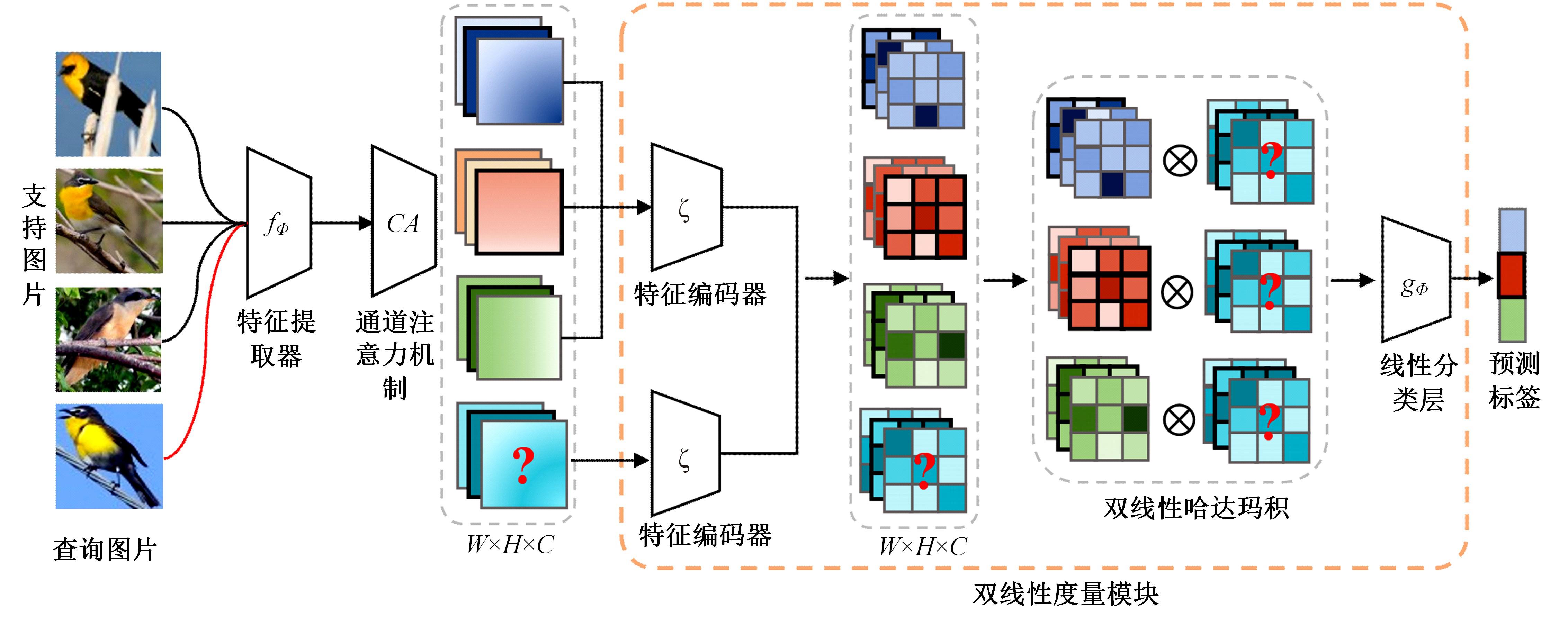
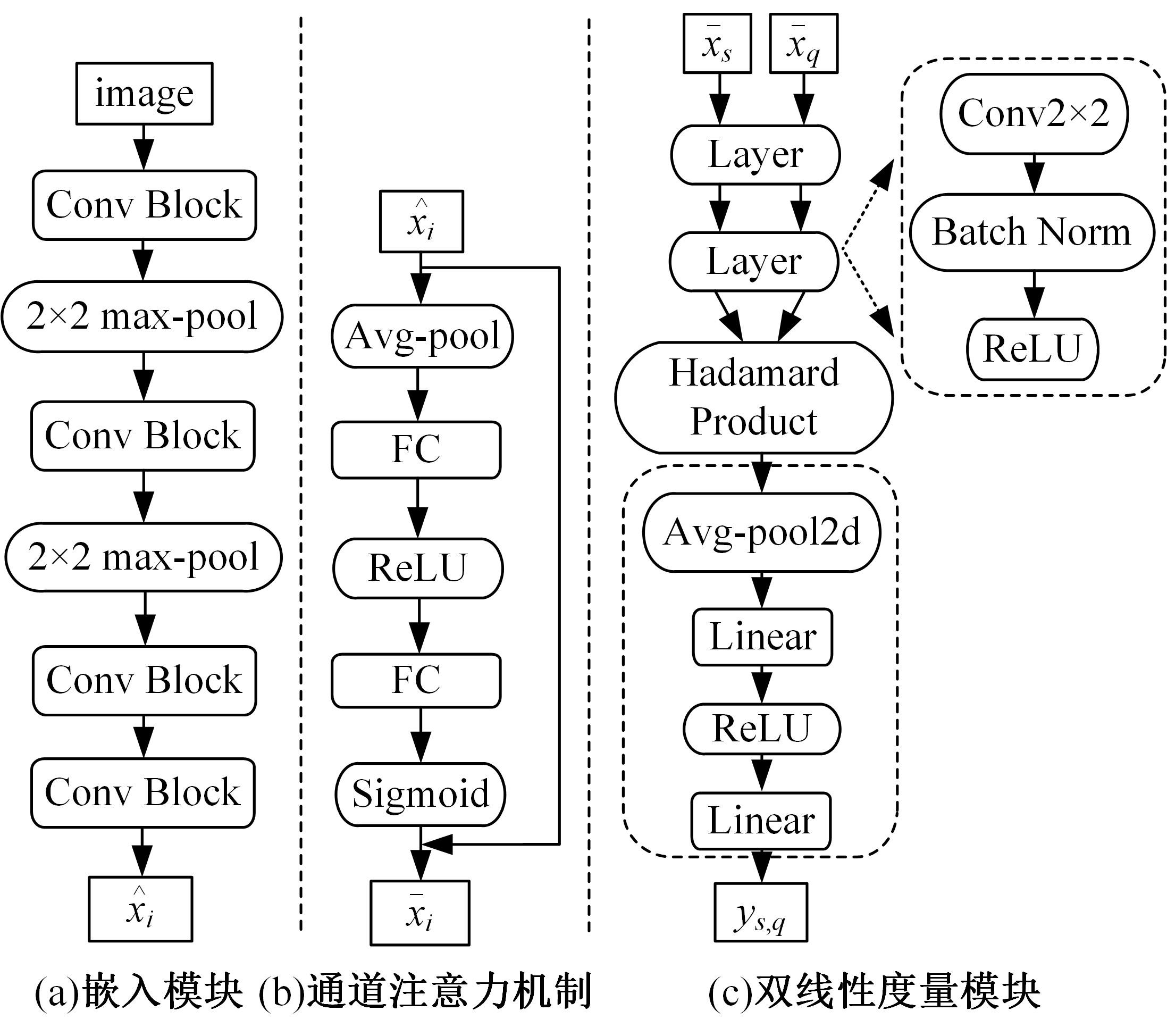
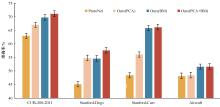
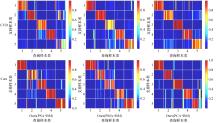
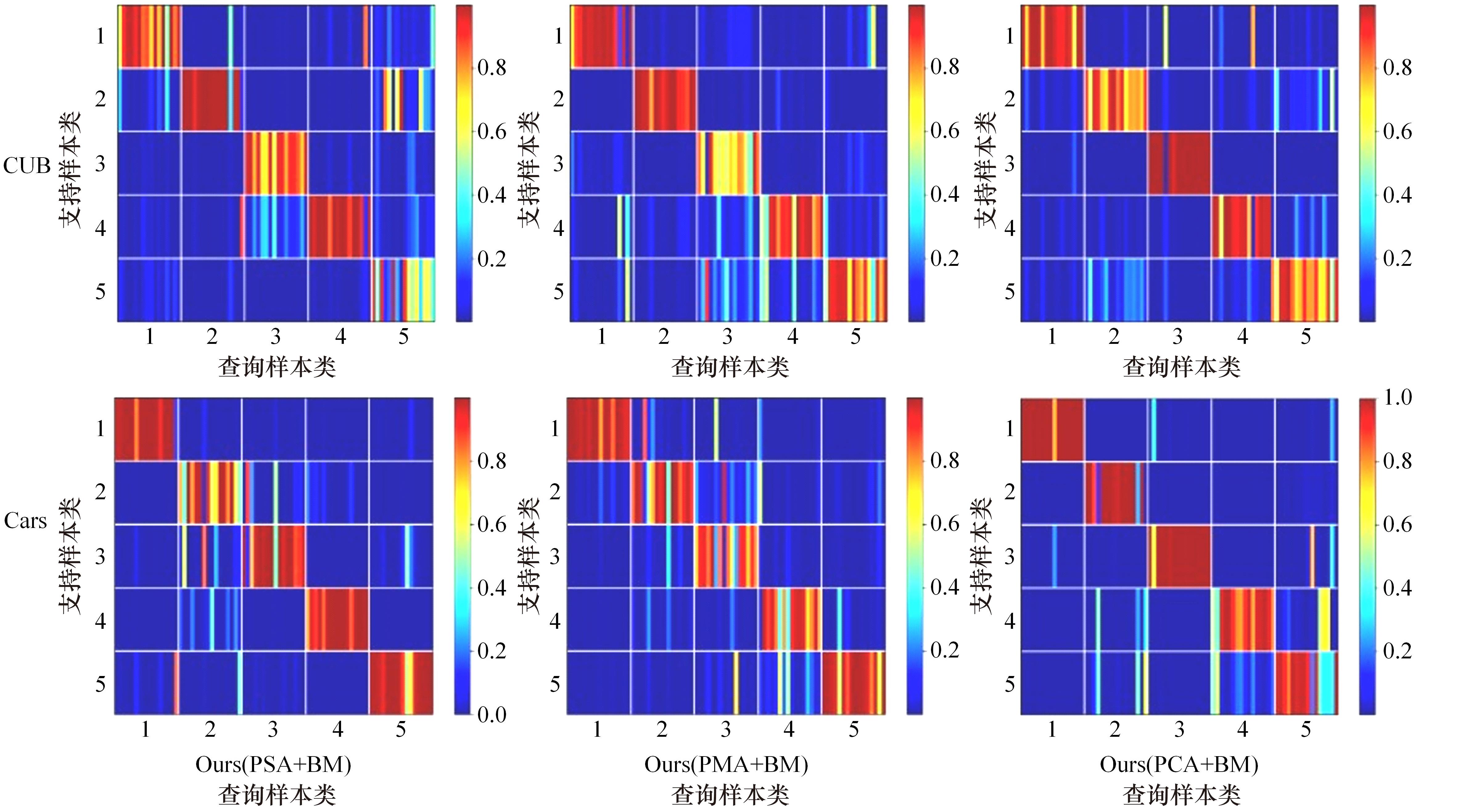
Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition) ›› 2024, Vol. 54 ›› Issue (2): 524-532.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb.20221176
Channel attention bilinear metric network
Xiao-xu LI1( ),Wen-juan AN1,Ji-jie WU1,Zhen LI1,Ke ZHANG2,3,Zhan-yu MA4
),Wen-juan AN1,Ji-jie WU1,Zhen LI1,Ke ZHANG2,3,Zhan-yu MA4
- 1.School of Computer and Communication,Lanzhou University of Technology,Lanzhou 730050,China
2.Department of Electronics and Communication Engineering,North China Electric Power University,Baoding 071003,China
3.Hebei Key Laboratory of Power Internet of Things Technology,North China Electric Power University,Baoding 071003,China
4.Laboratory of Pattern Recognition and Intelligent System,School of Artificial Intelligence,Beijing University of Posts and Telecommunications,Beijing 100876,China
CLC Number:
- TP391
| 1 | Huang H, Zhang J, Zhang J, et al. Low-rank pairwise alignment bilinear network for few-shot fine-grained image classification[J]. IEEE Transactions on Multimedia, 2020, 23: 1666-1680. |
| 2 | 曹洁, 屈雪, 李晓旭. 基于滑动特征向量的小样本图像分类方法[J]. 吉林大学学报: 工学版, 2021, 51(5): 1785-1791. |
| Cao Jie, Qu Xue, Li Xiao-xu. Few⁃shot image classification method based on sliding feature vectors[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Engineering and Technology Edition), 2021, 51(5): 1785-1791. | |
| 3 | Snell J, Swersky K, Zemel R. Prototypical networks for few-shot learning[C]∥Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Long Beach California, USA, 2017: 4080-4090. |
| 4 | Nguyen V N, Løkse S, Wickstrøm K, et al. Sen: a novel feature normalization dissimilarity measure for prototypical few-shot learning networks[C]∥European Conference on Computer Vision, Glasgow, UK, 2020: 118-134. |
| 5 | Vinyals O, Blundell C, Lillicrap T, et al. Matching networks for one shot learning[C]∥Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Barcelona, Spain, 2016: 3637-3645. |
| 6 | Zhang C, Cai Y, Lin G, et al. Deepemd: few-shot image classification with differentiable earth mover's distance and structured classifiers[C]∥IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, USA, 2020: 12203-12213. |
| 7 | 刘萍萍, 赵宏伟, 耿庆田, 等. 基于局部特征和视皮层识别机制的图像分类[J]. 吉林大学学报: 工学版, 2011, 41(5): 1401-1406. |
| Liu Ping-ping, Zhao Hong-wei, Geng Qing-tian, et al. Image classification method based on local feature and visual cortex recognition mechanism[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Engineering and Technology Edition), 2011, 41(5): 1401-1406. | |
| 8 | Huang K, Geng J, Jiang W, et al. Pseudo-loss confidence metric for semi-supervised few-shot learning[C]∥IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Montreal, Canada, 2021: 8671-8680. |
| 9 | Lin T Y, RoyChowdhury A, Maji S. Bilinear CNN models for fine-grained visual recognition[C]∥IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Santiago, USA, 2015: 1449-1457. |
| 10 | Wah C, Branson S, Welinder P, et al. The caltech-ucsd birds-200-2011 dataset[J]. California Institute of Technology, 2011, 7: 7138640. |
| 11 | Khosla A, Jayadevaprakash N, Yao B, et al. Novel dataset for fine-grained image categorization: Stanford dogs[J/OL]. [2022-09-12]. |
| 12 | Krause J, Stark M, Deng J, et al. 3D object representations for fine-grained categorization[C]∥IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision Workshops, Sydney, Australia, 2013: 554-561. |
| 13 | Maji S, Rahtu E, Kannala J, et al. Fine-grained visual classification of aircraft[J]. ArXiv Preprint, 2013, 7:13065151. |
| 14 | Russakovsky O, Deng J, Su H, et al. ImageNet large scale visual recognition challenge[J]. International Journal of Computer Vision, 2015, 115(3): 211-252. |
| 15 | Liu Y, Lee J, Park M, et al. Transductive propagation network for few-shot learning[J]. arXiv E-prints, 2018, 5: 180510002. |
| 16 | Sung F, Yang Y, Zhang L, et al. Learning to compare: relation network for few-shot learning[C]∥IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, USA, 2018:1199-1208. |
| 17 | Chen W Y, Liu Y C, Kira Z, et al. A closer look at few-shot classification[J]. arXiv E-prints, 2019, 4: 190404232. |
| 18 | Wu Z, Li Y, Guo L, et al. Parn: position-aware relation networks for few-shot learning[C]∥IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Seoul, Korea (South), 2019: 6659-6667. |
| 19 | Zhu Y, Liu C, Jiang S. Multi-attention meta learning for few-shot fine-grained image recognition[C]∥Proceedings of the Twenty-Ninth International Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence Main track, Yokohama, Japan, 2020: 1090-1096. |
| 20 | Li X, Wu J, Sun Z, et al. BSNet: bi-similarity network for few-shot fine-grained image classification[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2020, 30: 1318-1331. |
| 21 | Xu J, Le H, Huang M, et al. Variational feature disentangling for fine-Grained few-shot classification[C]∥IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Montreal, Canada, 2021: 8792-8801. |
| 22 | Afrasiyabi A, Lalonde J F, Gagné C. Mixture-based feature space learning for few-shot image classification[C]∥IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Montreal, Canada, 2021: 9041-9051. |
| 23 | Ye H J, Hu H, Zhan D C, et al. Few-shot learning via embedding adaptation with set-to-set functions[C]∥IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, USA, 2020: 8808-8817. |
| 24 | Kang D, Kwon H, Min J, et al. Relational embedding for few-shot classification[C]∥IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Montreal, Canada, 2021: 8822-8833. |
| 25 | Finn C, Abbeel P, Lwvine S. Model-agnostic meta-learning for fast adaptation of deep networks[C]∥International Conference on Machine Learning, Sydney, Australia, 2017: 1126-1135. |
| 26 | Cai Q, Pan Y, Yao T, et al. Memory matching networks for one-shot image recognition[C]∥IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake, USA, 2018: 4080-4088. |
| 27 | Li X, Wu J, Chang D, et al. Mixed attention mechanism for small-sample fine-grained image classification[C]∥Asia-Pacific Signal and Information Processing Association Annual Summit and Conference, Lanzhou, China, 2019: 80-85. |
| [1] | Guang HUO,Da-wei LIN,Yuan-ning LIU,Xiao-dong ZHU,Meng YUAN,Di GAI. Lightweight iris segmentation model based on multiscale feature and attention mechanism [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2023, 53(9): 2591-2600. |
| [2] | Xiao-xin GUO,Jia-hui LI,Bao-liang ZHANG. Joint segmentation of optic cup and disc based on high resolution network [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2023, 53(8): 2350-2357. |
| [3] | Fei-fei TANG,Hai-lian ZHOU,Tian-jun TANG,Hong-zhou ZHU,Yong WEN. Multi⁃step prediction method of landslide displacement based on fusion dynamic and static variables [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2023, 53(6): 1833-1841. |
| [4] | Yan-tao TIAN,Xing HUANG,Hui-qiu LU,Kai-ge WANG,Fu-qiang XU. Multi⁃mode behavior trajectory prediction of surrounding vehicle based on attention and depth interaction [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2023, 53(5): 1474-1480. |
| [5] | Wei LYU,Jia-ze HAN,Jing-hui CHU,Pei-guang JING. Multi⁃modal self⁃attention network for video memorability prediction [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2023, 53(4): 1211-1219. |
| [6] | Yan-tao TIAN,Fu-qiang XU,Kai-ge WANG,Zi-xu HAO. Expected trajectory prediction of vehicle considering surrounding vehicle information [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2023, 53(3): 674-681. |
| [7] | Gui-xia LIU,Yu-xin TIAN,Tao WANG,Ming-rui MA. Pancreas segmentation algorithm based on dual input 3D convolutional neural network [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2023, 53(12): 3565-3572. |
| [8] | Jing-hong LIU,An-ping DENG,Qi-qi CHEN,Jia-qi PENG,Yu-jia ZUO. Anchor⁃free target tracking algorithm based on multiple attention mechanism [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2023, 53(12): 3518-3528. |
| [9] | Sheng JIANG,Peng-lang WANG,Zhi-ji DENG,Yi-ming BIE. Image fusion algorithm for traffic accident rescue based on deep learning [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2023, 53(12): 3472-3480. |
| [10] | Ji-hong OUYANG,Ze-qi GUO,Si-guang LIU. Dual⁃branch hybrid attention decision net for diabetic retinopathy classification [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2022, 52(3): 648-656. |
| [11] | Xian-tong LI,Wei QUAN,Hua WANG,Peng-cheng SUN,Peng-jin AN,Yong-xing MAN. Route travel time prediction on deep learning model through spatiotemporal features [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2022, 52(3): 557-563. |
| [12] | Xiao⁃lei CHEN,Yong⁃feng SUN,Ce LI,Dong⁃mei LIN. Stable anti⁃noise fault diagnosis of rolling bearing based on CNN⁃BiLSTM [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2022, 52(2): 296-309. |
| [13] | Da-ke ZHOU,Chao ZHANG,Xin YANG. Self-supervised 3D face reconstruction based on multi-scale feature fusion and dual attention mechanism [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2022, 52(10): 2428-2437. |
| [14] | Jie CAO,Xue QU,Xiao-xu LI. Few⁃shot image classification method based on sliding feature vectors [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2021, 51(5): 1785-1791. |
| [15] | De-xing WANG,Ruo-you WU,Hong-chun YUAN,Peng GONG,Yue WANG. Underwater image restoration based on multi-scale attention fusion and convolutional neural network [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2021, 51(4): 1396-1404. |
|
||