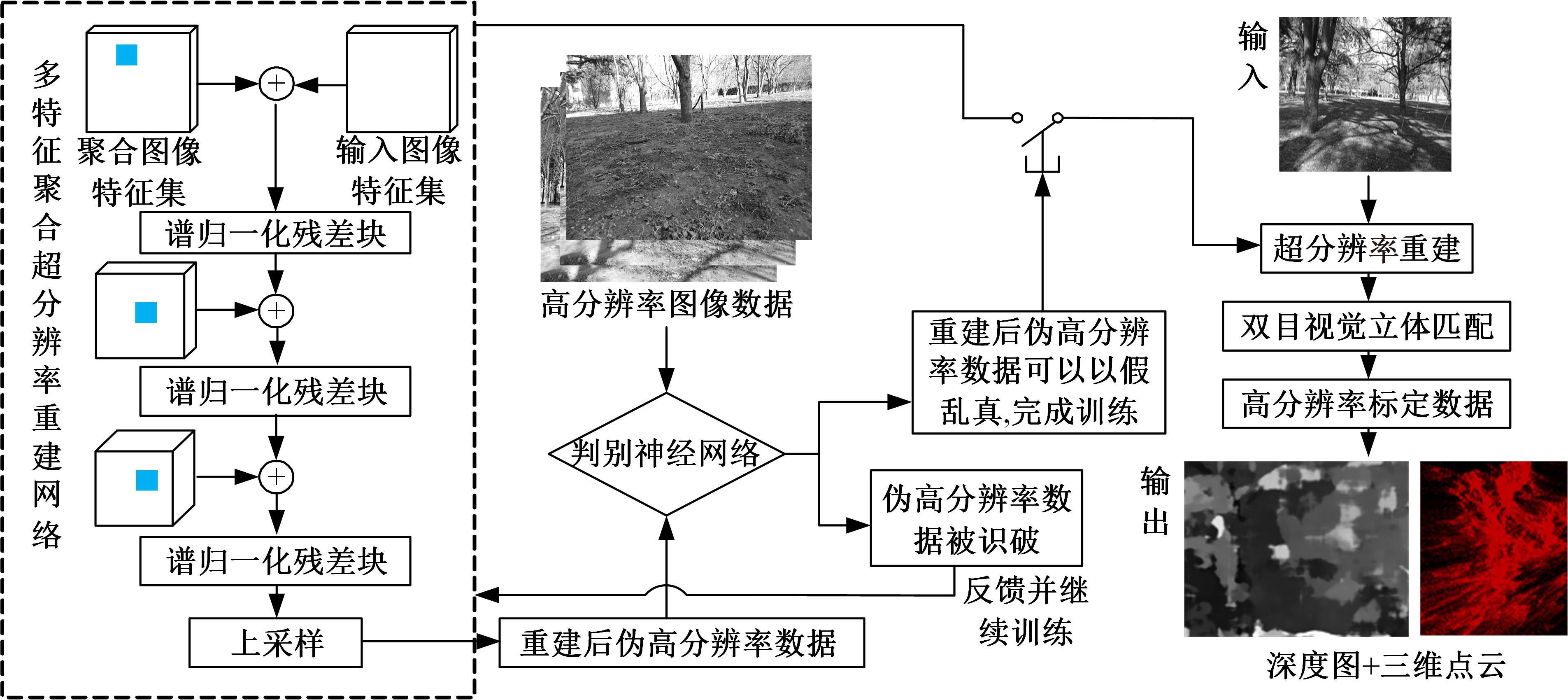
Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition) ›› 2024, Vol. 54 ›› Issue (5): 1469-1481.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb.20220816
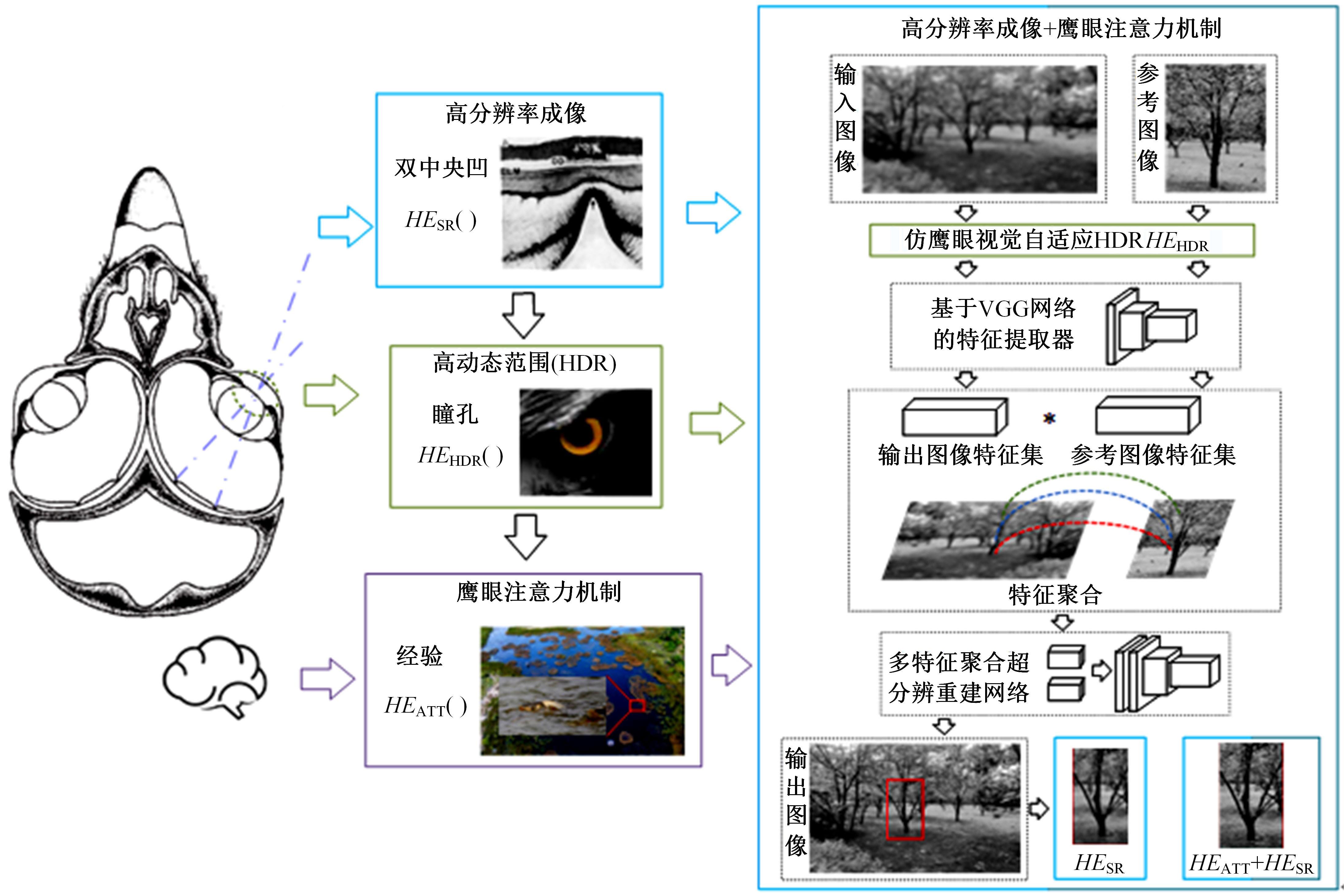
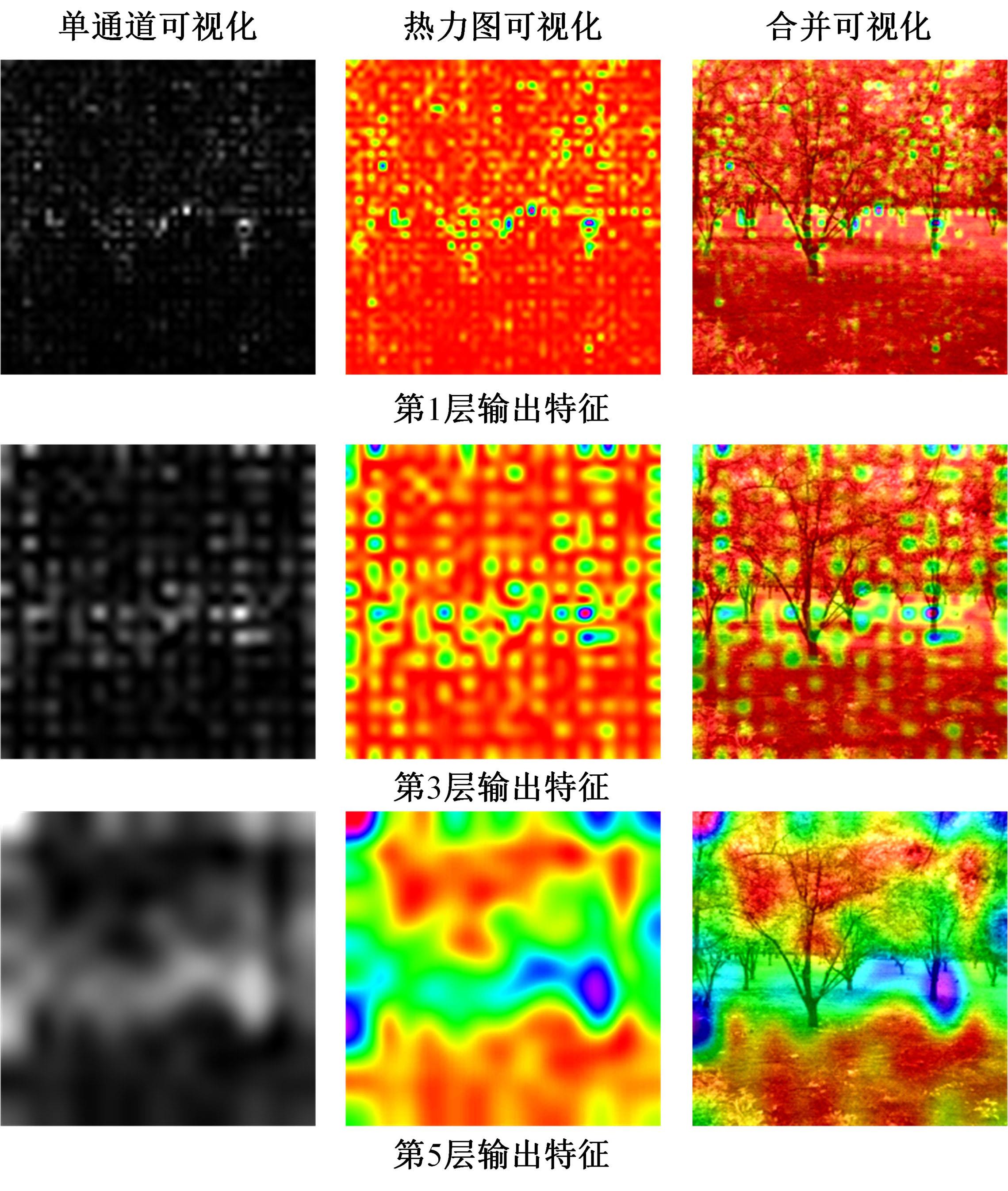
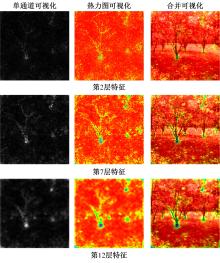
A mapping method using 3D orchard point cloud based on hawk-eye-inspired stereo vision and super resolution
Zi-chao ZHANG1,2( ),Jian CHEN1(
),Jian CHEN1( )
)
- 1.College of Engineering,China Agricultural University,Beijing 100083,China
2.Key Laboratory of Spatial-temporal Big Data Analysis and Application of Natural Resources in Megacities,MNR,Shanghai 200063,China
CLC Number:
- TP391.4
| 1 | 周云成, 许童羽, 邓寒冰, 等. 基于自监督学习的番茄植株图像深度估计方法[J]. 农业工程学报, 2019, 35(24): 173-182. |
| Zhou Yun-cheng, Xu Tong-yu, Deng Han-bing, et al. Method for estimating the image depth of tomato plant based on self-supervised learning[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering, 2019, 35(24): 173-182. | |
| 2 | Wang Y, Chao W L, Garg D, et al. Pseudo-lidar from visual depth estimation: bridging the gap in 3D object detection for autonomous driving[C]∥Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on CVPR, Long Beach, USA, 2019: 8445-8453. |
| 3 | 李秋洁, 丁旭东, 邓贤. 基于激光雷达的果园行间路径提取与导航[J]. 农业机械学报, 2020, 51(S2): 344-350. |
| Li Qiu-jie, Ding Xu-dong, Deng Xian. Intra-row path extraction and navigation for orchards based on LiDAR[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society for Agricultural Machinery, 2020, 51(S2): 344-350. | |
| 4 | Morgan G L K, Liu J G, Yan H S. Precise subpixel disparity measurement from very narrow baseline stereo[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2010, 48(9): 3424-3433. |
| 5 | 于晓丹, 张远杰, 王元元. 小型无人机载大视场复眼相机光学系统设计[J]. 光子学报, 2019, 48(7): 23-30. |
| Yu Xiao-dan, Zhang Yuan-jie, Wang Yuan-yuan, et al. Optical design of a compound eye camera with a large-field of view for unmanned aerial vehicles[J]. Acta Photomica Sinica, 2019, 48(7): 23-30. | |
| 6 | Nguyen C, Park J, Cho K. Novel descattering approach for stereo vision in dense suspended scatterer environments[J]. Sensors, 2017, 17(6): 14-25. |
| 7 | 杨燕, 张国强, 姜沛沛. 结合景深估计的高斯衰减与自适应补偿去雾[J]. 光学精密工程, 2019, 27(11): 2439-2449. |
| Yang Yan, Zhang Guo-qiang, Jiang Pei-pei. Gaussian decay and adaptive compensation dehazing algorithm combined with scene depth estimation[J]. Optics and Precision Engineering, 2019, 27(11): 2439-2449. | |
| 8 | 段海滨, 张奇夫, 邓亦敏, 等. 基于仿鹰眼视觉的无人机自主空中加油[J]. 仪器仪表学报, 2014, 35(7): 1450-1458. |
| Duan Hai-bin, Zhang Qi-fu, Deng Yi-min, et al. Biologically eagle-eye-based autonomous aerial refueling for unmanned aerial vehicles[J]. Chinese Journal of Scientific Instrument, 2014, 35(7): 1450-1458. | |
| 9 | 赵国治, 段海滨. 仿鹰眼视觉技术研究进展[J]. 中国科学: 技术科学, 2017, 47(5): 514-523. |
| Zhao Guo-zhi, Duan Hai-bin. Progresses in biological eagle-eye vision technology[J]. Science China Technological Sciences, 2017, 47(5): 514-523. | |
| 10 | Harmening W M, Nikolay P, Orlowski J, et al. Spatial contrast sensitivity and grating acuity of barn owls[J]. Journal of Vision, 2009, 9(7): 1-12. |
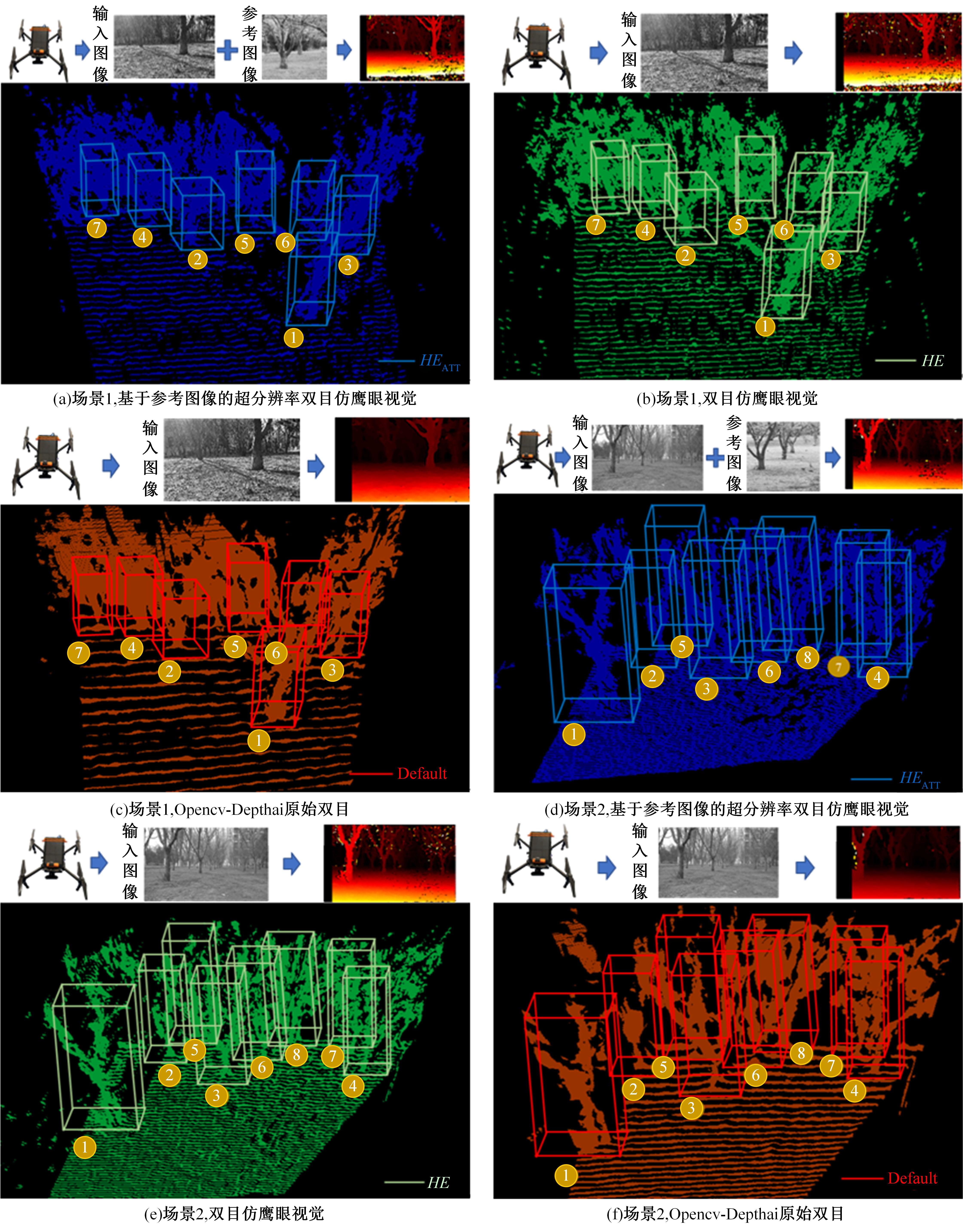
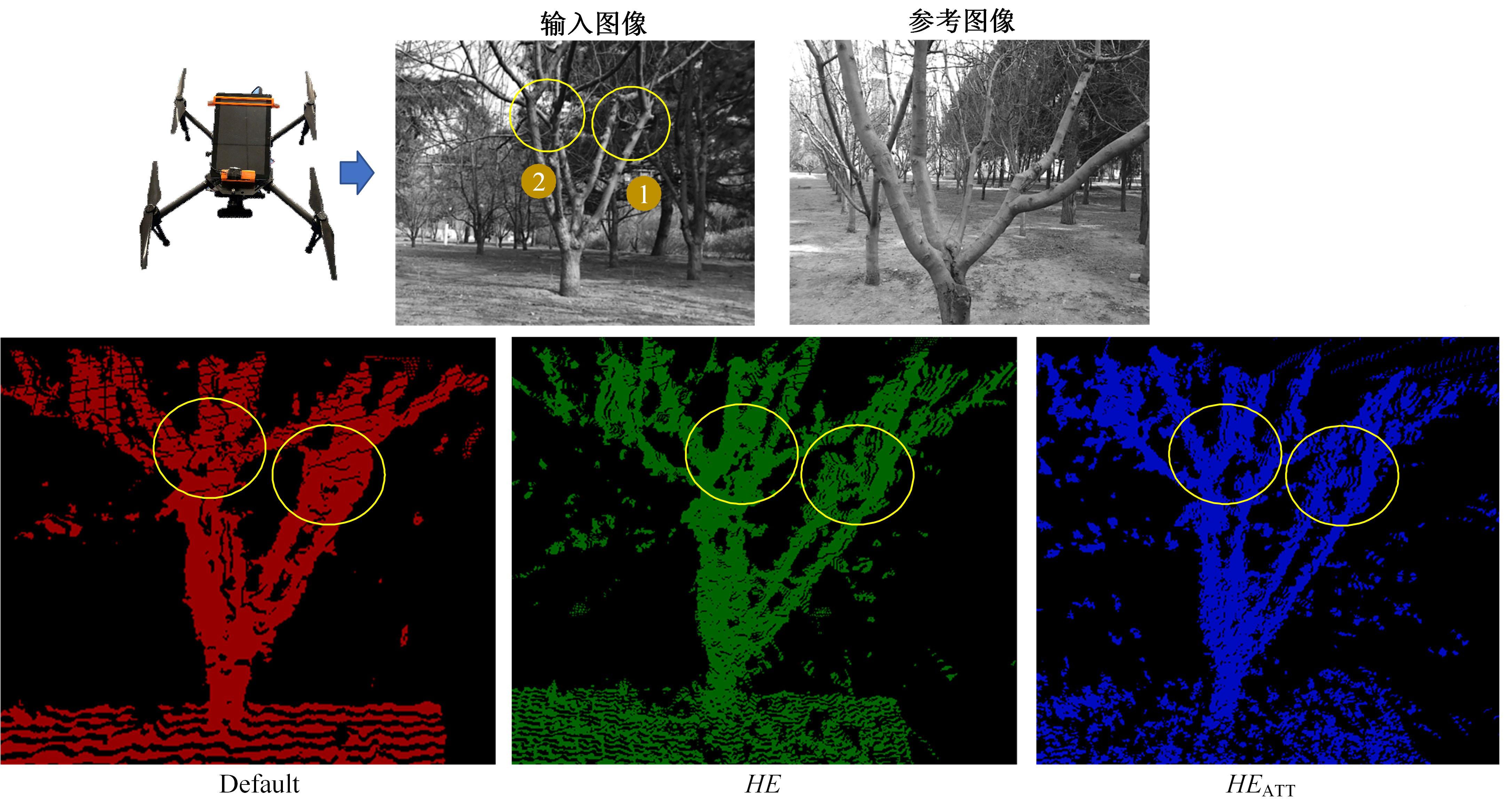
| 11 | Zhang Z C, Chen J, Xu X Y. Hawk-eye-inspired perception algorithm of stereo vision for orchard 3D points cloud navigation map obtaining[J]. CAAI Transactions on Intelligence Technology, 2023, 8(3): 987-1001. |
| 12 | Duan H B, Xu X B, Deng Y M, et al. Unmanned aerial vehicle recognition of maritime small-target based on biological eagle-eye vision adaptation mechanism[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2021, 57(5): 3368-3382. |
| 13 | 谭立东, 刘丹, 李文军. 基于蝇复眼的交通事故现场全景图像阵列仿生设计[J]. 吉林大学学报: 工学版, 2017, 47(6): 1738-1743. |
| Tan Li-dong, Liu dan, Li Wen-jun. Design of bionic compound eye array for traffic accident scene panorama based on fly compound eye[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Engineering and Technology Edition), 2017, 47(6): 1738-1743. | |
| 14 | Jaderberg M, Simonyan K, Zisserman A. Spatial transformer networks[C]∥Proceedings of the 28th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Bali, Indonesia, 2015: 2017-2025. |
| 15 | Almahairi A, Ballas N, Cooijmans T, et al. Dynamic capacity networks[C]∥Proceedings of the conference on ICML, New York, USA, 2016: 2549-2558. |
| 16 | Xu K, Ba J, Kiros R, et al. Show, attend and tell: neural image caption generation with visual attention[C]∥Proceedings of the conference on ICML, Lille, France, 2015: 2048-2057. |
| 17 | Lu J S, Xiong C M, Parikh D, et al. Knowing when to look: adaptive attention via a visual sentinel for image captioning[C]∥Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on CVPR, Honolulu, USA, 2017: 375-383. |
| 18 | Guzman-Pando A, Chacon-Murguia M I. DeepFoveaNet: deep fovea eagle-eye bioinspired model to detect moving objects[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2021, 30: 7090-7100. |
| 19 | 郭继昌, 吴洁, 郭春乐, 等. 基于残差连接卷积神经网络的图像超分辨率重构[J]. 吉林大学学报: 工学版, 2019, 49(5): 1726-1734. |
| Guo Ji-chang, Wu Jie, Guo Chun-le, et al. Image super-resolution reconstruction based on residual connection convolutional neural network[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Engineering and Technology Edition), 2019, 49(5): 1726-1734. | |
| 20 | Jiang Y M, Chan K, Wang X T, et al. Robust reference-based super-resolution via C2-matching[C]∥Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on CVPR, Nashville, USA, 2021: 2103-2112. |
| 21 | Xia B, Tian Y P, Hang Y C, et al. Coarse-to-fine embedded patchmatch and multi-scale dynamic aggregation for reference-based super-resolution[J]. AAAI, 2022, 3(3): 2768-2776. |
| 22 | Yan X, Zhao W B, Yuan K, et al. Towards content-independent multi-reference super-resolution: adaptive pattern matching and feature aggregation[C]∥ Proceedings of the conference on ECCV. Berlin:Springer, 2020: 52-68. |
| 23 | Lowe D. Object recognition from local scale-invariant features[C]∥Proceedings of the Seventh IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Kerkyra, Greece, 1999: 1150-1157. |
| 24 | Simonyan K, Zisserman A. Very deep convolutional networks for large-scale image recognition[C]∥Proceedings of the Conference of ICLR, Carnifolia, USA, 2015: 14091556. |
| 25 | Gatys L, Ecker A, Bethge M. Image style transfer using convolutional neural networks[C]∥Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on CVPR, Las Vegas, USA, 2016: 2424-2423. |
| 26 | Bertinetto L, Valmadre J, Henriques J F, et al. Fully-convolutional siamese networks for object tracking[C]∥Proceedings of the Conference of ECCV. Berlin: Springer, 2016: 850-865. |
| 27 | Li B, Yan J J, Wu W, et al. High performance visual tracking with siamese region proposal network[C]∥Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on CVPR, Salt Lake, USA, 2018: 8971-8980. |
| 28 | Li B, Wu W, Wang Q, et al. Siamrpn++: evolution of siamese visual tracking with very deep networks[C]∥Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on CVPR, Long Beach, USA, 2019: 4282-4291. |
| 29 | Krizhevsky A, Sutskever I, Hinton G. Imagenet classification with deep convolutional neural networks[J]. Communications of the ACM, 2012, 60(6): 84-90. |
| 30 | He K M, Zhang X Y, Ren S Q, et al. Deep residual learning for image recognition[C]∥Proceedings of the IEEE conference on CVPR, Las Vegas, USA, 2016: 770-778. |
| 31 | Jiang P T, Zhang C B, Hou Q B, et al. LayerCAM: exploring hierarchical class activation maps for localization[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2021, 30: 5875-5888. |
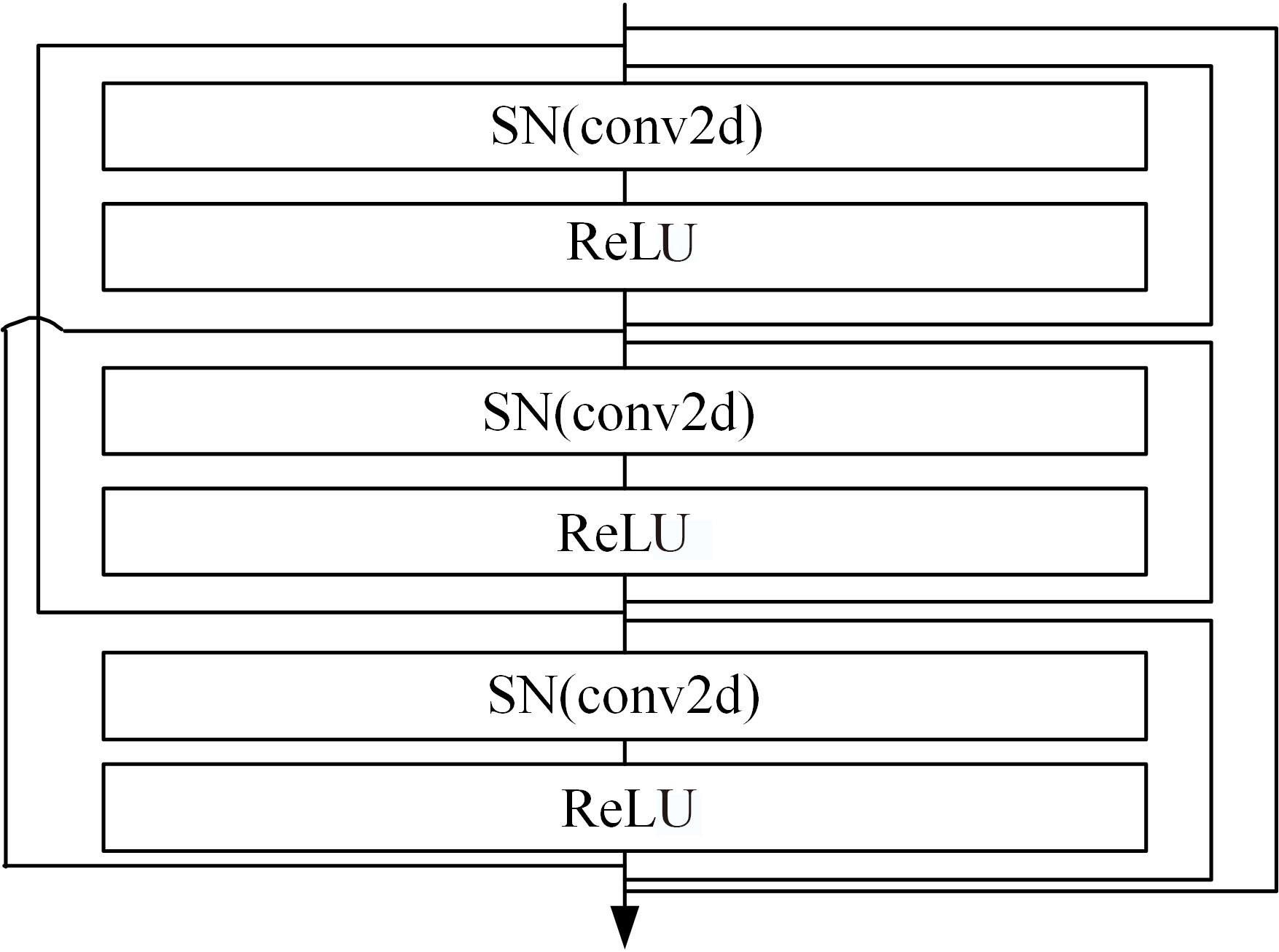
| 32 | Miyato T, Kataoka T, Koyama M, al et, Spectral normalization for generative adversarial networks[C]∥Proceedings of the Conference of ECCV, Munich, Germany, 2018: 1-26. |
| 33 | Hirschmuller H. Stereo processing by semiglobal matching and mutual information[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2007, 30(2): 328-341. |
| 34 | Chen J, Zhang Z C, Yi K, et al. Snake-hot-eye-assisted multi-process-fusion target tracking based on a roll-pitch semi-strapdown infrared imaging seeker[J]. Journal of Bionic Engineering, 2022, 19: 1124-1139. |
| 35 | Chen J, Zhang Z C, Zhang K, et al. UAV-borne LiDAR crop point cloud enhancement using grasshopper optimization and point cloud up-sampling network[J]. Remote Sensing, 2020, 12(19): 12193208. |
| 36 | Zhang Z C, Wang S B, Chen J, et al. A bionic dynamic path planning algorithm of the micro UAV based on the fusion of deep neural network optimization/filtering and hawk-eye vision[J]. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics: Systems, 2023, 53(6): 3728-3740. |
| 37 | Zhao R Y, Li X T, Chen J. Eagle-inspired manipulator with adaptive grasping and collapsible mechanism and modular DOF for UAV operations[J]. Computers and Electronics in Agriculture, 2023, 215: 108344. |
| 38 | Chen T, Zhao R Y, Chen J,et al. Data-driven active disturbance rejection control of plant-protection unmanned ground vehicle prototype: a fuzzy indirect iterative learning approach[J]. IEEE/CAA Journal of Automatica Sinica, 2022, 128: 593-605. |
| [1] | Guan-xu LONG,Xiu-shi ZHANG,Gong-feng XIN,Tao WANG,Gan YANG. Bridge weigh-in-motion combined with machine version [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2024, 54(1): 188-197. |
| [2] | Si-yuan LIU,Yue-qian HOU,Ying KOU,Zhen REN,Zheng-yi HU,Xue-wei ZHAO,Yu-peng GE. Flatness error measurement method based on line structured light vision [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2023, 53(12): 3358-3366. |
| [3] | Hao-jing BAO,Si-yuan LIU,Zhen REN,Yun-hui ZHANG,Zheng-yi HU,Yu-peng GE. Sprocket size measurement method based on machine vision [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2023, 53(10): 2795-2806. |
| [4] | Jing-bin LI,Yu-kun YANG,Bao-qin WEN,Za KAN,Wen SUN,Shuo YANG. Method of extraction of navigation path of post-autumn residual film recovery based on stubble detection [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2021, 51(4): 1528-1539. |
| [5] | LIU En-ze,WU Wen-fu. Agricultural surface multiple feature decision fusion disease judgment algorithm based on machine vision [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2018, 48(6): 1873-1878. |
| [6] | LIN Jin-hua, WANG Yan-jie, WANG Lu, YAO Yu. Real-time surface reconstruction based global camera pose optimization [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2018, 48(3): 909-918. |
| [7] | ZHANG Fei, SHAN Zhong-de, REN Yong-xin, NIE Jun-gang, LIU Feng. Calibration of line array camera for head defect detection system on cylinder cover [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2017, 47(2): 540-545. |
| [8] | ZHOU Xiao-dong, ZHANG Ya-chao, TAN Qing-chang, ZHANG Wei-jun. New method of cylindricity measurement based on structured light vision technology [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2017, 47(2): 524-529. |
| [9] | LIN Dong-mei, ZHANG Ai-hua, SHEN Rong, WANG Ping, YANG Li-ming, CHEN Xiao-lei. Dual-camera synchronous acquisition method for binocular vision pulse measurement system [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2015, 45(6): 1999-2006. |
| [10] | ZHANG Bo, WANG Wen-jun, WEE Minkooc, CHENG Bo. Detection handheld phone use by driver based on machine vision [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2015, 45(5): 1688-1695. |
| [11] | LIU Chang-ying, CAI Wen-jing, WANG Tian-hao, LI Ji-zhi, JIA Yan-mei, SONG Yu-he. Vision inspection technology of fracture splitting notch of auto connecting rod [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2014, 44(4): 1076-1080. |
| [12] | LIU Li-wei, MA Song-quan, MA Li-rong. Design and implementation of stereo measure system based on double digital signal processor [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2013, 43(增刊1): 335-339. |
| [13] | WAN Chuan, TIAN Yan-tao, LIU Shuai-shi, CHEN Hong-wei. Face tracking and facial expression recognition system based on active machine vision [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2013, 43(02): 459-465. |
| [14] | QU Xing-tian, WANG Bin, ZHANG Lei, SHAO Kui-wei, ZHANG Liang. Image preprocessing of grinding and polishing welded seams [J]. , 2012, (06): 1421-1425. |
| [15] | ZHAO Ding-Xuan, CUI Yu-Xin, GONG Jie, NI Tao, HOU Jing-Wei, ZHAO Ying, WANG Chao-Fei. Method of tracking and measuring moving object based on machine vision [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2010, 40(增刊): 257-0261. |
|
||