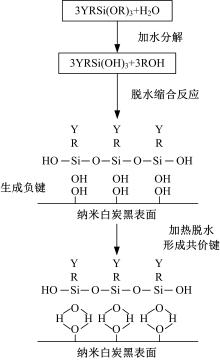
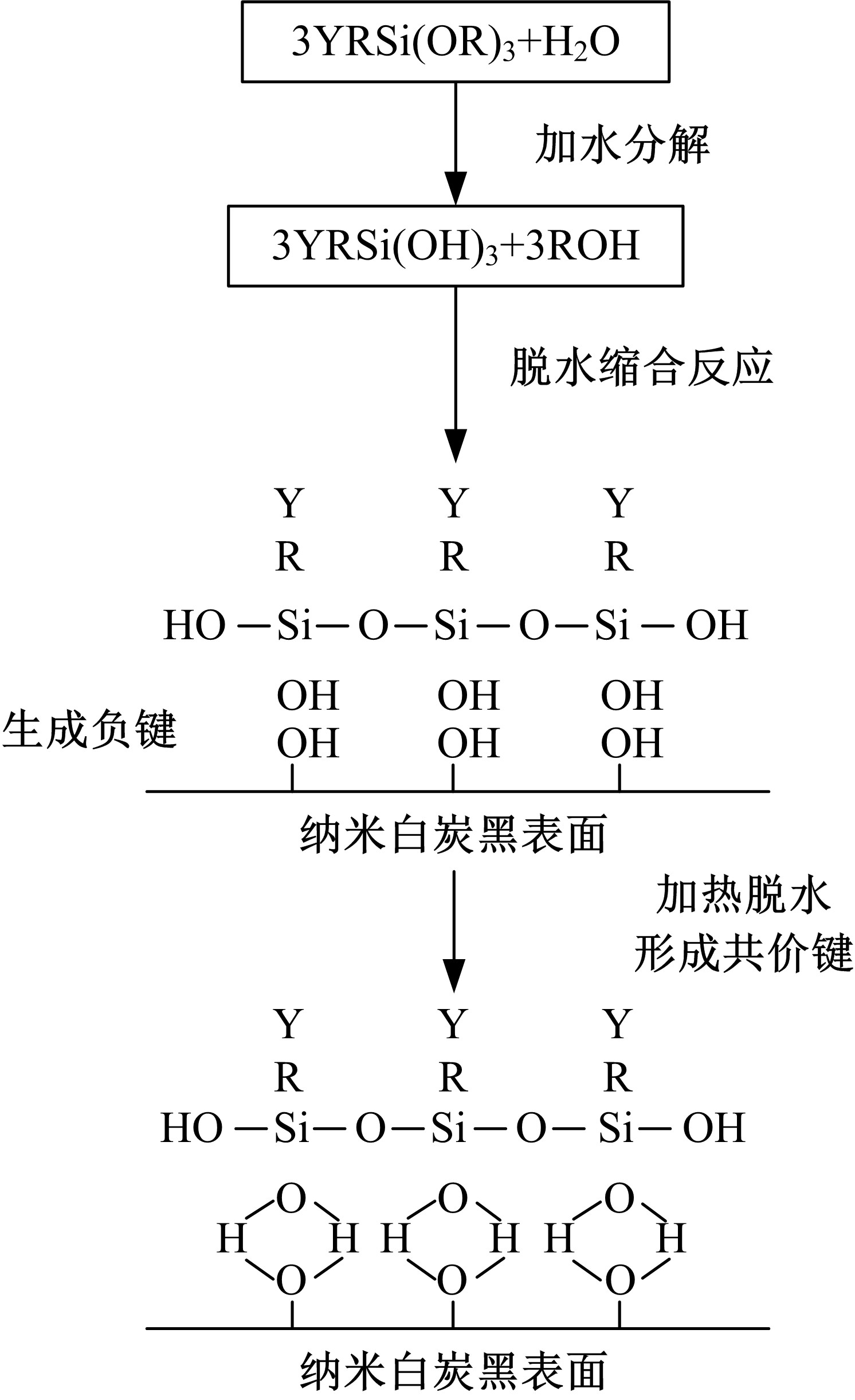
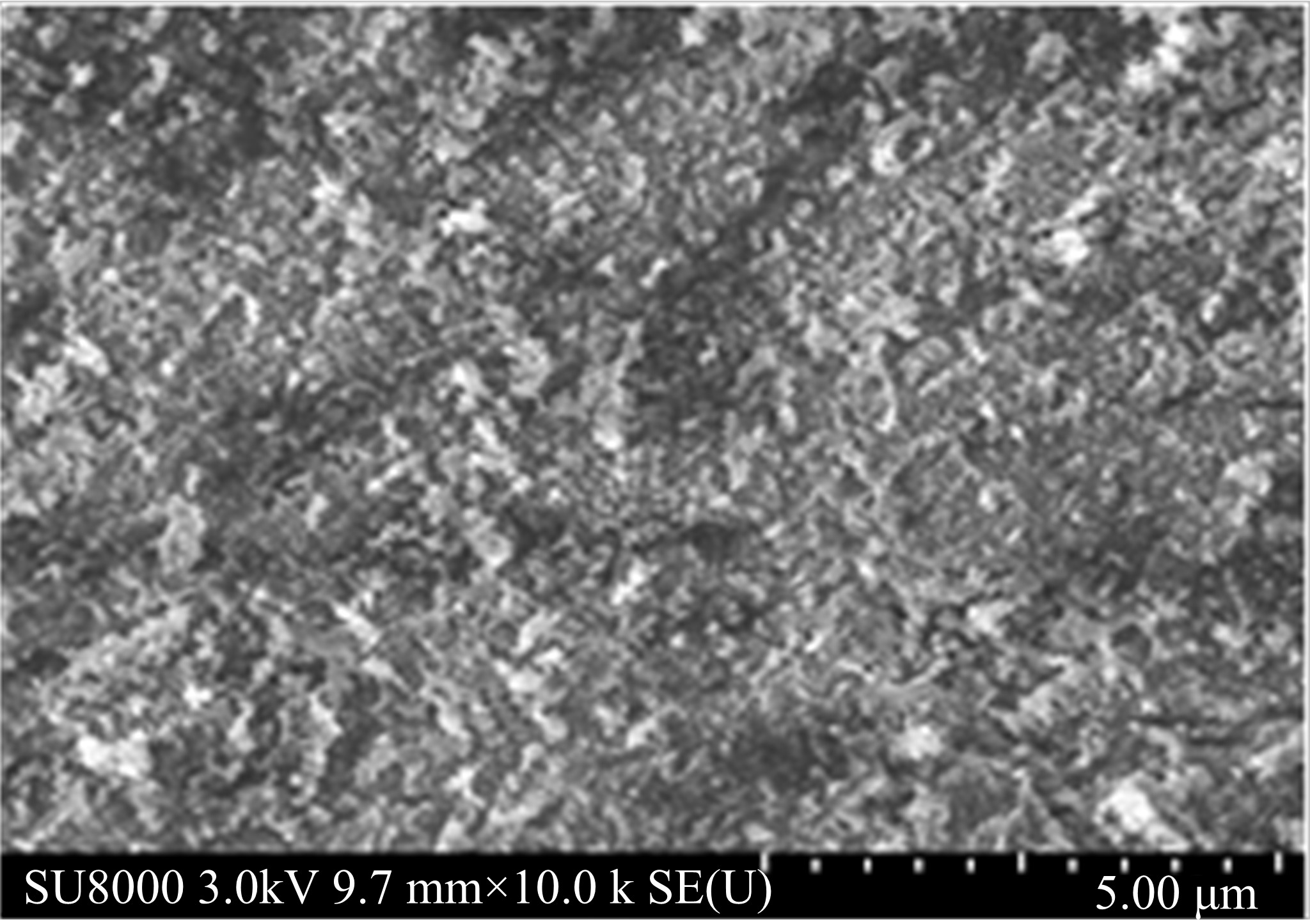
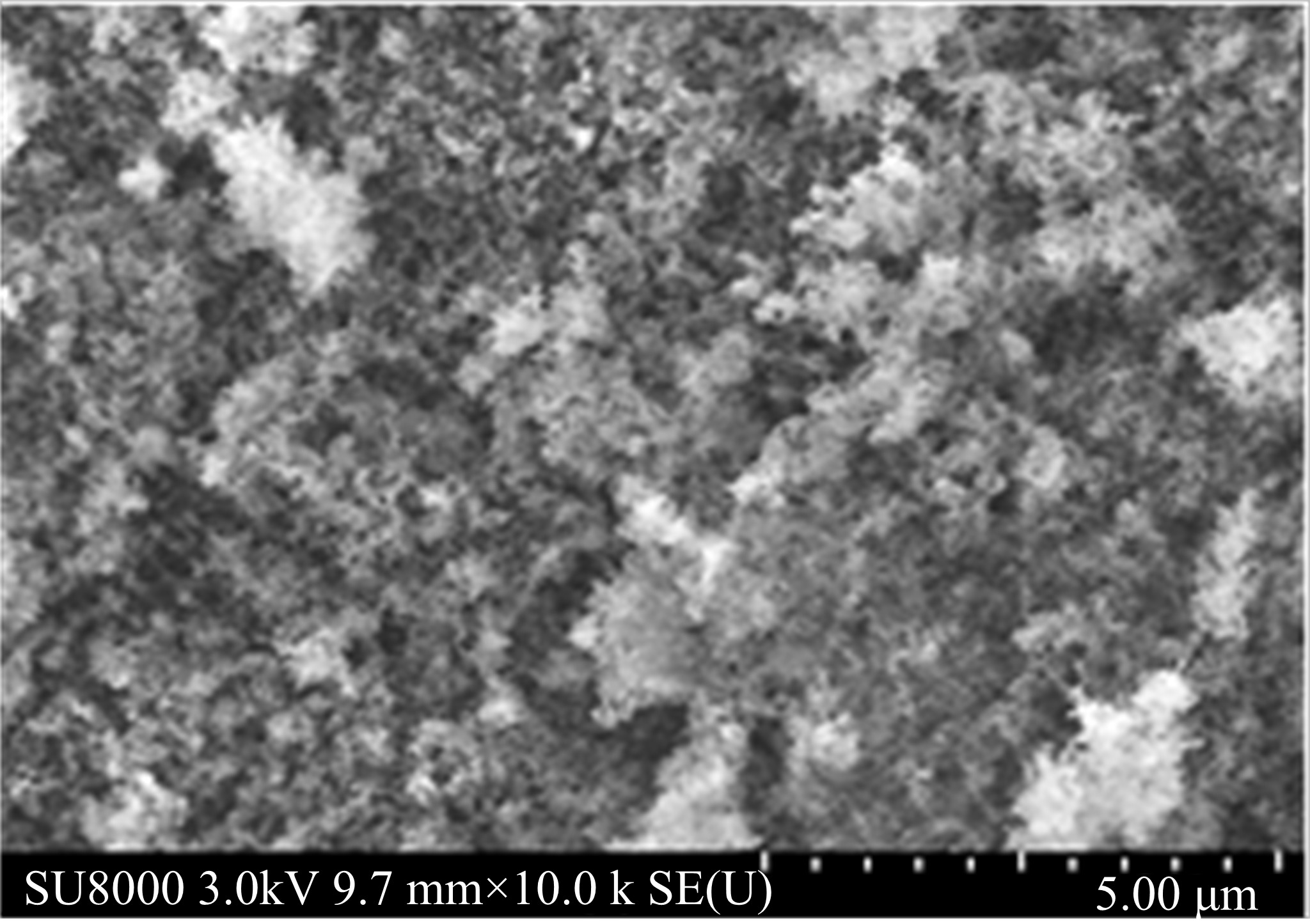
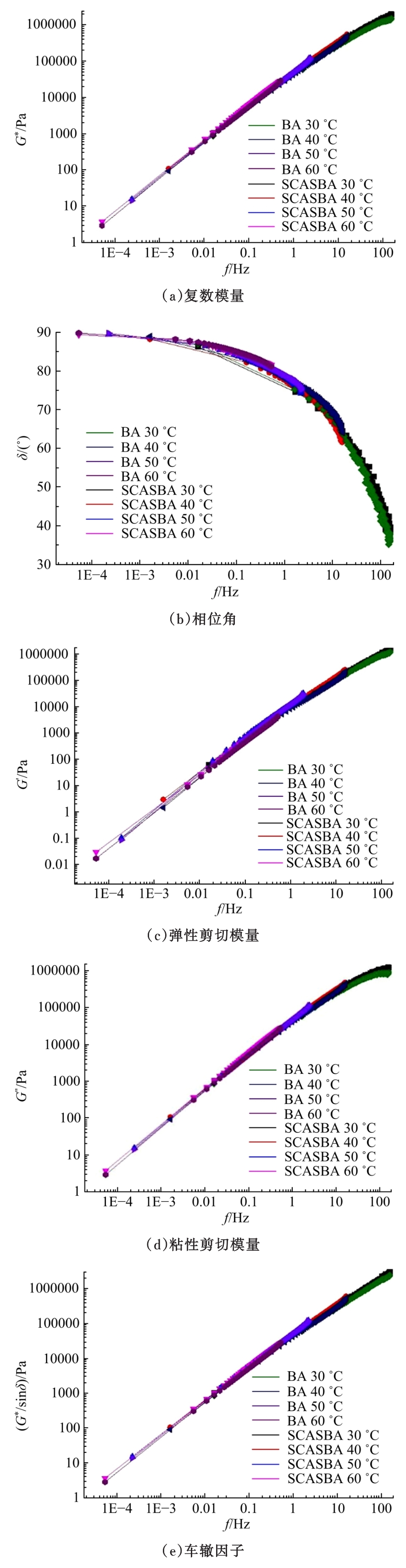
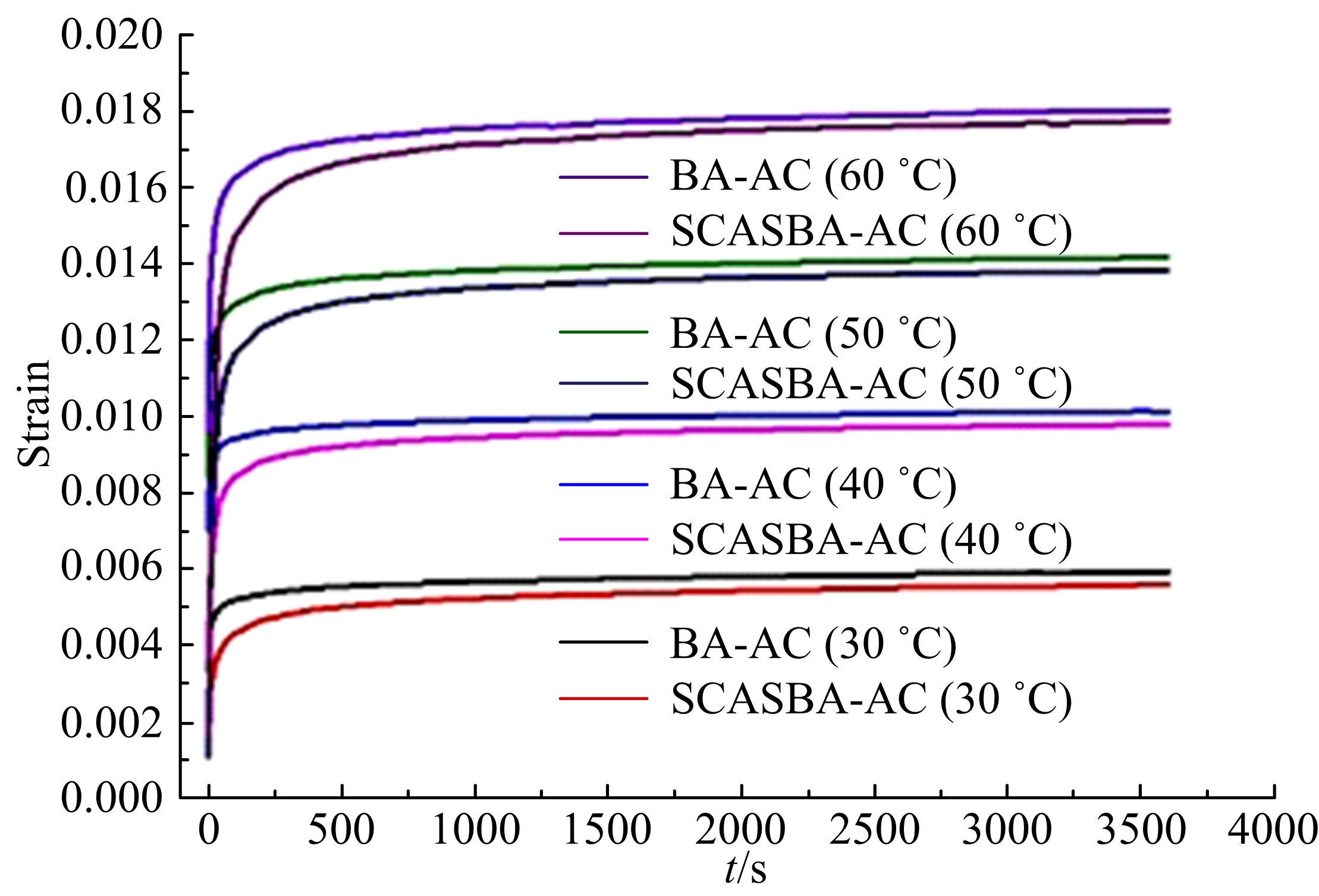
Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition) ›› 2020, Vol. 50 ›› Issue (5): 1709-1717.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb20190611
Viscoelasticity of hydrophobic nano⁃silica modified asphalt and asphalt mixture
Zi-wen WANG1( ),Xue-dong GUO2,Wei GUO2,Meng-yuan CHANG2,Wen-ting DAI2(
),Xue-dong GUO2,Wei GUO2,Meng-yuan CHANG2,Wen-ting DAI2( )
)
- 1.Changji Intercity Railway Co. Ltd. , Changchun 130021, China
2.College of Transportation, Jilin University, Changchun 130022, China
CLC Number:
- U416
| 1 | 韦大川, 王云鹏, 李世武. 橡胶粉与SBS复合改性沥青路用性能与微观结构[J]. 吉林大学学报: 工学版, 2008, 38(3): 525-529. |
| Wei Da-chuan, Wang Yun-peng, Li Shi-wu. Physical properties and microstructure of waste rubber powder and SBS complex modified asphalt[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2008, 38(3): 525-529. | |
| 2 | 樊亮, 张玉贞, 刘延军, 等. 纳米材料与技术在沥青路面中的应用研究进展[J]. 材料导报, 2010, 24(23): 72-75. |
| Fan Liang, Zhang Yu-zhen, Liu Yan-jun, et al. Recent application progress of nanometer material & technology in asphalt pavement[J]. Materials Review, 2010, 24(23): 72-75. | |
| 3 | 夏纬通. 白炭黑在灯泡工业中的应用[J]. 江苏化工, 1995(1): 7-11. |
| Xia Wei-tong. Application of silica in light bulb industry[J]. Jiangsu Chemical Industry, 1995(1): 7-11. | |
| 4 | 刘建国, 季桂娟, 郝磊, 等. 油页岩灰渣提取白炭黑的方法[J]. 吉林大学学报: 地球科学版, 2011, 41(4): 1192-1196. |
| Liu Jian-guo, Ji Gui-juan, Hao Lei, et al. Method for extracting white carbon black by oil shale ash[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Earth Science Edition), 2011, 41(4): 1192-1196. | |
| 5 | 张兴友, 谭忆秋, 王哲人. 白炭黑改性沥青及其混合料的路用性能研究[J]. 公路交通科技, 2005, 22(7): 23-40. |
| Zhang Xing-you, Tan Yi-qiu, Wang Zhe-ren. Study on performance of silica modified asphalt and its mixture[J]. Journal of Highway and Transportation Research and Development, 2005, 22(7): 23-40. | |
| 6 | 林桂. 纳米粉体在橡胶基质中的聚集和分散研究[D]. 北京: 北京化工大学材料科学与工程学院, 2004. |
| Lin Gui. Study on aggregation and dispersion of nano powders in rubber matrix[D]. Beijing: School of Materials Science and Engineering, Beijing University of Chemical Technology, 2004. | |
| 7 | 于欣伟, 陈姚. 白炭黑的表面改性技术[J]. 广州大学学报: 自然科学版, 2002, 1(6): 12-16. |
| Yu Xin-wei, Chen Yao. Surface modification technology of silica[J]. Journal of Guangzhou University(Natural Science Edition), 2002, 1(6): 12-16. | |
| 8 | Guo W, Guo X D, Sun M Z, et al. Evaluation of the durability and the property of an asphalt concrete with nano hydrophobic silane silica in spring-thawing Season[J]. Applied Science, 2018, 8(9): 1475-1493. |
| 9 | 赵延庆, 谭忆秋, 王国忠, 等. 粘弹性对沥青路面疲劳开裂的影响[J]. 吉林大学学报: 工学版, 2010, 40(3): 683-687. |
| Zhao Yan-qing, Tan Yi-qiu, Wang Guo-zhong, et al. Effect of viscoelasticity on fatigue cracking of asphalt pavement[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2010, 40(3): 683-687. | |
| 10 | Gao J F, Wang H N, You Z P, et al. Rheological behavior and sensitivity of wood-derived bio-oil modified asphalt binders[J]. Applied Science, 2018, 8(6): 919-936. |
| 11 | Stefan H. Comments on a priori and a posteriori evaluations of sub-grid scale models for the Burgers’ equation[J]. Computers & Fluids, 2016, 138: 35-37. |
| 12 | Yuan X F, Ma S, Jiang S H. Form-finding of tensegrity structures based on the Levenberg-Marquardt method[J]. Computers & Fluids, 2017, 192: 171-180. |
| [1] | WANG Zhi-chen, GUO Nai-sheng, ZHAO Ying-hua, CHEN Zhong-da. Dynamic shear modulus prediction of asphalt mastic based on micromechanics [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2017, 47(2): 459-467. |
| [2] | MA Bin, XU Hong-guo, LIU Hong-fei. Effects of road surface fractal and rubber characteristics on tire sliding friction factor [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2013, 43(02): 317-322. |
| [3] | CHENG Yong-chun, GUO Qing-lin, TAN Guo-jin. Improved viscoelastic parameter identification for asphalt mixture [J]. , 2012, (03): 629-633. |
| [4] | REN Li-Li, ZHOU Jiang, TONG Jin. Factors influencing degree of substitution of hydroxyl groups of surfacemodified starch films with alkenyl succinic anhydrides [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2010, 40(06): 1624-1628. |
| [5] | ZHAO Yan-qing,TAN Yi-qiu,WANG Guo-zhong,WANG Zhi-chao. Effect of viscoelasticity on fatigue cracking of asphalt pavement [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2010, 40(03): 683-0687. |
| [6] | ZHANG Yu-qing,HUANG Xiao-ming. Viscoelasticity prediction of asphalt mixture based on micromechanics [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2010, 40(01): 52-0057. |
| [7] | SUN Guoen, ZHANG Li, LI Hongji, ZHANG Chunling, LIANG Jicai, ZHANG Wanxi. Structure and Properties of EVA/Al2O3 Nanocomposite Materials [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2005, 35(06): 577-0581. |
| [8] | LIU Yan, YU Sirong, REN Luquan. Microstructure of powder metallurgy material surface layer modified by laser cladding nano-Al2O3 [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2004, (3): 392-396. |
| [9] | ZOU Hui, GUAN Qing-feng, ZHANG Qing-yu, DONG Chuang, LIANG Liang. Surface modification of 45# steel by high-current pulsed electron beam [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2004, (1): 127-131. |
| [10] | ZHAO Chang-fu, GAO Zhong-li, MA Zhong-sheng, MA Hong-shun. Experimental Study on Compressing Viscoelasticity of Cancellous Femur Upper Part [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2002, (2): 87-90. |
| [11] | LI Hong, WANG Yu-chen, MA Hong-shun . Experiment Study on the Viscoelasticity of Aorta Abdomen [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2001, (4): 38-41. |
|
||