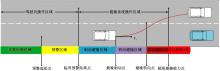
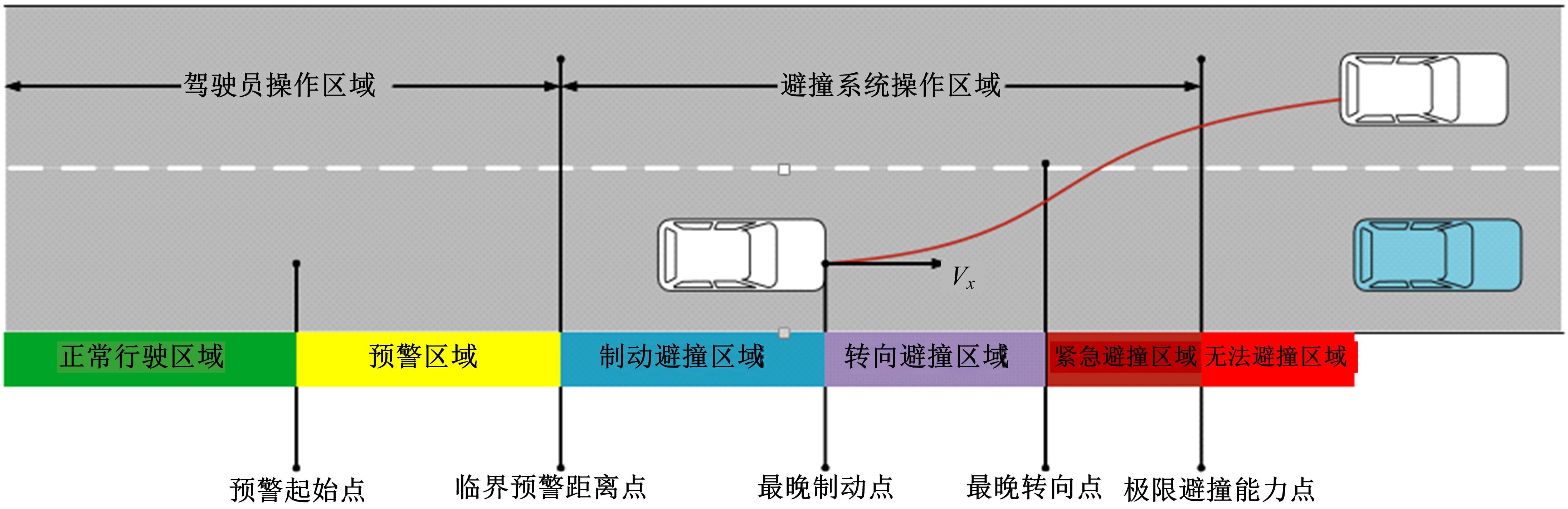
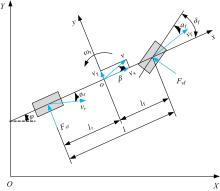
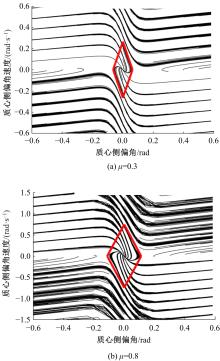
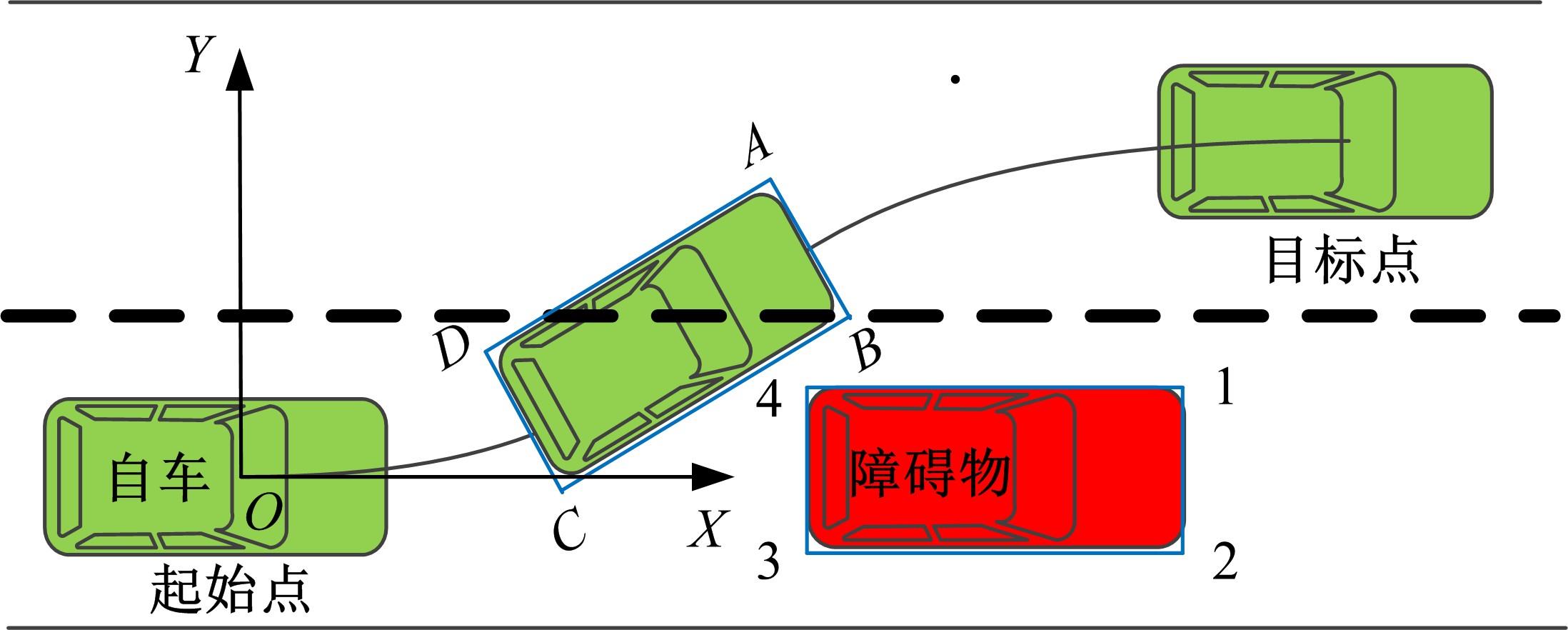
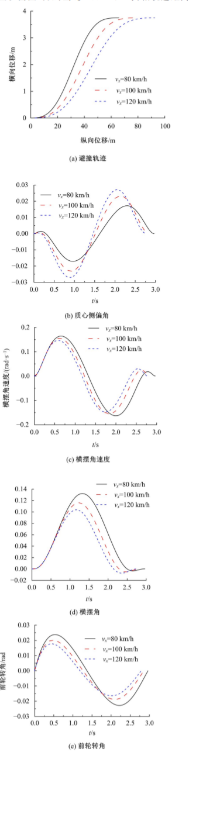
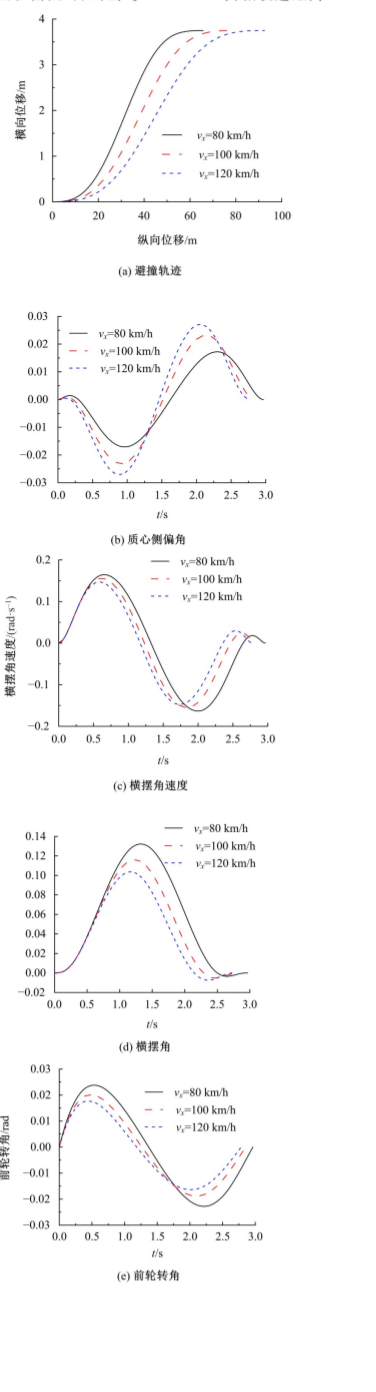
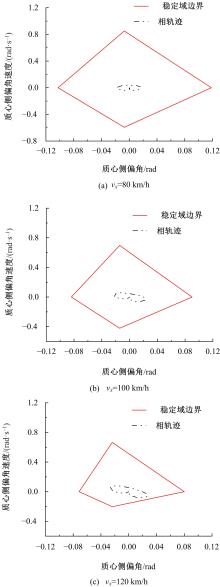
Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition) ›› 2022, Vol. 52 ›› Issue (7): 1515-1523.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb20210118
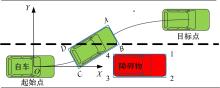
Collision avoidance trajectory planning for intelligent vehicles in emergency conditions
Wei ZHANG( ),Shu-pei ZHANG(
),Shu-pei ZHANG( ),Chong-en LUO,Sheng ZHANG,Guo-lin WANG
),Chong-en LUO,Sheng ZHANG,Guo-lin WANG
- School of Automotive and Traffic Engineering,Jiangsu University,Zhenjiang 212013,China
CLC Number:
- U491
| 1 | 周兵,万希,吴晓建,等. 紧急避撞工况下的路径规划与跟踪[J]. 湖南大学学报:自然科学版, 2020, 47 (10): 11-18. |
| Zhou Bing, Wan Xi, Wu Xiao-jian, et al. Path planning and tracking in scenario of emergency collision avoidance[J]. Journal of Hunan University(Natural Sciences), 2020, 47 (10): 11-18. | |
| 2 | Ji J, Khajepour A, Melek W W, et al. Path planning and tracking for vehicle collision avoidance based on model predictive control with multiconstraints[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2017, 66(2): 952-964. |
| 3 | Li B, Zhang Y, Feng Y, et al. Balancing computation speed and quality: a decentralized motion planning method for cooperative lane changes of connected and automated vehicles[J]. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Vehicles, 2018(3): 340-350. |
| 4 | 张友安,王丽英,张刚,等. 轨迹优化的直接数值解法综述[J].海军航空工程学院学报, 2012, 27(5): 481-486, 498. |
| Zhang You-an, Wang Li-ying, Zhang Gang, et al. A survey of numerical methods for trajectory optimization[J]. Journal of Naval Aeronautical Engineering Institute,2012,27(5):481-486, 498. | |
| 5 | 余卓平, 李奕姗, 熊璐. 无人车运动规划算法综述[J]. 同济大学学报:自然科学版, 2017, 45(8): 1150-1159. |
| Yu Zhuo-ping, Li Yi-shan, Xiong Lu. A review of the motion planning problem of autonomous vehicle[J]. Journal of Tongji University(Natural Science), 2017, 45(8):1150-1159. | |
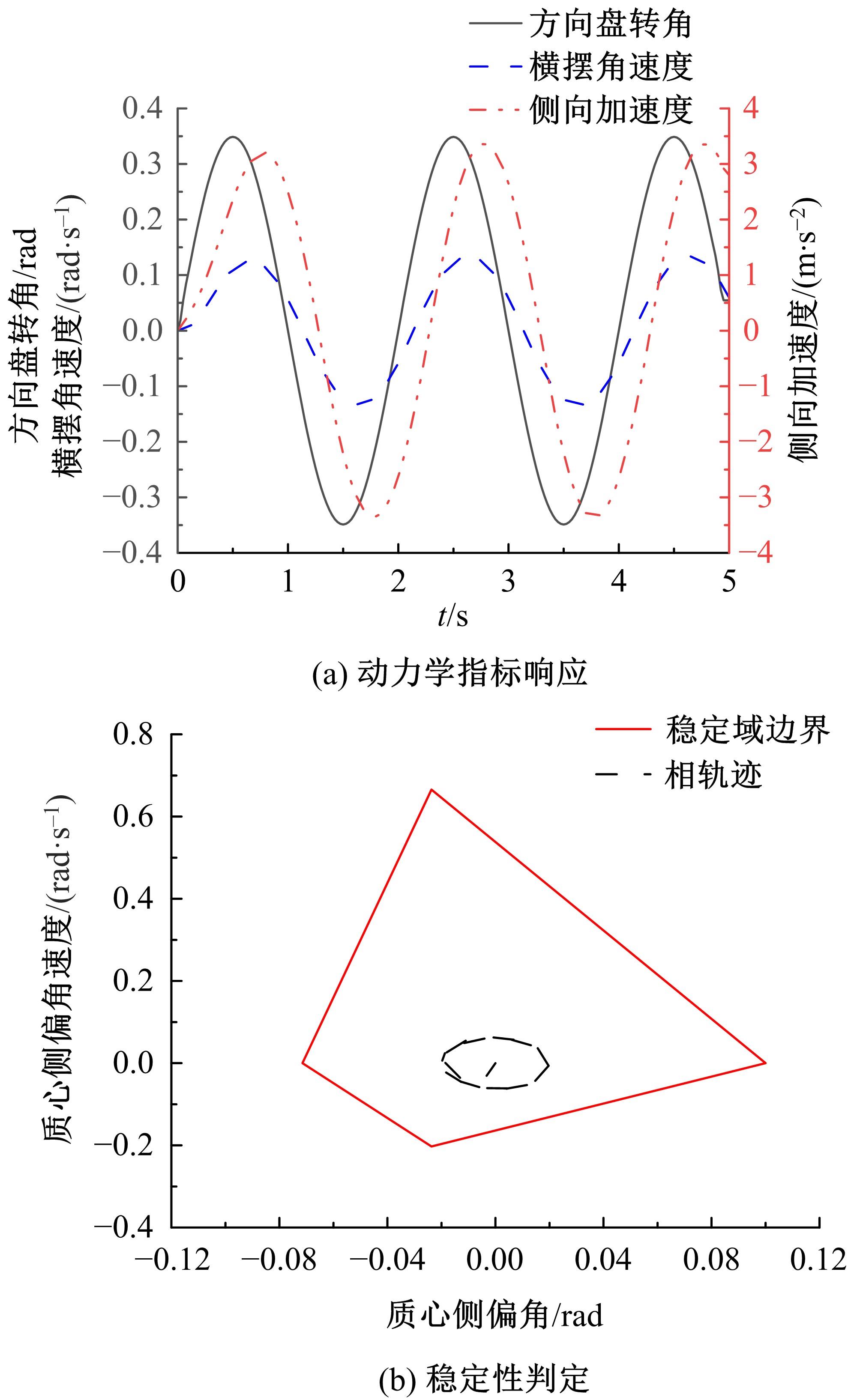
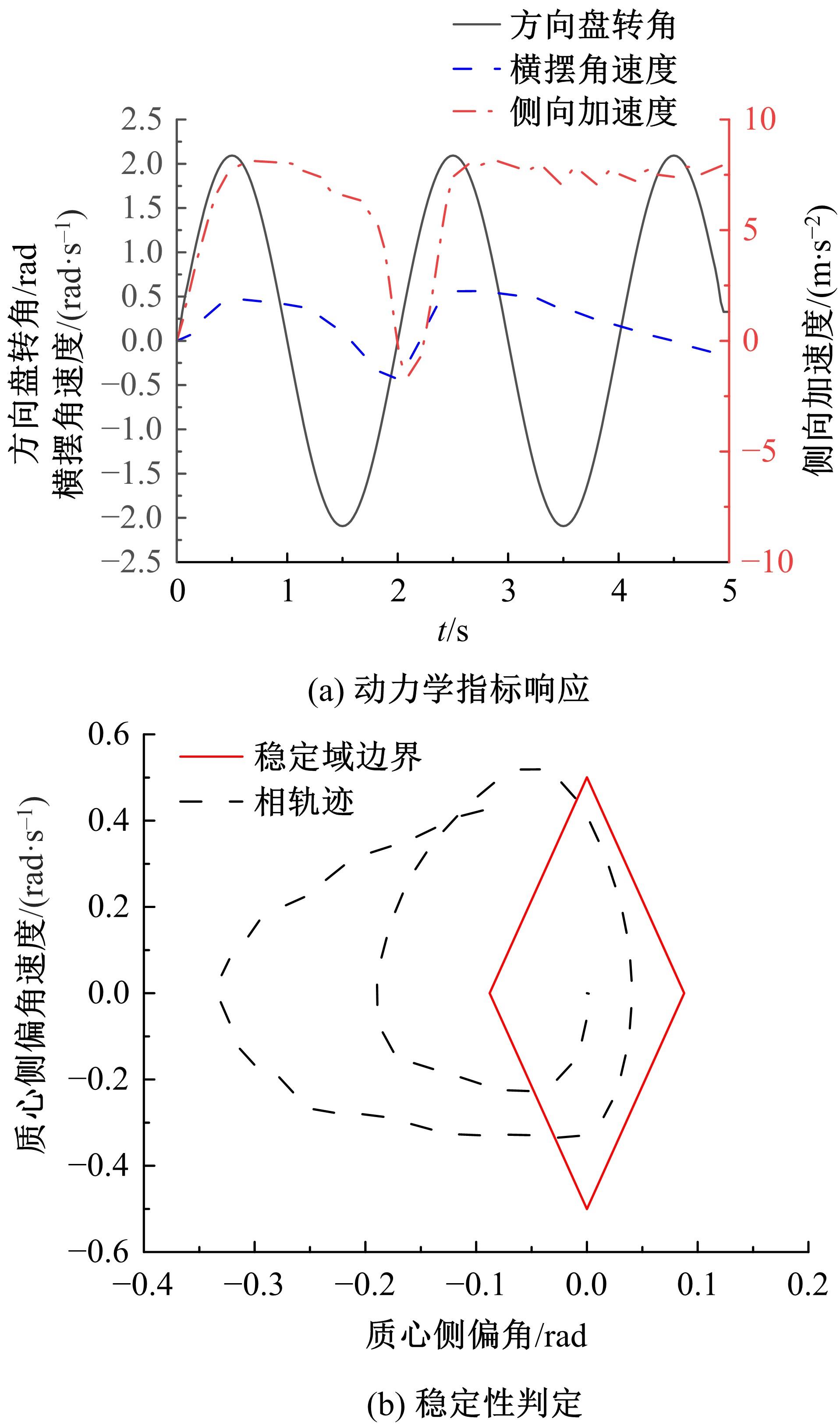
| 6 | Inagaki S, Kushiro I, Yamamoto M. Analysis on vehicle stability in critical cornering using phase-plane method[J]. JSAE Review, 1994, 16(2): 211-216. |
| 7 | 熊璐, 曲彤, 冯源,等. 极限工况下车辆行驶的稳定性判据[J]. 机械工程学报, 2015, 51(10): 103-111. |
| Xiong Lu, Qu Tong, Feng Yuan, et al. Stability criterion for the vehicle under critical driving situation[J]. Journal of Mechanical Engineering, 2015, 51(10): 103-111. | |
| 8 | Liu W, Xiong L, Leng B, et al. Vehicle stability criterion research based on phase plane method[C]∥ WCX™ SAE World Congress Experience,Detroit, USA,2017. |
| 9 | 孟少华,向锦武,罗漳平,等. 微小型无人直升机避障最优轨迹规划[J]. 北京航空航天大学学报, 2014, 40(2): 246-251. |
| Meng Shao-hua, Xiang Jin-wu, Luo Zhang-ping, et al. Optimal trajectory planning for small-scale unmanned helicopter obstacle avoidance[J]. Journal of Beijing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2014, 40(2): 246-251. | |
| 10 | Li B, Shao Z. A unified motion planning method for parking an autonomous vehicle in the presence of irregularly placed obstacles[J]. Knowledge Based Systems, 2015, 86: 11-20. |
| 11 | Patterson M A, Rao A V. GPOPS-II: a Matlab software for solving multiple-phase optimal control problems using hp-adaptive gaussian quadrature collocation methods and sparse nonlinear programming[J]. ACM Transactions on Mathematical Software, 2010, 41(1): 1-37. |
| [1] | Bin XIAN,Shi-jing ZHANG,Xiao-wei HAN,Jia-ming CAI,Ling WANG. Trajectory planning for unmanned aerial vehicle slung⁃payload aerial transportation system based on reinforcement learning [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2021, 51(6): 2259-2267. |
| [2] | Qing⁃ying LAI,Jun LIU,Ruo⁃yu ZHAO,Yong⁃ji LUO,Ling⁃yun MENG,Ya⁃zhi XU. Optimal trajectory planning for middle⁃to⁃high speed maglev based on dynamic programming with mutative spacing [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2019, 49(3): 749-756. |
| [3] | ZHANG Lin, ZHANG Xin-jie, GUO Kong-hui, WANG Chao, LIU Yang, LIU Tao. Rolling window optimization for intelligent vehicle trajectory planning in unknown environment [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2018, 48(3): 652-660. |
| [4] | QU Xing-tian, YAN Long-wei, SUN Hui-chao, ZHOU Wei, LI Guang-hui. Structure analysis of 3D printer device of reversible working platform [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2017, 47(5): 1489-1497. |
| [5] | CAO Fu-cheng, XING Xiao-xue, LI Yuan-chun, ZHAO Xi-lu. Adaptive trajectory sliding mode impedance control for lower limb rehabilitation robot [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2016, 46(5): 1602-1608. |
| [6] | XU Cheng, QU Zhao-wei, TAO Peng-fei. Estimation of bicycle path capacity under mixed bicycle traffic flow [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2016, 46(1): 63-69. |
| [7] | WANG Zhong-yu, CAI Qing, WU Bing, LI Lin-bo. Queue length estimation for signalized intersections based on multi-source data [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2015, 45(4): 1088-1094. |
| [8] | GUAN Cheng, WANG Fei, ZHANG Deng-yu. NURBS-based time-optimal trajectory planning on robotic excavators [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2015, 45(2): 540-546. |
| [9] | MIAO Dong-jing,WU Liao,XU Jing,CHEN Ken,XIE Ying,LIU Zhi. Automatic spraying robot system for aircraft surfaces and spraying operation planning [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2015, 45(2): 547-553. |
| [10] |
LI Ai-juan,LI Shun-ming,ZHAO Wan-zhong,SHEN Huan,JIANG Xing-xing, QIU Xu-yun,WANG Hui-jun. Optimal control theory based trajectory generation method for intelligent vehicle [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2014, 44(5): 1276-1282. |
| [11] | SUN Hao, DENG Wei-wen, ZHANG Su-min, WU Meng-xun. Micro vehicle dynamic trajectory plan with global optimality [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2014, 44(4): 918-924. |
| [12] | SHAO Min-hua, SUN Li-jun, SHAO Xian-zhi. Network location model of sensors and algorithm based on turning ratios [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2013, 43(06): 1476-1481. |
| [13] | LI Ai-juan, LI Shun-ming, SHEN Huan, MIAO Xiao-dong. ACT-R based dynamic trajectory optimization method for intelligent vehicles [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2013, 43(05): 1184-1189. |
| [14] | GUO Lie, HUANG Xiao-hui, GE Ping-shu, ZHANG Guang-xi, YUE Ming. Lane changing trajectory tracking control for intelligent vehicle on curved road based on backstepping [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2013, 43(02): 323-328. |
| [15] | JIA Hong-fei, CHEN Bin, LI Guo-wei, ZHANG Jing-shan. Collision avoidance method in pedestrian simulation based on blockade-angle [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2011, 41(6): 1577-1580. |
|
||