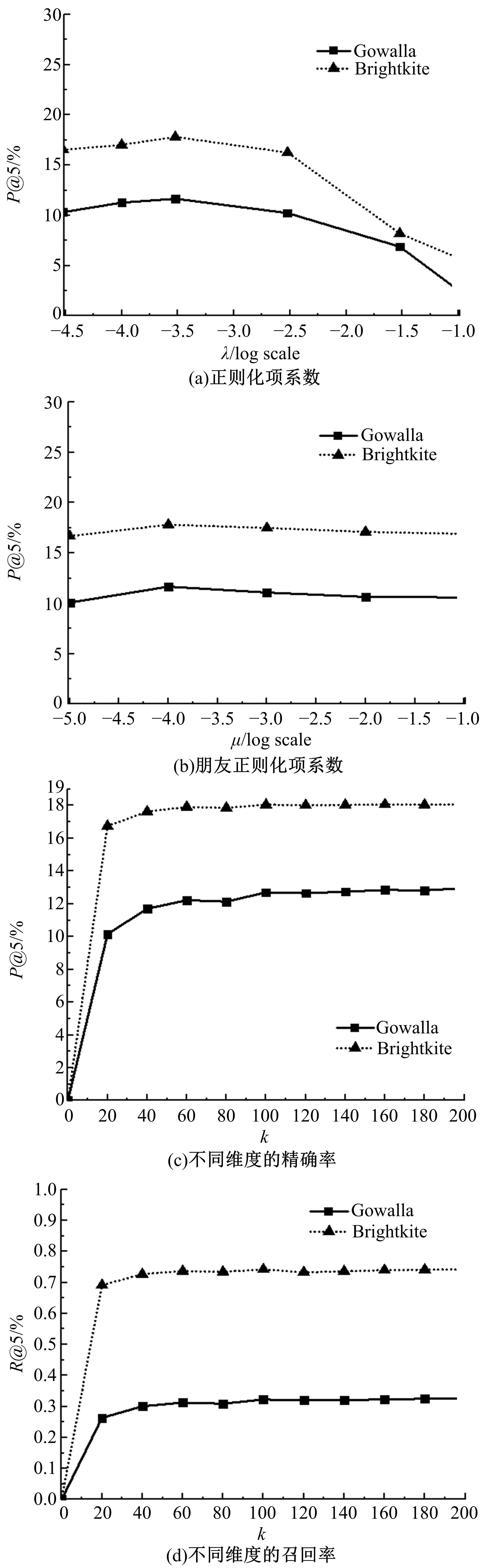
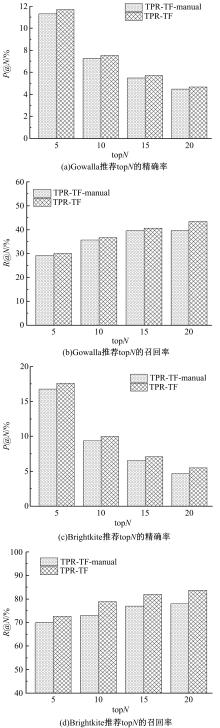
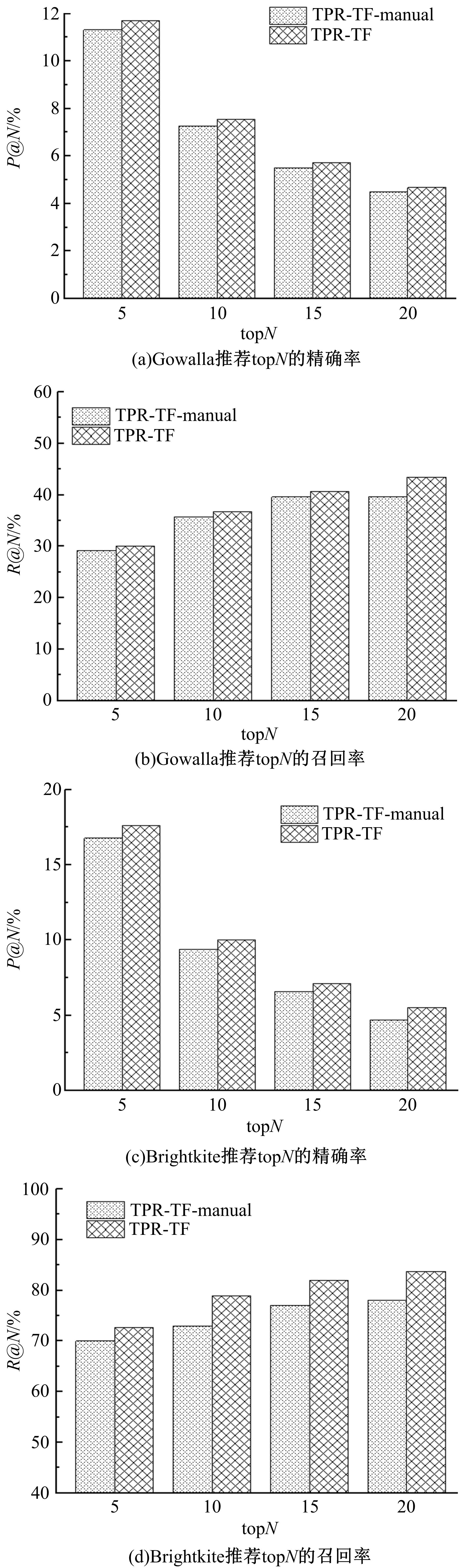
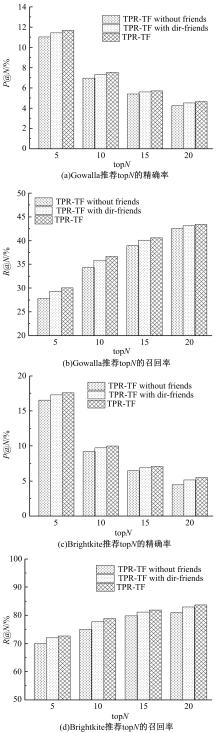
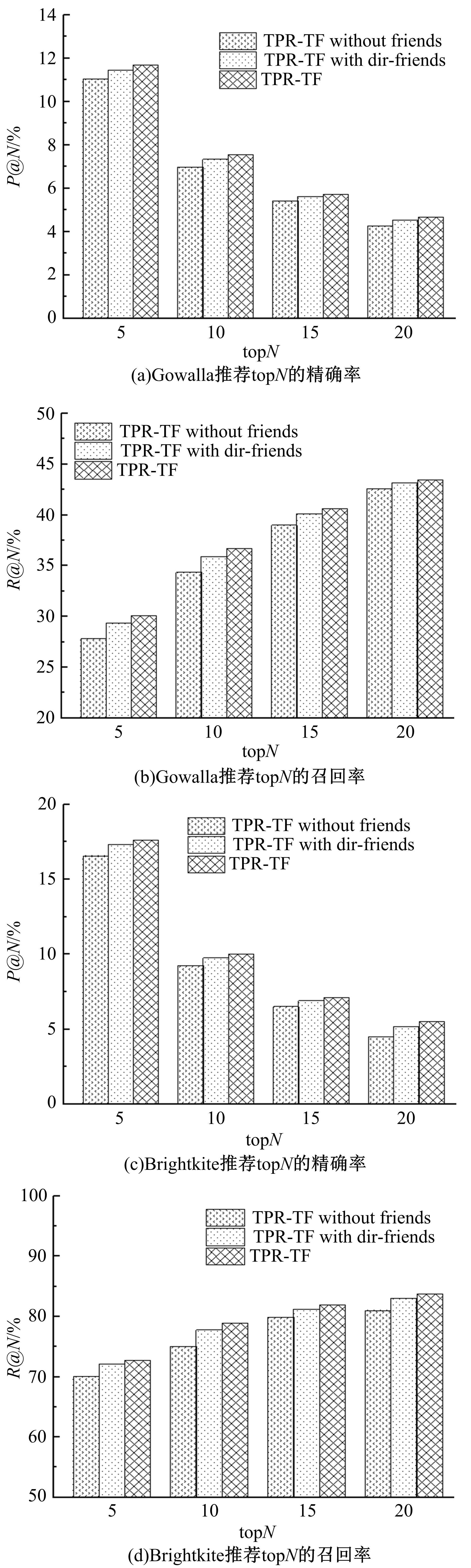
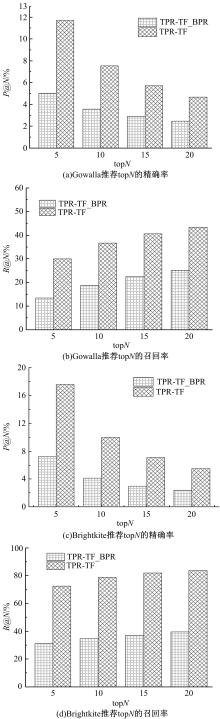
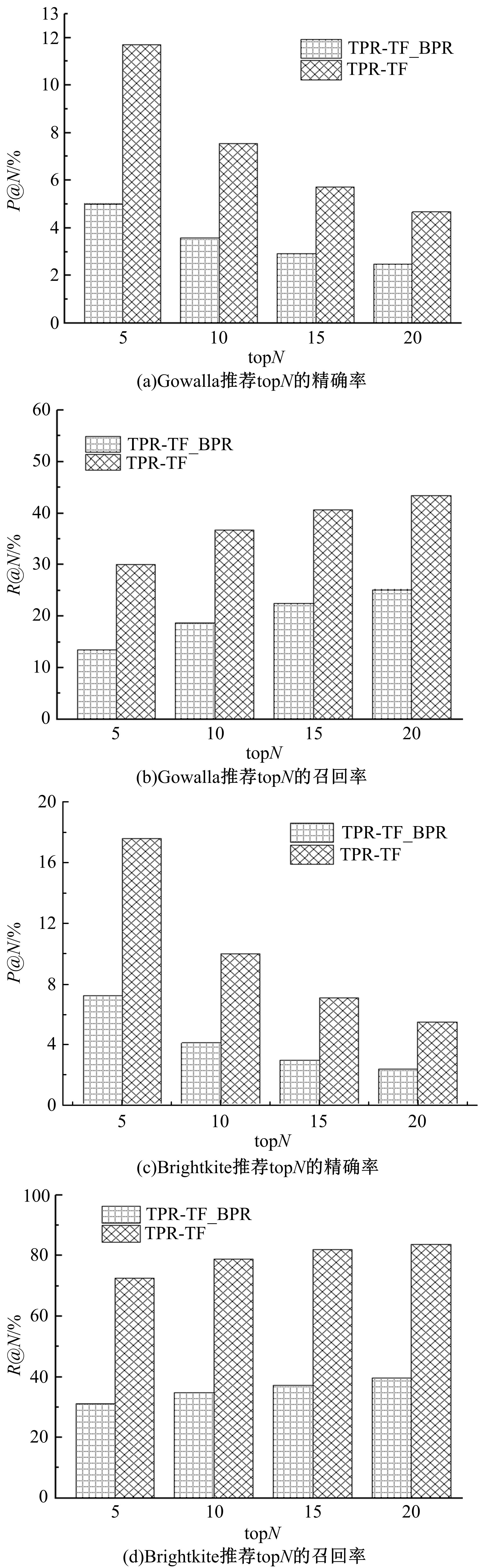
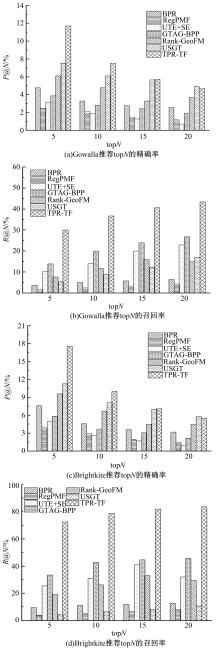
Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition) ›› 2019, Vol. 49 ›› Issue (3): 920-933.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb20180193
Previous Articles Next Articles
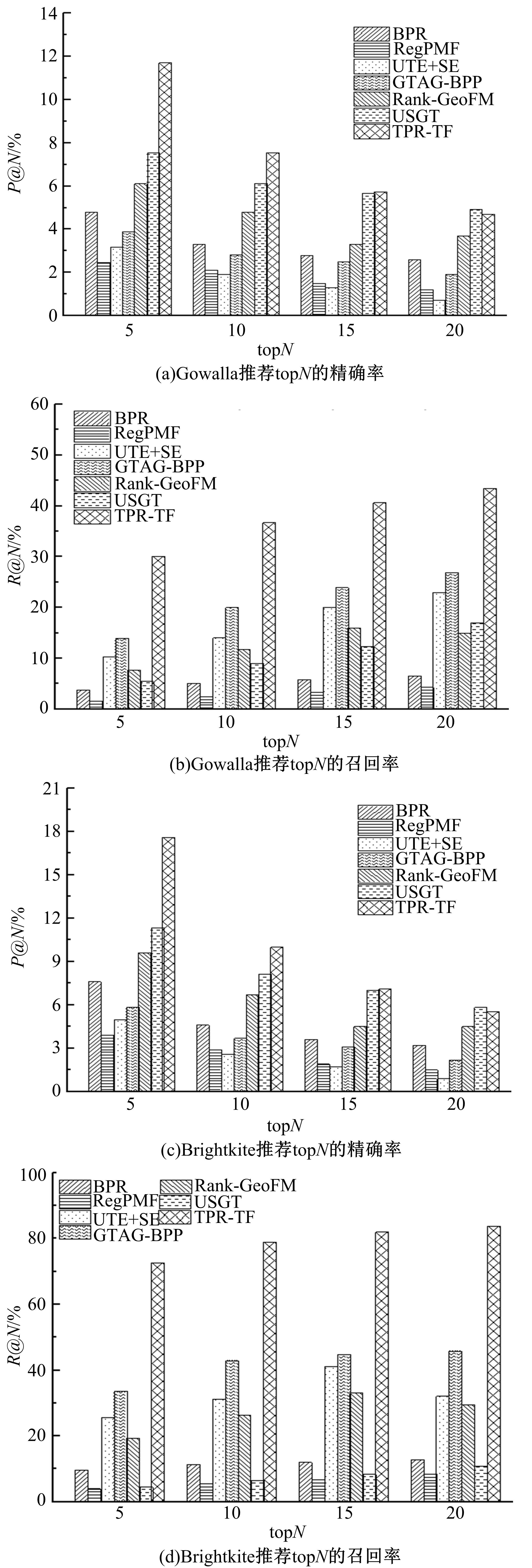
TPR⁃TF: time⁃aware point of interest recommendation model based on tensor factorization
Nan WANG1,2( ),Jin⁃bao LI1,2(
),Jin⁃bao LI1,2( ),Yong LIU1,2,Yu⁃jie ZHANG1,2,Ying⁃li ZHONG1,2
),Yong LIU1,2,Yu⁃jie ZHANG1,2,Ying⁃li ZHONG1,2
- 1. School of Computer Science and Technology, Heilongjiang University, Harbin 150080, China
2. Key Laboratory of Database and Parallel Computing, Heilongjiang University, Harbin 150080, China
CLC Number:
- TP391
| 1 | Ye M , Yin P F , Lee W , et al . Exploiting geographical influence for collaborative point⁃of⁃interest recommendation[C]∥Proceedings of the 34th International ACM SIGIR Conference on Research and Development in Information Retrieval, Beijing, China, 2011: 325⁃334. |
| 2 | Yuan Q , Cong G , Ma Z Y , et al . Time⁃aware point⁃of⁃interest recommendation[C]∥Proceedings of the 36th International ACM SIGIR Conference on Research and Development in Information Retrieval, Dublin, Ireland, 2013: 363⁃372. |
| 3 | Bao J , Zheng Y , Mokbel M , et al . Location⁃based and preference⁃aware recommendation using sparse geo⁃social networking data[C]∥Proceedings of the 20th International Conference on Advances in Geographic Information Systems, Redondo Beach, USA, 2012: 199⁃208. |
| 4 | Lian D , Zhao C , Xie X , et al . GeoMF: joint geographical modeling and matrix factorization for point⁃of⁃interest recommendation[C]∥Proceedings of the 20th ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining, New York, USA, 2014: 831⁃840. |
| 5 | Liu S D , Meng X W . Recommender systems in location⁃based social networks[J]. Chinese Journal of Computers, 2015, 38(2): 322⁃336. |
| 6 | Goodfellow I , Bengio Y , Courville A , et al . Deep Learning[M]. Cambridge: MIT press, 2016. |
| 7 | Yao Z , Fu Y , Liu B , et al . POI recommendation: a temporal matching between POI popularity and user regularity[C]∥Proceedings of International Conference on Data Mining, Barcelona, Spain, 2017: 549⁃558. |
| 8 | Cho E , Myers S A , Leskovec J . Friendship and mobility: user movement in location⁃based social networks[C]∥Proceedings of the 17th ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining, San Diego, USA, 2011: 1082⁃1090. |
| 9 | Gao H , Tang J , Hu X , et al . Exploring temporal effects for location recommendation on location⁃based social networks[C]∥Proceedings of the 7th ACM Conference on Recommender Systems, Hong Kong, China, 2013: 93⁃100. |
| 10 | Yuan Q , Cong G , Sun A . Graph⁃based point⁃of⁃interest recommendation with geographical and temporal influences[C]∥Proceedings of the 23rd ACM International Conference on Conference on Information and Knowledge Management, Shanghai, China, 2014: 659⁃668. |
| 11 | Hosseini S , Li L T . Point⁃of⁃interest recommendation using temporal orientations of users and locations[C]∥Proceedings of the 21st International Conference on Database Systems for Advanced Applications, Dallas, USA, 2016: 330⁃347. |
| 12 | Ma H , Zhou D , Liu C , et al . Recommender systems with social regularization[C]∥Proceedings of the Forth International Conference on Web Search and Web Data Mining, Kowloon, Hong Kong, 2011: 287⁃296. |
| 13 | Zhang J , Chow C . GeoSoCa: exploiting geographical, social and categorical correlations for point⁃of⁃interest recommendations[C]∥Proceedings of the 38th International ACM SIGIR Conference on Research and Development in Information Retrieval, Santiago, Chile, 2015: 443⁃452. |
| 14 | Jamali M , Ester M . A matrix factorization technique with trust propagation for recommendation in social networks[C]∥Proceedings of the Fourth ACM Conference on Recommender Systems, Barcelona, Spain, 2010:135⁃142. |
| 15 | Ma H , Zhou T C , Lyu M R , et al . Improving recommender systems by incorporating social contextual information[J]. ACM Transactions on Information Systems, 2011, 29(2):1⁃23. |
| 16 | Cheng C , Yang H , King I , et al . Fused matrix factorization with geographical and social influence in location⁃based social networks[C]∥Proceedings of the National Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Toronto, Canada, 2012: 17⁃23. |
| 17 | Rendle S , Freudenthaler C , Gantner Z , et al . BPR: Bayesian personalized ranking from implicit feedback[C]∥Proceedings of the 25th Conference on Uncertainty in Artificial Intelligence, Montreal, Canada, 2009: 452⁃461. |
| 18 | Zhao S L , King I , Lyu M R . A survey of point⁃of⁃interest recommendation in location⁃based social networks[J/OL].[2018⁃02⁃26].https:∥⁃of⁃interest_Recommendation_in_Location⁃based_Social_Networks/links/5787365a08ae36ad40a6a4e8 /A⁃Survey⁃of⁃Point⁃of⁃interest⁃Recommendation⁃in⁃Location⁃based⁃Social⁃Networks.pdf?origin=publication_detail. |
| 19 | Ye M , Yin P , Lee W C . Location recommendation for location⁃based social networks[C]∥Proceedings of the 18th SIGSPATIAL International Conference on Advances in Geographic Information Systems, San Jose, USA, 2010: 458⁃461. |
| 20 | Zhang W , Wang J . Location and time aware social collaborative retrieval for new successive point⁃of⁃interest recommendation[C]∥Proceedings of the 24th ACM International Conference on Information and Knowledge Management, Melbourne, Australia, 2015(19⁃23): 1221⁃1230. |
| 21 | Ye M , Liu X , Lee W C . Exploring social influence for recommendation: a generative model approach[C]∥Proceedings of the 35th International ACM SIGIR Conference on Research and Development in Information Retrieval, Portland, USA, 2012: 671⁃680. |
| 22 | Li H , Ge Y , Zhu H , et al . Point⁃of⁃interest recommendations: learning potential check⁃ins from friends[C]∥Proceedings of the 22nd ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining, San Francisco, USA, 2016(13⁃17): 975⁃984. |
| 23 | Zhang J , Chow C , Li Y , et al . LORE: exploiting sequential influence for location recommendations[C]∥Proceedings of the 22nd SIGSPATIAL International Conference on Advances in Geographic Information Systems, Dallas, Fort Worth, USA, 2014(4⁃7): 103⁃112. |
| 24 | Yao L , Sheng Q Z , Qin Y , et al . Context⁃aware point⁃of⁃interest recommendation using tensor factorization with social regularization[C]∥Proceedings of the 38th International ACM SIGIR conference on Research and Development in Information Retrieval, Santiago, Chile, 2015: 1007⁃1010. |
| 25 | Li X , Cong G , Li X L , et al . Rank⁃GeoFM: a ranking based geographical factorization method for point of interest recommendation[C]∥Proceedings of the 38th International ACM SIGIR Conference on Research and Development in Information Retrieval, Santiago, Chile, 2015: 433⁃442. |
| [1] | LIU Fu,ZONG Yu-xuan,KANG Bing,ZHANG Yi-meng,LIN Cai-xia,ZHAO Hong-wei. Dorsal hand vein recognition system based on optimized texture features [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2018, 48(6): 1844-1850. |
| [2] | WANG Li-min,LIU Yang,SUN Ming-hui,LI Mei-hui. Ensemble of unrestricted K-dependence Bayesian classifiers based on Markov blanket [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2018, 48(6): 1851-1858. |
| [3] | JIN Shun-fu,WANG Bao-shuai,HAO Shan-shan,JIA Xiao-guang,HUO Zhan-qiang. Synchronous sleeping based energy saving strategy of reservation virtual machines in cloud data centers and its performance research [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2018, 48(6): 1859-1866. |
| [4] | ZHAO Dong,SUN Ming-yu,ZHU Jin-long,YU Fan-hua,LIU Guang-jie,CHEN Hui-ling. Improved moth-flame optimization method based on combination of particle swarm optimization and simplex method [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2018, 48(6): 1867-1872. |
| [5] | LIU En-ze,WU Wen-fu. Agricultural surface multiple feature decision fusion disease judgment algorithm based on machine vision [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2018, 48(6): 1873-1878. |
| [6] | OUYANG Dan-tong, FAN Qi. Clause-level context-aware open information extraction [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2018, 48(5): 1563-1570. |
| [7] | LIU Fu, LAN Xu-teng, HOU Tao, KANG Bing, LIU Yun, LIN Cai-xia. Metagenomic clustering method based on k-mer frequency optimization [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2018, 48(5): 1593-1599. |
| [8] | GUI Chun, HUANG Wang-xing. Network clustering method based on improved label propagation algorithm [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2018, 48(5): 1600-1605. |
| [9] | LIU Yuan-ning, LIU Shuai, ZHU Xiao-dong, CHEN Yi-hao, ZHENG Shao-ge, SHEN Chun-zhuang. LOG operator and adaptive optimization Gabor filtering for iris recognition [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2018, 48(5): 1606-1613. |
| [10] | CHE Xiang-jiu, WANG Li, GUO Xiao-xin. Improved boundary detection based on multi-scale cues fusion [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2018, 48(5): 1621-1628. |
| [11] | ZHAO Hong-wei, LIU Yu-qi, DONG Li-yan, WANG Yu, LIU Pei. Dynamic route optimization algorithm based on hybrid in ITS [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2018, 48(4): 1214-1223. |
| [12] | HUANG Hui, FENG Xi-an, WEI Yan, XU Chi, CHEN Hui-ling. An intelligent system based on enhanced kernel extreme learning machine for choosing the second major [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2018, 48(4): 1224-1230. |
| [13] | FU Wen-bo, ZHANG Jie, CHEN Yong-le. Network topology discovery algorithm against routing spoofing attack in Internet of things [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2018, 48(4): 1231-1236. |
| [14] | CAO Jie, SU Zhe, LI Xiao-xu. Image annotation method based on Corr-LDA model [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2018, 48(4): 1237-1243. |
| [15] | HOU Yong-hong, WANG Li-wei, XING Jia-ming. HTTP-based dynamic adaptive streaming video transmission algorithm [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2018, 48(4): 1244-1253. |
|