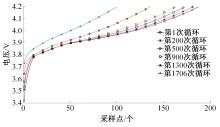
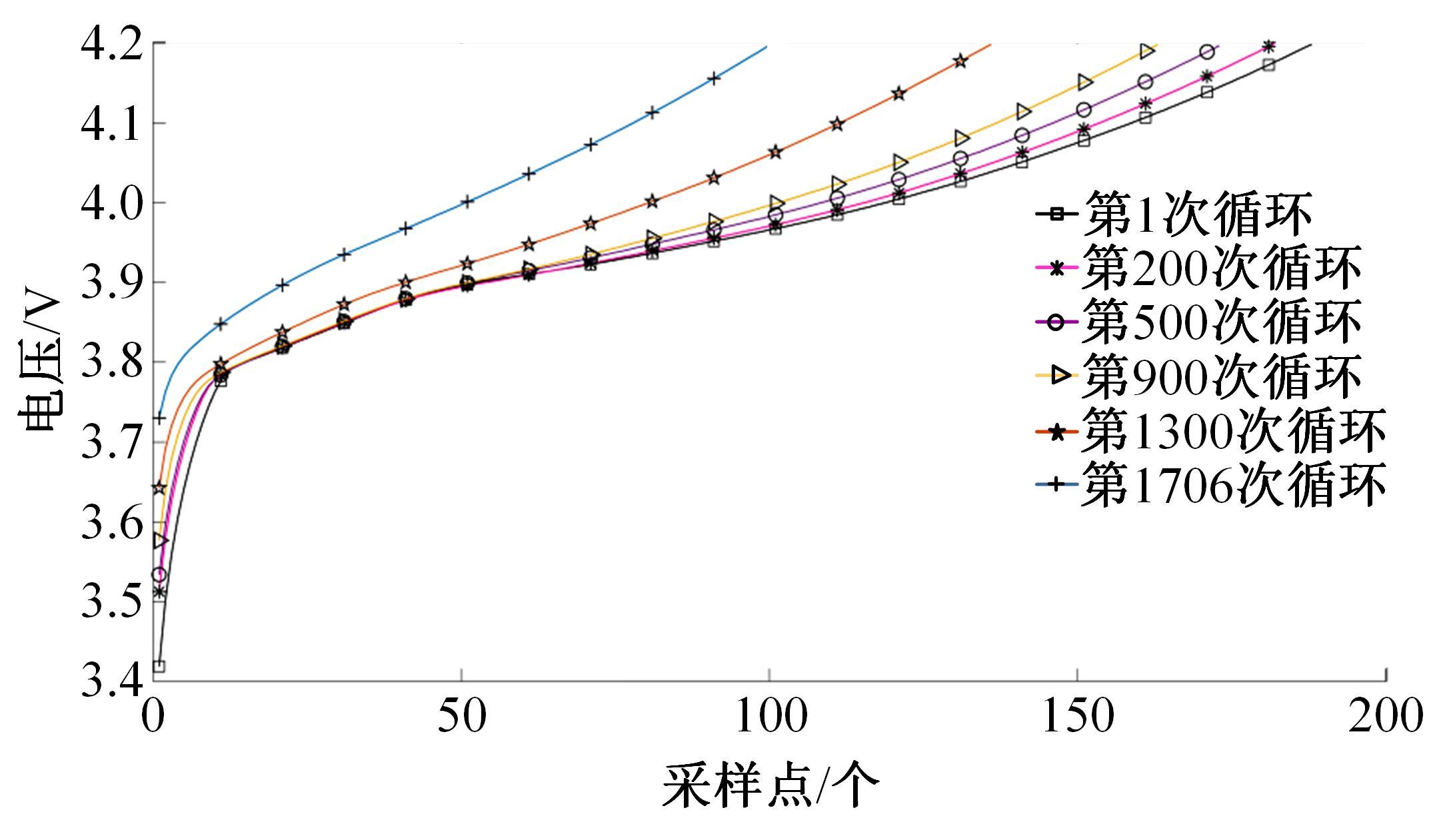
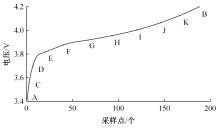
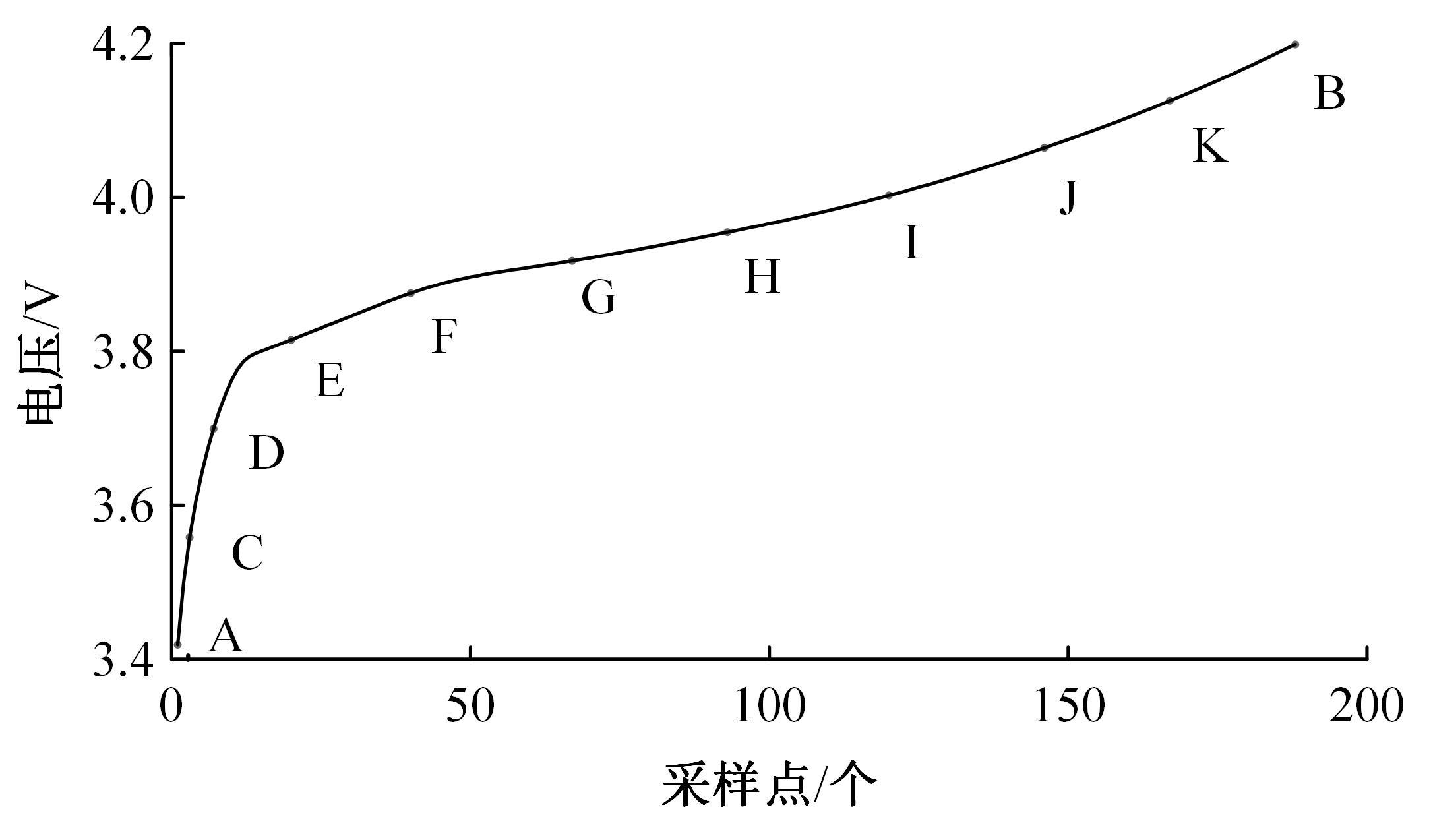
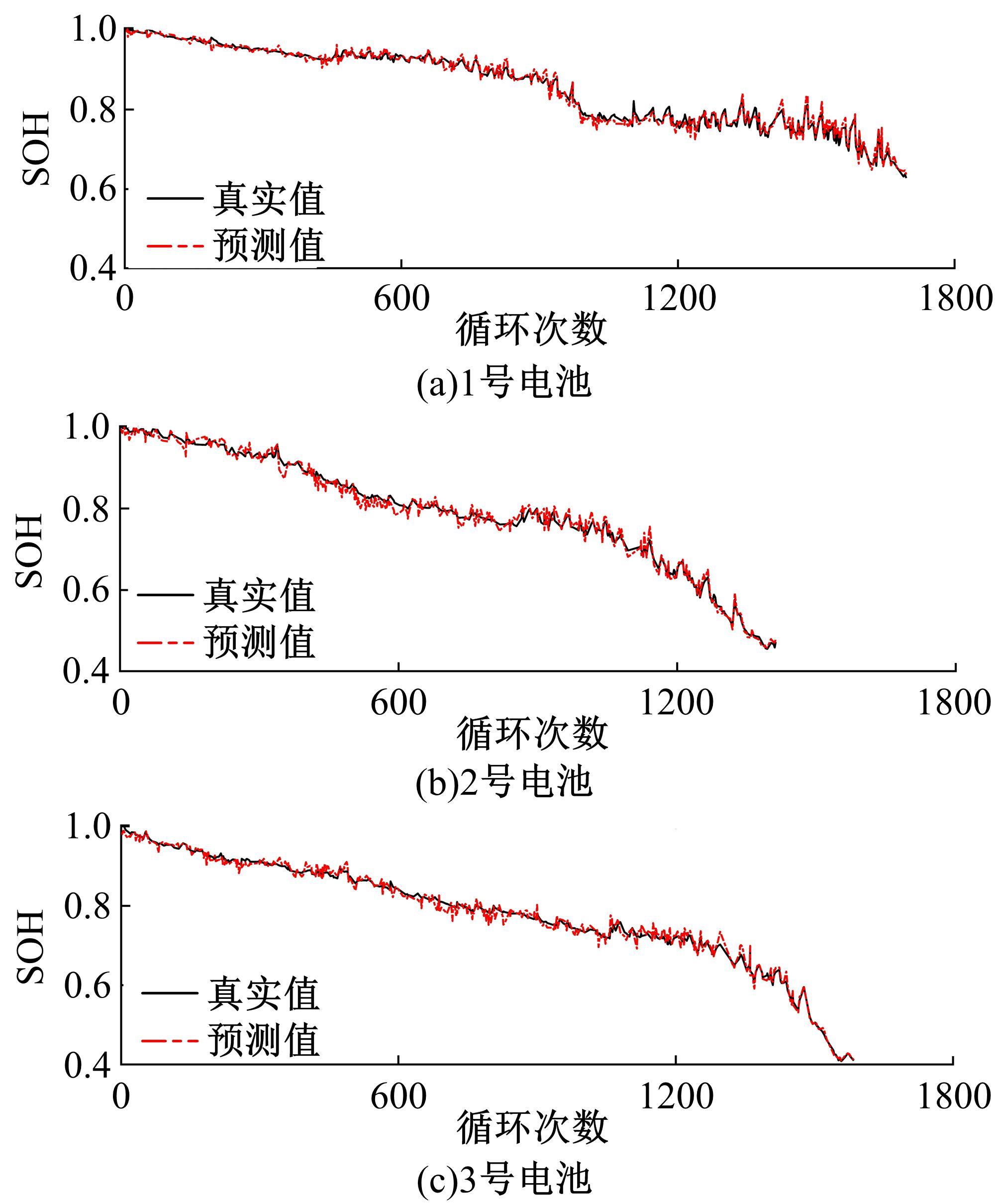
Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition) ›› 2022, Vol. 52 ›› Issue (6): 1273-1280.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb20210020
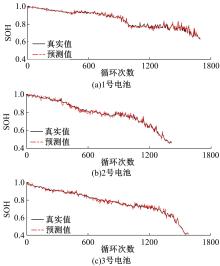
State of health estimation method for lithium⁃ion battery based on curve compression and extreme gradient boosting
Xing-tao LIU1,2( ),Xiao-jian LIU1,Ji WU1,2(
),Xiao-jian LIU1,Ji WU1,2( ),Yao HE3,Xin-tian LIU3
),Yao HE3,Xin-tian LIU3
- 1.School of Automotive and Transportation Engineering,Hefei University of Technology,Hefei 230009,China
2.Engineering Research Center for Intelligent Transportation and Cooperative Vehicle-Infrastructure of Anhui Province,Hefei University of Technology,Hefei 230009,China
3.Automotive Research Institute,Hefei University of Technology,Hefei 230009,China
CLC Number:
- TM91
| 1 | Wu Ji, Wang Yu-jie, Zhang Xu, et al. A novel state of health estimation method of Li-ion battery using group method of data handling[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2016, 327: 457-464. |
| 2 | 刘新天, 刘兴涛, 何耀, 等. 基于Vmin-EKF的动力锂电池组SOC估计[J]. 控制与决策, 2010, 25(3): 445-448. |
| Liu Xin-tian, Liu Xing-tao, He Yao, et al. Based-Vmin-EKF SOC estimation for power Li-ion battery pack[J]. Control and Decision, 2010, 25(3): 445-448. | |
| 3 | Tian Hui-xin, Qin Peng-liang, Li Kun, et al. A review of the state of health for lithium-ion batteries: research status and suggestions[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2020, 261: No. 120813. |
| 4 | 刘新天, 李涵琪, 魏增福, 等. 基于Drift-Ah积分法的CKF估算锂电池SOC[J]. 控制与决策, 2019, 34(3): 535-541. |
| Liu Xin-tian, Li Han-qi, Wei Zeng-fu, et al. CKF estimation Li-ion battery SOC based on Drift-Ah integral method[J]. Control and Decision, 2019, 34(3): 535-541. | |
| 5 | 陈猛, 乌江, 焦朝勇, 等. 锂离子电池健康状态多因子在线估计方法[J]. 西安交通大学学报, 2020, 54(1): 169-175. |
| Chen Meng, Wu Jiang, Jiao Chao-yong, et al. Multi-factor online estimation method for health status of lithium-ion battery[J]. Journal of Xi'an Jiaotong University, 2020, 54(1): 169-175. | |
| 6 | 颜湘武, 邓浩然, 郭琪, 等. 基于自适应无迹卡尔曼滤波的动力电池健康状态检测及梯次利用研究[J]. 电工技术学报, 2019, 34(18): 3937-3948. |
| Yan Xiang-wu, Deng Hao-ran, Guo Qi, et al. Study on the state of health detection of power batteries based on adaptive unscented Kalman filters and the battery echelon utilization[J]. Transactions of China Electrotechnical Society, 2019, 34(18): 3937-3948. | |
| 7 | Sankarasubramanian S, Krishnamurthy B. A capacity fade model for lithium-ion batteries including diffusion and kinetics[J]. Electrochimica Acta, 2012, 70: 248-254. |
| 8 | You G W, Park S, Oh D. Real-time state-of-health estimation for electric vehicle batteries: a data-driven approach[J]. Applied Energy, 2016, 176: 92-103. |
| 9 | Li Y, Zou C F, Berecibar M, et al. Random forest regression for online capacity estimation of lithium-ion batteries[J]. Applied Energy, 2018, 232(9): 197-210. |
| 10 | Deng Yuan-wang, Ying He-jie, Jia-qiang E, et al. Feature parameter extraction and intelligent estimation of the state-of-health of lithium-ion batteries[J]. Energy, 2019, 176: 91-102. |
| 11 | 潘海鸿, 吕治强, 付兵, 等. 采用极限学习机实现锂离子电池健康状态在线估算[J]. 汽车工程, 2017, 39(12):1375-1381, 1396. |
| Pan Hai-hong, Lv Zhi-qiang, Fu Bing, et al. Online estimation of lithium-ion battery's state of health using extreme learning machine[J]. Automotive Engineering, 2017, 39(12): 1375-1381, 1396. | |
| 12 | Zhao Lin, Wang Yi-peng, Cheng Jian-hua. A hybrid method for remaining useful life estimation of lithium-ion battery with regeneration phenomena[J]. Applied Sciences, 2019, 9(9): No.1890. |
| 13 | Yang Duo, Zhang Xu, Pan Rui, et al. A novel Gaussian process regression model for state-of-health estimation of lithium-ion battery using charging curve[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2018, 384: 387-395. |
| 14 | He W, Williard N, Osterman M, et al. Prognostics of lithium-ion batteries based on Dempster–Shafer theory and the bayesian monte carlo method[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2011, 196(23): 10314-10321. |
| 15 | Patil A, Patil V, Shin D W, et al. Issue and challenges facing rechargeable thin film lithium batteries[J]. Materials Research Bulletin, 2008, 43(8/9): 1913-1942. |
| 16 | 于靖, 陈刚, 张笑, 等. 面向自然岸线抽稀的改进道格拉斯-普克算法[J]. 测绘科学, 2015, 40(4): 23-27, 33. |
| Yu Jing, Chen Gang, Zhang Xiao, et al. An improved Douglas-Puck algorithm oriented to natural shoreline simplification[J]. Science of Surveying and Mapping, 2015, 40(4): 23-27, 33. | |
| 17 | Zhao Liang-bin, Shi Guo-you. A method for simplifying ship trajectory based on improved Douglas–Peucker algorithm[J]. Ocean Engineering, 2018, 166: 37-46. |
| 18 | Jiang Fu, Yang Jia-jun, Cheng Yi-jun, et al. An aging-aware SOC estimation method for lithium-ion batteries using XGBoost algorithm[C]∥2019 IEEE International Conference on Prognostics and Health Management, San Francisco, USA, 2019: 1-8. |
| 19 | Yang Jin-shan, Zhao Chen-yue, Yu Hao-tong, et al. Use GBDT to predict the stock market[J]. Procedia Computer Science, 2020, 174: 161-171. |
| 20 | 米学军, 盛广铭, 张婧, 等. GIS中面积偏差控制下的矢量数据压缩算法[J]. 地理科学, 2012, 32(10): 1236-1240. |
| Mi Xue-jun, Sheng Guang-ming, Zhang Jing, et al. A new algorithm of vector date compression based on the tolerance of area error in GIS [J]. Geographical Sciences, 2012, 32(10): 1236-1240. | |
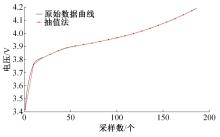
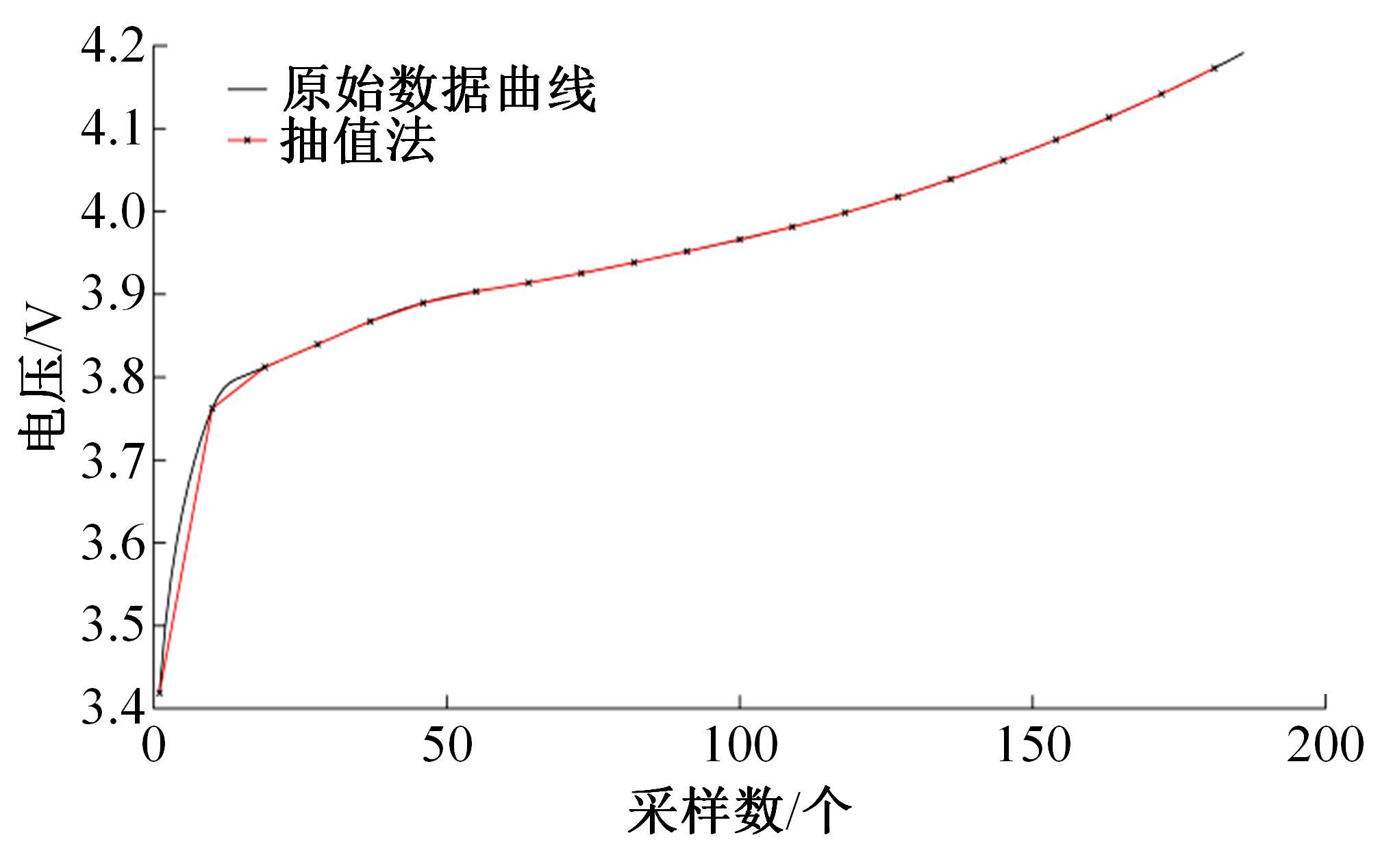
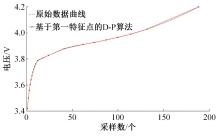
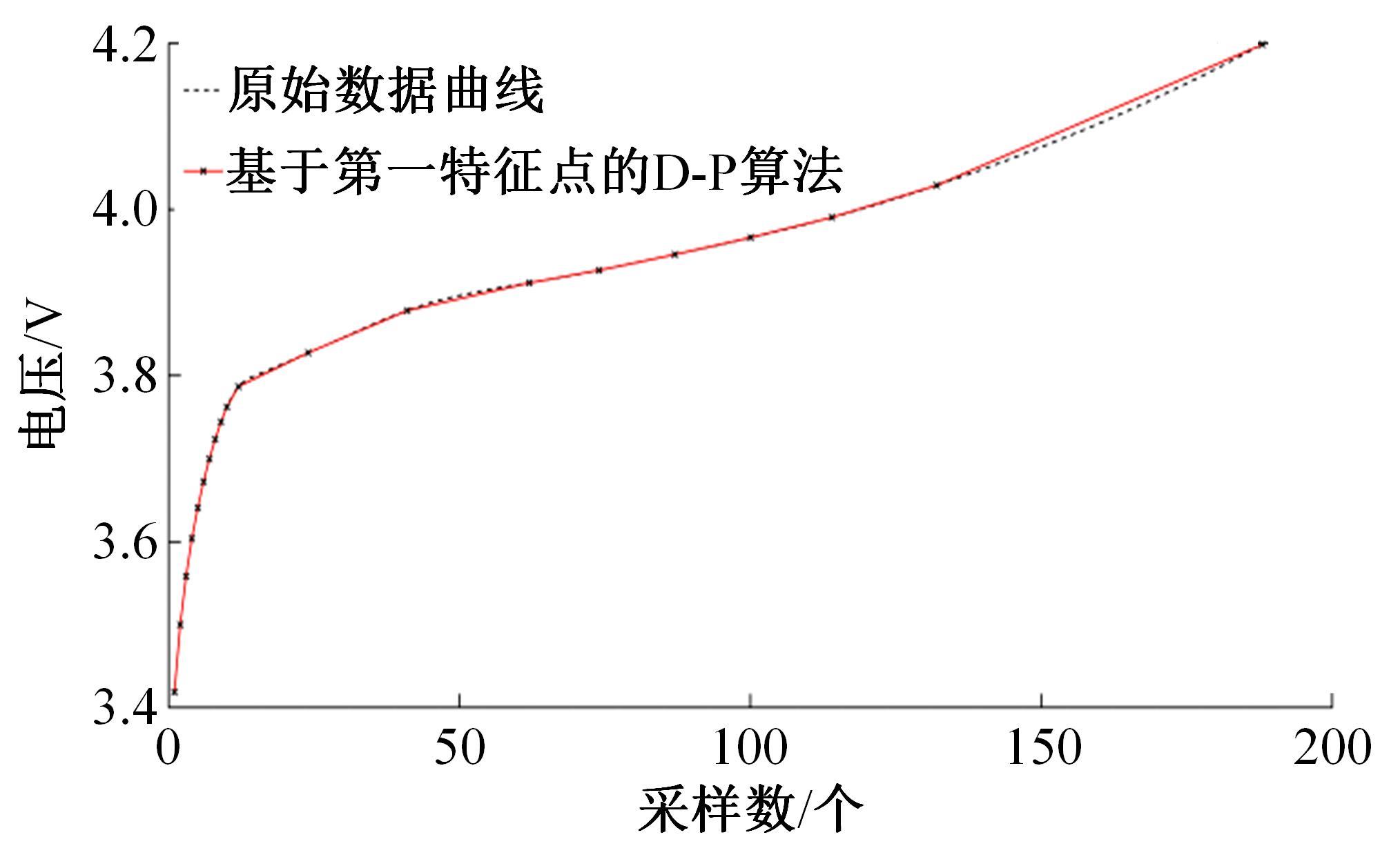
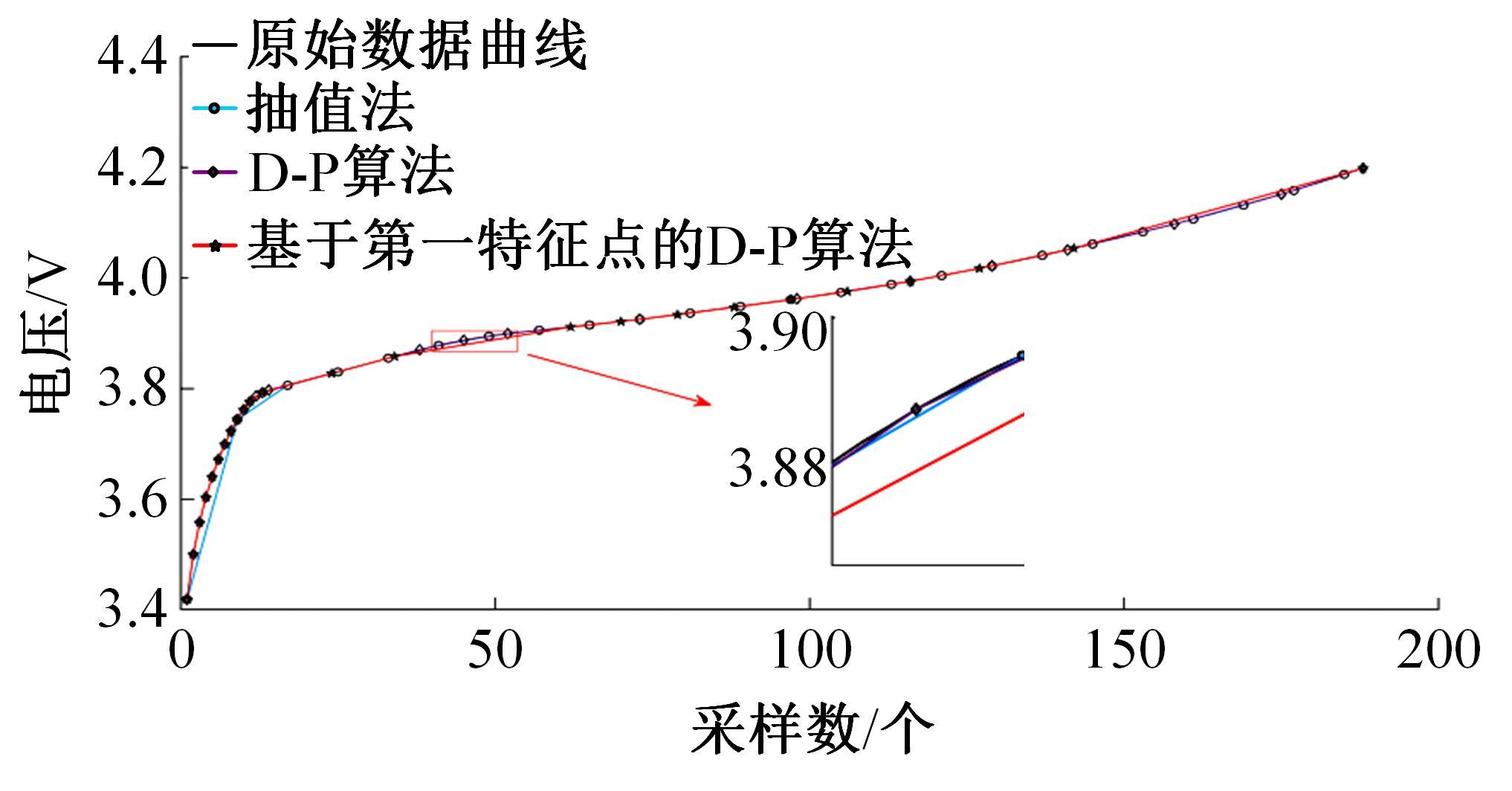
| 21 | 王笑天, 吕海洋. 基于第一特征点的道格拉斯-普克压缩算法[J]. 软件导刊, 2016, 15(11): 68-70. |
| Wang Xiao-tian, Lv Hai-yang. Douglas-Puck compression algorithm based on the first feature point[J]. Software Guide, 2016, 15(11): 68-70. |
| [1] | Feng-wen PAN,Dong-liang GONG,Ying GAO,Ming-wei XU,Bin MA. Fault diagnosis of current sensor based on linearization model of lithium ion battery [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2021, 51(2): 435-441. |
| [2] | Fei GAO,Yang XIAO,Wen-hua ZHANG,Jin-xuan QI,Zi-qiao LI,Xiao-yuan MA. Influence of coupling of elevated temperature and state of charge on mechanical response of Li⁃ion battery cells [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2020, 50(5): 1574-1583. |
| [3] | WANG Jun-nian, YE Tao, SUN Wen, WANG Qing-nian. Vibration isolation performance of energy-regenerative semi-active suspension with variable stiffness and damping [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2017, 47(3): 701-708. |
| [4] | LIU Yang, SUN Ze-chang, WANG Meng. Brake force cooperative control and test for integrated electro-hydraulic brake system [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2016, 46(3): 718-724. |
| [5] | CHEN Yan-hong, WU Wei-jing, LIU Hong-wei, SHEN Shuai, LI Ce-yuan, GENG Huan-liang. Thermal characteristics of battery for pure electric vehicles [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2014, 44(4): 925-932. |
| [6] | HAN Fei, ZHANG Su-min, LIU Jia-yi. Estimation of probability of blind zone of vehicle rearview mirror based on eyellipse [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2013, 43(增刊1): 521-525. |
| [7] | WANG Qing-nian, QU Xiao-dong, YU Yuan-bin. Optimal matching of HEV with composite electric power supply [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2013, 43(05): 1153-1159. |
| [8] | ZHANG Cai-ping, JIANG Jiu-chun. Extended Kalman filter algorithm for parameters identification of dynamic battery model based on genetic algorithm optimization [J]. , 2012, (03): 732-737. |
| [9] | SONG Chuanxue, CAI Zhanglin. Modeling and simulation of double wishbone suspension based on ADAMS/CAR [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2004, (4): 554-558. |
| [10] | JIN Liqiang, WANG Qingnian, SONG Chuanxue. Simulation of 4-wheel independent driving electric vehicle dynamics control system [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2004, (4): 547-553. |
|
||