Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition) ›› 2024, Vol. 54 ›› Issue (6): 1767-1776.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb.20220851
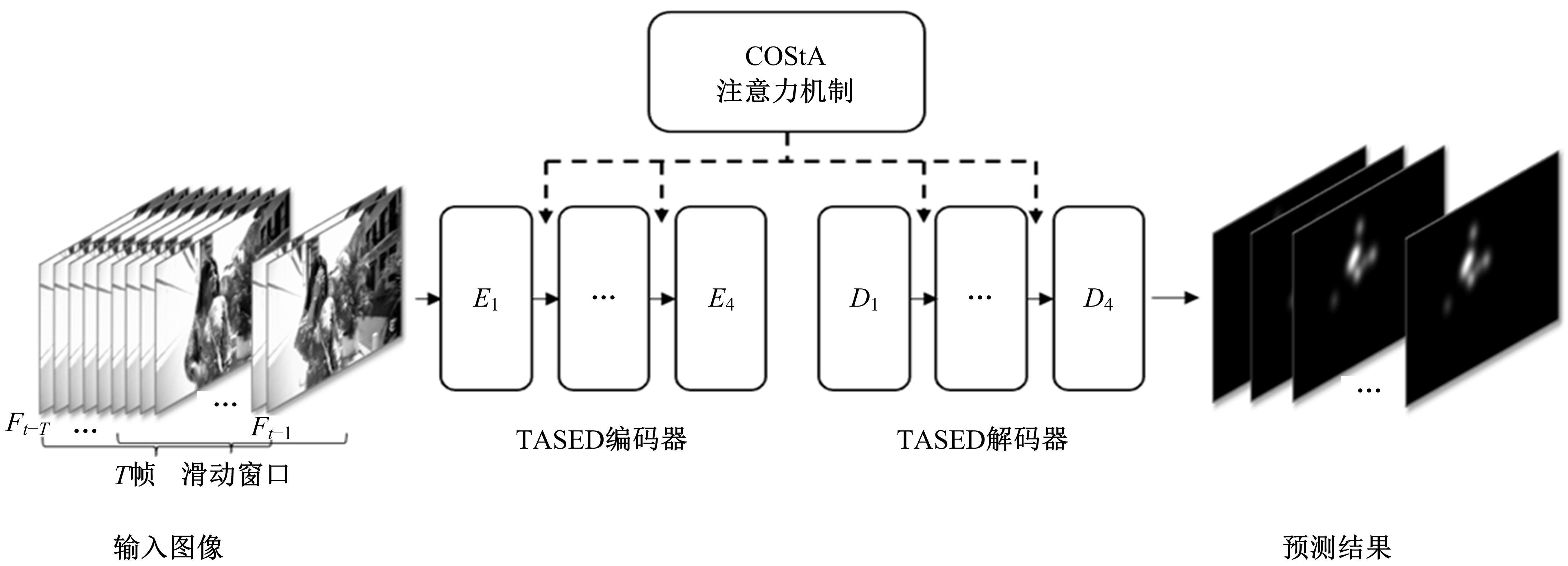
Video saliency prediction with collective spatio-temporal attention
Ming-hui SUN1,2( ),Hao XUE1,2,Yu-bo JIN3(
),Hao XUE1,2,Yu-bo JIN3( ),Wei-dong QU4,Gui-he QIN1,2
),Wei-dong QU4,Gui-he QIN1,2
- 1.College of Computer Science and Technology,Jilin University,Changchun 130012,China
2.Key Laboratory of Symbolic Computation and Knowledge Engineering of Ministry of Education,Jilin University,Changchun 130012,China
3.EXPERT Management Consulting Co. Ltd. ,Shanghai 200050,China
4.Key Laboratory of Optical Countermeasure Test and Evaluation Technology,Luoyang 471000,China
CLC Number:
- TP391
| 1 | Guo Q, Feng W, Zhou C, et al. Learning dynamic siamese network for visual object tracking[C]∥Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Venice, Italy, 2017: 1763-1771. |
| 2 | Feng W, Han R Z, Guo Q, et al. Dynamic saliency-aware regularization for correlation filter-based object tracking[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2019, 28(7): 3232-3245. |
| 3 | Wang H Y, Xu Y J, Han Y H. Spotting and aggregating salient regions for video captioning[C]∥Proce-edings of the 26th ACM International Conference on Multimedia, Seoul, Korea, 2018: 1519-1526. |
| 4 | Chen Y, Zhang G, Wang S H, et al. Saliency-based spatiotemporal attention for video captioning[C]∥2018 IEEE Fourth International Conference on Multimedia Big Data, Xi'an, China, 2018: 1-8. |
| 5 | Guo C L, Zhang L M. A novel multiresolution spatiotemporal saliency detection model and its applications in image and video compression[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2009, 19(1): 185-198. |
| 6 | Itti L, Dhavale N, Pighin F. Realistic avatar eye and head animation using a neurobiological model of visu-al attention[J/OL]. [2022-06-28]. |
| 7 | Zhong S H, Liu Y, Ren F F, et al. Video saliency detection via dynamic consistent spatio-temporal attention modelling[C]∥Twenty-seventh AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Bellevue, USA, 2013: 1063-1069. |
| 8 | Wang W G, Shen J B, Guo F, et al. Revisiting video saliency: a large-scale benchmark and a new model[C]∥Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, USA, 2018: 4894-4903. |
| 9 | Bak C, Kocak A, Erdem E, et al. Spatio-temporal saliency networks for dynamic saliency prediction[J]. IEEE Transactions on Multimedia, 2017, 20(7): 1688-1698. |
| 10 | Tran H D, Bak S, Xiang W, et al. Verification of deep convolutional neural networks using imagestars[J/OL]. [2022-06-28]. |
| 11 | Mathe S, Sminchisescu C. Actions in the eye: dynamic gaze datasets and learnt saliency models for visual recognition[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2014, 37(7): 1408-1424. |
| 12 | Bazzani L, Larochelle H, Torresani L. Recurrent mixture density network for spatiotemporal visual attention[J/OL]. [2022-06-28]. |
| 13 | Droste R, Jiao J, Noble J A. Unified image and video saliency modeling[C]∥European Conference on Computer Vision, Glasgow, UK, 2020: 419-435. |
| 14 | Wu X Y, Wu Z Y, Zhang J L, et al. SalSAC: a video saliency prediction model with shuffled attentions and correlation-based ConvLSTM[C]∥Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, New York, USA, 2020, 34(7): 12410-12417. |
| 15 | Min K, Corso J J. Tased-net: temporally-aggregating spatial encoder-decoder network for video saliency detection[C]∥Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Seoul, Korea, 2019: 2394-2403. |
| 16 | Vaswani A, Shazeer N, Parmar N, et al. Attention is all you need[C]∥Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, Los Angeles, USA, 2017: 5998-6008. |
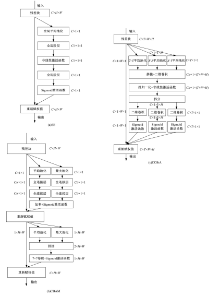
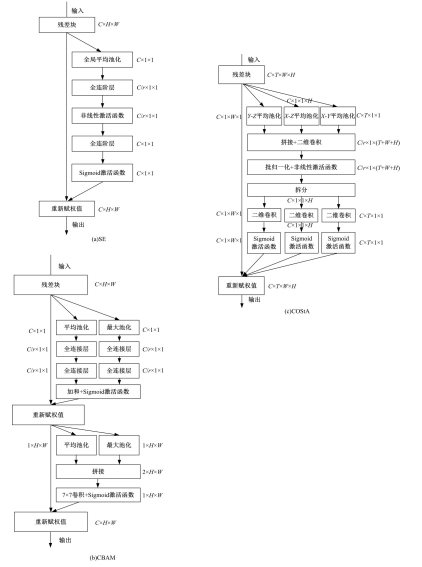
| 17 | Hu J, Shen L, Sun G. Squeeze-and-excitation networks[C]∥Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, USA, 2018: 7132-7141. |
| 18 | Woo S, Park J, Lee J Y, et al. Cbam: convolutional block attention module[C]∥Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), Munich, Germany, 2018: 3-19. |
| 19 | Riche N, Duvinage M, Mancas M, et al. Saliency and human fixations: state-of-the-art and study of comparison metrics[C]∥ Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Sydney, Australia, 2013: 1153-1160. |
| 20 | Bylinskii Z, Judd T, Oliva A, et al. What do different evaluation metrics tell us about saliency models?[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2018, 41(3): 740-757. |
| 21 | Wang W G, Shen J B. Deep visual attention prediction[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2017, 27(5): 2368-2378. |
| 22 | Kay W, Carreira J, Simonyan K, et al. The kinetics human action video dataset[J/OL]. [2022-06-28]. |
| 23 | He K M, Zhang X Y, Ren S Q, et al. Delving deep into rectifiers: surpassing human-level performance on imagenet classification[C]∥Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Santiago, Chile, 2015: 1026-1034. |
| 24 | Huang X, Shen C Y, Boix X, et al. Salicon: reducing the semantic gap in saliency prediction by adapting deep neural networks[C]∥Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Santiago, Chile, 2015: 262-270. |
| 25 | Cornia M, Baraldi L, Serra G, et al. Predicting human eye fixations via an LSTM-based saliency attentive model[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2018, 27(10): 5142-5154. |
| 26 | Jiang L, Xu M, Wang Z L. Predicting video saliency with object-to-motion CNN and two-layer convolutional LSTM[J/OL]. [2022-06-28]. |
| 27 | Lai Q X, Wang W G, Sun H Q, et al. Video saliency prediction using spatiotemporal residual attentive networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2019, 29: 1113-1126. |
| 28 | Wang L M, Tong Z, Ji B, et al. TDN: temporal difference networks for efficient action recognition[C]∥Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Virtual, 2021: 1895-1904. |
| 29 | Chen C F R, Panda R, Ramakrishnan K, et al. Deep analysis of CNN-based spatio-temporal representations for action recognition[J/OL]. [2022-06-30]. |
| [1] | Xiao-hui WEI,Chen-yang WANG,Qi WU,Xin-yang ZHENG,Hong-mei YU,Heng-shan YUE. Systolic array-based CNN accelerator soft error approximate fault tolerance design [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2024, 54(6): 1746-1755. |
| [2] | Li-ping ZHANG,Bin-yu LIU,Song LI,Zhong-xiao HAO. Trajectory k nearest neighbor query method based on sparse multi-head attention [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2024, 54(6): 1756-1766. |
| [3] | Yu-kai LU,Shuai-ke YUAN,Shu-sheng XIONG,Shao-peng ZHU,Ning ZHANG. High precision detection system for automotive paint defects [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2024, 54(5): 1205-1213. |
| [4] | Yun-long GAO,Ming REN,Chuan WU,Wen GAO. An improved anchor-free model based on attention mechanism for ship detection [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2024, 54(5): 1407-1416. |
| [5] | Yu WANG,Kai ZHAO. Postprocessing of human pose heatmap based on sub⁃pixel location [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2024, 54(5): 1385-1392. |
| [6] | Dian-wei WANG,Chi ZHANG,Jie FANG,Zhi-jie XU. UAV target tracking algorithm based on high resolution siamese network [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2024, 54(5): 1426-1434. |
| [7] | Chao XIA,Meng-jia WANG,Jian-yue Zhu,Zhi-gang YANG. Reduced-order modelling of a bluff body turbulent wake flow field using hierarchical convolutional neural network autoencoder [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2024, 54(4): 874-882. |
| [8] | Li-ming LIANG,Long-song ZHOU,Jiang YIN,Xiao-qi SHENG. Fusion multi-scale Transformer skin lesion segmentation algorithm [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2024, 54(4): 1086-1098. |
| [9] | Yun-zuo ZHANG,Wei GUO,Wen-bo LI. Omnidirectional accurate detection algorithm for dense small objects in remote sensing images [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2024, 54(4): 1105-1113. |
| [10] | Guo-jun YANG,Ya-hui QI,Xiu-ming SHI. Review of bridge crack detection based on digital image technology [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2024, 54(2): 313-332. |
| [11] | Xiong-fei LI,Zi-xuan SONG,Rui ZHU,Xiao-li ZHANG. Remote sensing change detection model based on multi⁃scale fusion [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2024, 54(2): 516-523. |
| [12] | Yue-lin CHEN,Zhu-cheng GAO,Xiao-dong CAI. Long text semantic matching model based on BERT and dense composite network [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2024, 54(1): 232-239. |
| [13] | Guang HUO,Da-wei LIN,Yuan-ning LIU,Xiao-dong ZHU,Meng YUAN,Di GAI. Lightweight iris segmentation model based on multiscale feature and attention mechanism [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2023, 53(9): 2591-2600. |
| [14] | Ying HE,Zhuo-ran WANG,Xu ZHOU,Yan-heng LIU. Point of interest recommendation algorithm integrating social geographical information based on weighted matrix factorization [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2023, 53(9): 2632-2639. |
| [15] | Yun-zuo ZHANG,Xu DONG,Zhao-quan CAI. Multi view gait cycle detection by fitting geometric features of lower limbs [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2023, 53(9): 2611-2619. |
|
||