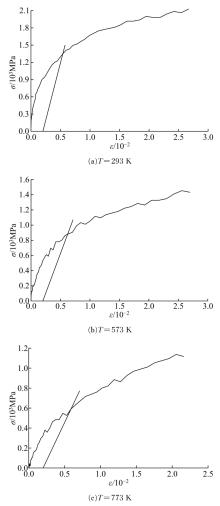
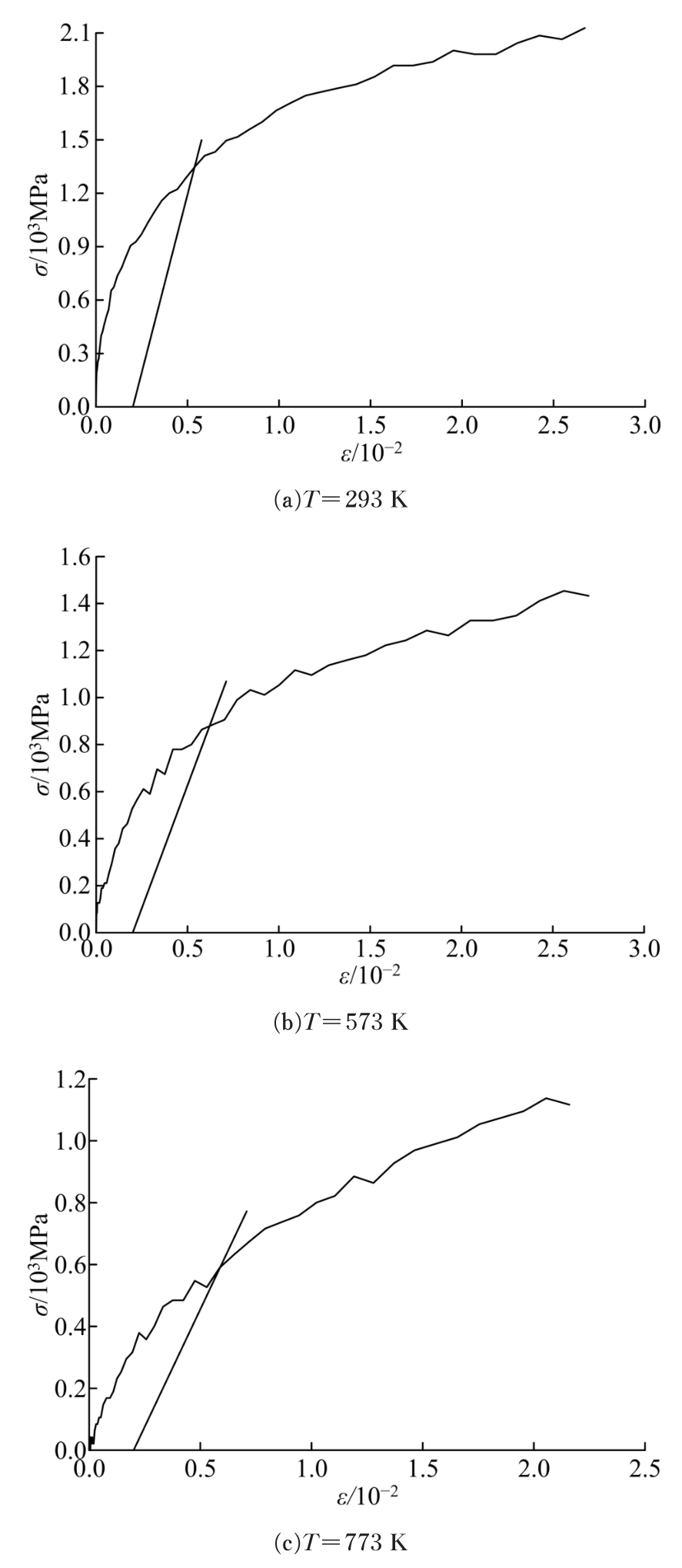
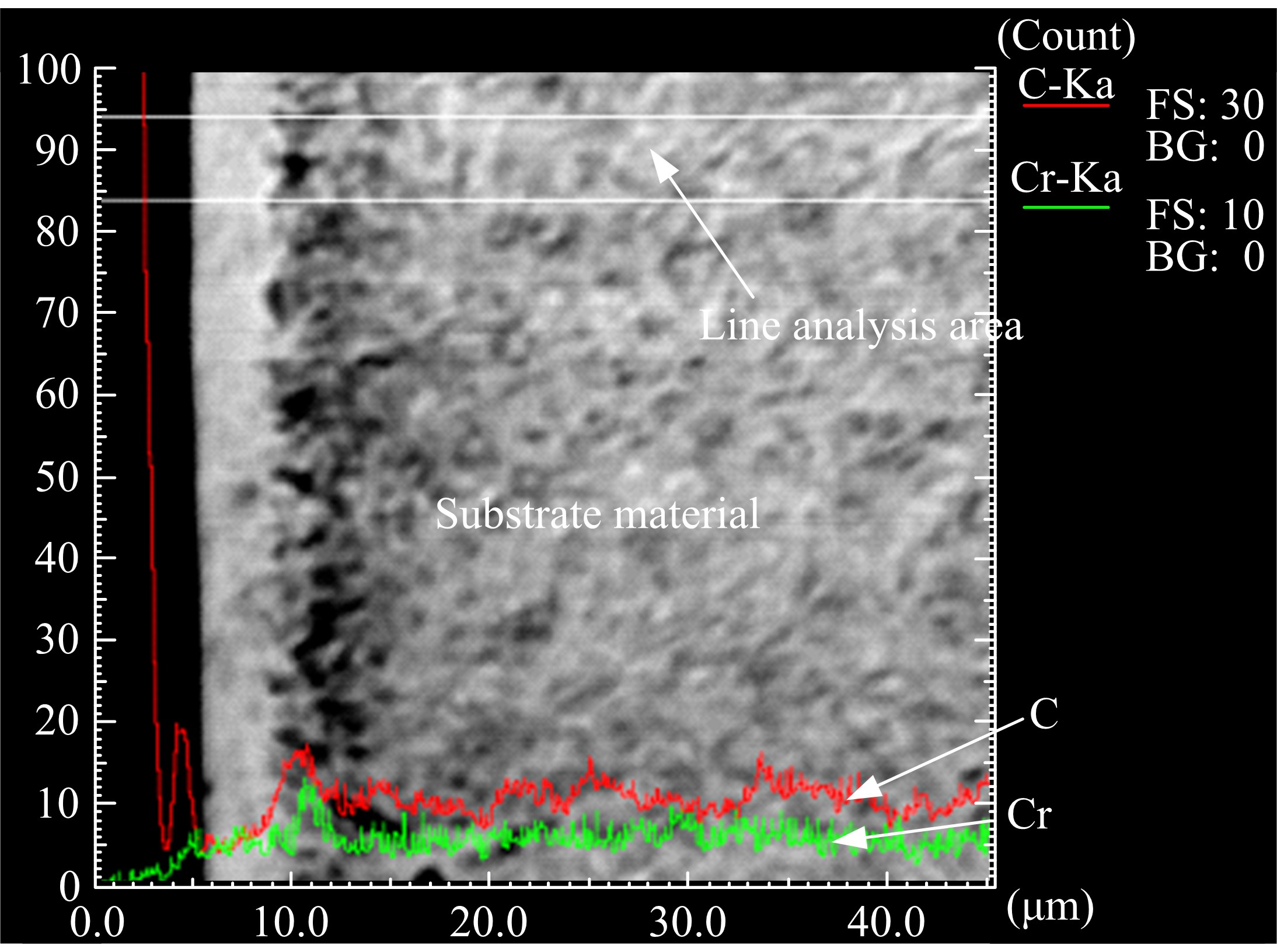
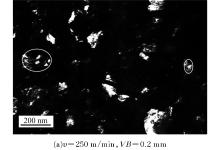
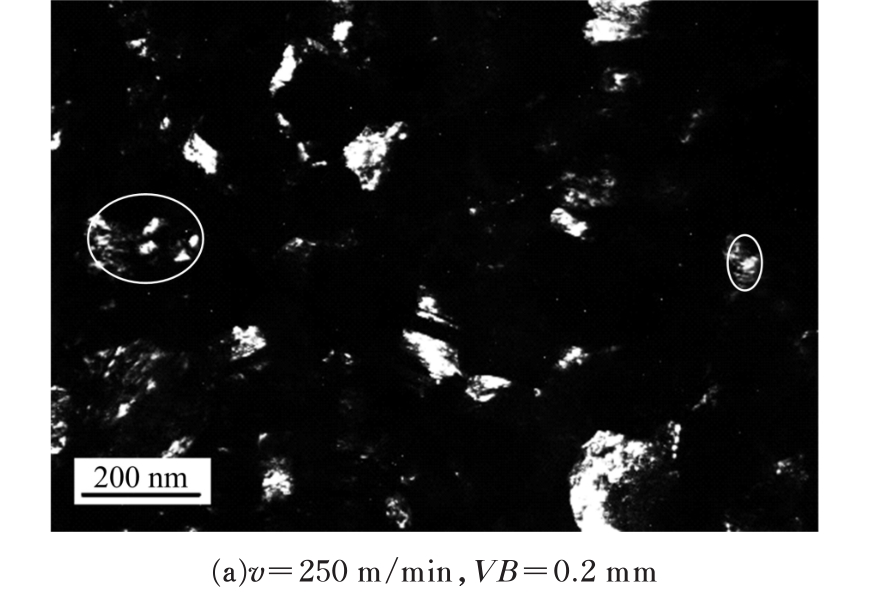
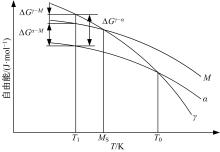
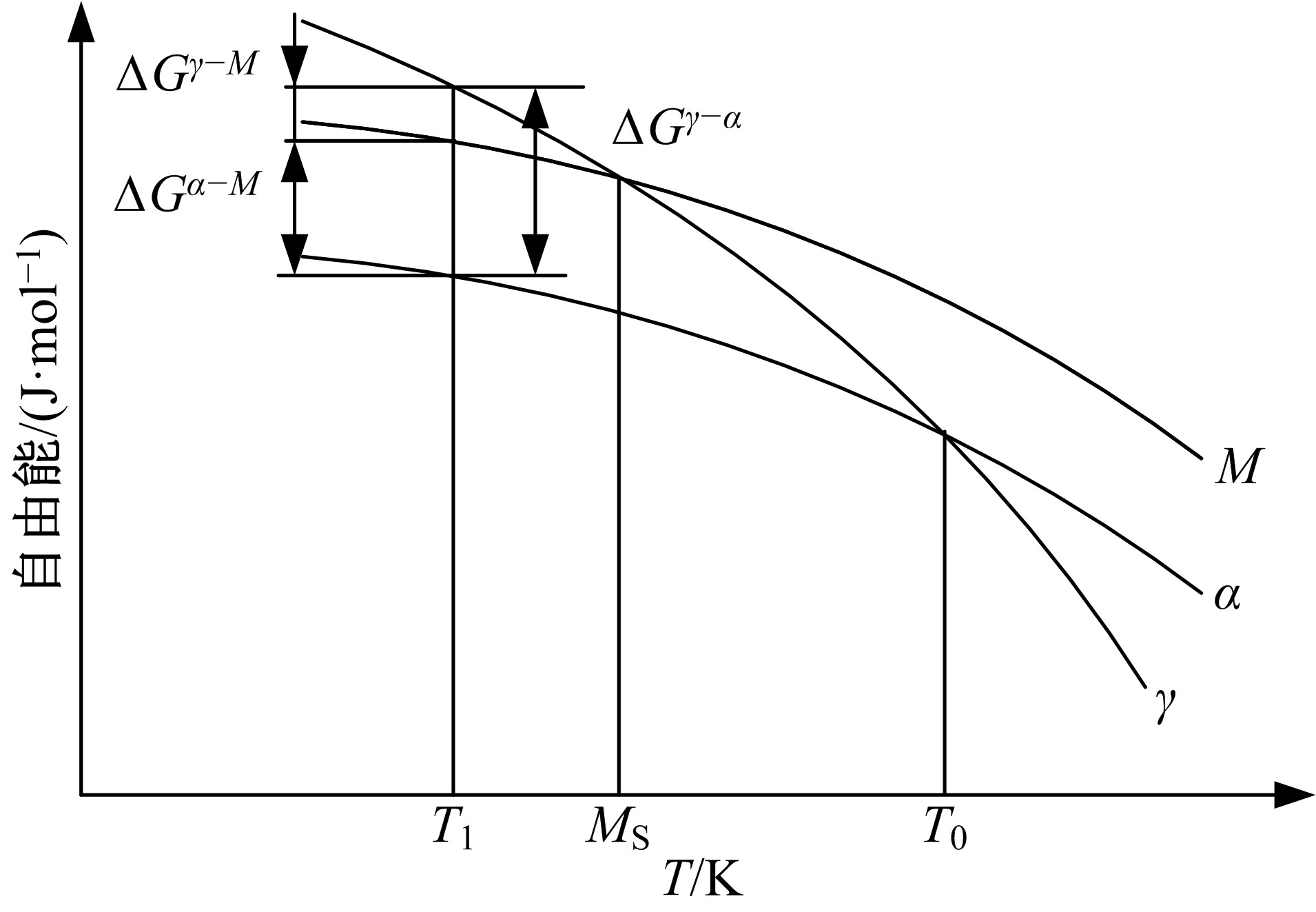
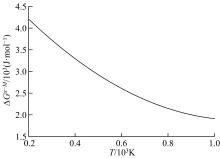
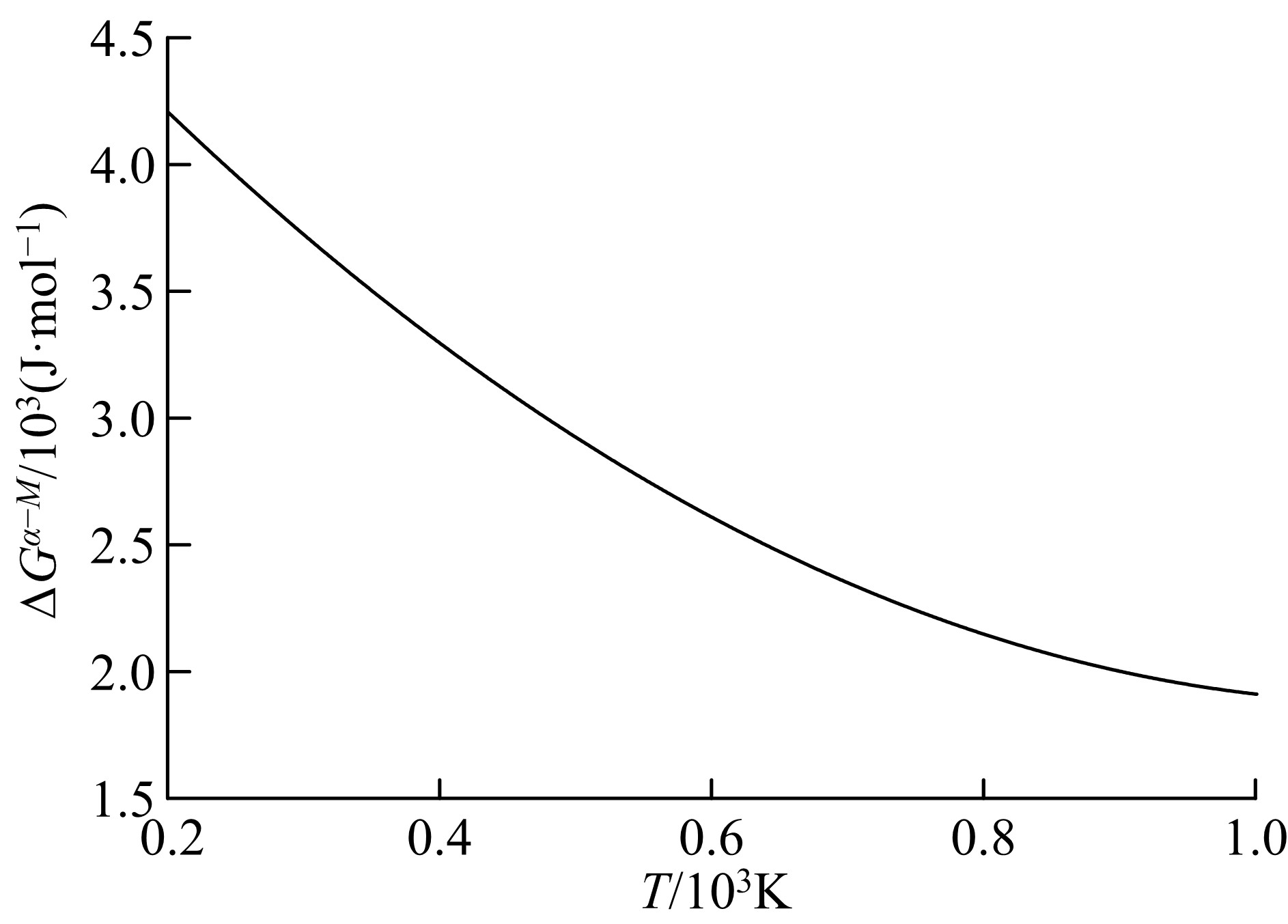
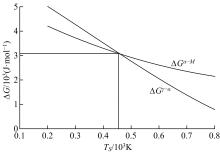
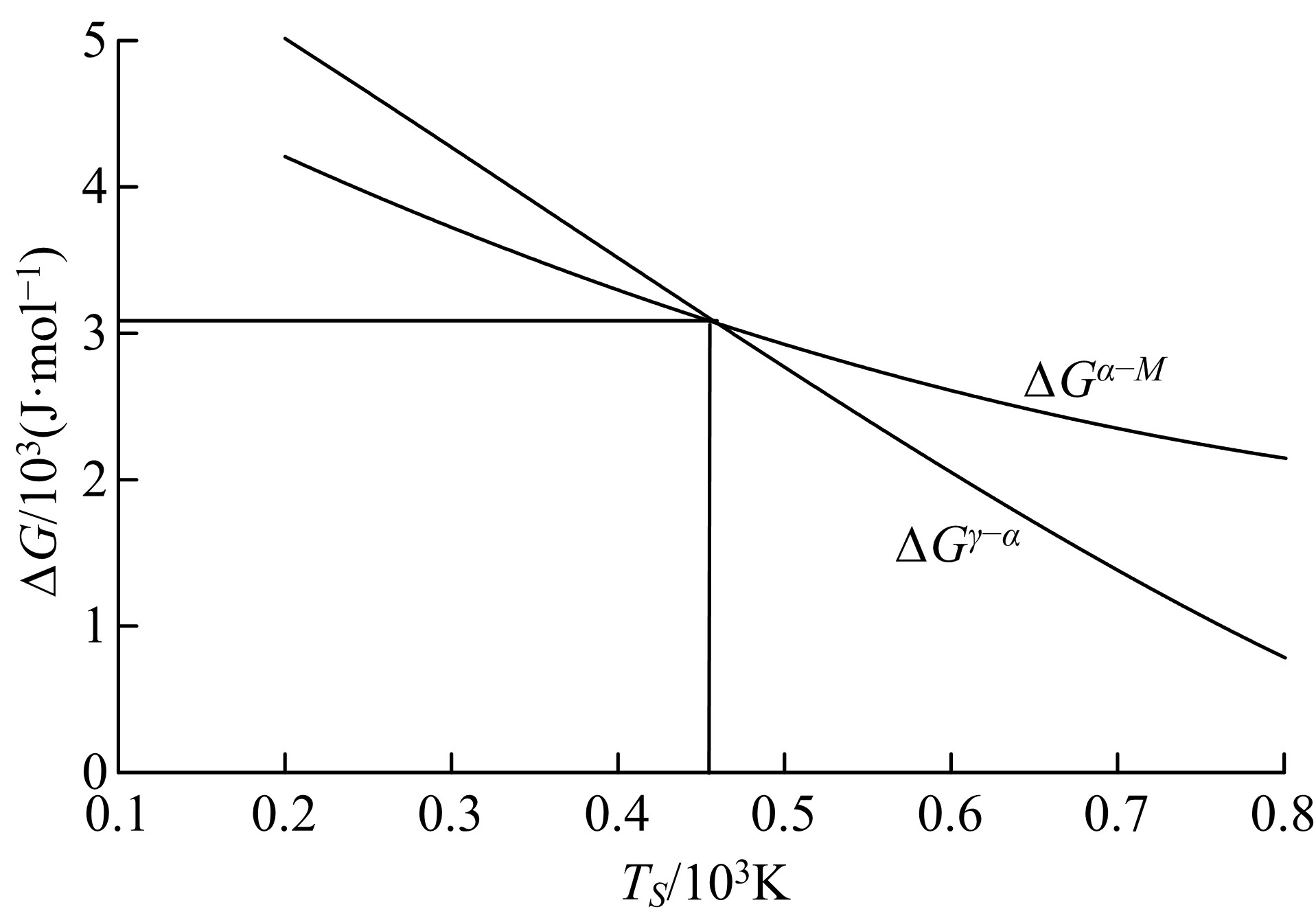
Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition) ›› 2019, Vol. 49 ›› Issue (5): 1575-1583.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb20180404
Martensitic transformation of surface white layer in high speed hard cutting
Chun-zheng DUAN( ),Fang-yuan ZHANG,Wen-neng KOU,Bin WEI
),Fang-yuan ZHANG,Wen-neng KOU,Bin WEI
- School of Mechanical Engineering, Dalian University of Technology, Dalian 116024, China
CLC Number:
- TG142.1
| 1 | Barbacki A , Kawalec M , Hamrol A . Turning and grinding as a source of microstructural changes in the surface layer of hardened steel[J]. Journal of Materials Processing Technology, 2003, 133(1): 21-25. |
| 2 | 刘战强, 吕绍瑜 . 镍基粉末高温合金切削加工表面白层形成热-力耦合作用机理[J]. 机械工程学报, 2014, 50(17): 186-193. |
| Liu Zhan-qiang , Shao-yu Lyu . Thermo-mechanical coupling mechanisms for white layer formation on machined surface of powder metallurgical nickel-based superalloy[J]. Journal of Mechanical Engineering, 2014, 50(17): 186-193. | |
| 3 | Chou Y K , Evans C J . White layers and thermal modeling of hard turned surfaces[J]. International Journal of Machine Tools & Manufacture, 1999, 39(12): 1863-1881. |
| 4 | 陈涛, 刘献礼, 李素燕, 等 . 高速硬切削加工表面白层形成机理研究[J]. 机械工程学报, 2015, 51(23): 182-188. |
| Chen Tao , Liu Xian-li , Li Su-yan , et al . Mechanism of white layer formation on machined surface of high-speed hard machining[J]. Journal of Mechanical Engineering, 2015, 51(23): 182-188. | |
| 5 | Hosseini S B , Klement U , Yao Y , et al . Formation mechanisms of white layers induced by hard turning of AISI 52100 steel[J]. Acta Materialia, 2015, 89: 258-267. |
| 6 | 段春争, 张方圆, 孔维森 . 干硬切削表面白层厚度的建模与预测[J]. 机械工程学报, 2015, 51(17): 194-202. |
| Duan Chun-zheng , Zhang Fang-yuan , Kong Wei-sen . Modeling and prediction of white layer thickness in dry and hard machining of hardened steel[J]. Journal of Mechanical Engineering, 2015, 51(17): 194-202. | |
| 7 | Umbrello D , Outeiro J C , Saoubi R M , et al . A numerical model incorporating the microstructure alteration for predicting residual stresses in hard machining of AISI 52100 steel[J]. CIRP Annals-Manufacturing Technology, 2010, 59(1): 113-116. |
| 8 | Ghosh G , Olson G B . Computational thermodynamics and the kinetics of martensitic transformation[J]. Journal of Phase Equilibria, 2001, 22(3): 199-207. |
| 9 | Stormvinter A , Borgenstam A , Ågren J . Thermodynamically based prediction of the martensite start temperature for commercial steels[J]. Metallurgical & Materials Transactions A, 2012, 43(10): 3870-3879. |
| 10 | Dieter G E . Mechanical Metallurgy[M]. New York: MacGraw-Hill. Inc., 1986. |
| 11 | 孔维森 . 高速切削淬硬钢已加工表面白层和残余应力的预测与实验研究[D]. 大连: 大连理工大学机械工程学院, 2013. |
| Kong Wei-sen . Prediction and experimental research of white layer and residual stress in high speed machining of hardened steel[D]. Dalian: School of Mechanical Engineering, Dalian University of Technology, 2013. | |
| 12 | Barry J , Byme G . TEM study on the surface white layer in two turned hardened steels[J]. Materials Science & Engineering A, 2002, 325(1/2): 356-364. |
| 13 | Sauvage X , Breton J M L , Guiliet A , et al . Phase transformations in surface layers of machined steels investigated by X-ray diffraction and Mössbauer spectrometry[J]. Materials Science & Engineering A, 2003, 362: 181-186. |
| 14 | 康煜平 . 金属固态相变及应用[M]. 北京: 化学工业出版社, 2007. |
| 15 | 徐祖耀 . 马氏体相变与马氏体[M]. 2版. 北京: 科学出版社, 1999. |
| 16 | Hsu T Y . An approximate approach for the calculation of Ms in iron-base alloys[J]. Journal of Materials Science, 1985, 20(1): 23-31. |
| 17 | John Ågren . A thermodynamic analysis of the Fe-C and Fe-N phase diagrams[J]. Metallurgical Transactions A, 1979, 10(12): 1847-1852. |
| 18 | Bhadeshia H K D H . Driving force for martensitic transformation in steels[J]. Metal Science, 1981, 15(4): 175-177. |
| 19 | Chipman J . Thermodynamics of the transformation in Fe-Cr alloys[J]. Metallurgical and Materials Transactions B, 1974, 5(2): 521-523. |
| 20 | Breedis J F , Kaufman L . The formation of Hcp and Bcc phases in austenitic iron alloys[J]. Metallurgical Transactions, 1971, 2(9): 2359-2371. |
| 21 | Ansell G S , Donachie S J , Mmessler R W . The effect of quench rate on the martensitic transformation in Fe-C alloys[J]. Metallurgical Transactions, 1971, 2(9): 2443-2449. |
| 22 | Hosseini S B , Beno T , Klement U , et al . Cutting temperatures during hard turning-measurements and effects on white layer formation in AISI 52100[J]. Journal of Materials Processing Technology, 2014, 214(6): 1293-1300. |
| 23 | Koistinen D P , Marbuger R E . A general equation prescribing the extent of the austenite-martensite transformation in pure iron-carbon alloys and plain carbon steels[J]. Acta Metallurgica, 1959, 7(1): 59-60. |
| 24 | van Bohemen S M C , Sietsma J . Effect of composition on kinetics of athermal martensite formation in plain carbon steels[J]. Materials Science and Technology, 2009, 25(8): 1009-1012. |
| 25 | Zhang F Y , Duan C Z , Xu X X . Influence of cutting condition on white layer induced by high speed machining of hardened steel[J]. International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology, 2017, 98(1): 1-8. |
| 26 | 朱丽娟, 谷诤巍, 吕义, 等 . 超高强钢热冲压硬化机理[J]. 吉林大学学报: 工学版, 2013, 43(2): 376-379. |
| Zhu Li-juan , Gu Zheng-wei , Lyu Yi, et al . Mechanism of hot stamping hardening for ultra-high strength steel[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Engineering and Technology Edition), 2013, 43(2): 376-379. | |
| 27 | 徐虹, 刘亚楠, 于婷, 等 . 双相钢DP780在循环加载-卸载过程中的非弹性回复行为及其微观机理[J]. 吉林大学学报: 工学版, 2017, 47(1): 191-198. |
| Xu Hong , Liu Ya-nan , Yu Ting , et al . Inelastic recovery behavior and microscopic mechanism of high strength DP780 steel during cyclic loading-unloading[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Engineering and Technology Edition), 2017, 47(1): 191-198. | |
| 28 | 韩宝军 . 奥氏体动态再结晶晶粒超细化及其马氏体相变研究[D]. 上海: 上海交通大学材料科学与工程学院, 2008. |
| Han Bao-jun . Research on the grain ultra-refinement in austenite by dynamic recrystallization and its martensitic transformation[D]. Shanghai: School of Materials Science and Engineering, Shanghai Jiaotong University, 2008. | |
| 29 | Mironov S , Salishchev G , Myshlyaey M M , et al . Evolution of misorientation distribution during warm 'abc' forging of commercial-purity titanium[J]. Materials Science & Engineering A, 2006, 418(1/2): 257-267. |
| 30 | Saito Y , Utsunomiya H , Tsuji N , et al . Novel ultra-high straining process for bulk materials—development of the accumulative roll-bonding (ARB) process[J]. Acta Materialia, 1999, 47(2): 579-583. |
| 31 | 王蕾 . 热轧带钢的相变和力学性能模型研究及应用[D]. 北京: 北京科技大学材料科学与工程学院, 2017. |
| Wang Lei . Research and application of phase transformation and mechanical properties models in hot strip rolling[D]. Beijing: School of Materials Science and Engineering, University of Science and Technology Beijing, 2017. | |
| 32 | 付秀丽 . 高速切削航空铝合金变形理论及加工表面形成特征研究[D]. 济南: 山东大学机械工程学院, 2007. |
| Fu Xiu-li . Research on deformation theory and characteristics of machined surface for high-speed milling aviation aluminum alloy[D]. Jinan: School of Mechanical Engineering, Shandong University, 2007. |
| [1] | REN Shu-nan, YANG Xiang-dong, WANG Guo-lei, LIU Zhi, CHEN Ken. Base position planning of mobile manipulator for large parts painting [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2016, 46(6): 1995-2002. |
| [2] | GUO Li-bin, ZHANG Bin, CUI Hai, ZHANG Zhi-hang. Structural parameters of 3D roughness for micro wire electrical discharge machining surface [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2015, 45(3): 851-856. |
| [3] | ZHANG Lei, ZHAO Yun-wei, YANG Zhuo, ZHAO Ji. Shear yield property of electrorheological polishing fluid [J]. , 2012, 42(05): 1145-1150. |
| [4] | ZHANG Lei,HE Xin-sheng,ZHANG Ying,YANG He-ran. Development of new type ER fluid-assisted polishing tool and its polishing experiment [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2010, 40(04): 1009-1014. |
| [5] | Meng Fan-zhong,Zhang Jin-ping,Xu Shu-xin . Engine assembly test and wear characteristics of automotive chain [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2008, 38(增刊): 99-0102. |
| [6] | YANG Xiao-dong, REN Lu-quan. Analysis of Deformation Mechanism of the Creature Flexibility, Elastic and Plastic Models [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2002, (4): 78-80. |
|
||