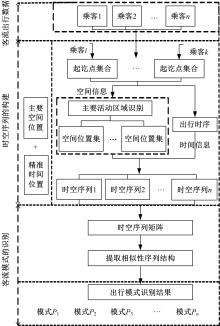
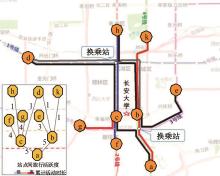
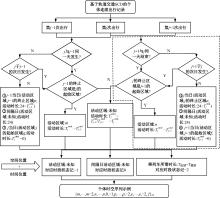
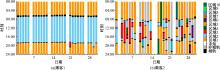
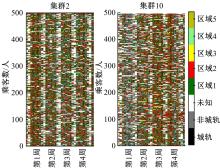
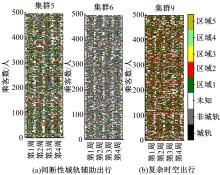
Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition) ›› 2024, Vol. 54 ›› Issue (9): 2588-2599.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb.20221413
Recognition of travel patterns for urban rail transit passengers based on spatiotemporal sequence similarity
Na ZHANG1( ),Feng CHEN2(
),Feng CHEN2( ),Jian-po WANG3,Ya-di ZHU2
),Jian-po WANG3,Ya-di ZHU2
- 1.School of Resources Engineering,Xi'an University of Architecture and Technology,Xi'an 710055,China
2.School of Civil Engineering,Beijing Jiaotong University,Beijing 100044,China
3.School of Transportation Engineering,Chang'an University,Xi'an 710064,China
CLC Number:
- U491.1
| 1 | 赵娟娟. 城市轨道交通乘客时空出行模式挖掘及动态客流分析[D].深圳:中国科学院大学深圳先进技术研究院,2017. |
| Zhao Juan-juan. Spatio-temporal travel pattern mining and dynamic passenger flow analysis in urban rail transit system[D]. Shenzhen: Shenzhen Institutes of Advance Technology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2017. | |
| 2 | 朱亚迪,陈峰,王子甲,等.基于概率图模型的乘客出行链提取方法[J].吉林大学学报:工学版,2019,49(1):60-65. |
| Zhu Ya-di, Chen Feng, Wang Zi-jia, et al. Passengers' trip chains extraction method based on probabilistic graph model[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Engineering and Technology Edition), 2019,49(1):60-65. | |
| 3 | Ma X L, Wu Y J, Wang Y H, et al. Mining smart card data for transit riders' travel patterns[J]. Transportation Research Part C: Emerging Technologies, 2013, 36: 1-12. |
| 4 | Cui Z Y, Long Y. Perspectives on stability and mobility of transit passenger's travel behavior through smart card data[J]. IET Intelligent Transport Systems, 2019, 13(12):1761-1769. |
| 5 | 彭飞,宋国华,朱珊.城市公共交通常乘客通勤出行提取方法[J].交通运输系统工程与信息,2021,21(2):158-165, 172. |
| Peng Fei, Song Guo-hua, Zhu Shan. A method for extracting commuting trips of frequent passengers in urban public transportation[J]. Journal of Transportation Systems Engineering and Information Technology, 2021,21(2):158-165, 172. | |
| 6 | 周航,陈学武.集时空聚类和指标筛选的公共交通通勤者识别[J].交通运输工程与信息学报,2022,20(1):89-97. |
| Zhou Hang, Chen Xue-wu. Public transportation commuter identification based on spatiotemporal clustering and index screening[J]. Journal of Transportation Engineering and Information, 2022,20(1):89-97. | |
| 7 | Hagerstraand T. What about people in regional science [J]. Papers in Regional Science,1970, 24(1): 7-24. |
| 8 | Langlois G G, Koutsopoulos H N, Zhao J. Inferring patterns in the multi-week activity sequences of public transport users[J]. Transportation Research Part C, 2016, 64:1-16. |
| 9 | 刘永鑫.基于多源数据融合的城市公交系统乘客出行模式挖掘及其应用研究[D].广州: 华南理工大学土木与交通学院, 2018. |
| Liu Yong-xin. Study on key technologies of transit passengers' travel pattern mining and applications based on multiple sources of data[D]. Guangzhou: School of Civil Engineering & Transportation, South China University of Technology, 2018. | |
| 10 | Kieu L M, Bhaskar A, Chung E. Passenger segmentation using smart card data[J]. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems, 2015, 16(3):1537-1548. |
| 11 | 姚志刚,杨杰,王元庆.基于个体出行模式的公交乘客活动规律性度量[J].北京交通大学学报, 2022, 46(4): 68-75. |
| Yao Zhi-gang, Yang Jie, Wang Yuan-qing. Measurement of public transport passenger behavior regularity based on individual travel pattern[J]. Journal of Beijing Jiaotong University, 2022, 46(4): 68-75. | |
| 12 | Joh C H, Arentze T, Timmermans H. Pattern recognition in complex activity travel patterns: comparison of Euclidean distance,signal-processing theoretical, and multidimensional sequence alignment methods[J]. Transportation Research Record, 2001, 1752(1):16-22. |
| 13 | Day W H E, Edelsbrunner H. Efficient algorithms for agglomerative hierarchical clustering methods[J]. Journal of Classification, 1984, 1: 7-24. |
| 14 | Ortega-Tong M A. Classification of London's public transport users using smart card data[D]. Cambridge, Massachusetts: Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering, Massachusetts Institute of Technology, 2013. |
| 15 | Roweis S T, Saul L K. Nonlinear dimensionality reduction by locally linear embedding[J]. Science, 2000, 290(5500): 2323-2326. |
| 16 | Tenenbaum J B, Silva V, Langford J C. A global geometric framework for nonlinear dimensionality reduction[J]. Science, 2000, 290(5500): 2319-2323. |
| 17 | Levada A L M. PCA-KL: a parametric dimensionality reduction approach for unsupervised metric learning[J]. Advances in Data Analysis and Classification, 2021, 15(4): 829-868. |
| 18 | Pham D T, Dimov S S, Nguyen C D. Selection of K in K-means clustering[J]. Proceedings of the Institution of Mechanical Engineers, Part C: Journal of Mechanical Engineering Science, 2005, 219(1): 103-119. |
| 19 | 2022年度中国主要城市共享单车/电单车骑行报告[R].北京: 中国城市规划设计研究院, 2022. |
| 2022 Annual report on sharing bikes/motorcycle riding in major Chinese cities[R].Beijing: China Academy of Urban Planning & Design, 2022. | |
| 20 | 周世兵,徐振源,唐旭清. K-means算法最佳聚类数确定方法[J].计算机应用, 2010, 30(8): 1995-1998. |
| Zhou Shi-bing, Xu Zhen-yuan, Tang Xu-qing. Method for determining optimal number of clusters in K-means clustering algorithm[J]. Journal of Computer Applications, 2010, 30(8): 1995-1998. | |
| 21 | Day W H E, Edelsbrunner H. Efficient algorithms for agglomerative hierarchical clustering methods[J]. Journal of Classification, 1984, 1(1): 7-24. |
| [1] | Bo-song FAN,Chun-fu SHAO. Urban rail transit emergency risk level identification method [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2024, 54(2): 427-435. |
| [2] | Jian-hua LI,Ze-ding WANG. Planning of urban car distributed charging pile point selection considering path time-consuming [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2023, 53(8): 2298-2303. |
| [3] | Jing WANG,Feng WAN,Chun-jiao DONG,Chun-fu SHAO. Modelling on catchment area and attraction intensity of urban rail transit stations [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2023, 53(2): 439-447. |
| [4] | Qing-yong WANG,Wei-qiang QU. Optimization algorithm of urban rail transit operation scheduling based on linear programming [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2023, 53(12): 3446-3451. |
| [5] | Wei ZHANG,Shu-pei ZHANG,Chong-en LUO,Sheng ZHANG,Guo-lin WANG. Collision avoidance trajectory planning for intelligent vehicles in emergency conditions [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2022, 52(7): 1515-1523. |
| [6] | ZHAO Xue-yu, YANG Jia-qi, PENG Ya-mei. Competitive and cooperative relationship evolution mechanism between urban rail transit and traditional bus [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2017, 47(3): 756-764. |
| [7] | XU Cheng, QU Zhao-wei, TAO Peng-fei. Estimation of bicycle path capacity under mixed bicycle traffic flow [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2016, 46(1): 63-69. |
| [8] | YAO Xiang-ming, ZHAO Peng, YU Dan-dan. Dynamic origin-destination matrix estimation for urban rail transit based on averaging strategy [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2016, 46(1): 92-99. |
| [9] | WANG Zhong-yu, CAI Qing, WU Bing, LI Lin-bo. Queue length estimation for signalized intersections based on multi-source data [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2015, 45(4): 1088-1094. |
| [10] | SHAO Min-hua, SUN Li-jun, SHAO Xian-zhi. Network location model of sensors and algorithm based on turning ratios [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2013, 43(06): 1476-1481. |
| [11] | CAO Yang, ZHAO Shu-zhi, TIAN Qing-fei. Urban rail transit subsidy policy based on maximum welfare [J]. , 2012, (03): 618-622. |
| [12] | ZHAO Shu-zhi, CAO Yang, TIAN Qing-fei. Urban rail transit scheduling decision based on information fusion [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2011, 41(增刊1): 85-88. |
| [13] | JIA Hong-fei, CHEN Bin, LI Guo-wei, ZHANG Jing-shan. Collision avoidance method in pedestrian simulation based on blockade-angle [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2011, 41(6): 1577-1580. |
| [14] | JIANG Gui-Yan, ZHANG Wei, CHANG An-De. Data organization method for traffic information acquisition system based on GPSequipped floating vehicle [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2010, 40(02): 397-0401. |
| [15] | CAO Shou-hua,YUAN Zhen-zhou,ZHAO Dan. Queuing mechanism of passengers at exit stairs of urban rail transit [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2009, 39(06): 1463-1468. |
|
||