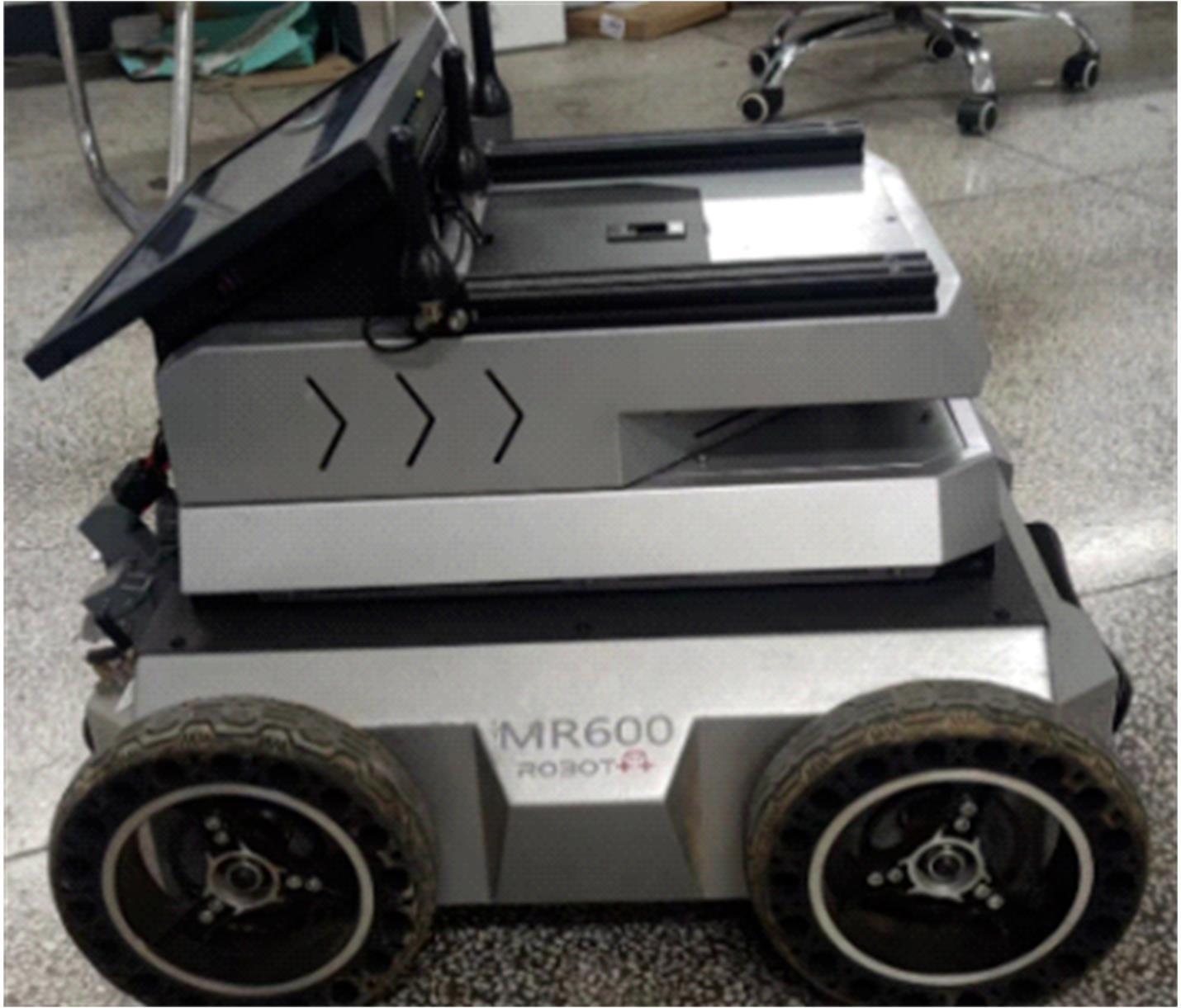
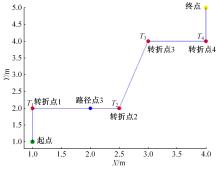
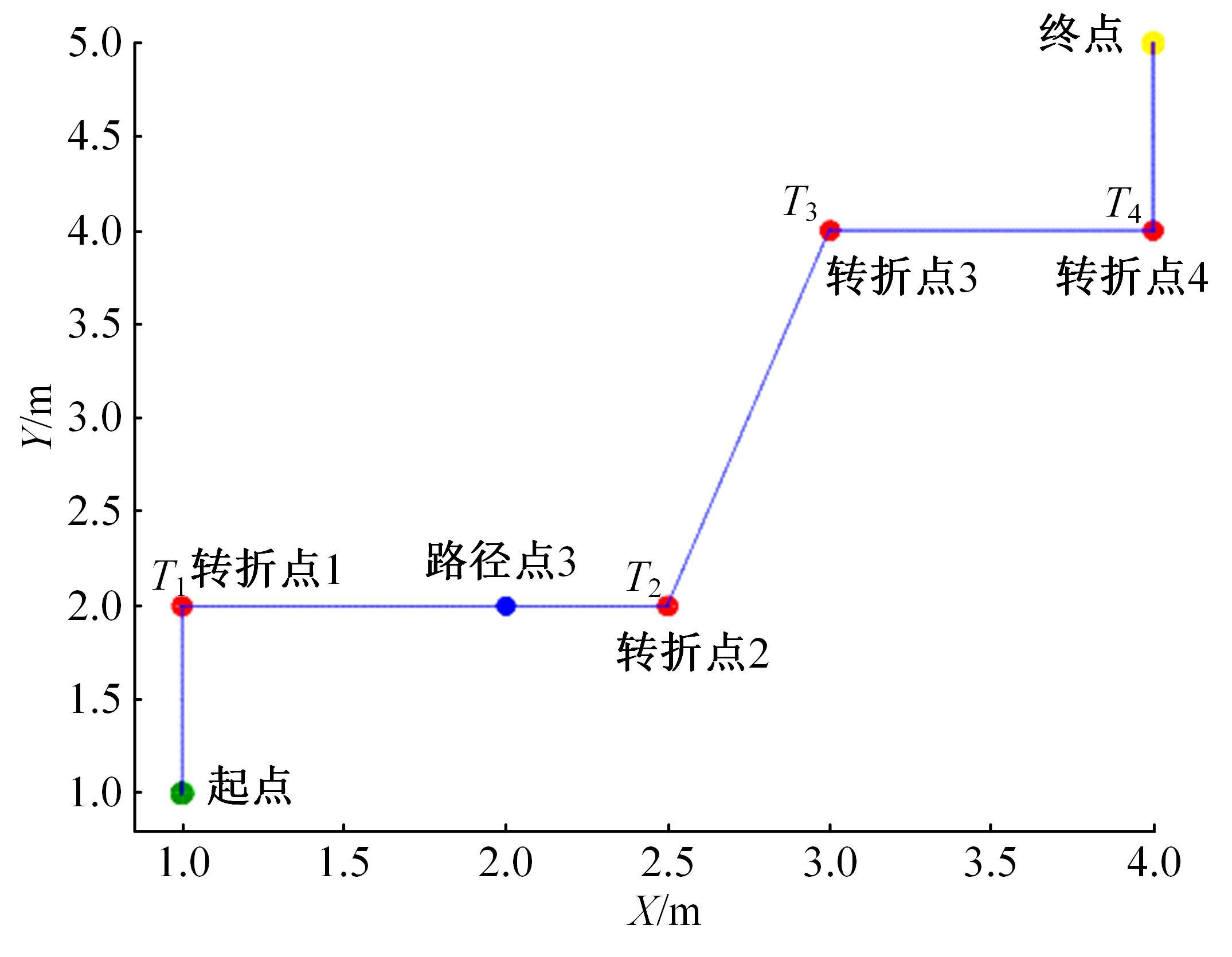
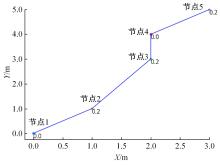
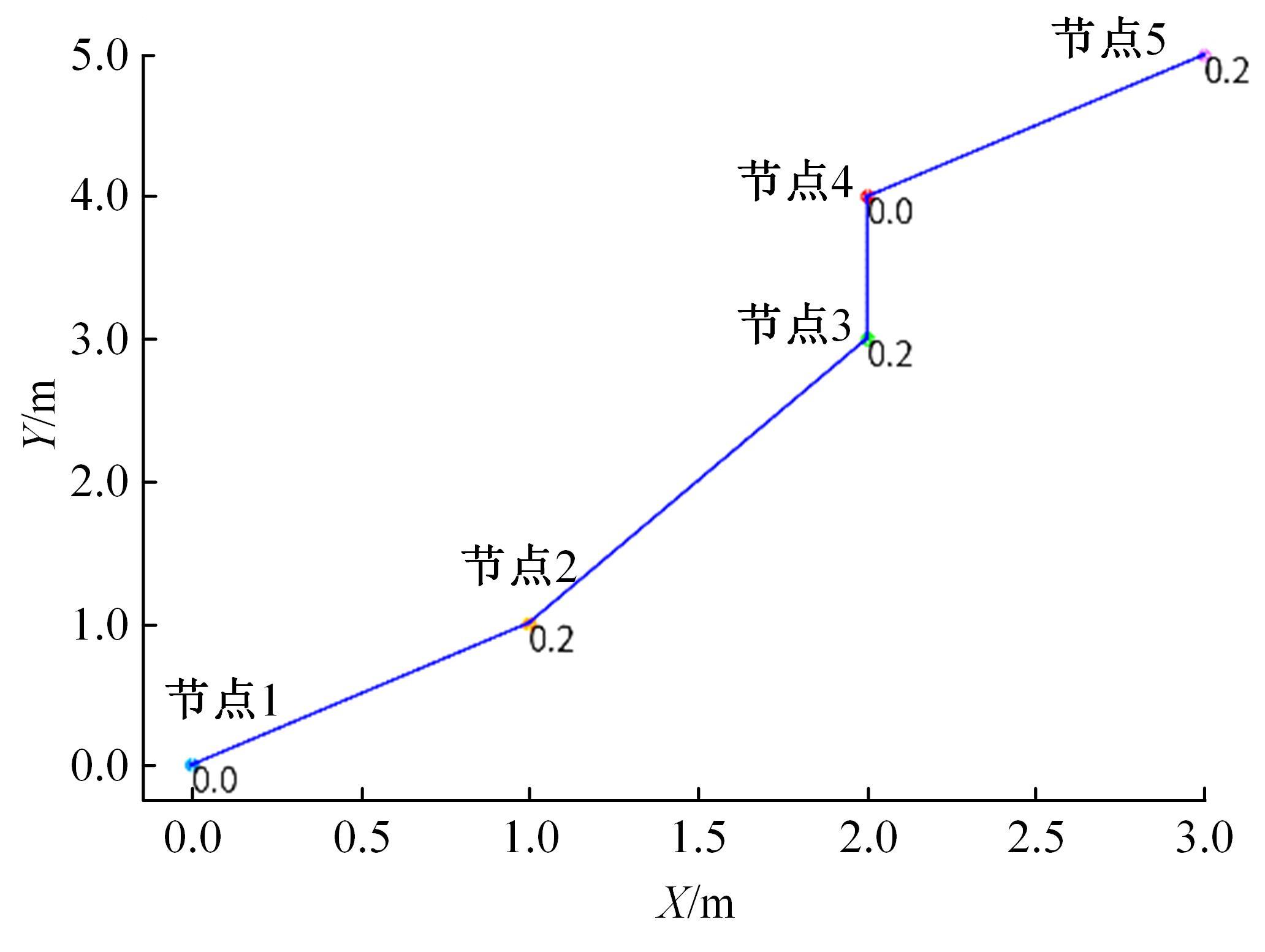
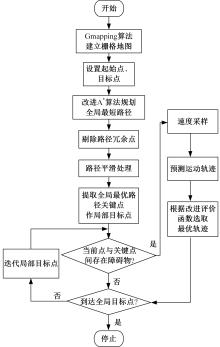
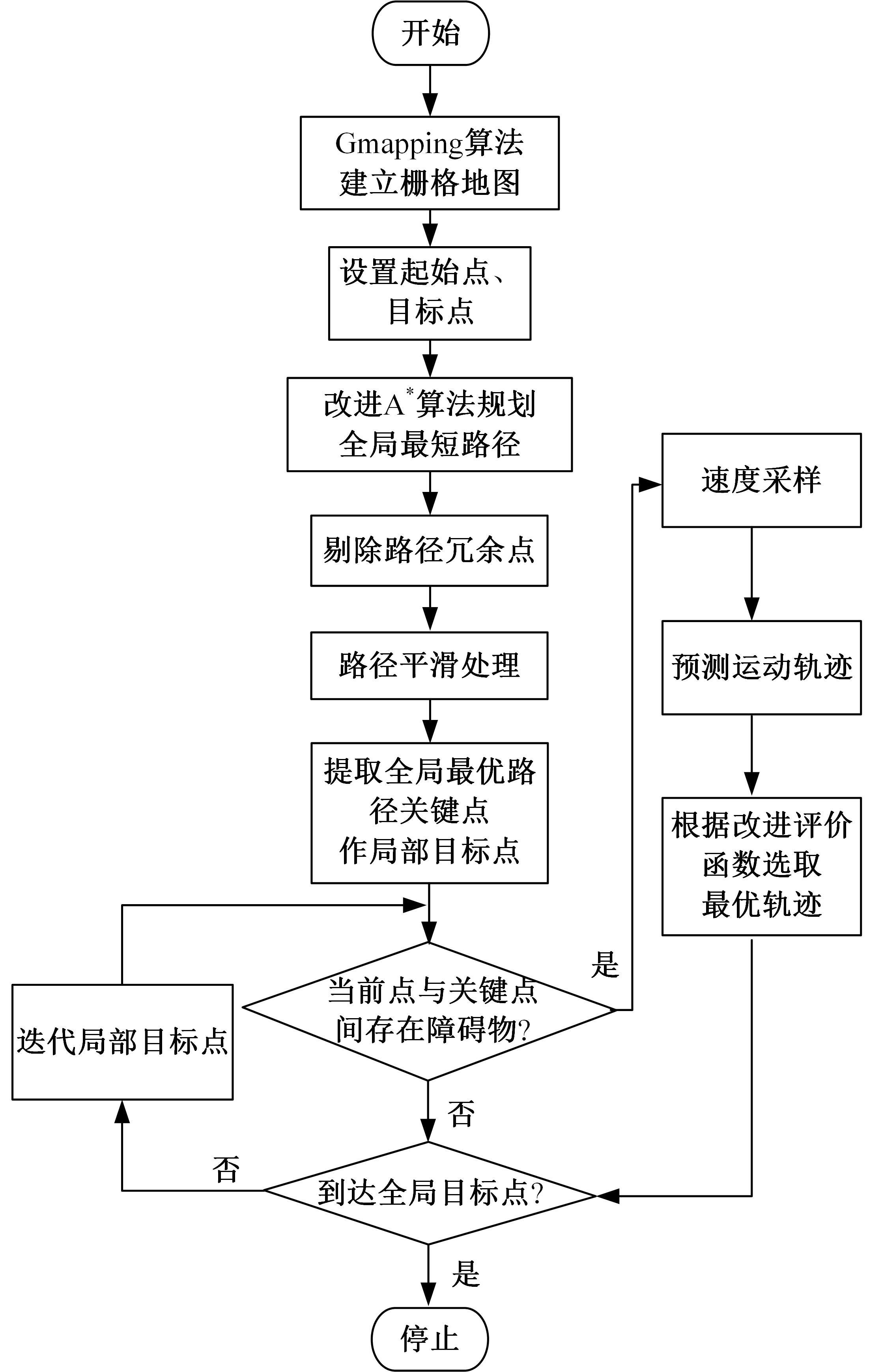
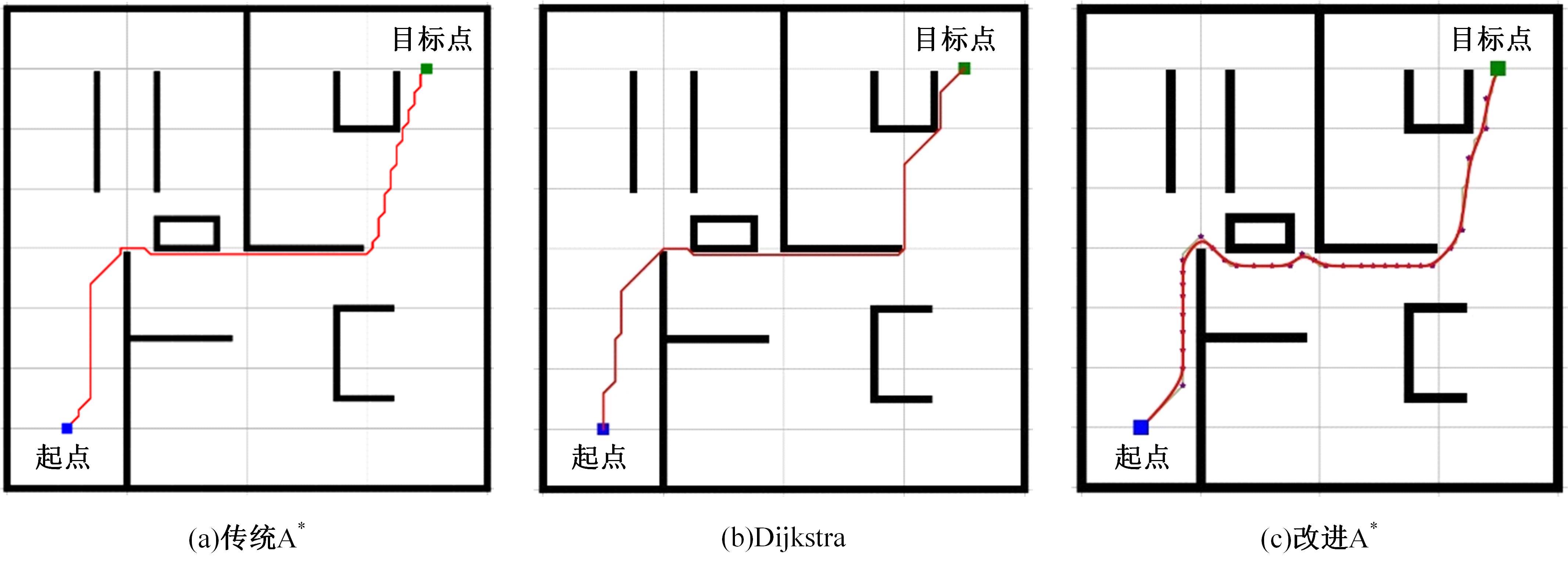
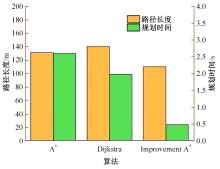
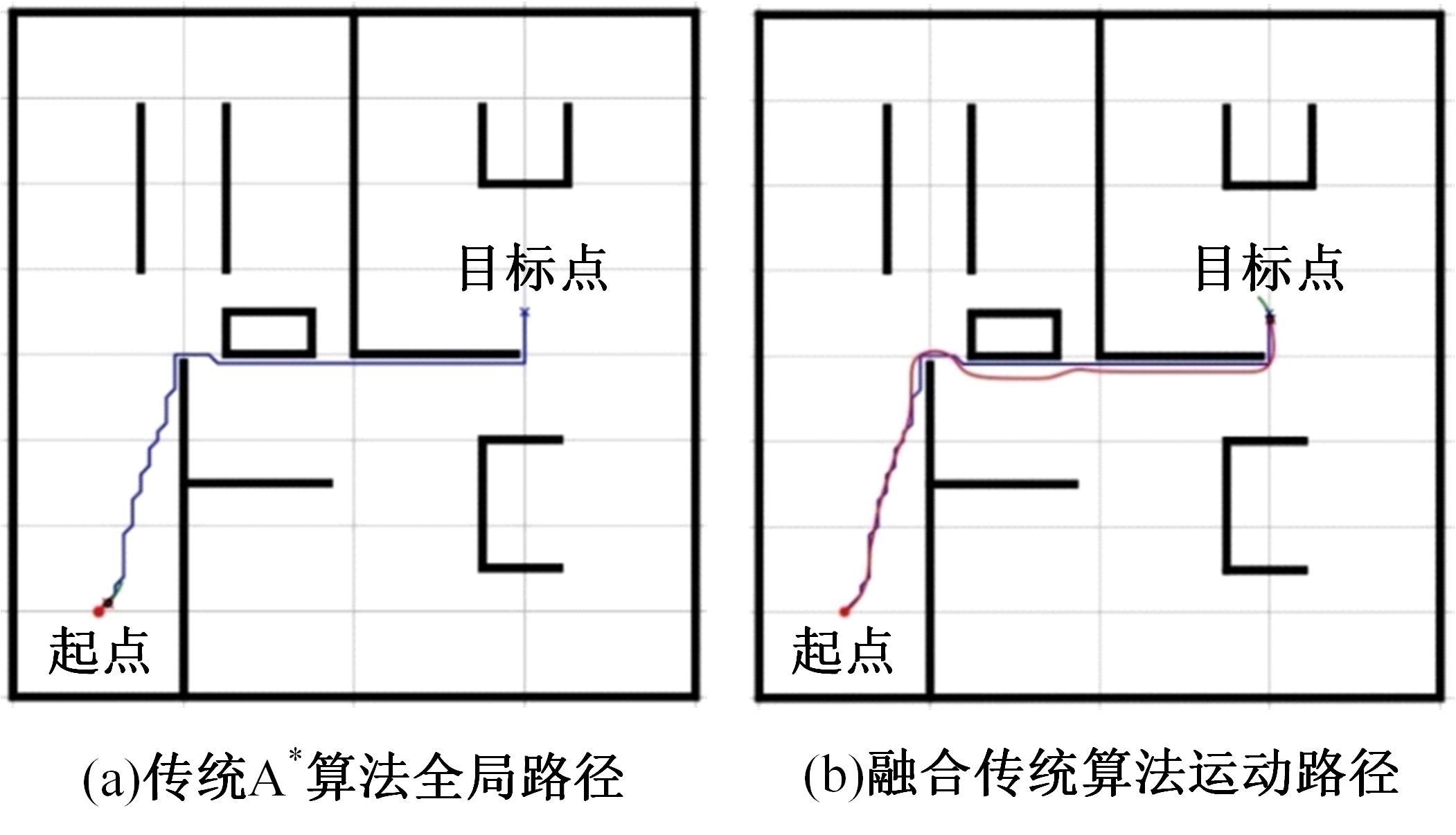
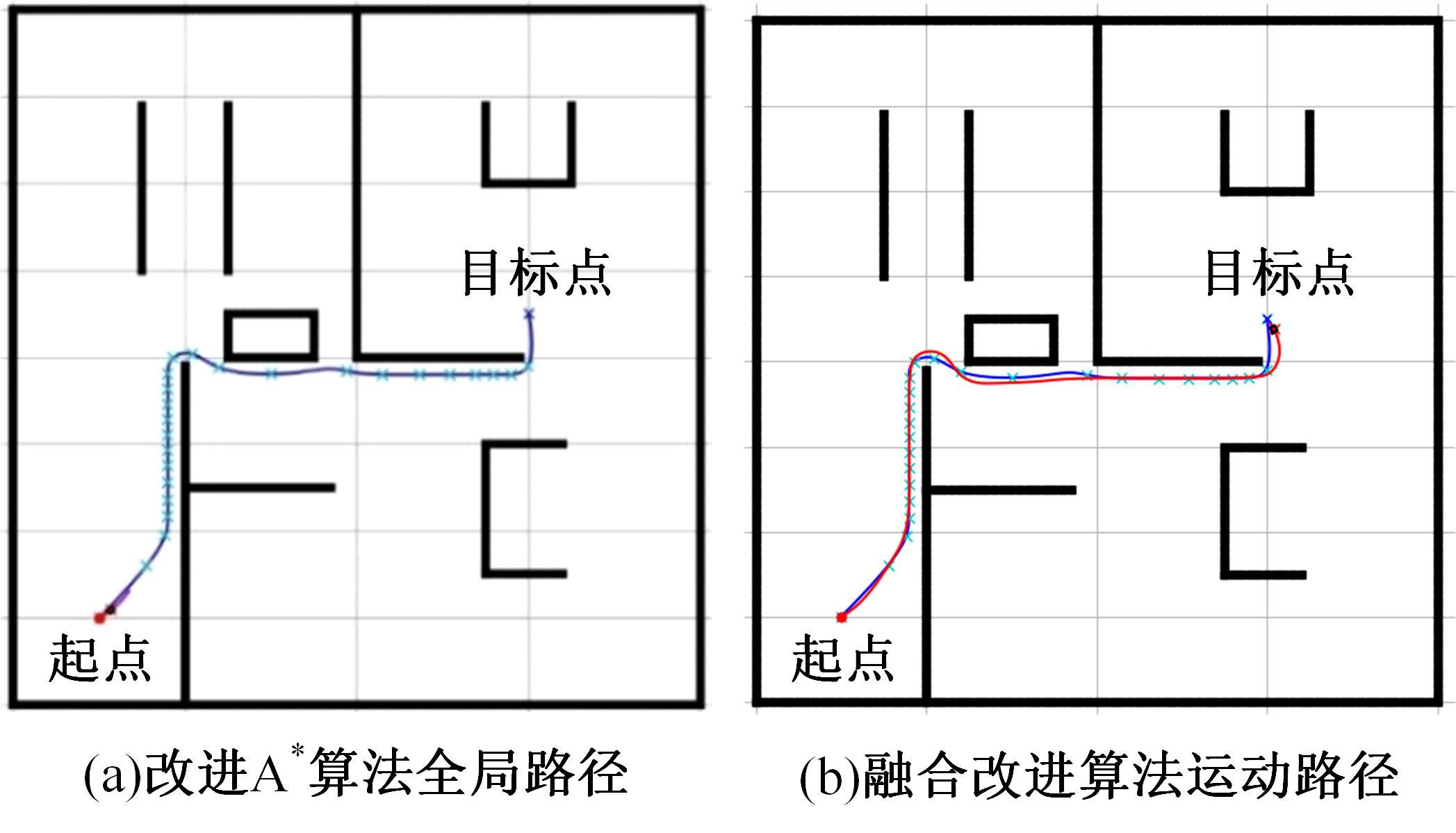
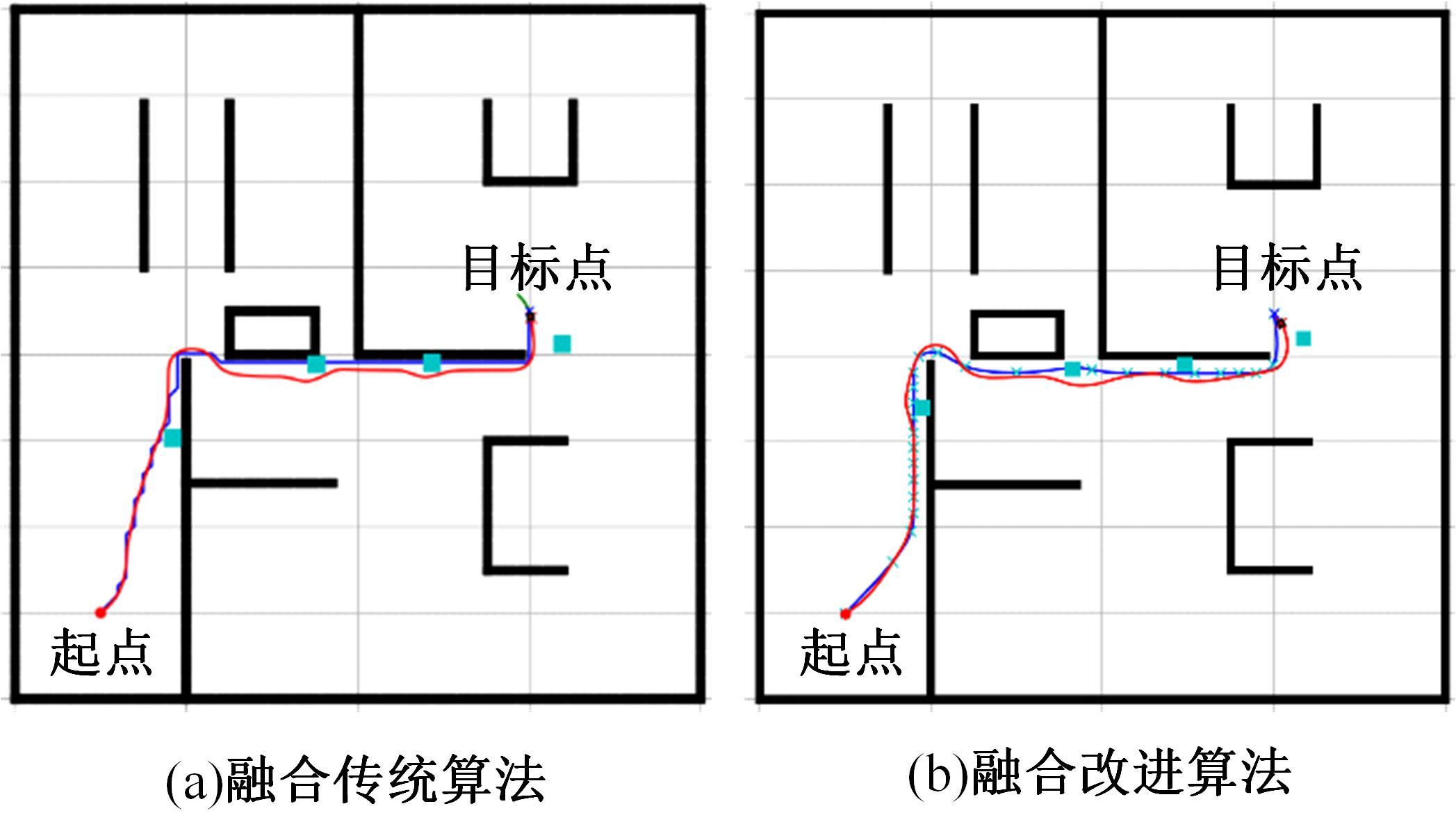
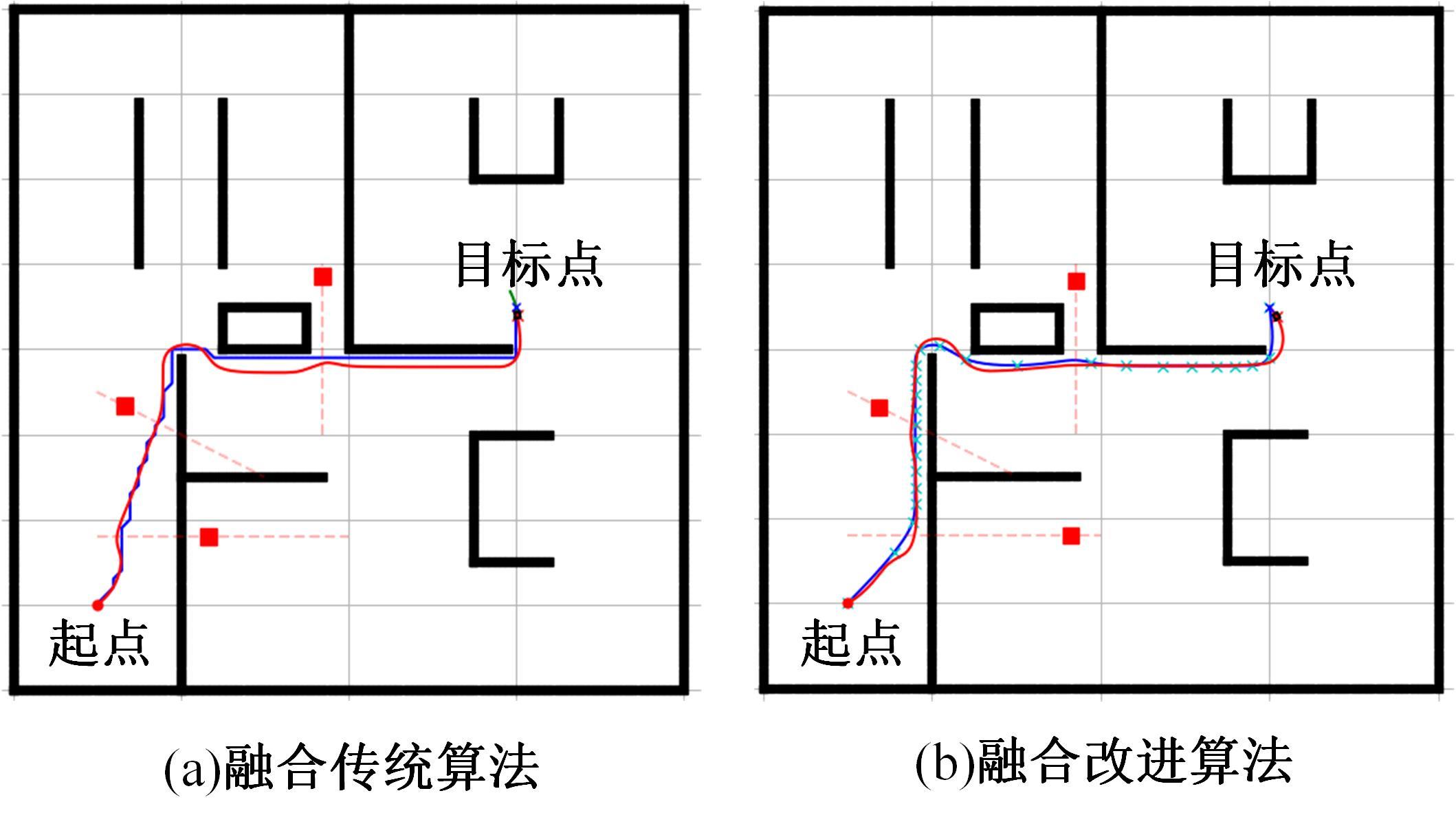
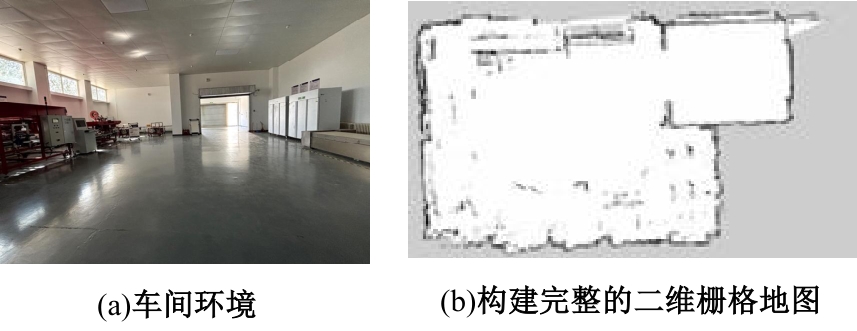
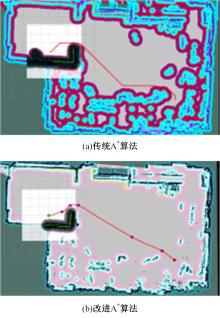
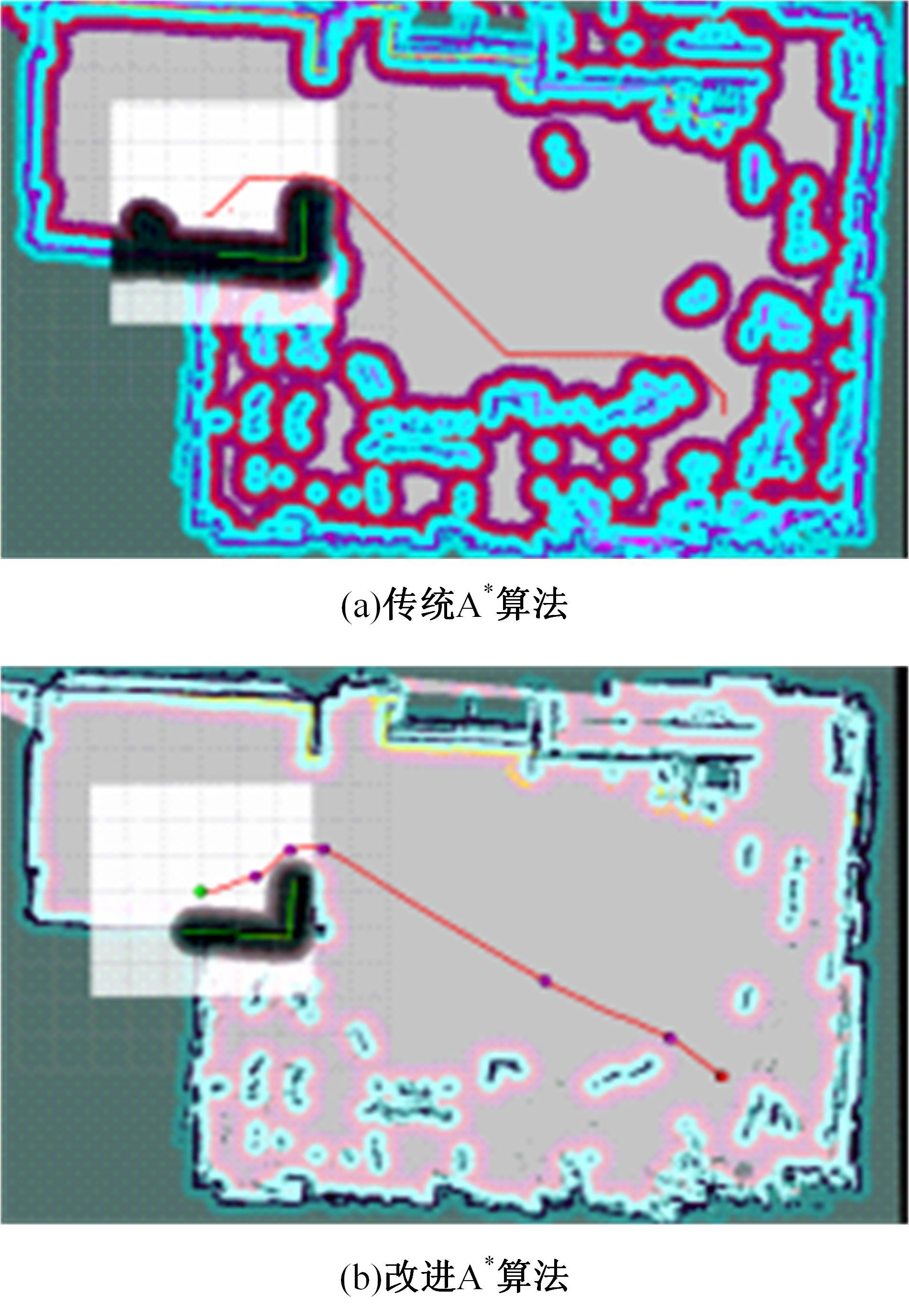
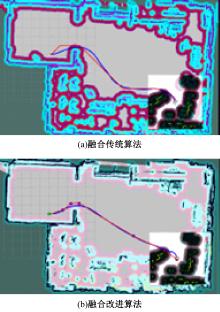
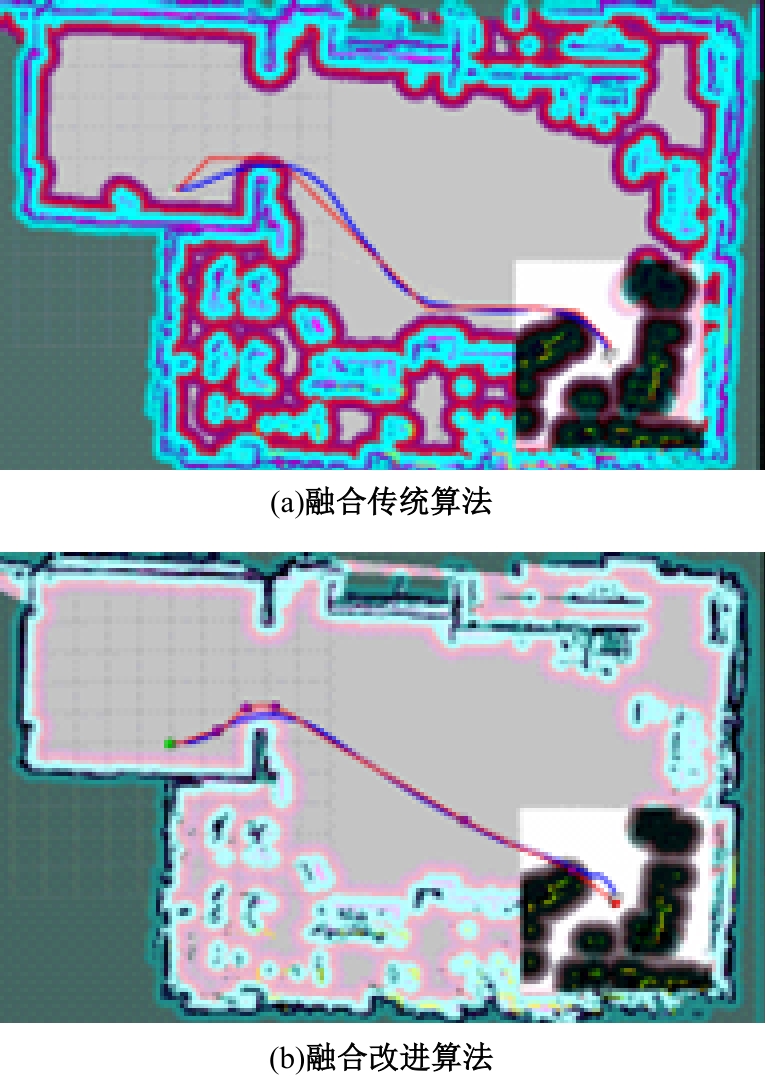
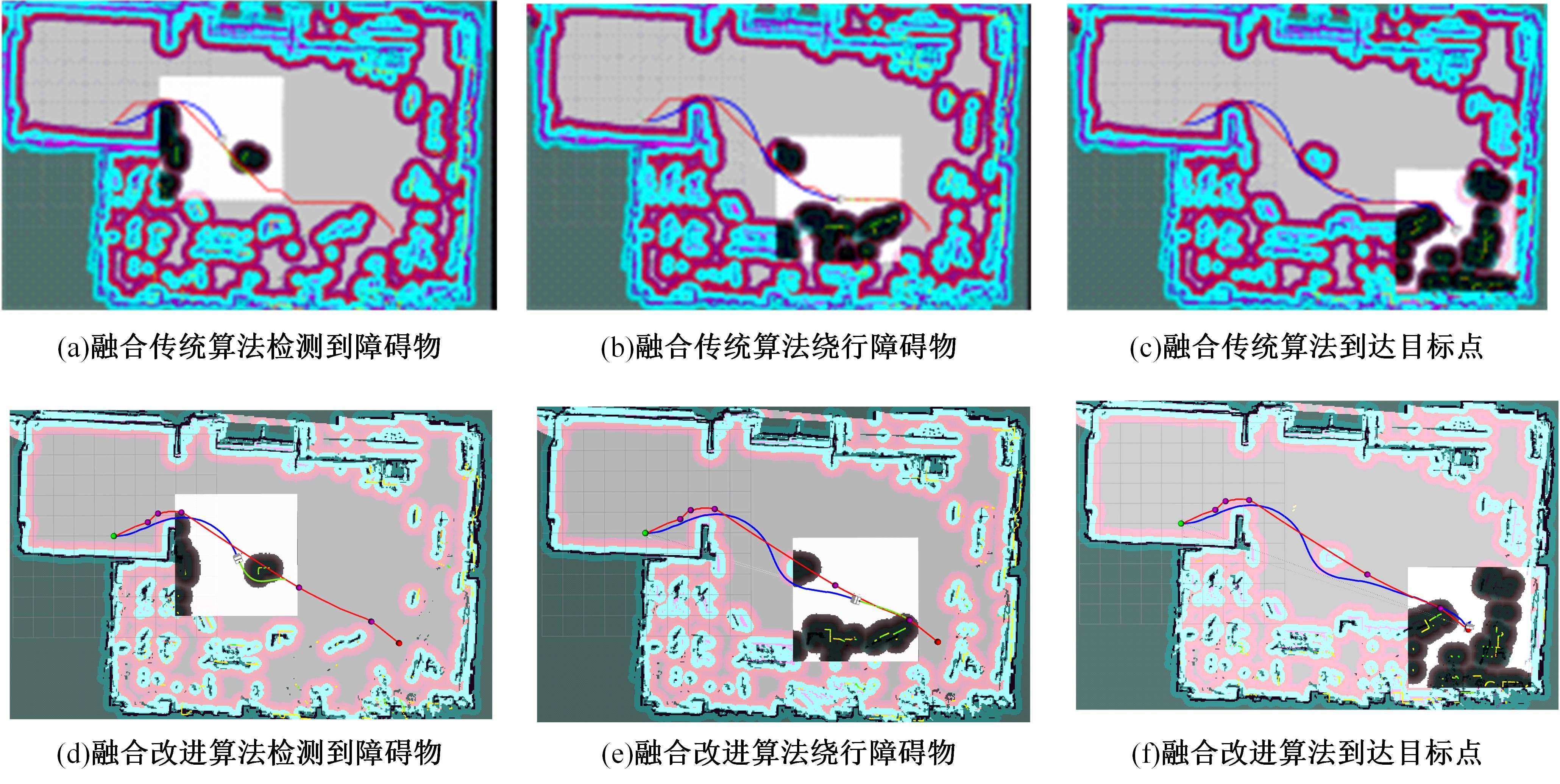
Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition) ›› 2025, Vol. 55 ›› Issue (9): 3020-3031.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb.20250381
Path planning of workshop mobile robots integrated with improved A* and DWA algorithms
Fu ZHANG1( ),Wei-dong HAN1,Ruo-fei BAO1,Ya-kun ZHANG1,Ya-fei WANG2,San-ling FU3
),Wei-dong HAN1,Ruo-fei BAO1,Ya-kun ZHANG1,Ya-fei WANG2,San-ling FU3
- 1.College of Agricultural Equipment Engineering,Henan University of Science and Technology,Luoyang 471003,China
2.College of Agricultural Engineering,Jiangsu University,Zhenjiang 212013,China
3.College of Physics Engineering,Henan University of Science and Technology,Luoyang 471003,China
CLC Number:
- TP242
| [1] | 向抒林, 陈炜, 程伟, 等. 石油化工储罐区巡检机器人研究现状与展望[J]. 石油化工腐蚀与防护, 2024, 41(6): 1-8. |
| Xiang Shu-lin, Chen Wei, Cheng Wei, et al. Research status and prospect of inspection robot for petrochemical storage tank area[J]. Petrochemical Corrosion and Protection,2024, 41(6): 1-8. | |
| [2] | Zhang H J, Jiang F, Liu C K, et al. Review of autonomous path planning for planetary rovers[J]. Chinese Journal of Engineering, 2024, 46(11): 2063-2075. |
| [3] | Zhong J K, Kong D Y, Wei Y L, et al. Efficiency-optimized path planning algorithm for car-like mobile robots in bilateral constraint corridor environments[J]. Robotics and Autonomous Systems, 2025, 186: No.104923. |
| [4] | Zhang Z W, Wu L H, Zhang W Q, et al. Energy-efficient path planning for a single-load automated guided vehicle in a manufacturing workshop[J]. Computers & Industrial Engineering, 2021, 158: No.107397. |
| [5] | Katona K, Neamah H A, Korondi P. Obstacle avoidance and path planning methods for autonomous navigation of mobile robot[J]. Sensors, 2024, 24(11): No.2411. |
| [6] | 霍凤财, 迟金, 黄梓健, 等. 移动机器人路径规划算法综述[J]. 吉林大学学报: 信息科学版, 2019, 36(6): 639-647. |
| Huo Feng-cai, Chi Jin, Huang Zi-jian, et al. A review of path planning algorithms for mobile robots[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Information Science Edition), 2019, 36(6): 639-647. | |
| [7] | 姚得鑫, 伞红军, 王雅如, 等. 移动机器人路径规划中A*算法的改进研究[J]. 系统仿真学报, 2024, 36(11): 2684-2698. |
| Yao De-xin, Hong-jun San, Wang Ya-ru, et al. Research on the improvement of A* algorithm in path planning of mobile robot[J]. Journal of System Simulation, 2024, 36(11): 2684-2698. | |
| [8] | 杨姝慧, 郝子鑫, 李彬. 机器人路径规划算法研究分析与综述[J]. 齐鲁工业大学学报, 2024, 38(5): 37-46. |
| Yang Shu-hui, Hao Zi-xin, Li Bin. Research analysis and summary of robot path planning algorithm[J]. Journal of Qilu University of Technology, 2024, 38(5): 37-46. | |
| [9] | Chen H, Lin Z, Chen Z, et al. Adaptive DWA algorithm with decision tree classifier for dynamic planning in USV navigation[J]. Ocean Engineering, 2025, 321: No.120328. |
| [10] | Wang Y C, Li J L, Zhao S Q, et al. Hybrid path planning for USV with kinematic constraints and COLREGS based on improved APF-RRT and DWA[J]. Ocean Engineering, 2025, 318: No.120128. |
| [11] | 王云亮, 张赛, 吴艳娟. 基于改进A*平滑性路径规划算法研究[J]. 计算机应用与软件, 2025, 42(1): 258-263, 276. |
| Wang Yun-liang, Zhang Sai, Wu Yan-juan. Research on path planning algorithm based on improved A* smoothness[J]. Computer Applications and Software, 2025, 42(1): 258-263, 276. | |
| [12] | 张宸威, 黄平, 张国恒, 等. 基于改进A*算法的自适应路径规划研究[J]. 通信与信息技术, 2025(1): 43-45, 122. |
| Zhang Chen-wei, Huang Ping, Zhang Guo-heng, et al. Research on adaptive path planning based on improved A* algorithm[J]. Communication and Information Technology, 2025(1): 43-45, 122. | |
| [13] | Zhang J Q, Ling H J, Tang Z H, et al. Path planning of USV in confined waters based on improved A∗ and DWA fusion algorithm[J]. Ocean Engineering, 2025, 322: No.120475. |
| [14] | Wang Y C, Fu C H, Huang R Y, et al. Path planning for mobile robots in greenhouse orchards based on improved A* and fuzzy DWA algorithms[J]. Computers and Electronics in Agriculture, 2024, 227: No.109598. |
| [15] | Guo H, Li Y, Wang H, et al. Path planning of greenhouse electric crawler tractor based on the improved A* and DWA algorithms[J]. Computers and Electronics in Agriculture, 2024, 227: No.109596. |
| [16] | Ayalew W, Menebo M, Merga C, et al. Optimal path planning using bidirectional rapidly-exploring random tree star-dynamic window approach (BRRT*-DWA) with adaptive Monte Carlo localization (AMCL) for mobile robot[J]. Engineering Research Express, 2024, 6(3): No.035212. |
| [17] | Jathunga T, Rajapaksha S. Improved path planning for multi-robot systems using a hybrid probabilistic roadmap and genetic algorithm approach[J]. Journal of Robotics and Control, 2025, 6(2): 715-733. |
| [1] | Jian LI,Xiao-hai SUN,Chang-yi LIAO,Jian-ping YANG. Robot path planning method based on double-origin ant colony algorithm [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2025, 55(1): 325-332. |
| [2] | Jin ZHU,Qi HUANG. Automated terminal horizontal transportation scheduling and route planning under network resource allocation [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2024, 54(8): 2245-2255. |
| [3] | Shuai-shuai SUN,Chun-xiao FENG,Liang ZHANG. Path planning for multimodal quadruped robots based on discrete sampling [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2024, 54(4): 1120-1128. |
| [4] | Hao ZHENG,Li-jun YU,Peng-peng ZHI,Zhong-lai WANG. Dynamic obstacle avoidance strategy for flapping⁃wing micro air vehicles [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2023, 53(9): 2732-2740. |
| [5] | Zhen-yu WU,Xiao-fei LIU,Yi-pu WANG. Trajectory planning of unmanned system based on DKRRT*⁃APF algorithm [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2023, 53(3): 781-791. |
| [6] | Fan YANG,Zhi-qiang ZHAI,Yuan-yuan WANG,Zhong-xiang ZHU,Yue-feng DU,En-rong MAO. Design of assembly system for tractor transmission based on virtual reality [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2023, 53(10): 3038-3044. |
| [7] | Jia-xu ZHANG,Chen WANG,Jian ZHAO,Chun-yan BU. Path planning and tracking control for narrow parallel parking space [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2021, 51(5): 1879-1886. |
| [8] | Jia-xu ZHANG,Xin-zhi WANG,Jian ZHAO,Zheng-tang SHI. Path planning and discrete sliding mode tracking control for high⁃speed lane changing collision avoidance of vehicle [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2021, 51(3): 1081-1090. |
| [9] | Xiao-jian HAN,Wei-qiang ZHAO,Li-jun CHEN,Hong-yu ZHENG,Yang LIU,Chang-fu ZONG. Local path planning of bus based on RS-RRT algorithm [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2019, 49(5): 1428-1440. |
| [10] | QIAN Li-jun, HU Wei-long, LIU Qing, WU Bing. Multiple segment method for automatic parking path planning and its key technology [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2016, 46(3): 785-791. |
| [11] | ZHOU Bing-hai, ZHOU Qi. Impending deadlock-free scheduling method for unified AMHS in semiconductor FABs [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2016, 46(2): 595-601. |
| [12] | KANG Bing, WANG Xi-hui, LIU Fu. Path planning of searching robot based on improved ant colony algorithm [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2014, 44(4): 1062-1068. |
| [13] | LIU Hou-de, LIANG Bin, XU Wen-fu, MU Qing-tao, YU Jiang-hua. Motion prediction and autonomous path planning for spinning target capturing [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2014, 44(3): 757-764. |
| [14] | LIU Gang, LIU Yu-bin, ZHAO Jie, ZHU Lei. Path planning for a new mine rescue robot base on visual tangent graphs [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2011, 41(4): 1107-1112. |
| [15] | ZHAO Yang, ZHAO Ji, ZHANG Lei, JI Li-Zhe. Robotic blade grinding based on reverse engineering [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2009, 39(05): 1176-1180. |
|
||