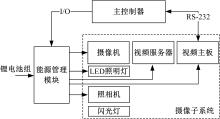
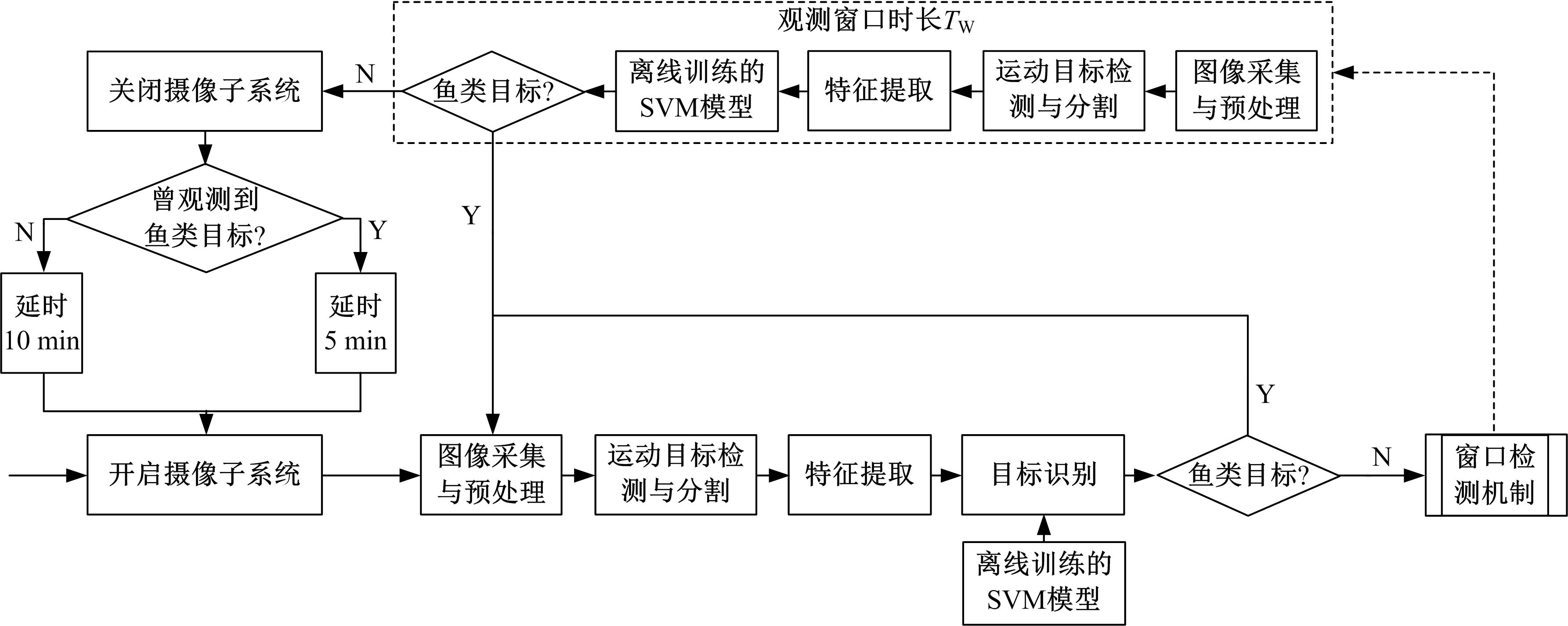
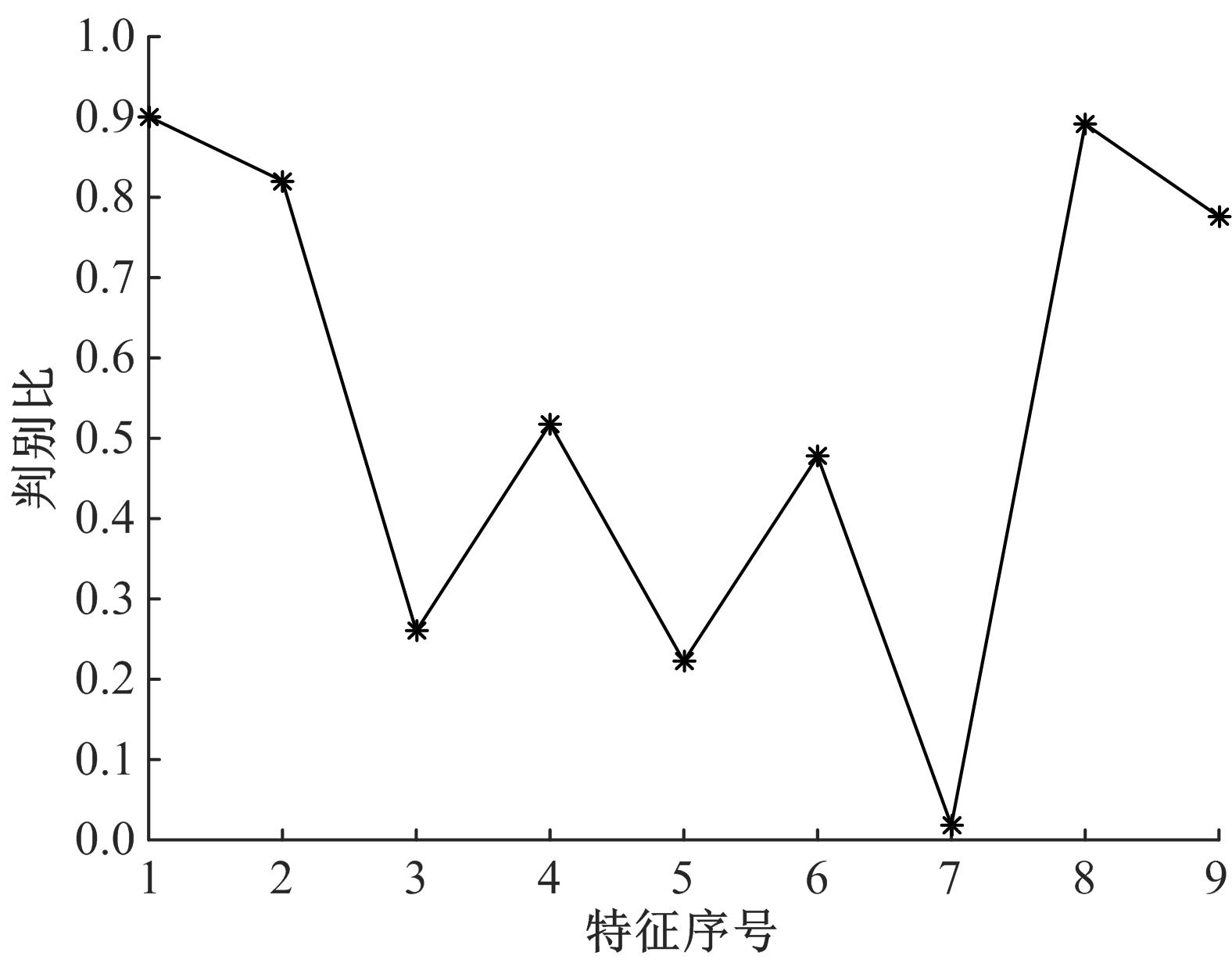
Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition) ›› 2019, Vol. 49 ›› Issue (3): 953-962.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb20180160
Previous Articles Next Articles
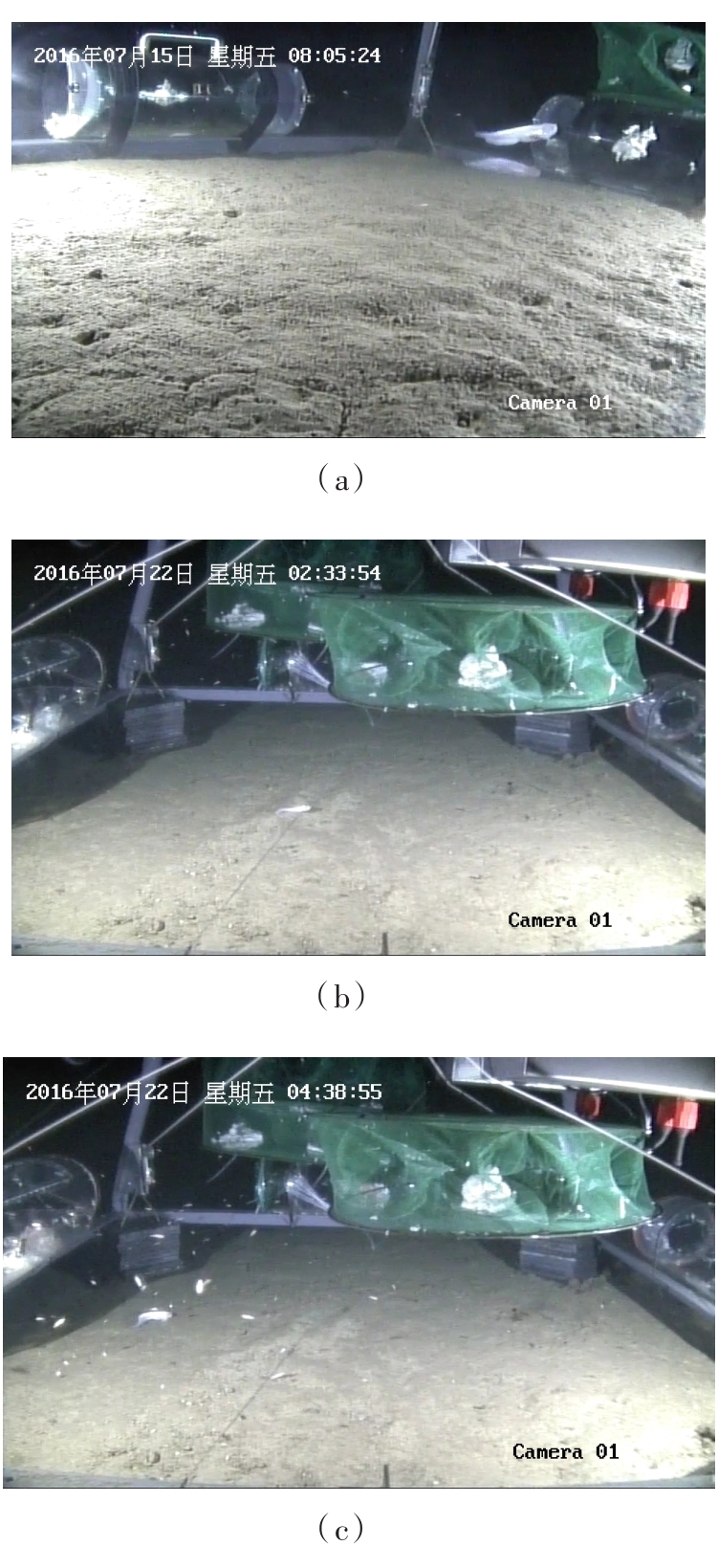
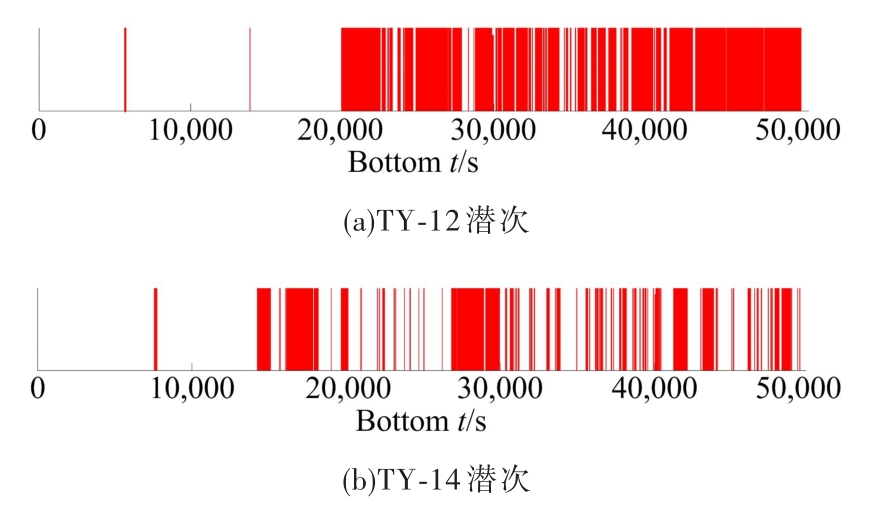
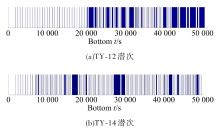
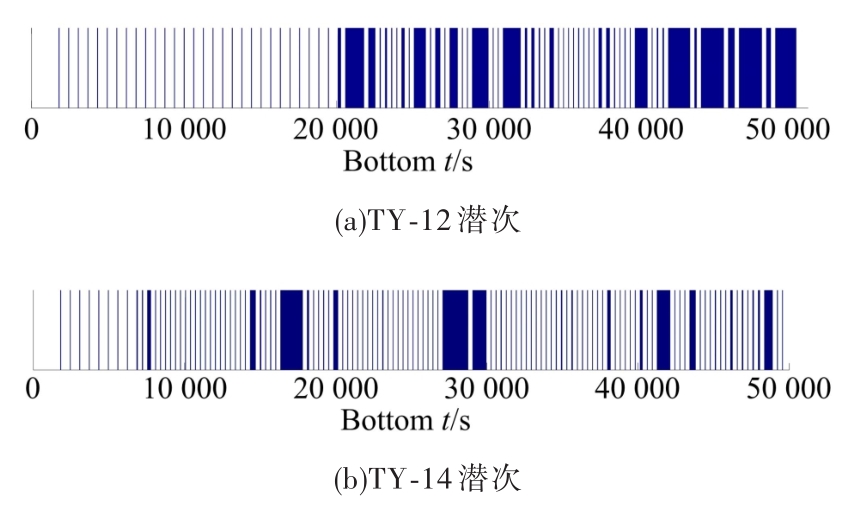
In⁃situ autonomous observation method based onhadal fish recognition
Jun CHEN1,2( ),Qi⁃feng ZHANG1(
),Qi⁃feng ZHANG1( ),Ai⁃qun ZHANG1,3,Du⁃si CAI3
),Ai⁃qun ZHANG1,3,Du⁃si CAI3
- 1. State Key Laboratory of Robotics, Shenyang Institute of Automation, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Shenyang 110016, China
2. University of Chinese Academy of Science, Beijing 100049, China
3. Institute of Deep?sea Science and Engineering, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Sanya 572000, China
CLC Number:
- TP274
| 1 | JamiesonA J, FujiiT, MayorD J, et al. Hadal trenches: the ecology of the deepest places on earth[J]. Trends in Ecology & Evolution, 2010,25(3):190⁃197. |
| 2 | LinleyT D, GerringerM E, YanceyP H, et al. Fishes of the hadal zone including new species, in situ, observations and depth records of Liparidae[J]. Deep Sea Research Part I Oceanographic Research Papers, 2016, 114:99⁃110. |
| 3 | LinleyT D, StewartA L , McmillanP J, et al. Bait attending fishes of the abyssal zone and hadal boundary: Community structure, functional groups and species distribution in the Kermadec, New Hebrides and Mariana trenches[J]. Deep Sea Research Part I: Oceanographic Research Papers, 2017, 121:38⁃53. |
| 4 | JamiesonA. The hadal zone: life in the deepest oceans[M]. Cambridge UK: Cambridge University Press, 2015. |
| 5 | BaileyD M, KingN J, PriedeI G. Cameras and carcasses: historical and current methods for using artificial food falls to study deep⁃water animals[J]. Marine Ecology Progress Series, 2007, 350: 179⁃191. |
| 6 | WhitmarshS K, FairweatherP G, HuveneersC. What is big BRUVver up to? Methods and uses of baited underwater video[J]. Reviews in Fish Biology & Fisheries, 2016: 1⁃21. |
| 7 | JamiesonA J, FujiiT, SolanM, et al. HADEEP: free⁃falling landers to the deepest places on earth[J]. Marine Technology Society Journal, 2009, 43(5):151⁃160. |
| 8 | WHOI. HADal Ecosystem Studies[EB/OL]. 2018-01-10.https:⫽web.whoi.edu/hades/. |
| 9 | JamiesonA J, KilgallenN M, RowdenA A, et al. Bait⁃attending fauna of the Kermadec Trench, SW Pacific Ocean: evidence for an ecotone across the abyssal–hadal transition zone[J]. Deep Sea Research Part I: Oceanographic Research Papers, 2011, 58(1):49⁃62. |
| 10 | JamiesonA J, PriedeI G, CraigJ. Distinguishing between the abyssal macrourids Coryphaenoides yaquinae and C. armatus from in situ photography[J]. Deep Sea Research Part I: Oceanographic Research Paper, 2012, 64:78⁃85. |
| 11 | StaufferC, GrimsonW E L. Adaptive background mixture models for real⁃time tracking[C]⫽IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Piscataway, IEEE, 1999. |
| 12 | PiccardiM. Background subtraction techniques: a review[C]⫽IEEE International Conference on Systems, Man and Cybernetics, Piscataway, IEEE, 2005. |
| 13 | 刘鑫, 刘辉, 强振平, 等. 混合高斯模型和帧间差分相融合的自适应背景模型[J]. 中国图象图形学报, 2008, 13(4):729⁃734. |
| LiuXin, LiuHui, QiangZhen⁃ping, et al. Adaptive Background Modeling Based on Mixture Gaussian Model and Frame Subtraction[J]. Journal of Image and Graphics, 2008, 13(4):729⁃734. | |
| 14 | HsiaoY H, ChenC C, LinS I, et al. Real⁃world underwater fish recognition and identification, using sparse representation[J]. Ecological Informatics, 2014, 23:13⁃21. |
| 15 | SpampinatoC, GiordanoD, SalvoR D, et al. Automatic fish classification for underwater species behavior understanding[C]⫽ACM International Workshop on Analysis and Retrieval of Tracked Events and Motion in Imagery Streams. ACM Paper, 2010:45⁃50. |
| 16 | SunX, ShiJ, DongJ, et al. Fish recognition from low⁃resolution underwater images[C]⫽International Congress on Image and Signal Processing, Biomedical Engineering and Informatics, Datong, China, 2016:15⁃17. |
| 17 | ChenJ, ZhangQ, ZhangA, et al. 7000M lander design for hadal research[C]⫽OCEANS, St. John's, NL, Canada, 2014:1⁃4. |
| 18 | ChenJ, ZhangQ, ZhangA, et al. Sea trial and free⁃fall hydrodynamic research of a 7000⁃meter lander[C]⫽OCEANS, Piscataway, Washington, DC,USA,2015:1⁃5. |
| 19 | 陈俊, 张奇峰, 李俊,等. 深渊着陆器技术研究及马里亚纳海沟科考应用[J]. 海洋技术学报, 2017, 36(1):63⁃69. |
| ChenJun, ZhangQi⁃feng, LiJun, et al. Research on the application of the hadal lander technology in the mariana trench[J]. Journal of Ocean Technology, 2017, 36(1):63⁃69. | |
| 20 | 曾祥进, 黄心汉, 王敏. 不变矩的改进支持向量机在显微目标识别中的应用研究[J]. 机器人, 2009,31(2): 118⁃123. |
| ZengXiang⁃jin, HuangXin⁃han, WangMin. Application of invariant moment's improved support vector machine to micro⁃target identification[J]. Robot, 2009,31(2): 118⁃123. | |
| 21 | HuM K. Visual pattern recognition by moment invariants[J]. IRE Transactions on Information Theory, 1962,8(2): 179⁃187. |
| 22 | 李强, 薛开, 徐贺, 等. 基于振动采用支持向量机方法的移动机器人地形分类[J]. 机器人, 2012, 34(6): 660⁃667. |
| LiQiang, XueKai, XuHe, et al. Vibration⁃based terrain classification for mobile robots using support vector machine[J]. Robot, 2012, 34(6): 660⁃667. | |
| 23 | 陈建华, 奚如如, 王兴松, 等. 外骨骼机器人的非结构地面行走步态分类算法[J]. 机器人, 2017, 39(4): 505⁃513. |
| ChenJian⁃hua, XiRu⁃ru, WangXing⁃song, et al. Walking gait classification algorithm for exoskeleton robot on unstructured ground[J]. Robot, 2017, 39(4): 505⁃513. | |
| 24 | Azimi⁃SadjadiM R, YaoD, JamshidiA A, et al. Underwater target classification in changing environments using an adaptive feature mapping[J]. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks, 2002, 13(5):1099⁃1111. |
| [1] | KUI Hai-lin, BAO Cui-zhu, LI Hong-xue, LI Ming-da. Idling time prediction method based on least square support vector machine [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2018, 48(5): 1360-1365. |
| [2] | GENG Qing-tian, YU Fan-hua, WANG Yu-ting, GAO Qi-kun. New algorithm for vehicle type detection based on feature fusion [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2018, 48(3): 929-935. |
| [3] | CAI Zhen-nao, LYU Xin-en, CHEN Hui-ling. Prediction model of somatization disorder based on an oppositional bacterial foraging optimization based support vector machine [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2018, 48(3): 936-942. |
| [4] | YUAN Zhe-ming, ZHANG Hong-yang, CHEN Yuan. HIV-1 protease cleavage site prediction based on feature selection and support vector machine [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2017, 47(2): 639-646. |
| [5] | LIANG Shi-li, WEI Ying, PAN Di, ZHANG Ling, XU Ting-fa, WANG Shuang-wei. Recognition to specific two words Chinese vocabulary based on projection matrix of spectrogram [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2017, 47(1): 294-300. |
| [6] | ZHAO Yun-peng, YU Tian-lai, JIAO Yu-bo, GONG Ya-feng, SONG Gang. Damage identification method and factor evaluation for irregular-shaped bridge [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2016, 46(6): 1858-1866. |
| [7] | SHANG Qiang, YANG Zhao-sheng, ZHANG Wei, Bing Qi-chun, ZHOU Xi-yang. Short-term traffic flow prediction based on singular spectrum analysis and CKF-LSSVM [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2016, 46(6): 1792-1798. |
| [8] | ZHOU Bing-hai, XU Jia-hui. SVM-based real-time scheduling approach of multi-load carries [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2016, 46(6): 2027-2033. |
| [9] | LU Ying, WANG Hui-qin, QIN Li-ke. Accurate fire location method in high and large-span space buildings [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2016, 46(6): 2067-2073. |
| [10] | MA Zhi-xing, ZHAO Qi, ZHANG Hao. Fourier analysis model for housekeeping gene [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2016, 46(5): 1639-1643. |
| [11] | WANG Pin, HE Xuan, LYU Yang, LI Yong-ming, QIU Ming-guo, LIU Shu-jun. Automatic segmentation of articular cartilages using multi-feature SVM and elastic region growing [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2016, 46(5): 1688-1696. |
| [12] | ZHANG Jing, LIU Xiang-dong. Prediction of concrete strength based on least square support vector machine optimized by chaotic particle swarm optimization [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2016, 46(4): 1097-1102. |
| [13] | SHEN Xuan-jing, ZHAI Yu-jie, LU Yu-tong, WANG Yu, CHEN Hai-peng. Speaker recognition algorithm based on channel compensation [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2016, 46(3): 870-875. |
| [14] | DAI Kun, YU Hong-yi, QIU Wen-bo,LI Qing. Unsupervised feature selection algorithm based on support vector machine for network data [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2015, 45(2): 576-582. |
| [15] | XU Miao,ZHAO Ding-xuan,NI Tao,XU Chun-bo. Load prediction of hybrid excavator based on least square support vector machine [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2015, 45(1): 133-138. |
|