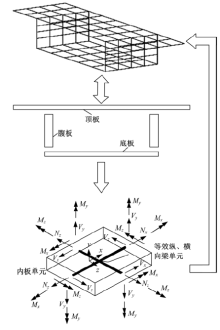
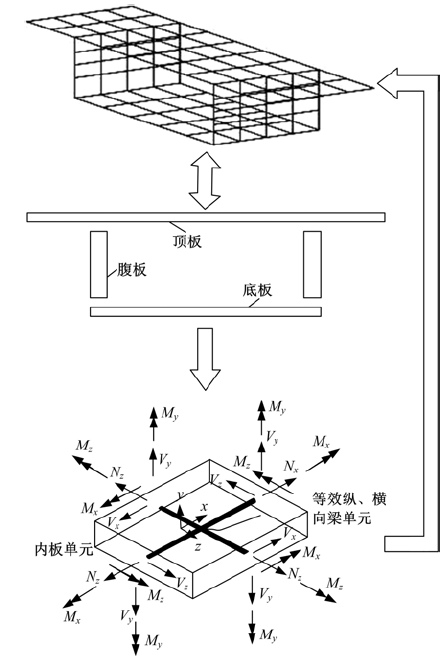
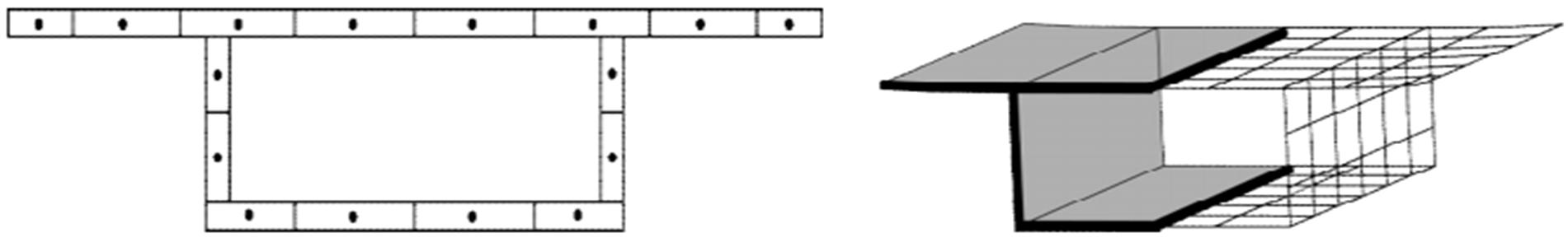
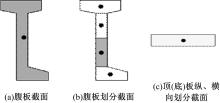
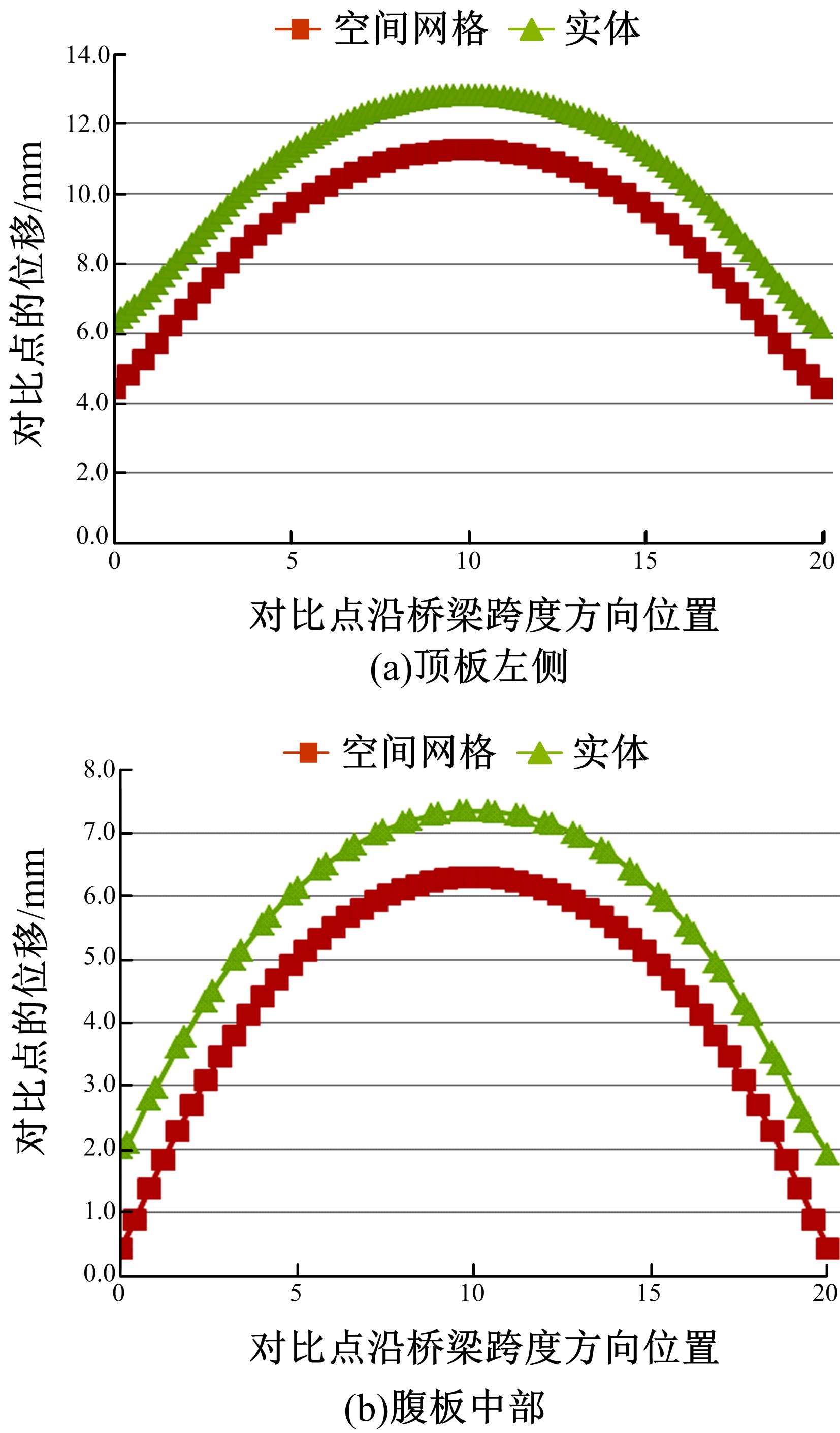
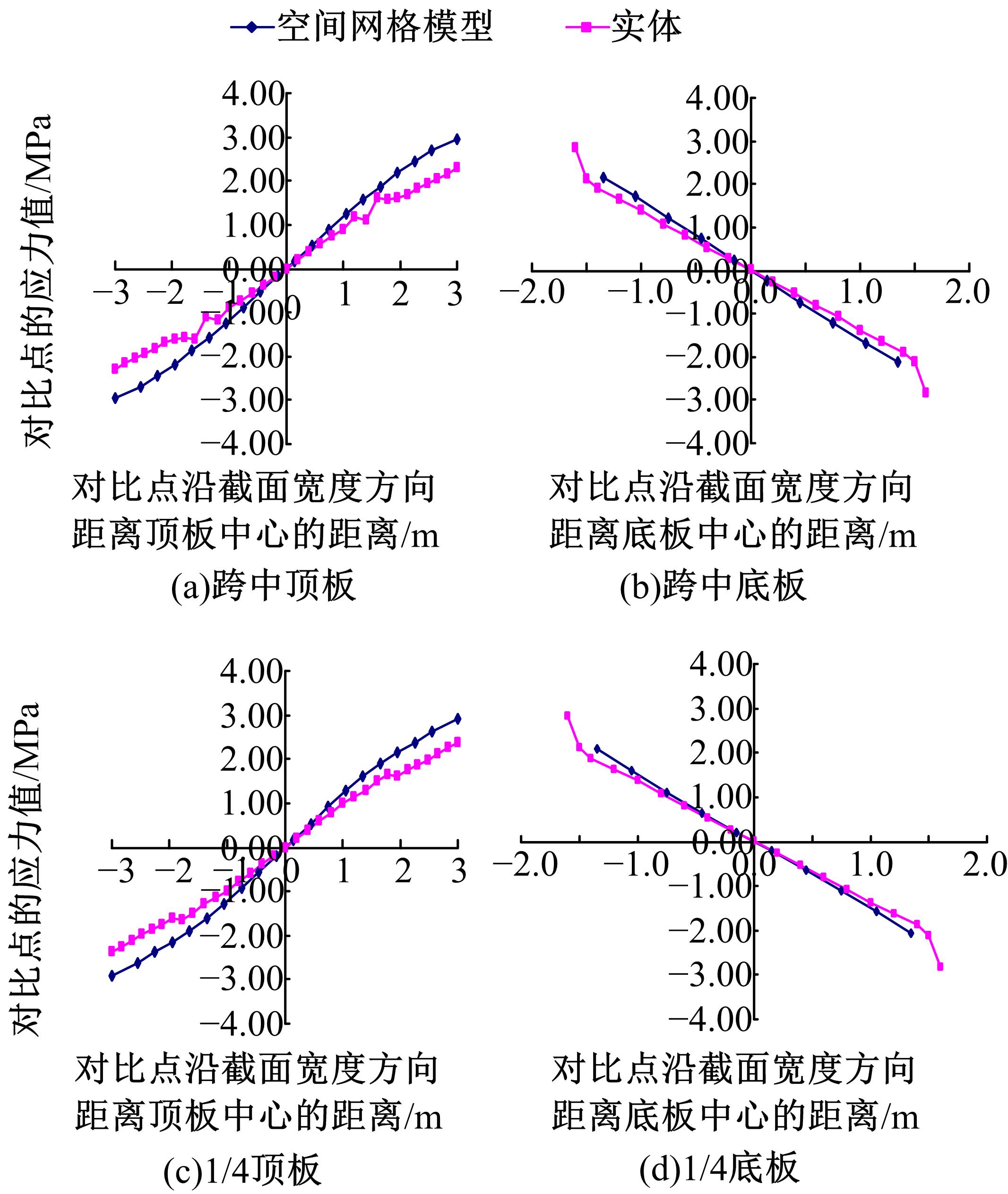
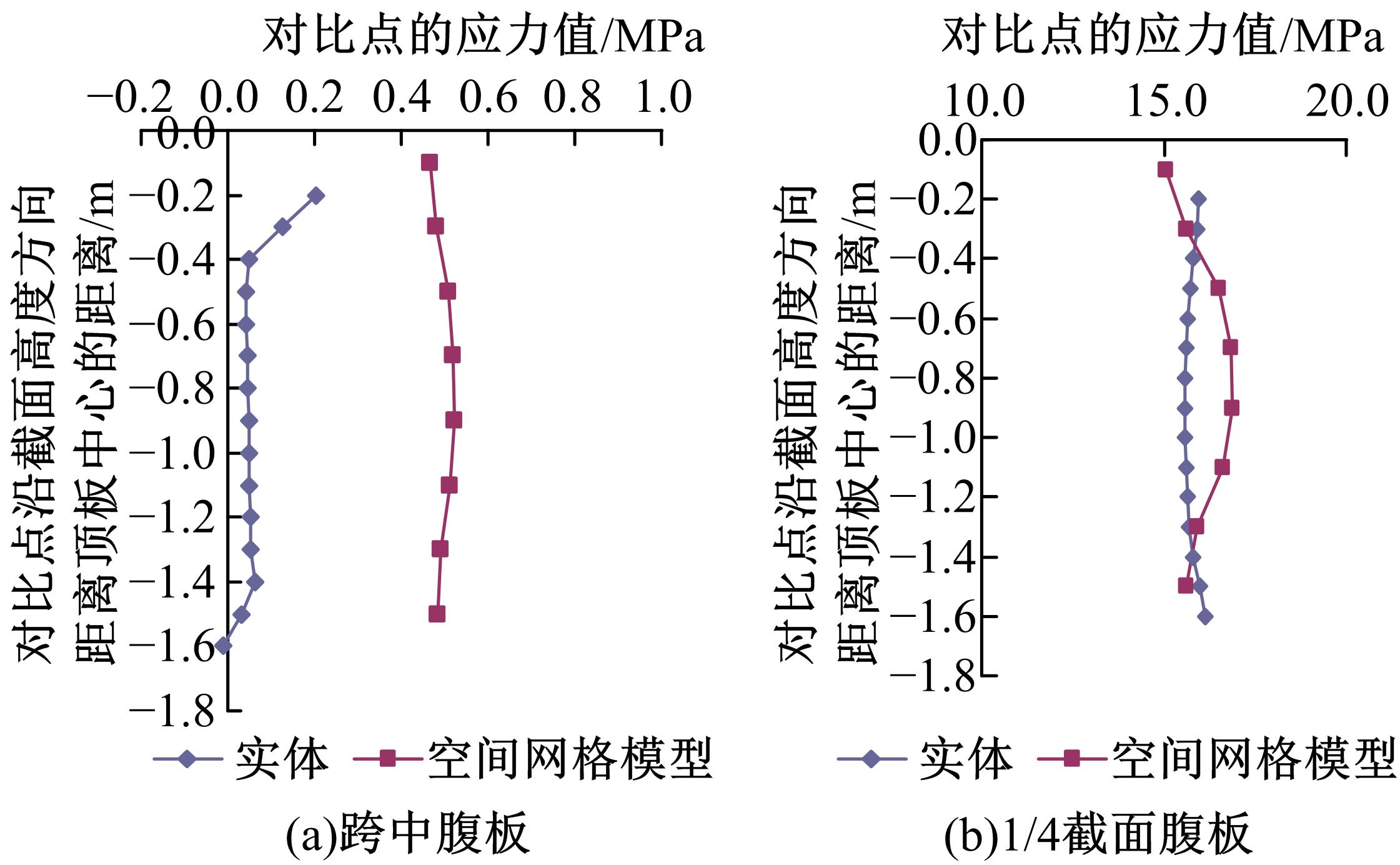
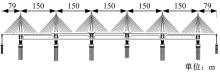
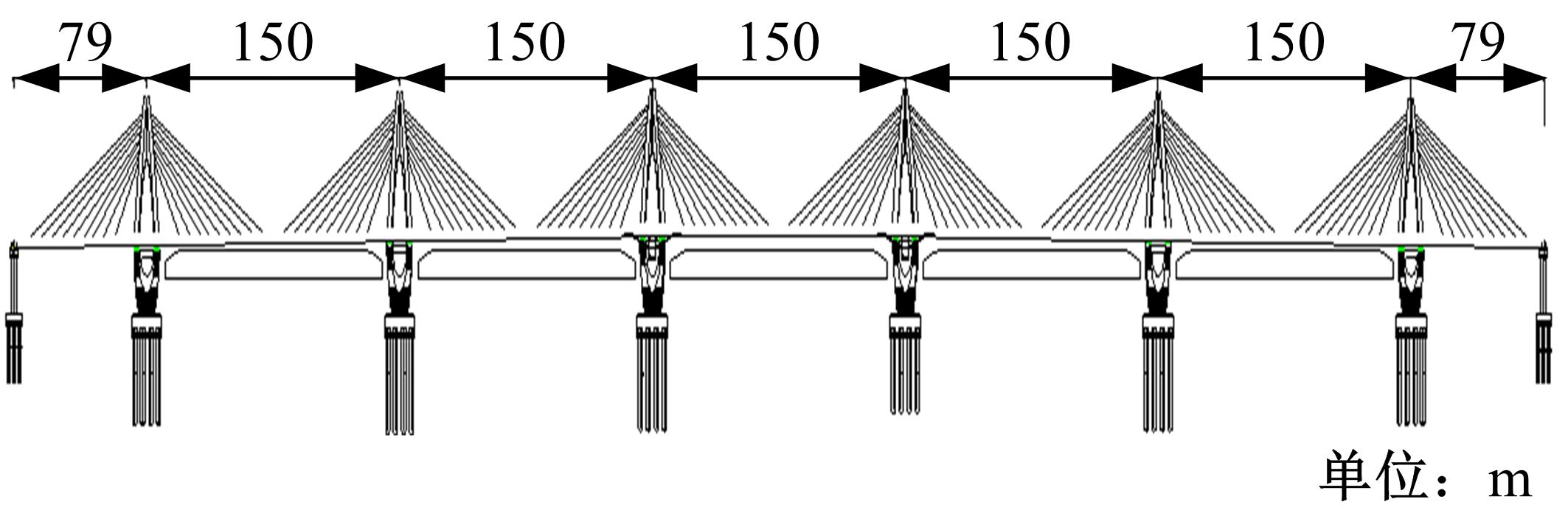
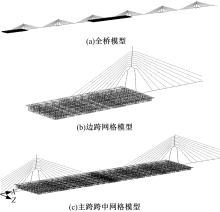
Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition) ›› 2018, Vol. 48 ›› Issue (6): 1735-1746.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb20170719
Previous Articles Next Articles
Shear distribution of multi-cell corrugated steel web composite beams based on space grid analysis
NI Ying-sheng1( ),SUN Qi-xin2(
),SUN Qi-xin2( ),MA Ye1,XU Dong2,LIU Chao2
),MA Ye1,XU Dong2,LIU Chao2
- 1. Research Institute of Highway,Ministry of Transport,Beijing 100088, China
2. School of Civil Engineering,Tongji University,Shanghai 200092,China
CLC Number:
- TU318
| [1] |
肖湘, 黄恩厚, 尼颖升 . 预应力混凝土梁板体系有效翼缘的理论分析及试验[J]. 吉林大学学报:工学版, 2015,45(6):1784-1790.
doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb201506008 |
|
Xiao Xiang, Huang En-hou, Ni Ying-sheng . Theoretic analysis and experimental study of effective flange width on beam-plates system of prestressed concrete[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2015,45(6):1784-1790.
doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb201506008 |
|
| [2] |
Jung K H, Kim K S, Sim C W , et al. Verification of incremental launching construction safety for the llsun bridge:the world's longest and widest prestressed concrete box girder with corrugated steel web section[J]. Journal of Bridge Engineering, 2011,16(3):453-460.
doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)BE.1943-5592.0000165 |
| [3] |
Li Guo-qiang, Wang Wei-yong . A simplified approach for fire-resistance design of steel-concretecomposite beams[J]. Steel and Composite Structures, 2013,14(3):295-312.
doi: 10.12989/scs.2013.14.3.295 |
| [4] | 贺君 . 波折钢腹板组合桥梁力学性能与设计方法研究[D]. 上海:同济大学土木工程学院, 2011. |
| He Jun . Mechanical performance and design method of composite bridge with corrugated steel webs[D]. Shanghai:School of Civil Engineering, Tongji University, 2011. | |
| [5] |
Nguyen N D, Kim S N, Han S R , et al. Elastic lateral-torsional buckling strength of I-girder with trapezoidal web corrugations using a new warping constant under uniform moment[J]. Engineering Structures, 2010,32(8):2157-2165.
doi: 10.1016/j.engstruct.2010.03.018 |
| [6] |
Liu Chao, Xu Dong . Space frame lattice model for stress analysis of bridge[J]. The Baltic Journal of Road and Bridge Engineering, 2010,5(2):98-103.
doi: 10.3846/bjrbe.2010.14 |
| [7] |
Liu Chao, Xu Dong . Influence of cracking on deflections of concrete box girder bridges[J]. Baltic Journal of Road and Bridge Engineering, 2012,7(2):104-111.
doi: 10.3846/bjrbe.2012.15 |
| [8] | 徐栋, 赵瑜, 刘超 . 混凝土桥梁的实用精细化分析与设计[M]. 北京: 人民交通出版社, 2013. |
| [9] | Xu Dong, Zhao Yu. Application of spatial grid model in structural analysis of concrete box girder bridges [C]//18th Congress of International Association for Bridge and Structural Engineering, Seoul, 2012: 2009-2016. |
| [10] |
ValsaIpe T, Sharada B H, Manjula V K , et al. Flexural behavior of cold-formed steel concrete composite beams[J]. Steel and Composite Structures, 2013,14(2):105-120.
doi: 10.12989/scs.2013.14.2.105 |
| [11] |
Mo Y L, Fan Y L . Torsional design of hybrid concrete box girders[J]. Journal of Bridge Engineering, 2006,11(3):329-339.
doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)1084-0702(2006)11:3(329) |
| [12] |
Machimdamrong C, Watanabe E, Utsunomiya T . Analysis of corrugated steel web girders by an efficient beam bending theory[J]. Structural Engineering/Earthquake Engineering, 2004,21(2):131-142.
doi: 10.2208/jsceseee.21.131s |
| [13] |
Huang L, Hikosaka H, Komine K . Simulation of accordion effect in corrugated steel web with concrete flanges[J]. Computers and Structures, 2004,82(23-26):2061-2069.
doi: 10.1016/j.compstruc.2003.07.010 |
| [1] | MA Ye, NI Ying-sheng, XU Dong, DIAO Bo. External prestressed strengthening based on analysis of spatial grid model [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2018, 48(1): 137-147. |
| [2] | NI Ying-sheng, SUN Qi-xin, MA Ye, XU Dong. Calculation of capacity reinforcement about composite box girder with corrugated steel webs based on tensile stress region theory [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2018, 48(1): 148-158. |
| [3] | NI Ying-sheng, MA Ye, XU Dong, LI Jin-kai. Space mesh analysis method for shear lag effect of cable-stayed bridge with corrugated steel webs [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2017, 47(5): 1453-1464. |
| [4] | YAN Ya-bin, WANG Xiao-yuan, WAN Qiang. Low-cycle fatigue fracture behavior of nanoscale interface [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2017, 47(4): 1201-1206. |
| [5] | CHEN Jiang-yi, LIU Bao-yuan. Influence of fiber fracture damage on dispersion characteristic of guided wave in composite plate [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2017, 47(1): 180-184. |
| [6] | MENG Guang-wei, FENG Xin-yu, ZHOU Li-ming, Li Feng. Structural reliability analysis based on dimension reduction algorithm [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2017, 47(1): 174-179. |
| [7] | YANG Hui-yan, HE Xiao-cong, ZHOU Sen. Simulation and calculation methods for clinched joint strength [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2015, 45(3): 864-871. |
| [8] | ZHANG Qing,WANG Lei. Internal force analysis of multiple rows of piles based on differential equation set [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2014, 44(5): 1327-1333. |
| [9] | ZHANG Jin-bo, YUAN Chao-wei, WANG Qiu-cai, HAN Xi. Interference alignment scheme for multicell multiuser system through THP [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2014, 44(2): 531-537. |
| [10] | ZHAO Shi-jia, XU Tao, CHEN Wei, TAN Li-hui. Efficient approach for modal sensitivity analysis for near defective systems [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2013, 43(增刊1): 497-499. |
| [11] | XU Tao, ZHAO Shi-jia, ZHANG Wei, TAN Li-hui, LV Gang, LI Heng. Perturbed origin shift combined approximation method of N repeated defective systems [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2012, 42(增刊1): 147-150. |
| [12] | YAN Guang, FAN Zhou, LI Zhong-hai, CHENG Xiao-quan, LIU Ke-ge, ZUO Chun-cheng. Analysis and design of composite cylindrical shell with cover [J]. , 2012, (06): 1437-1441. |
| [13] | JIANG Hao, GUO Xue-dong. Concrete bridge modal parameter identification under seismic excitations [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2011, 41(增刊2): 185-188. |
| [14] | TIAN Wei, GUO Xue-dong, YIN Xin-sheng. Theoretical and experimental research on oblique cross-section cracking resistance of wall-beam by concrete hollow block [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2011, 41(增刊2): 189-193. |
| [15] | LI Chun-liang, WANG Guo-qiang, LIU Fu-shou, ZHAO Kai-jun. Mechanical behavior analysis of shield segment structure [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2011, 41(6): 1669-1674. |
|